Licensing Requirements
For a complete explanation of Cisco NX-OS licensing recommendations and how to obtain and apply licenses, see the Cisco NX-OS Licensing Guide and the Cisco NX-OS Licensing Options Guide.
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
This chapter contains information about Cisco's IP fabric for media solution.
For a complete explanation of Cisco NX-OS licensing recommendations and how to obtain and apply licenses, see the Cisco NX-OS Licensing Guide and the Cisco NX-OS Licensing Options Guide.
Starting with Cisco NX-OS release 7.0(3)I7(1), use the Nexus Switch Platform Support Matrix to know from which Cisco NX-OS releases various Cisco Nexus 9000 and 3000 switches support a selected feature.
Today, the broadcast industry uses a serial digital interface (SDI) router and SDI cables to transport video and audio traffic. The SDI cables can carry only a single unidirectional signal. As a result, many cables, frequently stretched over long distances, are required, making it difficult and time-consuming to expand or change an SDI-based infrastructure.
Cisco’s IP fabric for media solution helps transition from an SDI router to an IP-based infrastructure. In an IP-based infrastructure, a single cable can carry multiple bidirectional traffic flows and can support different flow sizes without requiring changes to the physical infrastructure.
The IP fabric for media solution consists of a flexible spine and leaf architecture or a single modular switch topology. The solution uses Cisco Nexus 9000 Series switches with the Cisco non-blocking multicast (NBM) algorithm (an intelligent traffic management algorithm) and with or without the Cisco Data Center Network Manager (DCNM) Media Controller. Using open APIs, the Cisco DCNM Media Controller can integrate with various broadcast controllers. The solution provides a highly reliable (zero drop multicast), highly visible, highly secure, and highly available network.
Cisco’s IP fabric for media solution supports the following types of deployments:
Spine-leaf topology—Flexible architecture for large-scale deployments that are typically seen in an IP studio.
Single modular switch—Architecture suitable for fixed deployments, with the controller providing features such as flow visibility, security, and monitoring.
Cisco's IP fabric for media solution supports a spine-leaf topology that consists of multiple spine and leaf switches. The topology supports any combination of leaf switches, including using just one type of leaf switch.
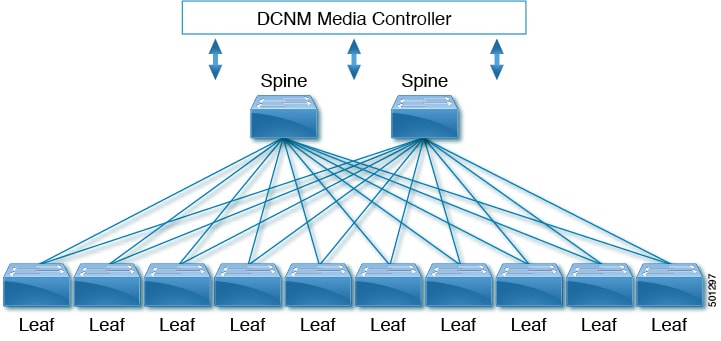
Media sources and receivers connect to the leaf switches, and receivers initiate IGMP join requests to the leaf switches in order to receive the media traffic.
Cisco's IP fabric for media solution supports a single modular switch topology that consists of one Cisco Nexus 9500 Series switch.

