Cisco SD-Access Zero-Trust Security Solution
Networks need protection against external and internal threats. Cisco SD-Access provides a zero-trust security solution for your workplace. The Cisco SD-Access zero-trust security solution provides secure access to users and devices from all locations across the network.
The Cisco SD-Access zero-trust security solution includes the following capabilities:
-
Identify and verify all endpoints: SD-Access establishes an initial level of trust with each connecting endpoint.
-
Establish policy and segmentation: SD-Access ensures least-privilege access based on the endpoint and user type.
-
Continuously monitor endpoints: SD-Access continuously monitors the endpoints to ensure compliance.
-
Threat mitigation: SD-Access allows you to quarantine the endpoints that are noncompliant or exhibit malicious behavior.
The Cisco SD-Access zero-trust security solution provides the flexibility to adopt a path to a zero-trust workplace based on your network settings and services. You can configure how users connect to the network using dynamic rules and automated segmentation.
The Cisco SD-Access zero-trust security solution provides the capability to automate network access policies using the following features:
-
Endpoint visibility: You can identify and group endpoints. You can map their interactions through traffic flow analysis and define access policies.
-
Trust monitoring: You can continuously monitor the endpoint behavior, scan for vulnerabilities, verify trustworthiness for continued access, and isolate rogue or compromised endpoints.
-
Network Segmentation: You can enforce group-based access policies and secure network through multilevel segmentation.
The Cisco SD-Access zero-trust security solution enables you to explore various paths to zero-trust workplace based on your network settings and services. You can discover your optimal path based on your current network status, and explore the benefits of each added step on the zero-trust journey.
Zero-Trust Overview Dashboard
The SD-Access Zero-Trust Overview dashboard provides an overview of your zero-trust workplace journey. Click the menu icon (![]() ) and choose
to view this dashboard.
) and choose
to view this dashboard.
The zero-trust workplace journey has the following phases:
-
Day 0: For starting your zero-trust workplace journey. For more information, see Day 0 View of Zero-Trust Overview Dashboard.
-
Day n: For ongoing monitoring and configuration changes of your zero-trust workplace journey. For more information, see Day n View of Zero-Trust Overview Dashboard.
Day 0 View of Zero-Trust Overview Dashboard
Before you start your SD-Access zero-trust workplace journey, the day 0 view of the Zero-Trust Overview dashboard consists of the following sections:
