- Read Me First
- MPLS Virtual Private Networks
- Multiprotocol BGP MPLS VPN
- MPLS VPN OSPF PE and CE Support
- MPLS VPN Support for EIGRP Between PE and CE
- IPv6 VPN over MPLS
- Assigning an ID Number to an MPLS VPN
- Remote Access MPLS VPNs
- Multi-VRF Support
- Multi-VRF Selection Using Policy-Based Routing
- MPLS VPN VRF Selection Using Policy-Based Routing
- MPLS VPN Per VRF Label
- MPLS VPN per Customer Edge (CE) Label
- VRF Aware System Message Logging
- MPLS VPN Show Running VRF
- MPLS VPN Half-Duplex VRF
- MPLS VPN BGP Local Convergence
- MPLS VPN Route Target Rewrite
- MPLS VPN VRF CLI for IPv4 and IPv6 VPNs
- MPLS over GRE
- MPLS VPN 6VPE Support Over IP Tunnels
- IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
- Restrictions for IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
- Information About IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
- How to Configure IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
- Configuration Examples for IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
- Additional References for IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
- Feature Information for IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
IPv6 VRF Aware
System Message Logging
The IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging feature enables a device to send system logging (syslog) messages to an IPv6-enabled syslog server connected through a VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) interface. You can use the logging information for network monitoring and troubleshooting. This feature extends this capability to network traffic connected through VRFs.
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
- Restrictions for IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
- Information About IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
- How to Configure IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
- Configuration Examples for IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
- Additional References for IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
- Feature Information for IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Prerequisites for IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
You must configure a VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) instance on a routing device and associate the VRF with an interface before you can configure the IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging feature.
Restrictions for IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
You cannot specify a source address for virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) system logging messages. The IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging feature uses the VRF interface address as the source address for all VRF aware system logging messages.
Information About IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
Benefits of VRF Aware System Message Logging
A VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) instance is an extension of IP routing that provides multiple routing instances. A VRF provides a separate IP routing and forwarding table to each VPN. You must configure a VRF on a routing device before you configure the VRF Aware System Message Logging feature.
After you configure the VRF Aware System Message Logging feature on a routing device, the device can send system logging (syslog) messages to a syslog host through a VRF interface. Then you can use logging messages to monitor and troubleshoot network traffic connected through a VRF. If the VRF Aware System Message Logging feature is not configured on a routing device, the routing device sends syslog messages to the syslog host only through the global routing table.
You can receive system logging messages through a VRF interface on any device configured with a VRF, that is:
-
On a provider edge (PE) device that is used with Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) and multiprotocol Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to provide a Layer 3 MPLS VPN network service.
-
On a customer edge (CE) device that is configured for VRF-Lite, which is a VRF implementation without multiprotocol BGP.
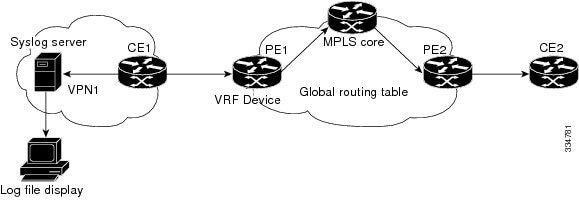
VRF Aware System Message Logging on a Provider Edge Device in an MPLS VPN Network
You can configure the VRF Aware System Message Logging feature on a provider edge (PE) device in a Layer 3 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN network. The PE device can then send system logging (syslog) messages through a VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) interface to a syslog server located in the VPN.
The figure below shows an MPLS VPN network and the VRF Aware System Message Logging feature configured on a PE device associated with VRF VPN1. The PE device sends log messages through a VRF interface to a syslog server located in VPN1. You can display the messages from the syslog server on a terminal.
VRF Aware System Message Logging on a Customer Edge Device with VRF-Lite Configured
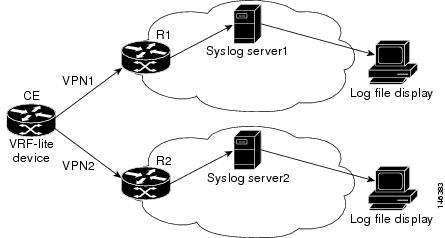
You can configure the VRF Aware System Message Logging feature on a customer edge (CE) device configured with the VRF-Lite feature. The CE device can then send system logging (syslog) messages through a VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) interface to syslog servers in multiple VPNs. The CE device can be either a router or a switch.