The following Cisco Nexus 9000 Series switches are used to transport video and audio traffic through the IP fabric:
|
Cisco Nexus 9000 Series Switch |
Number and Size of Ports |
Role in Topology* |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Cisco Nexus 9236C switch |
36 x 40/100-Gbps ports |
Spine or leaf in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 9272Q switch |
72 x 40-Gbps ports |
Spine or leaf in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 92160YC-X switch |
48 x 1/10/25-Gbps ports |
Leaf in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 9336C-FX2 switch |
36 x 40/100-Gbps ports |
Spine or leaf in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 9348GC-FXP switch |
48 x 100-Mbps/1-Gbps ports |
Leaf in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 9364C switch |
64 x 40/100-Gbps ports |
Spine in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 93108TC-EX switch |
48 x 1/10-Gbps ports |
Leaf in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 93108TC-FX switch |
48 x 10-Gbps ports |
Leaf in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 93180LC-EX switch |
32 x 40/100-Gbps ports |
Leaf in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 93180YC-EX switch |
48 x 1/10/25-Gbps ports |
Leaf in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 93180YC-FX switch |
48 x 10/25-Gbps ports |
Leaf in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 93216TC-FX2 switch |
96 x 1/10-Gbps ports |
Leaf in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 93240YC-FX2 switch |
48 x 10/25-Gbps ports |
Leaf in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 93360YC-FX2 switch |
96 x 10/25-Gbps ports |
Leaf in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 9504 or 9508 switch with the following line cards:
|
36 x 40/100-Gbps ports (for N9K-X9636C-R line cards) 36 x 40/100-Gbps ports (for N9K-X9636C-RX line cards) 36 x 40-Gbps ports (for N9K-X9636Q-R line cards) |
Spine in spine-leaf topology or single modular switch |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 9316D-GX switch |
16 x 400/100-Gbps QSFP-DD ports |
Leaf in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 9364C-GX switch |
64 x 100/40-Gbps Quad Small Form-Factor Pluggable (QSFP28) ports |
Leaf in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 93600CD-GX switch |
28 x 100/40-Gbps Quad Small Form-Factor Pluggable (QSFP28) and 8 x 400/100-Gbps QSFP-DD ports |
Leaf in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 93180YC-FX3S switch |
48 25/50/100-Gigabit Ethernet SFP28 ports (ports 1-48) and 6 10/25/40/50/100-Gigabit QSFP28 ports (ports 49-54) |
Leaf in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 93180YC-FX3 |
48 x 1/10/25 Gbps fiber ports and 6 x 40/100 Gbps QSFP28 ports |
Leaf in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 93108TC-FX3P |
48 x 100M/1/2.5/5/10 Gbps BASE-T ports 6 x 40/100 Gbps Quad small form-factor pluggable 28 (QSFP28) ports |
Leaf in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
N9K-X9624D-R2 line card |
Line card with 24 400G QSFP-DD ports (only to be used with 8-slot chassis) |
Spine or leaf in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 9508-FM-R2 line card |
Fabric module for 400G line card (only to be used with 8-slot chassis) |
Spine or leaf in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 9364D-GX2A switch |
64 x 40/100/400G QSFP-DD ports 2 x 1/10G SFP+ ports |
Spine or leaf switch in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 9348D-GX2A switch |
48 x 40/100/400G QSFP-DD ports 2 x 1/10G SFP+ ports |
Spine or leaf switch in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 9332D-GX2B switch |
32 x 40/100/400G QSFP-DD ports 2 x 1/10G SFP+ ports |
Spine or leaf switch in spine-leaf topology |
||
|
Cisco Nexus 9808 switch with the following line cards: Cisco Nexus X9836DM-A Cisco Nexus 9808-FM-A |
36 x 40/100/400G QSFP-DD ports (only to be used with 8-slot chassis) Fabric module for Nexus 9808 |
Spine in spine-leaf topology or single modular switch |
*The role indicates the place in the fabric that makes the most sense given the port speeds supported by each switch. There are no restrictions as such on the role for which a switch can be used.
Through open APIs, the Cisco DCNM Media Controller seamlessly integrates with the broadcast controller and provides a similar operator workflow with all the benefits of an IP-based infrastructure. The DCNM Media Controller features an intuitive GUI that enables you to configure your IP fabric using predefined templates that are designed for media networks.
The DCNM Media Controller enables you to do the following:
Configure secure generic or multicast-specific policies for individual hosts and allow or deny hosts based on their role.
Configure secure multicast-specific policies for multiple hosts and flows.
View the traffic flow and bandwidth utilization to identify problem areas (such as link failures or oversubscriptions) in your fabric.
Use flow analytics to measure and store bit rates and to display the details for individual traffic flows.
View an audit log of actions that are performed on the fabric.
Beginning with Cisco NX-OS Release 10.6(1)F, enhancements provide more granular and user-friendly fault and notification information within the Nexus Dashboard. This allows for faster identification and resolution of network issues. Key improvements include:
Clearer fault reasons and resolutions.
Key information, previously embedded within the Distinguished Name (DN), is now included as individual attributes in the payload. These attributes include:
source: The source IP address.
group: The multicast group IP address.
faultCode: The code that identifies the fault.
vrf: The Virtual Routing and Forwarding instance.