-
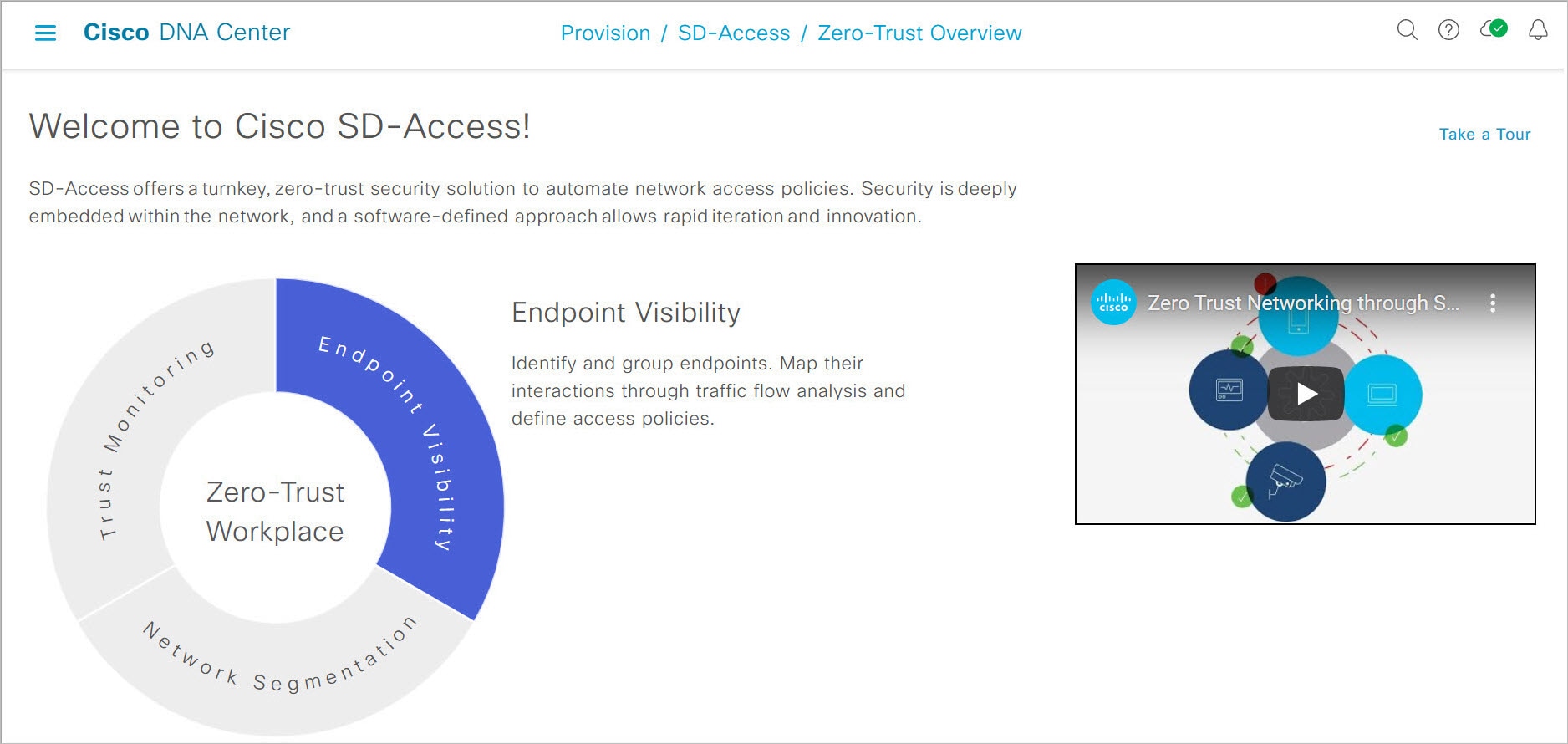
Welcome to Cisco SD-Access!: This section consists of an overview video that provides a short overview of the multiple paths towards a full SD-Access zero-trust workplace. It also consists of a circle containing sections for each pillar of the SD-Access zero-trust workplace:
-
Endpoint Visibility
-
Trust Monitoring
-
Network Segmentation
Hover your cursor over each section to view more information.
-
-
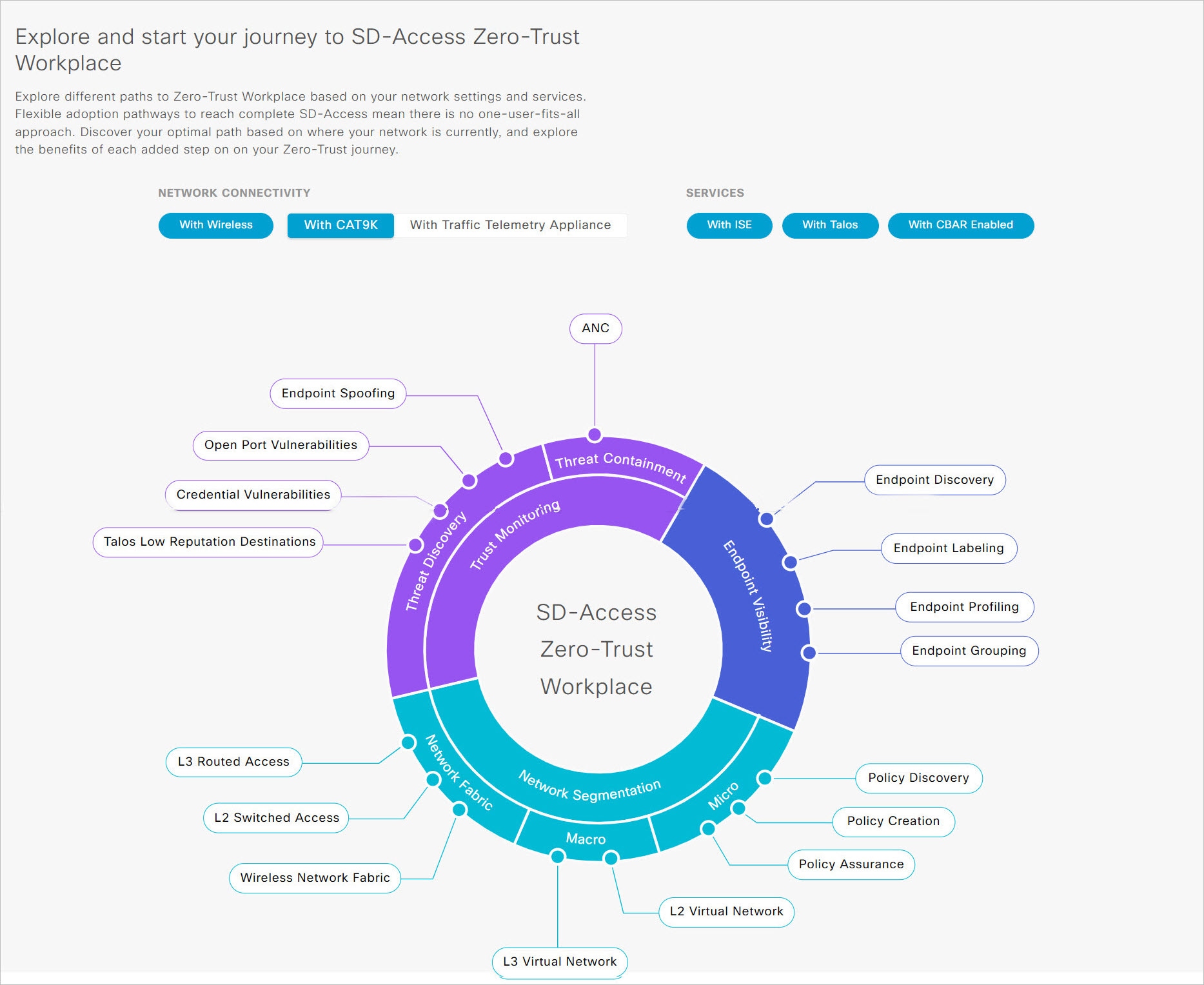
Explore and start your journey to SD-Access Zero-Trust Workplace: This section allows you to explore the different paths to a zero-trust workplace based on your network settings and services, and discover the optimal path for your network. This section consists of the Network Connectivity and Services options, and a circular journey map with details about the paths. Based on the options that you choose for network connectivity and services, the journey map displays the available paths to your zero-trust workplace journey.
To view details about each recommended step in the journey map, hover your cursor over the corresponding step around the journey map.
-
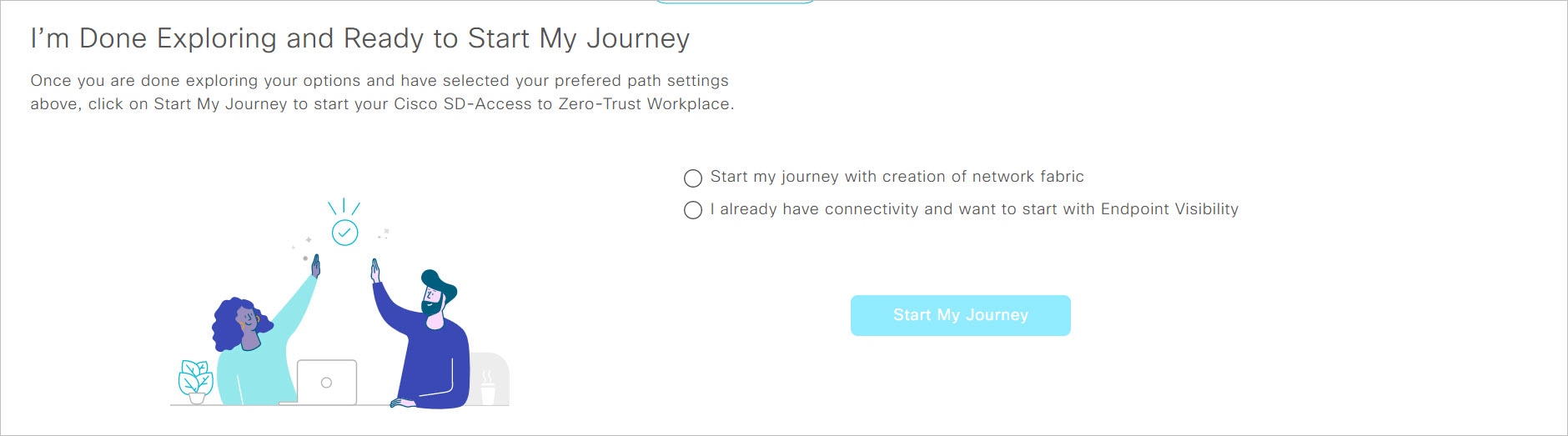
I’m Done Exploring and Ready to Start My Journey: After exploring the paths and selecting your preferred settings, use this section to start your journey to a zero-trust workplace.
