About Certificate Authorities and Digital Certificates
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) support provides the means for the Cisco MDS 9000 Family switches to obtain and use digital certificates for secure communication in the network. PKI support provides manageability and scalability for IPsec/IKE and SSH.
Purpose of Certificate Authorities and Digital Certificates
Certificate Authorities (CAs) manage certificate requests and issue certificates to participating entities such as hosts, network devices, or users. The CAs provide centralized key management for the participating entities.
Digital signatures, based on public key cryptography, digitally authenticate devices and individual users. In public key cryptography, such as the RSA encryption system, each device or user has a key-pair consisting of both a private key and a public key. The private key is kept secret and is known only to the owning device or user. However, the public key is known to everybody. The keys act as complements. Anything encrypted with one of the keys can be decrypted with the other. A signature is formed when data is encrypted with a sender’s private key. The receiver verifies the signature by decrypting the message with the sender’s public key. This process relies on the receiver having a copy of the sender’s public key and knowing with a high degree of certainty that it really does belong to the sender and not to someone pretending to be the sender.
Digital certificates link the digital signature to the sender. A digital certificate contains information to identify a user or device, such as the name, serial number, company, department, or IP address. It also contains a copy of the entity’s public key. The certificate is itself signed by a CA, a third party that is explicitly trusted by the receiver to validate identities and to create digital certificates.
To validate the signature of the CA, the receiver must first know the CA’s public key. Normally this process is handled out-of-band or through an operation done at installation. For instance, most web browsers are configured with the public keys of several CAs by default. Internet Key Exchange (IKE), an essential component of IPsec, can use digital signatures at scale to authenticate peer devices before setting up security associations.
Trust Model, Trust Points, and Identity Certificate Authorities
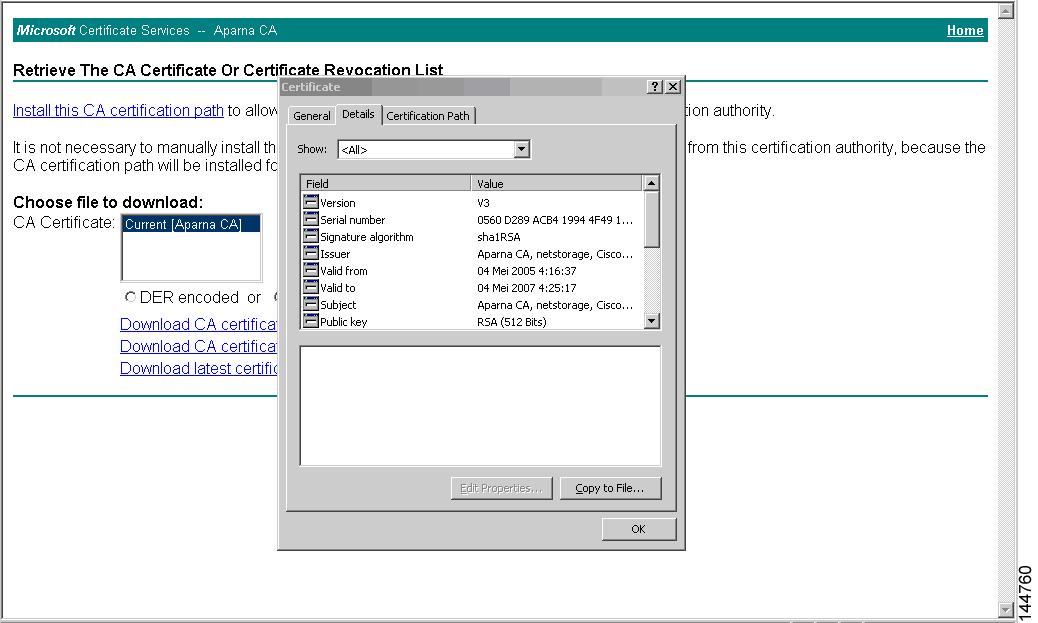
The trust model that is used in PKI support is hierarchical with multiple configurable trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs). Each participating entity is configured with a list of CAs to be trusted so that the peer’s certificate that is obtained during the security protocol exchanges can be verified, provided it has been issued by one of the locally trusted CAs. To accomplish this, the CA’s self-signed root certificate (or certificate chain for a subordinate CA) is locally stored. The process of securely obtaining and storing this locally is called CA authentication. This is a mandatory step in trusting a CA.
The information about a trusted CA that is locally configured is called the trust point and the CA itself is called a trust point CA. This information consists of CA certificate (or certificate chain in case of a subordinate CA) and the certificate revocation checking information.
An identity is the name of device. An identity certificate (also known as public key or digital certificates) is a public key certificate of a device that has been signed by a trust point. An identity CA is a trust point that can issue identity certificates.
The process of enrolling an MDS switch with a trust point to obtain an identity certificate for a set of applications (for example, IPsec/IKE) is called enrollment. This trust point is called an identity CA.
