As an aid to
diagnosing basic network connectivity, many network protocols support an echo
protocol. The protocol involves sending a special datagram to the destination
host, then waiting for a reply datagram from that host. Results from this echo
protocol can help in evaluating the path-to-host reliability, delays over the
path, and whether the host can be reached or is functioning.
Configuration
for Checking Network Connectivity
The following
configuration shows an extended
ping command
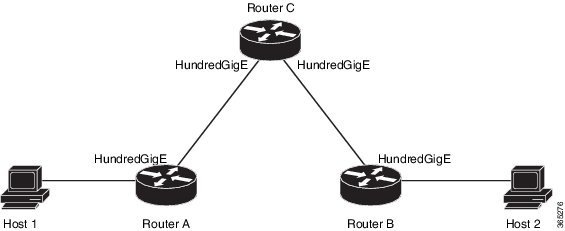
sourced from the Router A
HundredGigEinterface and
destined for the Router B
HundredGigE interface.
If this ping succeeds, it is an indication that there is no routing problem.
Router A knows how to get to the
HundredGigEinterface of
Router B, and Router B knows how to get to the
HundredGigE interface of
Router A. Also, both hosts have their default gateways set correctly.
If the extended
ping command
from Router A fails, it means that there is a routing problem. There could be a
routing problem on any of the three routers: Router A could be missing a route
to the subnet of Router B's interface, or to the subnet between Router C and
Router B; Router B could be missing a route to the subnet of Router A's subnet,
or to the subnet between Router C and Router A; and Router C could be missing a
route to the subnet of Router A's or Router B's Ethernet segments. You should
correct any routing problems, and then Host 1 should try to ping Host 2. If
Host 1 still cannot ping Host 2, then both hosts' default gateways should be
checked. The connectivity between the
HundredGigE interface of
Router A and the
HundredGigE interface of
Router B is checked with the extended
ping command.
With a normal ping
from Router A to Router B's
HundredGigE interface,
the source address of the ping packet would be the address of the outgoing
interface; that is the address of the
HundredGigE interface,
(10.0.0.2). When Router B replies to the ping packet, it replies to the source
address (that is, 10.0.0.2). This way, only the connectivity between the
HundredGigE interface of
Router A (10.0.0.2) and the 10gige interface of Router B (10.0.0.1) is tested.
To test the
connectivity between Router A's
HundredGigE interface
(10.0.0.2) and Router B's
interface (10.0.0.1 .), we use the extended
ping command.
With extended
ping, we get
the option to specify the source address of the
ping packet.
Configuration
Example
In this use case,
the extended
ping command
verifies the IP connectivity between the two IP addresses Router A (10.0.0.2)
and Router B (10.0.0.1) .
Router# ping 10.0.0.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.0.0.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5)
Router#!!!!!
*/If you do not enter a hostname or an IP address on the same line as the ping command,
the system prompts you to specify the target IP address and several other command parameters.
After specifying the target IP address, you can specify alternate values for the
remaining parameters or accept the displayed default for each parameter /*
Router# ping
Protocol [ipv4]:
Target IP address: 10.0.0.1
Repeat count [5]: 5
Datagram size [100]: 1000
Timeout in seconds [2]: 1
Interval in milliseconds [10]: 1
Extended commands? [no]: no
Sweep range of sizes? [no]:
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 1000-byte ICMP Echos to 10.0.0.1, timeout is 1 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5)
Router#!!!!!


 Feedback
Feedback