The figure below shows the VRF Aware System Message Logging feature configured on a VRF-Lite CE device. The CE device can send VRF syslog messages to syslog servers in the VPN1 network or the VPN2 network or to servers in both VPN1 and VPN2 networks. You can configure multiple VRFs on a VRF-Lite CE device, and the device can serve many customers.
Message Levels for Logging Commands
The table below lists message levels for logging commands that you can use when you configure the VRF Aware System Message Logging feature. Information provided in the table below includes keyword level names and numbers, their description, and the associated syslog definitions. You can use either the level name or the level number with the logging trap level and logging buffered severity-level commands.
|
Level Name |
Level Number |
Description |
Syslog Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
|
emergencies |
0 |
System unusable |
LOG_EMERG |
|
alerts |
1 |
Immediate action needed |
LOG_ALERT |
|
critical |
2 |
Critical conditions |
LOG_CRIT |
|
errors |
3 |
Error conditions |
LOG_ERR |
|
warnings |
4 |
Warning conditions |
LOG_WARNING |
|
notifications |
5 |
Normal but significant condition |
LOG_NOTICE |
|
informational |
6 |
Informational messages only |
LOG_INFO |
|
debugging |
7 |
Debugging messages |
LOG_DEBUG |
How to Configure IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
Configuring VRF on a Routing Device
Configuring a VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) instance on a routing device helps provide customer connectivity to a VPN. The routing device can be a provider edge (PE) device connected to a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN network or a customer edge (CE) device that is configured for VRF-Lite.
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
vrf definition
vrf-name
4.
address-family ipv6
5.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Associating a VRF with an Interface
 Note | You cannot configure a source address for VRF system logging messages. The VRF Aware System Message Logging feature uses the VRF interface address as the source address for all VRF-aware system logging messages. |
A VRF must be associated with an interface before you can forward VPN traffic.
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface
type
number
4.
vrf forwarding
vrf-name
5.
no ipv6 address
6.
ipv6 address
address.prefix
7.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring VRF as a Source Interface for Logging on a Routing Device
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
logging source-interface
interface-type
interface-number
vrf
vrf-name
4.
logging host ipv6
ipv6-address
vrf
vrf-name
5.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Verifying IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
1.
enable
2.
show running-config | include logging
3.
show logging
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
Example: Configuring VRF on a Routing Device
Device> enable Device# configure terminal Device(config)# vrf definition syslog_v6 Device(config-vrf)# address-family ipv6 Device(config-vrf-af)# end
Example: Associating a VRF with an Interface
Device> enable Device# configure terminal Device(config)# interface FastEthernet 0/0/0 Device(config-if)# vrf forwarding vpn1 Device(config-if)# no ipv6 address Device(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:DB8::1/32 Device(config-if)# end
Example: Configuring VRF as a Source Interface for Logging on a Routing Device
Device> enable Device# configure terminal Device(config)# logging source-interface FastEthernet 0/0/0 vrf vpn1 Device(config)# logging host ipv6 address 2001:DB8::1 vrf vpn1 Device(config)# end
Additional References for IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
Related Documents
|
Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS commands |
|
|
MPLS and MPLS applications commands |
|
|
Concepts and tasks for configuring VRF-lite on a Catalyst 4500 switch |
“Configuring VRF-lite” chapter in the Catalyst 4500 Series Switch Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide |
|
Concepts and tasks for configuring VRF Lite on ML-Series Ethernet cards |
“Configuring VRF-lite” chapter in the Ethernet Card Software Feature and Configuration Guide for the Cisco ONS 15454 SDH, ONS 15454, and ONS 15327 |
Technical Assistance
|
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online resources, including documentation and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. To receive security and technical information about your products, you can subscribe to various services, such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter, and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.|
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging |
The IPv6 VRF Aware System Message Logging feature enables a device to send system logging (syslog) messages to an IPv6-enabled syslog server connected through a VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) interface. You can use the logging information for network monitoring and troubleshooting. This feature extends this capability to network traffic connected through VRFs. The following commands were modified: logging source-interface and logging host. |
 Feedback
Feedback