When a secure client makes a connection to a server, it does not offer an identity certificate to the server, but the server does offer an identity certificate to the client. Thus, for switch client applications such as the SSH or DHCP clients, it is required to have an authenticated CA, but not required to install identity certificates.
The client validates the incoming identity certificate chain from server using an authenticated CA. The CA is chosen from either the bundled trust pool (public root CA certificates prepackaged with the image) or the user installed trust points. User trust points may be used if the switch is air-gapped and cannot reach public root CAs or the user has a local trust domain with local root CAs.
Secure switch-based servers, such as the HTTPS NX-API service, need both an authenticated CA (trust point) and identity certificates.
RSA Key-Pairs and Identity Certificates
You can generate one or more RSA key-pairs and associate each RSA key-pair with a trust point CA where the MDS switch intends to enroll to obtain an identity certificate. The MDS switch needs only one identity per CA, which consists of one key-pair and one identity certificate per CA.
Cisco MDS NX-OS allows you to generate RSA key-pairs with a configurable key size (or modulus). Key-pairs may also be generated on other devices and imported on to the MDS switch. You can configure a label for each RSA key-pair. For information about RSA key-pair maximums and defaults, see the Table 1 Maximum Limits for CA and Digital Certificate and Table 2 Default CA and Digital Certificate Parameters.
The following list summarizes the relationship between trust points, RSA key-pairs, and identity certificates:
-
A trust point corresponds to a specific CA that the MDS switch trusts for peer certificate verification for any application (such as IKE or SSH).
-
An MDS switch can have many trust points and all applications on the switch can trust a peer certificate issued by any of the trust point CAs.
-
A trust point is not restricted to a specific application.
-
An MDS switch enrolls with the CA corresponding to the trust point to obtain an identity certificate. You can enroll your switch with multiple trust points thereby obtaining a separate identity certificate from each trust point. The identity certificates are used by applications depending upon the purposes specified in the certificate by the issuing CA. The purpose of a certificate is stored in the certificate as certificate extensions.
-
When enrolling with a trust point, you must specify an RSA key-pair to be certified. This key-pair must be generated and associated to the trust point before generating the enrollment request. The association between the trust point, key-pair, and identity certificate is valid until it is explicitly removed by deleting the certificate, key-pair, or trust point.
-
The subject name in the identity certificate is the fully qualified domain name for the MDS switch.
-
You can generate one or more RSA key-pairs on a switch and each can be associated to one or more trust points. But no more than one key-pair can be associated to a trust point, which means only one identity certificate is allowed from a CA.
-
If multiple identity certificates (each from a distinct CA) have been obtained, the certificate that an application selects to use in a security protocol exchange with a peer is application-specific.
-
You do not need to designate trust points for an application. Any application can use any certificate issued by any trust point as long as the certificate purpose satisfies the application requirements.
-
You do not need more than one identity certificate from a trust point or more than one key-pair to be associated to a trust point. A CA certifies a given identity (name) only once and does not issue multiple certificates with the same subject name. If you need more than one identity certificate for a CA, then define another trust point for the same CA, associate another key-pair to it, and have it certified, provided CA allows multiple certificates with the same subject name.
Multiple Trusted Certificate Authorities
Multiple trusted (Certificate Authorities) CA support enables a switch to verify the identity of devices enrolled in different CA domains. With multiple trusted CAs, you do not have to enroll a switch with the specific CA that issued a certificate to a peer. Instead, you configure the switch with multiple trusted CAs that the peer also trusts. A switch can then use a configured trusted CA to verify certificates offered by a peer that were not issued by the same CA defined in the identity certificate of the local switch. This can be used by IKE when establishing IPsec tunnels.
Multiple Identity Certificate Authorities
Multiple identity Certificate Authorities (CA) support enables a switch to enroll with more than one trust point. This results in multiple identity certificates; each from a distinct CA. This allows the switch to participate in IPsec and other applications with many peers using certificates issued by appropriate CAs that are acceptable to those peers.
The multiple RSA key-pair support feature allows the switch to maintain a distinct key-pair for each CA with which it is enrolled. Thus, it can match policy requirements for each CA without conflicting with the requirements specified by the other CAs, such as key length. When enrolling with a trust point, the associated key-pair is used to construct the certificate signing request.
PKI Enrollment
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) Enrollment is the process of obtaining an identity certificate for the switch that is used for applications such as IPsec/IKE or SSH. It occurs between the MDS switch requesting the certificate and the Certificate Authority.
The figure below and the following steps describe the certificate enrollment process.
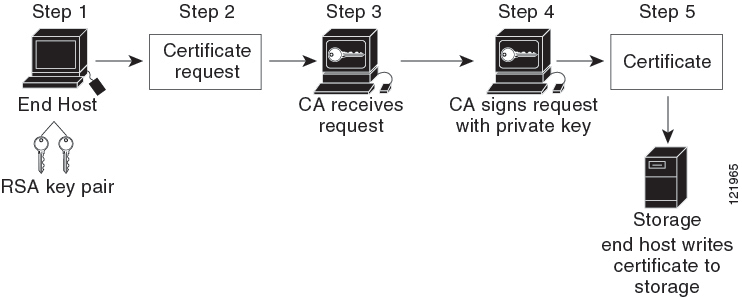
The process involves the following steps:
-
Generate an RSA private and public key-pair.