This change eliminates the need to parse the DN to extract these values, providing a more direct way to access the information.
Improved presentation of switch critical events in the Nexus Dashboard UI.
The enhancements to flow analytics, with the new fault categories and payload structure, provide a more detailed and actionable view of network behavior. This allows for more precise troubleshooting and optimization of traffic flows.
The new fault categories provide a more specific classification of fault conditions. This allows administrators to quickly pinpoint the source and nature of a problem.
The faultReason and faultResolution attributes in the enhanced payload provide clear explanations of the fault and specific steps to resolve it.
The new notification categories provide more granular information about network events. This allows administrators to proactively identify potential issues and optimize traffic flows before they impact performance.
The following example highlights the changes to the payload structure for flow faults:
|
Before Enhancement |
After Enhancement |
|---|---|
|
|
Starting with Cisco NX-OS Release 10.6(1)F, new fault and notification categories provide clearer and more useful information for troubleshooting and optimizing the network. The following sections detail the new Fault and Notification Managed Objects (MO), along with examples of their enhanced payload structures.
The nbmFlowFaults Managed Object provides information about faults related to a specific flow, such as bandwidth or policer issues.
"nbmFlowFaults": {
"attributes": {
"dn": "sys/nbm/show/faults/dom-default/flowfaults-[s-[47.20.20.9]-g-[233.1.4.255]]",
"faultCode": "2076",
"faultDn": "s-[47.20.20.9]-g-[233.1.4.255]",
"faultReason": "Policer resources exhausted. Configured TCAM max has been reached",
"faultResolution": "Review TCAM configuration if needed",
"group": "233.1.4.255",
"modTs": "2025-04-01T14:35:04.081+00:00",
"source": "47.20.20.9",
"tStamp": "1743518104080",
"vrf": "default"
}The nbmSenderFaults Managed Object provides information about faults originating from the media sender, such as host policy denials or resource limitations.
"nbmSenderFaults": {
"attributes": {
"dn": "sys/nbm/show/faults/dom-default/senderfaults-[sys/nbm/show/endpoints/dom-default/h-[47.20.20.9]-if-0/g-[227.10.10.1]]",
"faultCode": "2001",
"faultDn": "sys/nbm/show/endpoints/dom-default/h-[47.20.20.9]-if-0/g-[227.10.10.1]",
"faultReason": "Denied by Sender Host Policy",
"faultResolution": "Review Sender Host Policy Config and modify if needed",
"group": "227.10.10.1",
"modTs": "2025-04-01T14:25:13.635+00:00",
"senderEndpoint": "47.20.20.9",
"tStamp": "1743517513635",
"vrf": "default"
}The nbmReceiverFaults Managed Object provides information about faults related to the media receiver, such as bandwidth limitations or connectivity issues.
"nbmReceiverFaults": {
"attributes": {
"dn": "sys/nbm/show/faults/dom-default/receiverfaults-[sys/nbm/show/endpoints/dom-default/h-[47.20.10.1]-if-436231169/s-[47.20.20.9]-g-[227.10.10.1]]",
"faultCode": "1026",
"faultDn": "sys/nbm/show/endpoints/dom-default/h-[47.20.10.1]-if-436231169/s-[47.20.20.9]-g-[227.10.10.1]",
"faultReason": "No Bandwidth currently available for Receiver",
"faultResolution": "Please review flow policy, if receiver needs to be stitched",
"group": "227.10.10.1",
"modTs": "2025-04-01T14:27:46.801+00:00",
"receiverEndpoint": "47.20.10.1",
"receiverInterface": "Ethernet1/47.1",
"source": "47.20.20.9",
"tStamp": "1743517666801",
"vrf": "default"
}The nbmFlowIngressFaults Managed Object provides information about faults related to the ingress interface of a media flow, such as VRF context issues or invalid interface configurations.
