Overview of Manually Quarantining an IP Address
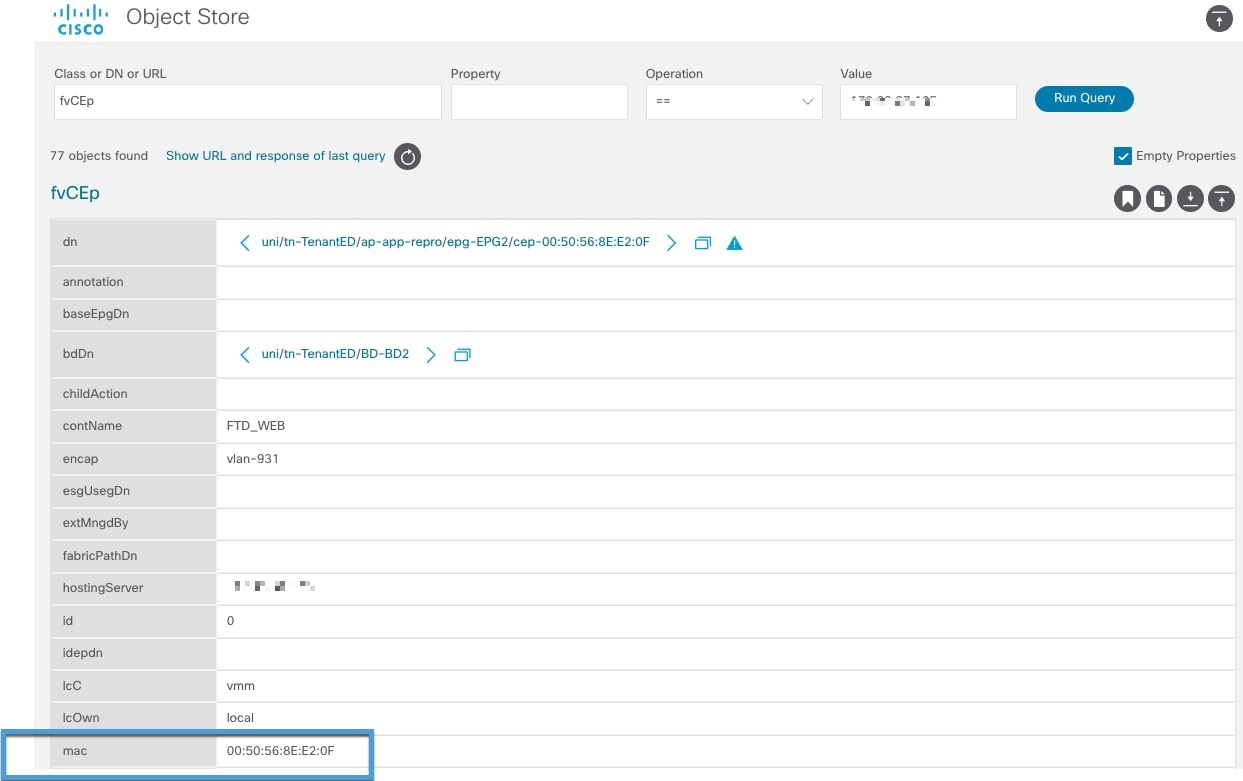
If a quarantine fails as discussed in earlier sections in this guide, you can manually quarantine that IP address. You must find the IP address and MAC address to quarantine. The IP address is shown in the Secure Firewall Management Center and the MAC address is shown in APIC.
 Feedback
Feedback