-
Generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) in standard format and forward it to the CA.
-
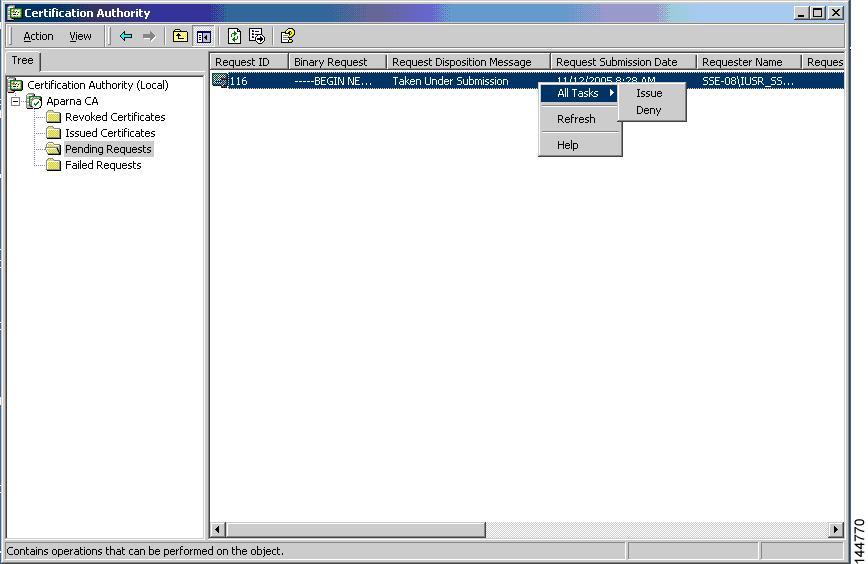
Approve the CSR on the CA to generate the identity certificate, signed by the CA’s private key, and forward it to the MDS switch administrator. Manual intervention on the CA by the CA administrator may be required to approve the request.
-
Install the identity certificate from the CA on the MDS switch.
-
Save the certificate into a nonvolatile storage area on the MDS switch.
RSA key-pairs and CSRs may be generated either on the switch or on another device with suitable utilities. If key-pairs are generated on another device they must be installed on the MDS switch as well as the identity certificates. The MDS switch does not support all