-
Cisco Aironet Access Point Software Configuration Guide for VxWorks
-
Preface
-
Overview
-
Using the Management Interfaces
-
Configuring the Radio and Basic Settings
-
Configuring VLANs
-
Configuring Filters and Quality of Service
-
Configuring Proxy Mobile IP
-
Configuring Other Settings
-
Security Setup
-
Network Management
-
Managing Firmware and Configurations
-
Management System Setup
-
Special Configurations
-
Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
-
Appendix A - Protocol Filter Lists
-
Appendix B - Channels, Power Levels, and Antenna Gains
-
Appendix C - Event Log Messages
-
Index
-
Table Of Contents
Configuring Filters and Quality of Service
Entering Information on the Quality of Service Setup Page
Settings on the Quality of Service Setup Page
A Wireless QoS Deployment Example
WEP Not Set on the Wireless Phone
Configuring Filters and Quality of Service
This chapter provides information and configuration procedures for setting up filters. The chapter also provides information and procedures for setting up QoS using filters you create.
This chapter contains the following sections:
•
A Wireless QoS Deployment Example
Filter Setup
This section describes how to set up filtering to control the flow of data through the access point. You can filter data based on protocols and MAC addresses. Each type of filtering is explained in the following sections:
Protocol Filtering
Protocol filters prevent or allow the use of specific protocols through the access point. You can set up individual protocol filters and enable each filter for one or more VLANs. You can filter protocols for wireless client devices, users on the wired LAN, or both. For example, an SNMP filter on the access point's radio port prevents wireless client devices from using SNMP with the access point but does not block SNMP access from the wired LAN.
Use the Protocol Filters Setup page create and enable protocol filters for the access point's Ethernet port and for the access point's radio port. The Protocol Filters Setup page is shown on Figure 5-1.
Figure 5-1 Protocol Filters Setup Page
Follow this link path to reach the Protocol Filters Setup page:
1.
On the Summary Status page, click Setup.
2.
On the Setup page, click Protocol Filters in the Protocol Filters row under Associations.
You can create protocol filters or view existing filters by clicking Filters in the Ethernet or Radio rows of the Network Ports section of the Setup page. The screens are identical except for the name. Figure 5-2 shows the Protocol Filters page.
Figure 5-2 Protocol Filters Page
Follow this link path to reach the AP Radio or Ethernet Protocol Filters page:
1.
On the Summary Status page, click Setup.
2.
On the Setup page, click Filters in the AP Radio or Ethernet row under Network Ports.
The left side of the Protocol Filters page contains links to the Ethertype Filters, the IP Protocol Filters, and the IP Port Filters pages.
Use the Protocol Filters pages to assign protocols to a filter set. Table A-1, Table A-2, and Table A-3 in Appendix B list the protocols available on each page.
Creating a Protocol Filter
Follow these steps to create a protocol filter:
Step 1
Follow the link path to the Protocol Filters Setup page.
Step 2
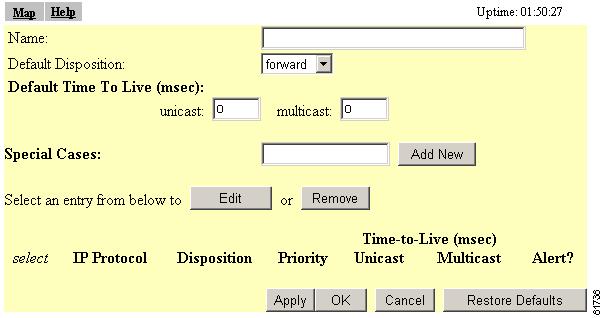
Click Ethertype, IP Protocol, or IP Port to display the Filters page that contains the protocols you want to filter. Figure 5-3 shows the IP Protocol Filters page.
Figure 5-3 IP Protocol Filters Page
Step 3
Enter a descriptive filter set name in the Set Name field.
Step 4
Enter an identification number in the Set ID entry field if you want to assign a specific SNMP identifier to the filter set. If you don't enter an ID, an SNMP identifier will be assigned to the set automatically, starting with 1 for the first filter set and incrementing by one for each additional set.
Step 5
Click Add New. The Filter Set page appears. Figure 5-4 shows the Filter Set page.
Figure 5-4 Filter Set Page
Step 6
Select forward or block from the Default Disposition drop-down menu. This setting is the default action for the protocols you include in the filter set. You can override this setting for specific protocols.