Get Started with SD-Access Zero-Trust Workplace Journey
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Click the menu icon ( |
|
Step 2 |
Under Explore and start your journey to SD-Access Zero-Trust Workplace, do the following: |
|
Step 3 |
Under I’m Done Exploring and Ready to Start My Journey, choose one of the following options:
|
|
Step 4 |
Click Start My Journey. |
|
Step 5 |
In the Modify Journey Map dialog box, do the following: |
Day n View of Zero-Trust Overview Dashboard
After starting your SD-Access zero-trust workplace journey, the day n view of the Zero-Trust Overview dashboard consists of the following sections:
-
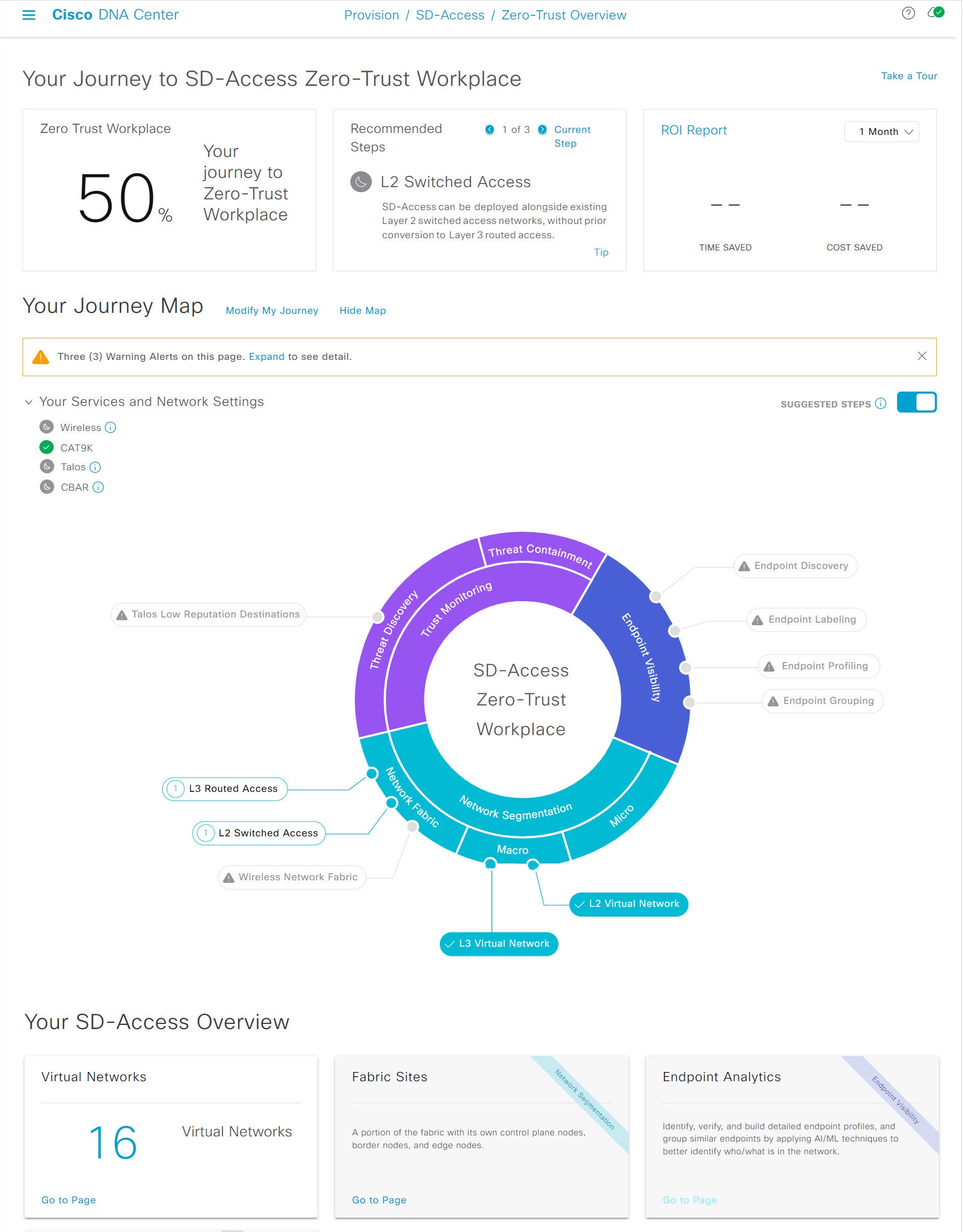
Your Journey to SD-Access Zero-Trust Workplace: This section consists of the following dashlets:
-
The Zero Trust Workplace dashlet displays the percentage progress of your zero-trust workplace journey.
-
The Recommended Steps dashlet displays the next recommended steps for your zero-trust workplace journey. Use the arrow buttons (
 and
and  ) to scroll through all the steps. This dashlet also displays the tips for some steps. If available, click Tip to view the tips for the corresponding step.
) to scroll through all the steps. This dashlet also displays the tips for some steps. If available, click Tip to view the tips for the corresponding step.
-
The ROI Report dashlet displays the time and cost savings based on the implemented steps as you progress through your zero-trust workplace journey. Use the drop-down in this dashlet to choose the time period for the report. Click ROI Report to view the report.
-
-
Your Journey Map: This section displays the details of network connectivity and service settings for your zero-trust workplace journey. Click Modify My Journey to modify your zero-trust workplace journey. Click Hide Map to hide the journey map.
This section displays the warning alerts for your journey, if available. Click Expand to view the details of the alerts. If a selected service is currently unavailable in your network and you want to remove it from your journey, click the corresponding Remove From Journey option. If you want to get a selected service that is currently unavailable in your network, click the corresponding hyperlink to get the service.