the possible fields for CSRs. CSR generating tools on other devices may allow specification of more fields than enrollment done from the MDS switch.
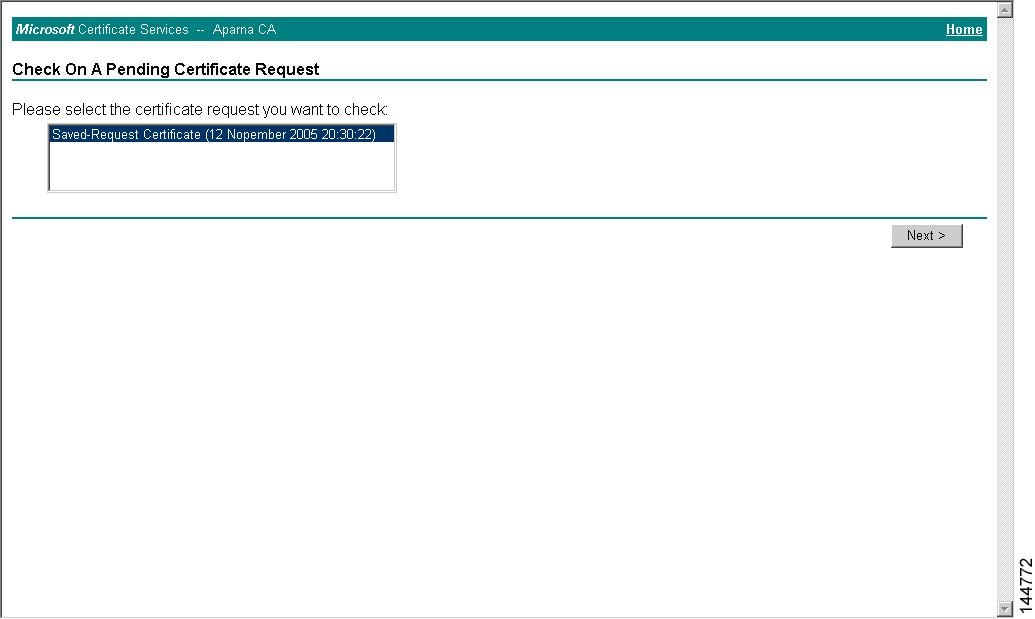
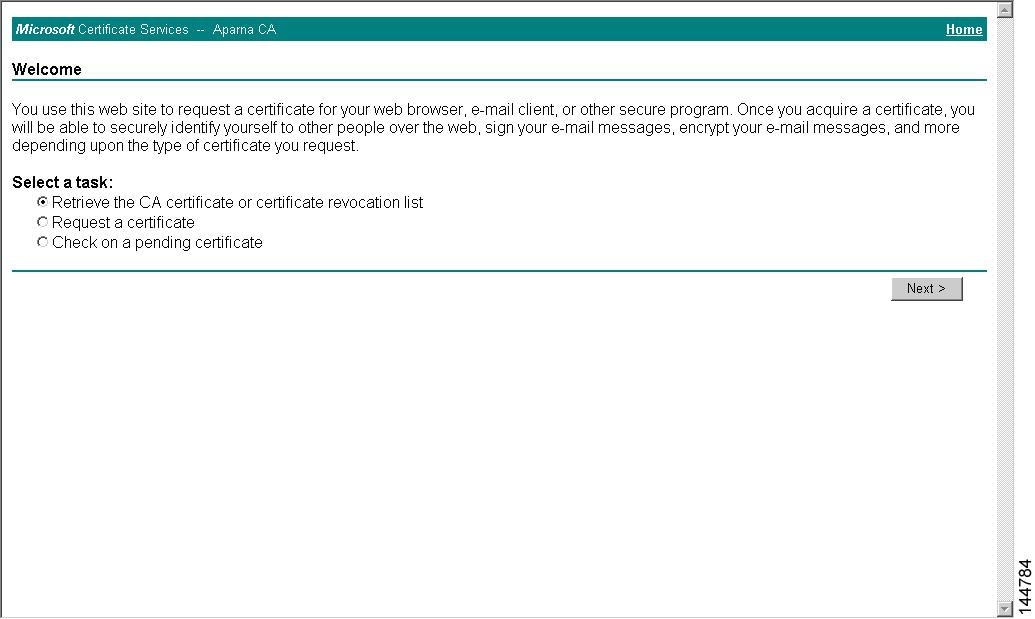
Manual Enrollment Using the Cut-and-Paste Method
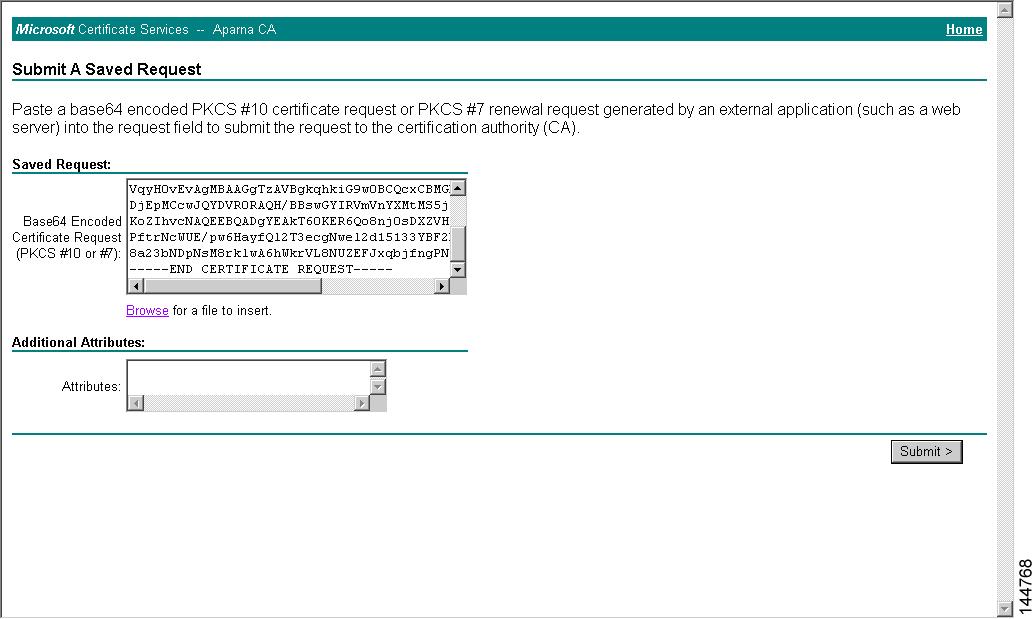
Cisco MDS NX-OS supports certificate retrieval and enrollment using the manual cut-and-paste method. Cut-and-paste enrollment means you must cut and paste the certificate requests and resulting certificates between the switch and the CA, as follows:
-
Create an enrollment certificate signing request, which is displayed in base64 encoded textform.
-
Cut and paste the encoded certificate request text in an e-mail message and send itto the CA or in a web form on the CA.