Step 7
In the Default Time to Live fields, enter the number of milliseconds unicast and multicast packets should stay in the access point's buffer before they are discarded. These settings will be the default time-to-live values for the protocols you include in the filter set, but you can override the settings for specific protocols. If you leave these settings at 0, the time-to-live settings default to 3 seconds for multicast packets and 5 seconds for unicast packets.
Note
If you plan to block multicast traffic, you must set the Default Multicast Address Filter parameter to disallowed in the AP Radio Advanced Page and the The Ethernet Advanced Page.
Step 8
Type the name or the ISO numeric designator for the protocol you want to add in the Special Cases entry field and click Add New. For example, to add Telnet to an IP port filter set, type telnet or 23.
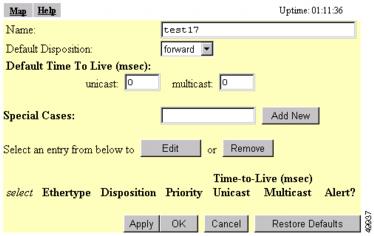
The Protocol Filter Set page appears. Figure 5-5 shows the Protocol Filter Set page.
Figure 5-5 Protocol Filter Set Page
Step 9
Select forward or block from the Disposition drop-down menu to forward or block the protocol traffic, or leave this setting at default to use the default disposition that you selected for the filter set in Step 6.
Step 10
Select a priority for the protocol from the Priority drop-down menu. The menu includes the following options:
•
background—Use this setting for bulk transfers and other activities that are allowed on the network but should not impact network use by other users and applications.
•
default—This setting is the same as best effort, which applies to normal LAN traffic.
•
excellentEffort—Use this setting for a network's most important users.
•
controlledLoad—Use this setting for important business applications that are subject to some form of admission control.
•
interactiveVideo—Use this setting for traffic with less than 100 ms delay.
•
interactiveVoice—Use this setting for traffic with less than 10 ms delay.
•
networkControl—Use this setting for traffic that must get through to maintain and support the network infrastructure.
Step 11
Enter milliseconds in the Time-to-Live entry fields. If you leave these settings at 0, the protocol adopts the default time-to-live values you entered in Step 7.
Note
The time-to-live values you enter should be compatible with the priority you select for the protocol. For example, if you select interactiveVoice as the priority and enter high time-to-live values, voice packets will stay in the access point buffer longer than necessary, causing delivery of stale, useless packets.
Step 12
Select Alert? yes to send an alert to the event log when a user transmits or receives the protocol through the access point.
Step 13
Click OK. The Filter Set page appears with the protocol listed at the bottom of the page.
To edit the protocol entry, type the protocol name in the Special Cases entry field or click the select button beside the entry and click Edit. To delete the protocol, type the protocol name in the Special Cases entry field or click the select button beside the entry and click Remove.
Step 14
To add another protocol to the filter set, repeat Step 8 through Step 13. When you have included all the protocols you need in the filter set, click OK. The EtherType Filters, IP Protocol Filters, or IP Port Filters page appears, and the filter sets you defined appear in the filter set list at the bottom of the page.
Note
After defining the protocol filter set, follow the steps in the Enabling a Protocol Filter section to activate the filter.
Enabling a Protocol Filter
Follow these steps to enable a protocol filter:
Step 1
Complete the steps listed in the "Creating a Protocol Filter" section to define a protocol filter.
Step 2
Follow the link path to the Ethernet Protocol Filters page or the AP Radio Protocol Filters page.
Step 3
Select the protocol filter set that you want to enable from the Ethertype, IP Protocol, or IP Port drop-down menu.
Step 4
Click OK. The filter set is enabled.
MAC Address Filtering
MAC address filters allow or disallow the forwarding of unicast and multicast packets either sent from or addressed to specific MAC addresses. You can create a filter that passes traffic to all MAC addresses except those you specify, or you can create a filter that blocks traffic to all MAC addresses except those you specify.
Note
MAC address filters are powerful, and you can lock yourself out of the access point if you make a mistake setting up the filters. If you accidentally lock yourself out of your access point, follow the instructions in the "Using the Command-Line Interface" section to use the CLI to disable the filters.