"nbmFlowIngressFaults": {
"attributes": {
"dn": "sys/nbm/show/faults/dom-default/flowingressfaults-[sys/nbm/conf/flows/dom-default/s-[47.20.20.9]-g-[230.1.0.1]]",
"faultCode": "4230",
"faultDn": "sys/nbm/conf/flows/dom-default/s-[47.20.20.9]-g-[230.1.0.1]",
"faultReason": "IIF is not part of valid VRF context",
"faultResolution": "Please update VRF context on IIF, if needed; Then, delete and re-add DN in fault",
"group": "230.1.0.1",
"ingressif": "null0_iif",
"modTs": "2025-04-01T15:07:15.248+00:00",
"source": "47.20.20.9",
"tStamp": "1743520035248",
"vrf": "default"
}The nbmFlowEgressFaults Managed Object provides information about faults related to the egress interface of a media flow, such as invalid interface IP addresses or configuration errors.
"nbmFlowEgressFaults": {
"attributes": {
"dn": "sys/nbm/show/faults/dom-default/flowegressfaults-[sys/nbm/conf/flows/dom-default/s-[47.20.20.9]-g-[230.1.0.1]/if-[eth1/47.1]]",
"egressif": "Eth1/47.1",
"faultCode": "4227",
"faultDn": "sys/nbm/conf/flows/dom-default/s-[47.20.20.9]-g-[230.1.0.1]/if-[eth1/47.1]",
"faultReason": "Invalid Interface IP on OIF",
"faultResolution": "Please configure Interface IP address. Then, delete and re-add DN in fault",
"group": "230.1.0.1",
"modTs": "2025-04-01T15:06:59.738+00:00",
"source": "47.20.20.9",
"tStamp": "1743520019738",
"vrf": "default"
}The nbmEgressEvent and nbmIngressEvent Managed Objects provide information about interface-level usage, such as bandwidth utilization on egress and ingress interfaces.
"nbmEgressEvent": {
"attributes": {
"dn": "sys/nbm/show/notify/dom-vrf_pmn1/egressevent-[vrf:vrf_pmn1-INTF:Eth1/47.2-EGRESS]",
"egressinterface": "Eth1/47.2",
"modTs": "2025-04-03T08:12:36.338+00:00",
"notifyCode": "5301",
"notifyDn": "vrf:vrf_pmn1-INTF:Eth1/47.2-EGRESS",
"reason": "CRITICAL: EGRESS bw usage is at or above 90%",
"tStamp": "1743667956338",
"vrf": "vrf_pmn1"
}"nbmIngressEvent": {
"attributes": {
"dn": "sys/nbm/show/notify/dom-vrf_pmn1/ingressevent-[vrf:vrf_pmn1-INTF:Eth1/42.1-INGRESS]",
"ingressinterface": "Eth1/42.1",
"modTs": "2025-04-03T08:16:11.366+00:00",
"notifyCode": "5302",
"notifyDn": "vrf:vrf_pmn1-INTF:Eth1/42.1-INGRESS",
"reason": "SEVERE: INGRESS bw usage is at or above 75%",
"tStamp": "1743668171366",
"vrf": "vrf_pmn1"
}The nbmEvent Managed Object provides information about flow rate events, such as when the flow rate falls below a configured threshold.
"nbmEvent": {
"attributes": {
"dn": "sys/nbm/show/notify/dom-default/event-[vrf:default-BW:s-47.20.20.1-g-225.1.1.1]",
"group": "225.1.1.1",
"modTs": "2025-04-01T14:09:01.530+00:00",
"notifyCode": "5304",
"notifyDn": "vrf:default-BW:s-47.20.20.1-g-225.1.1.1",
"reason": "Rate below 60% of the configured flow policy",
"source": "47.20.20.1",
"tStamp": "1743516541530",
"vrf": "default"
}The nbmFlowEvent Managed Object provides information about flow provisioning events, such as when a flow is successfully provisioned.
nbmFlowEvent": {
"attributes": {
"dn": "sys/nbm/show/notify/dom-default/flowevent-[vrf:default-FLOW:s-[47.20.20.1]-g-[226.1.1.1]/oif-[Lo1]]",
"egressinterface": "Lo1"
"group": "226.1.1.1",
"modTs": "2025-04-01T14:02:43.330+00:00",
"notifyCode": "5201",
"notifyDn": "vrf:default-FLOW:s-[47.20.20.1]-g-[226.1.1.1]/oif-[Lo1]",
"reason": "FLOW Provisioned Successfully",
"source": "47.20.20.1",
"tStamp": "1743516163330",
"vrf": "default"
}The nbmInatOversubscriptionEvent Managed Object provides information about NAT oversubscription events, such as when the cumulative pre-NAT bandwidth exceeds the post-NAT bandwidth.