-
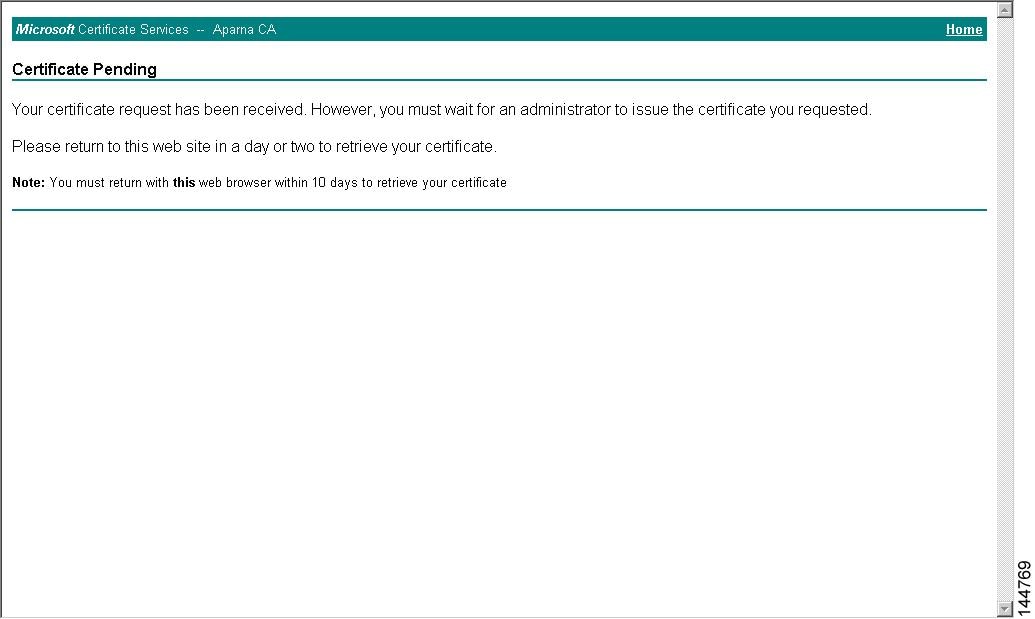
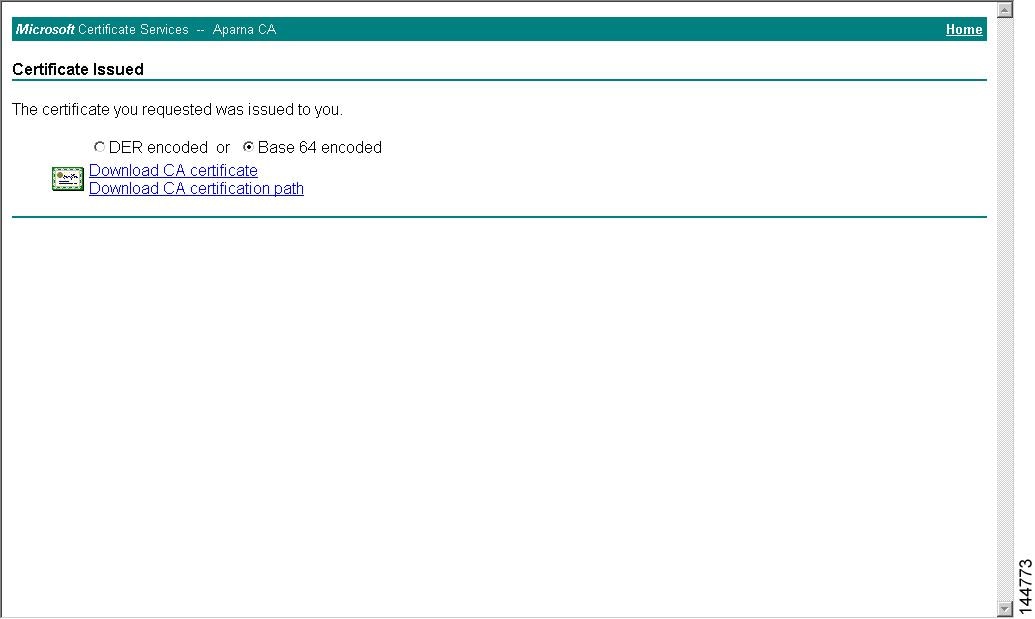
Receive the issued certificate in base64 encoded text form from the CA in an e-mail message or ina web browser download.
-
Cut and paste the issued certificate to the switch using the certificate import command.
Peer Certificate Verification
PKI support on an MDS switch provides the means to verify peer certificates. The switch verifies certificates presented by peers during security exchanges for applications, such as IPsec/IKE and SSH. The applications verify the validity of the peer certificates presented to them. The peer certificate verification process involves the following steps:
-
Verifies that the peer certificate is issued by one of the locally trusted CAs.
-
Verifies that the peer certificate is valid (not expired) with respect to current time.