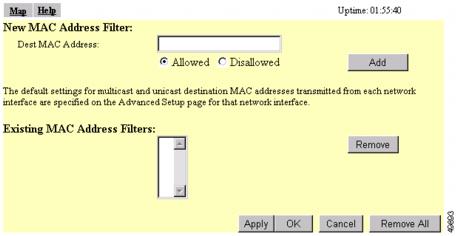
Use the Address Filters page to create MAC address filters for the access point. Figure 5-6 shows the Address Filters page.
Figure 5-6 Address Filters Page
Follow this link path to reach the Address Filters page:
1.
On the Summary Status page, click Setup.
2.
On the Setup page, click Address Filters under Associations.
Creating a MAC Address Filter
Follow these steps to create a MAC address filter:
Step 1
Follow the link path to the Address Filters page.
Step 2
Type a destination MAC address in the New MAC Address Filter: Dest MAC Address field. You can type the address with colons separating the character pairs (00:40:96:12:34:56, for example) or without any intervening characters (004096123456, for example).
Note
If you plan to disallow traffic to all MAC addresses except those you specify as allowed, put your own MAC address in the list of allowed MAC addresses. If you plan to disallow multicast traffic, add the broadcast MAC address (ffffffffffff) to the list of allowed addresses.
Step 3
Click Allowed to pass traffic to the MAC address or click Disallowed to discard traffic to the MAC address.
Step 4
Click Add. The MAC address appears in the Existing MAC Address Filters list. To remove the MAC address from the list, select it and click Remove.
Tip
You can create a list of allowed MAC addresses on an authentication server on your network. Consult the "Setting Up MAC-Based Authentication" section for instructions on using MAC-based authentication.
Step 5
Click OK. You return automatically to the Setup page.
Step 6
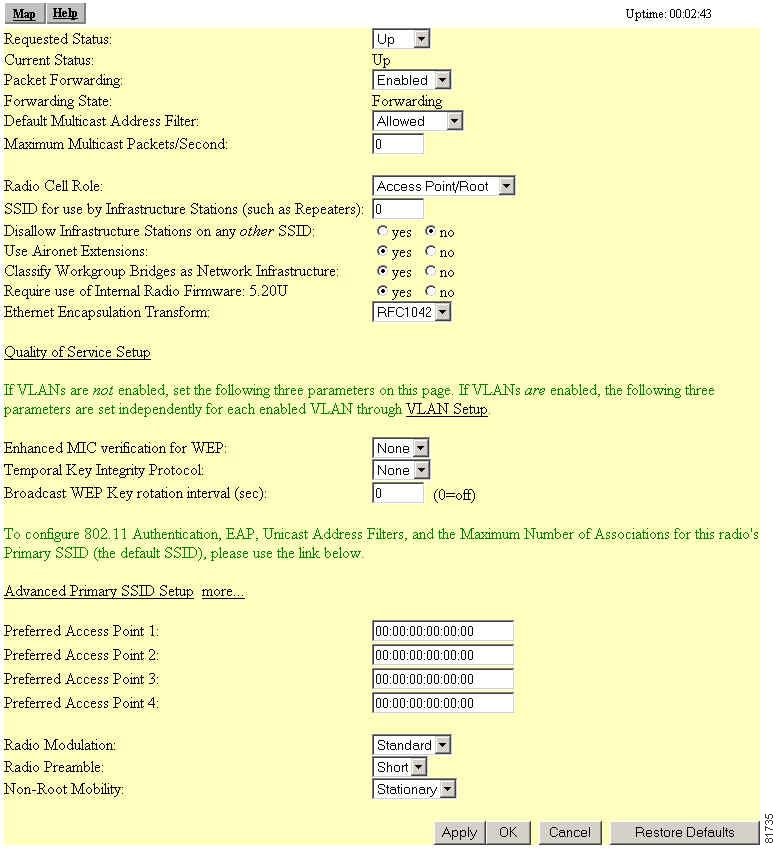
Click Advanced in the AP Radio row of the Network Ports section at the bottom of the Setup page. The AP Radio Advanced page appears. Figure 5-7 shows the AP Radio Advanced page.