Expand the Your Services and Network Settings drop-down to view the list of selected services for your journey. The
 icon next to a service indicates that the service is currently available in your network. The
icon next to a service indicates that the service is currently available in your network. The  icon next to a service indicates that the service is currently unavailable in your network. Hover your cursor over the corresponding
icon next to a service indicates that the service is currently unavailable in your network. Hover your cursor over the corresponding
 icon to view the Update Needed dialog box with details about the unavailable service. In the Update Needed dialog box, do the following:
icon to view the Update Needed dialog box with details about the unavailable service. In the Update Needed dialog box, do the following:
-
To remove the service from your journey, click Remove From Journey.
-
To get the unavailable service in your network, click the corresponding hyperlink.
Enable the Suggested Steps toggle button to view the suggested order of steps around your journey map.
To view details about each step in the journey map, hover your cursor over the corresponding step around the journey map.
The
 icon next to a step indicates that the corresponding configurations are incomplete. A number next to a step (for example,
icon next to a step indicates that the corresponding configurations are incomplete. A number next to a step (for example,
 ) indicates the suggested order of the recommended steps for your journey map. The
) indicates the suggested order of the recommended steps for your journey map. The  icon next to a step indicates that the corresponding configurations are complete.
icon next to a step indicates that the corresponding configurations are complete.
-
-
Your SD-Access Overview: This section consists of dashlets for each functional area of your zero-trust workplace journey. Click the corresponding Go to Page option to open the relevant window. Each dashlet indicates its corresponding pillar of the zero-trust workplace journey in its upper-right corner.