-
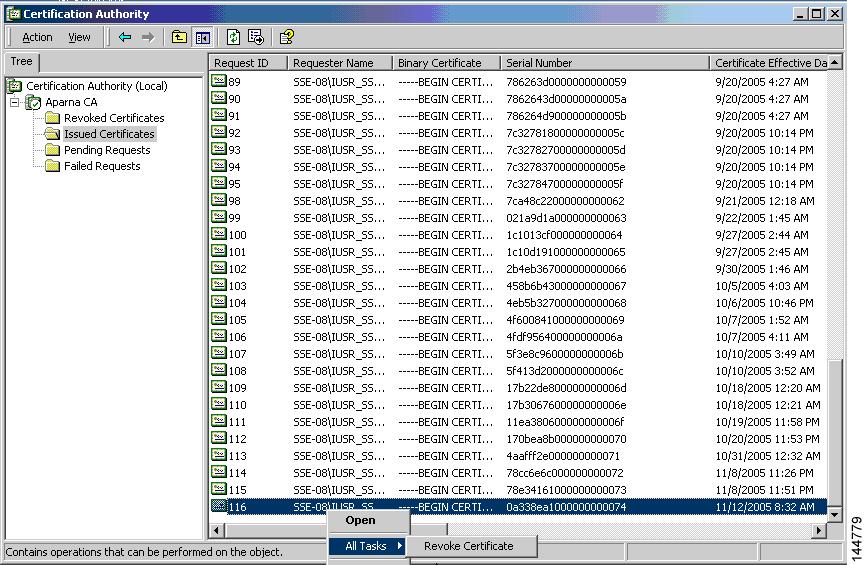
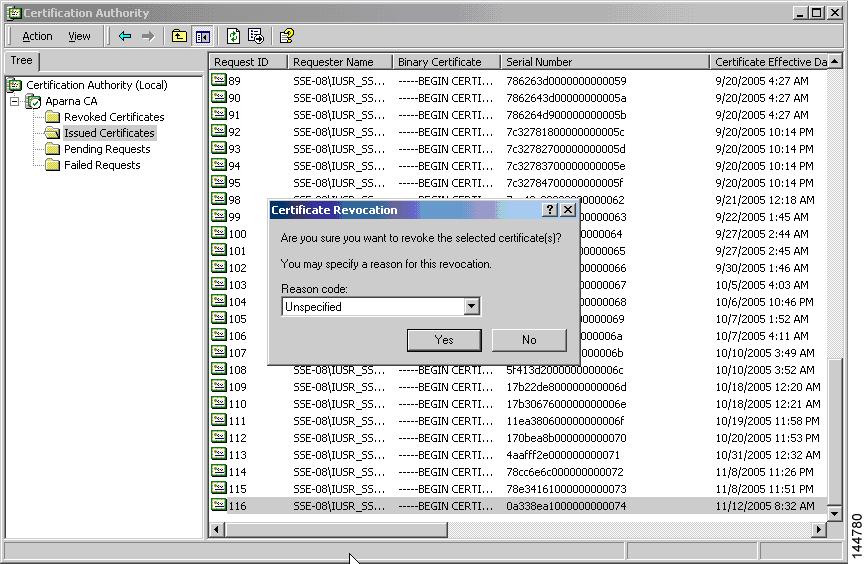
Verifies that the peer certificate is not yet revoked by the issuing CA.
For revocation checking, the switch can use the certificate revocation list (CRL) method. A trust point uses the CRL method to verify that the peer certificate has not been revoked.
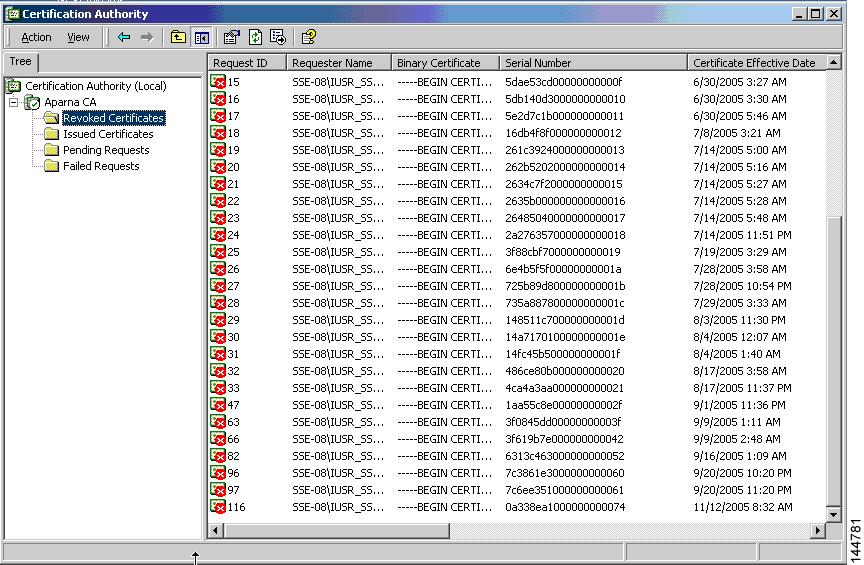
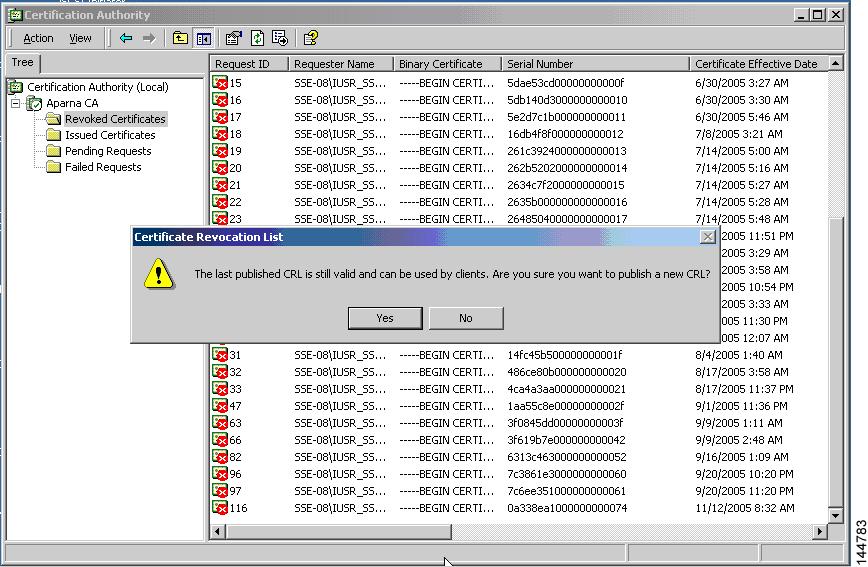
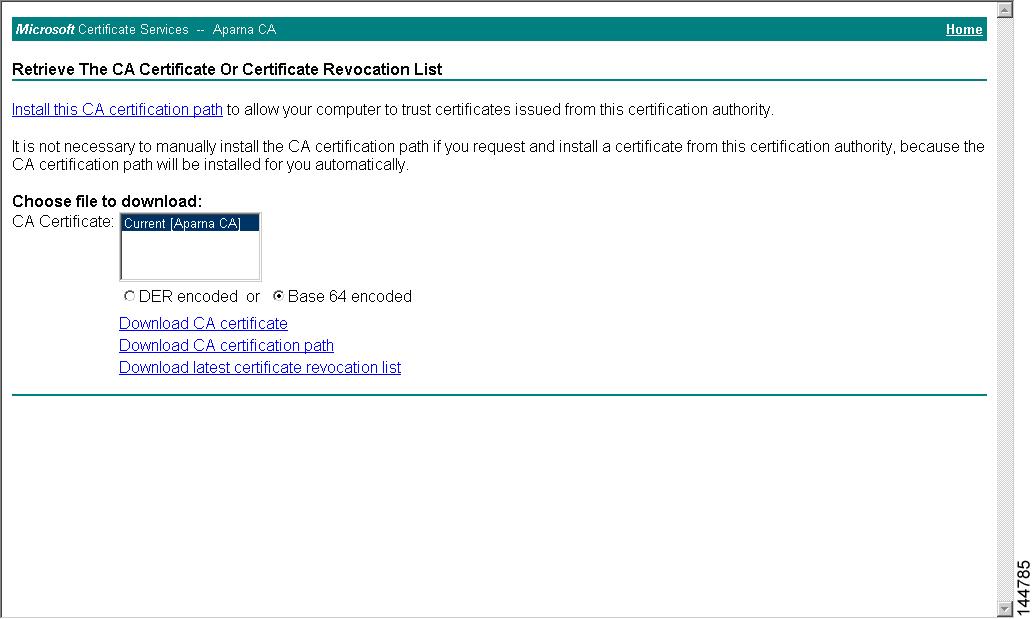
CRL Downloading, Caching, and Checking Support
Certificate revocation lists (CRLs) are maintained by CAs to give information of revoked certificates, and are published in a repository. The download URL is made public and also specified in all issued certificates. A client verifying a peer’s certificate should obtain the latest CRL from the issuing CA and use it to determine if the certificate has been revoked. A client can cache the CRLs of some or all of its trusted CAs locally and use them later, if necessary, until the CRLs expire.
Cisco MDS NX-OS allows the manual configuration of pre-downloaded of CRLs for the trust points, and then caches them in the switch certificate store. During the verification of a peer certificate, the issuing CA’s CRL is consulted only if the CRL has already been cached locally and the revocation checking is configured to use CRL. Otherwise, CRL checking is not performed and the certificate is considered to be not revoked if no other revocation checking methods are configured. This mode of CRL checking is called CRL optional.