"nbmInatOversubscriptionEvent": {
"attributes": {
"dn": "sys/nbm/show/notify/dom-default/inatoversubscriptionevent-[vrf:default-post_s-[51.51.51.51]-post_g-[226.1.1.1]-ingress]",
"group": "226.1.1.1",
"modTs": "2025-04-01T14:19:04.393+00:00",
"notifyCode": "5305",
"notifyDn": "vrf:default-post_s-[51.51.51.51]-post_g-[226.1.1.1]-ingress",
"reason": "Oversubscription - cumulative pre NAT bandwidth is higher than post NAT bandwidth from the respective flow policies",
"source": "51.51.51.51",
"tStamp": "1743517144393",
"vrf": "default"
}The nbmEnatBandwidthmismatchEvent Managed Object provides information about NAT bandwidth mismatch events, such as when there is a mismatch between the pre-NAT and post-NAT flow bandwidth.
"nbmEnatBandwidthmismatchEvent": {
"attributes": {
"destPort": "0",
"dn": "sys/nbm/show/notify/dom-default/enatbandwidthmismatchevent-[vrf:default-post_s-[100.1.1.1]-post_g-[226.1.2.1]-pre_s-[47.20.20.1]-pre_g-[226.1.1.1]-S[0]-D[0]-egress/if-[Eth1/47.1]]",
"group": "226.1.2.1",
"modTs": "2025-04-01T14:02:44.123+00:00",
"notifyCode": "5307",
"notifyDn": "vrf:default-post_s-[100.1.1.1]-post_g-[226.1.2.1]-pre_s-[47.20.20.1]-pre_g-[226.1.1.1]-S[0]-D[0]-egress/if-[Eth1/47.1]",
"preGroup": "226.1.1.1",
"preSource": "47.20.20.1",
"reason": "Pre and Post Translation Flow BW Mismatch",
"source": "100.1.1.1",
"sourcePort": "0",
"tStamp": "1743516164123"
"vrf": "default"
}Cisco's IP fabric for media solution supports deterministic failure handling.
During a link or switch failure, the affected flows are moved to alternate links, provided sufficient bandwidth is available. With SMPTE 2022-7, redundancy is built on the endpoints, which ensures that the link or switch failure does not affect production traffic.
Cisco NX-OS Release 10.6(1)F introduces enhancements to failure handling that provide more detailed and actionable fault information. This allows administrators to effectively understand fault information displayed in the Nexus Dashboard, identify the root cause of failures, and implement appropriate remediation steps.
Cisco's IP fabric for media solution provides the following benefits:
Replaces specialized hardware (SDI routers) with a general-purpose switching infrastructure.
Supports various types and sizes of broadcasting equipment endpoints with port speeds up to 100 Gbps.
Supports the latest video technologies, including 4K and 8K ultra HD.
Scales horizontally. When you need more capacity, you can add a leaf switch to support more endpoints.
Provides a deterministic network with zero packet loss, ultra low latency, and minimal jitter.
Capable of synchronizing all media sources and receivers.
Provides deterministic failure handling that sends traffic to the receiver when a link fails between a leaf and the spine.
Supports the coexistence of live and file-based traffic flows for postproduction work.
Offers increased network security.
Provides a non-blocking network design to prevent the oversubscription of links.
Requires no changes to the existing operator workflow.
|
Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Cisco DCNM Media Controller |
Cisco DCNM Installation and Upgrade Guide for Media Controller Deployment |
|
Cisco NX-OS release information |
Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS IP Fabric for Media Release Notes |
|
Cisco NX-OS software upgrades |
Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Software Upgrade and Downgrade Guide |
|
IGMP snooping and PIM |
Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Multicast Routing Configuration Guide |
|
IP fabric for media scalability numbers |
|
|
NX-API REST |
Cisco Nexus 3000 and 9000 Series NX-API REST SDK User Guide and API Reference |
|
OSPF |
Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Unicast Routing Configuration Guide |
|
PTP |
Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS System Management Configuration Guide |
|
QoS |
Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Quality of Service Configuration Guide |
|
TCAM carving |
|
|
VLANs |
Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Layer 2 Switching Configuration Guide |