Modify SD-Access Zero-Trust Workplace Journey
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Click the menu icon ( |
|
Step 2 |
Under Your Journey Map, click Modify My Journey. |
|
Step 3 |
Under Explore and start your journey to SD-Access Zero-Trust Workplace, do the following: |
|
Step 4 |
Under I’m Done Exploring and Ready to Start My Journey, choose one of the following options:
|
|
Step 5 |
Click Modify My Journey. |
|
Step 6 |
In the Modify Journey Map dialog box, do the following: |

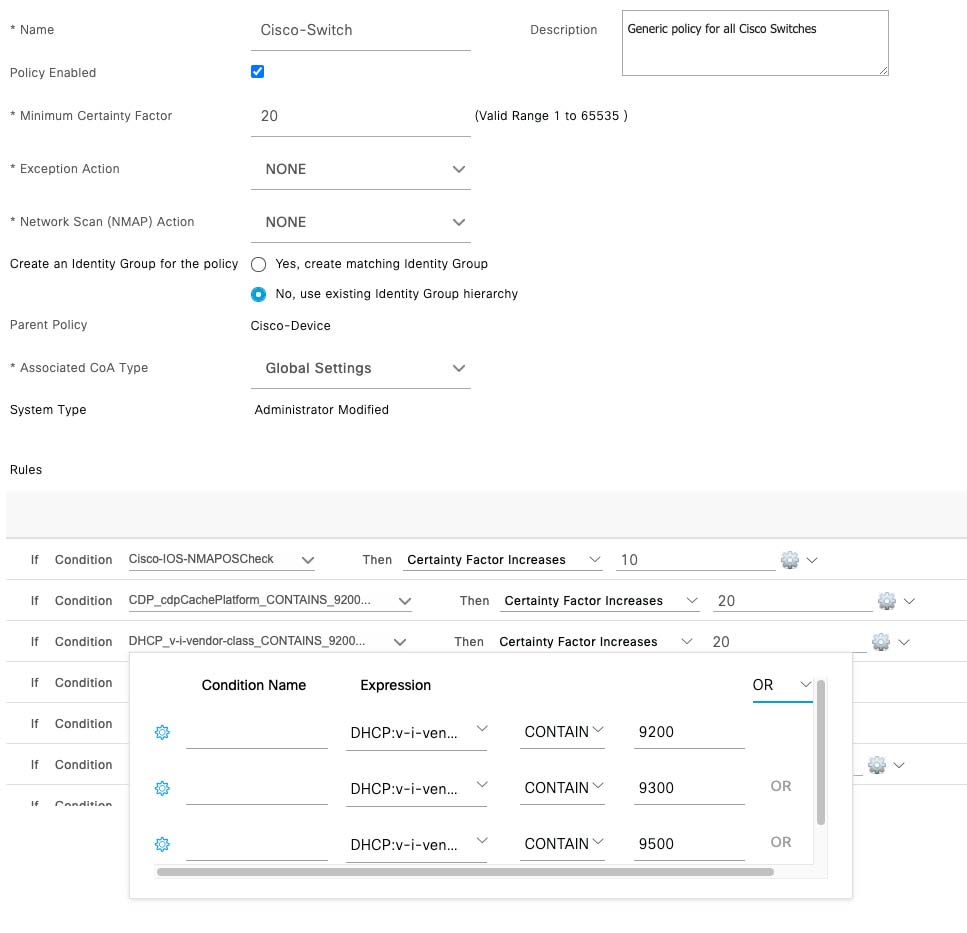
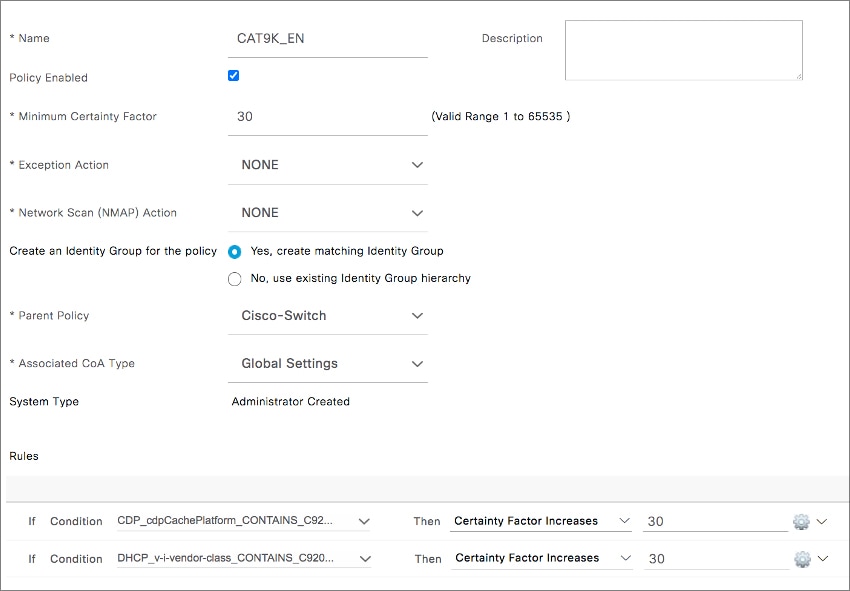

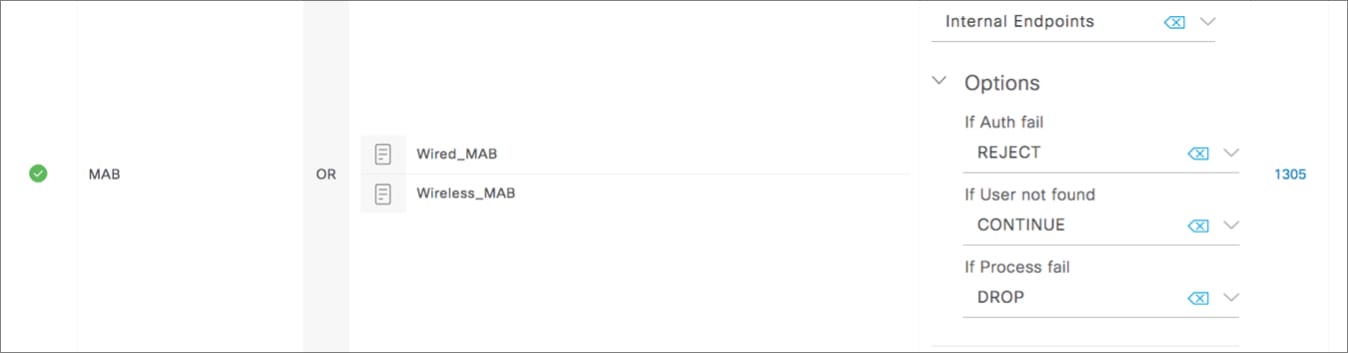
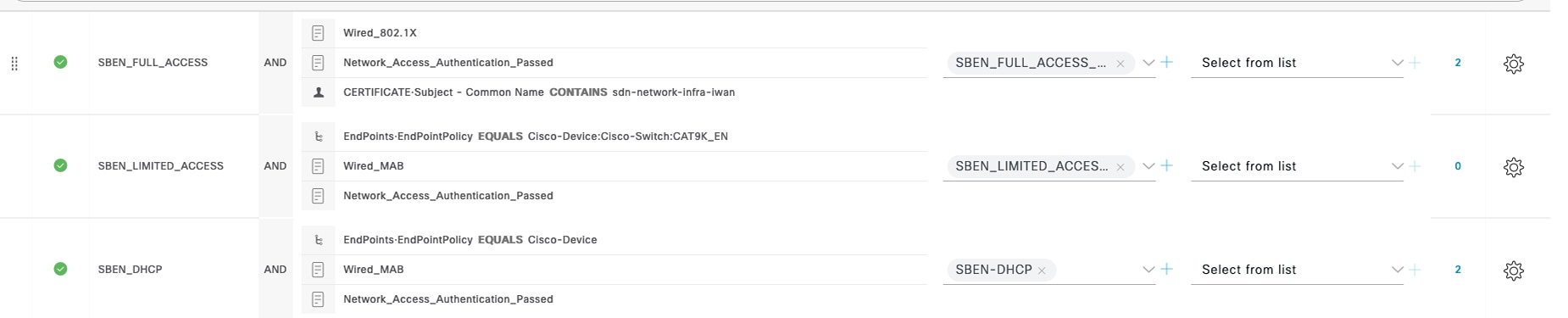
 Feedback
Feedback