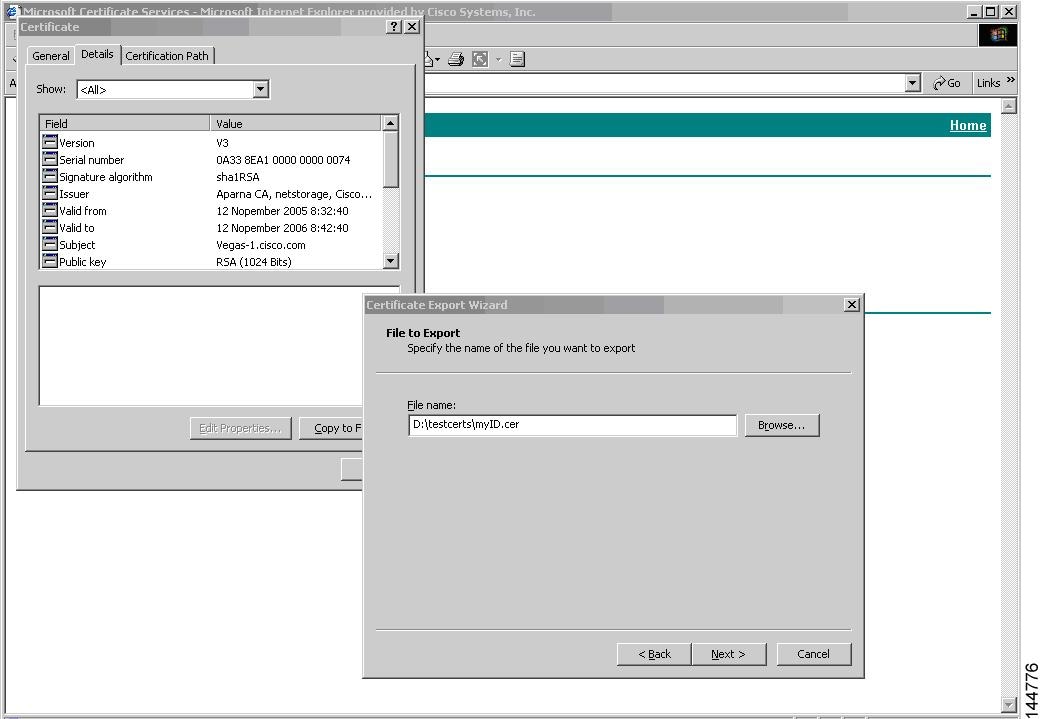
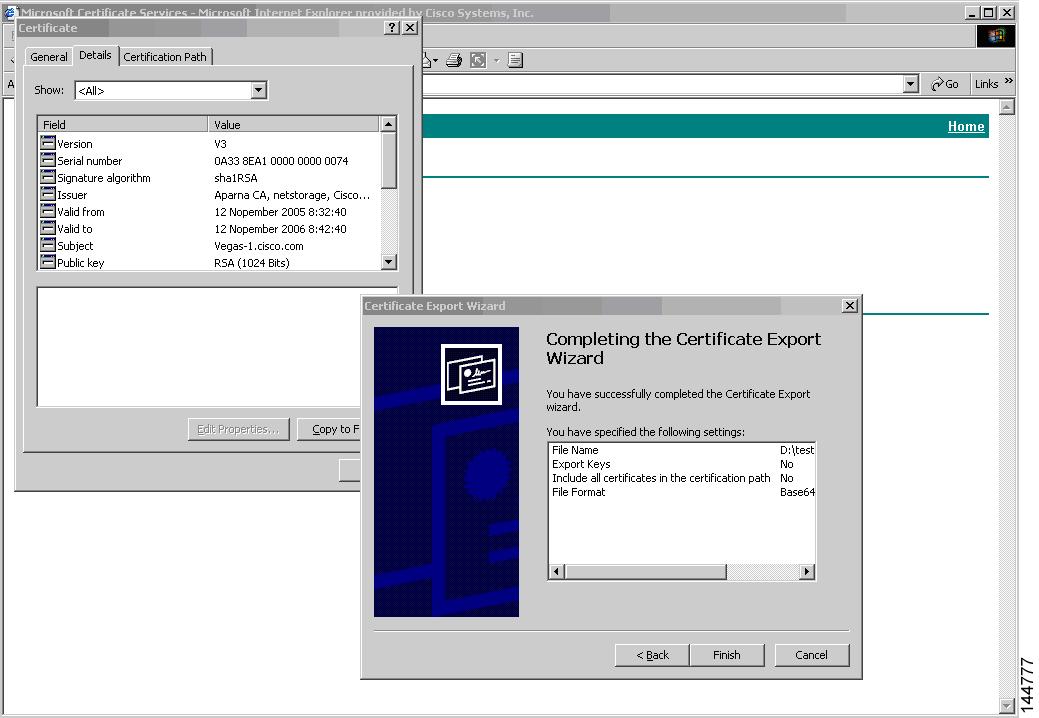
Import and Export of Certificates and Associated Key-Pairs
As part of the CA authentication and enrollment process, the subordinate CA certificate (or certificate chain) and identity certificates are imported in standard PEM (base64) format. If key-pairs have been externally generated they need to be imported in a separate step.
The complete identity information in a trust point can be exported to a file in the password-protected PKCS12 standard format. It can be later imported to the same switch (for example, after a system crash) or to a replacement switch. The information in a PKCS12 file consists of the RSA key-pair, the identity certificate, and the CA certificate (or chain).


 Feedback
Feedback