Figure 5-7 AP Radio Advanced Page
Step 7
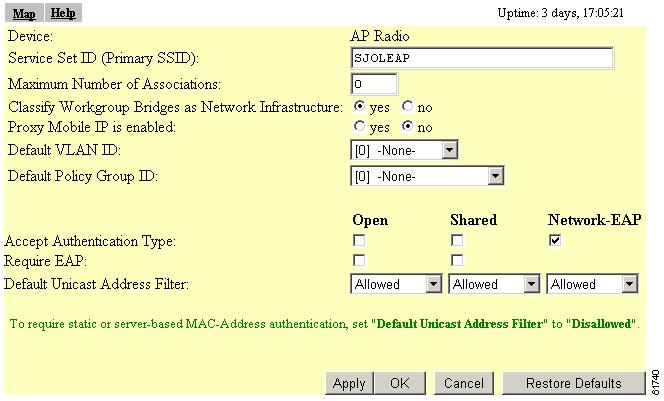
Click Advanced Primary SSID Setup. The AP Radio Primary SSID page appears. Figure 5-8 shows the AP Radio Primary SSID page.
Figure 5-8 AP Radio Primary SSID Page
Select Open, Shared Key, or Network-EAP to set the authentications the access point recognizes. See the "Security Overview" section for a description of authentication types.
If you use open or shared authentication as well as EAP authentication, select Require EAP under Open or Shared to block client devices that are not using EAP from authenticating through the access point.
Unicast MAC address filters allow or disallow the forwarding of unicast packets sent to specific MAC addresses. You can create a filter that passes traffic to all MAC addresses except those you specify, or you can create a filter that blocks traffic to all MAC addresses except those you specify.
Read the "Setting Up MAC-Based Authentication" section for complete instructions on using MAC-based authentication on an authentication server. Read the "Creating a MAC Address Filter" section for complete instructions on setting up MAC address filters.
The drop-down menus for unicast address filters contain two options:
•
Allowed—The access point forwards all traffic except packets sent to the MAC addresses listed as disallowed on the Address Filters page.
•
Disallowed—The access point discards all traffic except packets sent to the MAC addresses listed as allowed on the Address Filters page or on your authentication server.
Select Disallowed for each authentication type that also uses MAC-based authentication.
Note
If you plan to discard traffic to all MAC addresses except those you specify (the Disallowed setting), be sure to enter your own MAC address as allowed on the Address Filters page or on your authentication server.
Step 8
Click OK. Your settings are saved and you return to the AP Radio Advanced Setup page.
If clients are not filtered immediately, click WARM RESTART SYSTEM NOW on the Manage System Configuration page to restart the access point. To reach the Manage System Configuration page, Click Cisco Services on the main Setup page and click Manage System Configuration on the Cisco Services Setup page.
Note
The Ethernet Advanced page contains the Default Unicast and Multicast Address Filter settings for the Ethernet port. These settings work as described above, but you should use extra caution changing the settings on the Ethernet Advanced page because they can lock you out of your access point. To reach the Ethernet Advanced page, click Advanced in the Ethernet row of the Network Ports section at the bottom of the Setup page.
Note
Client devices with blocked MAC addresses cannot send or receive data through the access point, but they might remain in the Association Table as unauthenticated client devices. Client devices with blocked MAC addresses disappear from the Association Table when the access point stops monitoring them or they associate with another access point. See the "Association Table Advanced Page" section for information on setting a monitoring timeout for each device class.
QoS Configuration
You can assign QoS attributes to enable various devices on the network to communicate more effectively. The access point supports QoS for voice over IP (VoIP) telephones and downlink prioritized channel access for streaming audio and video traffic. This section describes how to configure the access point's QoS feature.
Entering Information on the Quality of Service Setup Page
Access the Quality of Service Setup page (see Figure 5-9) from the Summary Status page by clicking the Setup tab. From the Associations section of the Setup page, click Protocol Filters. This page is also accessed through the AP Radio Advanced page in the Network Ports section of the Setup page.
Figure 5-9 Quality of Service Setup Page
Follow this link path to reach the Quality of Service setup page:
1.
On the Summary Status page, click Setup. The Setup page appears.
2.
In the Associations section, click Protocol Filters. The Protocol Filters Setup page appears.
3.
Click Quality of Service. The AP Radio Quality of Service page appears.
Settings on the Quality of Service Setup Page
The Quality of Service setup page contains the following settings:
Generate QBSS Element
Determines whether a QoS basic service set (QBSS) element is generated. The QBSS element determines the best access point with which to associate.
Use Symbol Extensions
Configures the access point to use Symbol Voice over IP (VoIP) phones. When this setting is enabled, the access point uses the Symbol Phone Support protocol. This protocol identifies Symbol handsets and classifies traffic for them as interactive voice.
Send IGMP General Query
Configures the access point to perform IP multicast filtering on behalf of its clients. When Internet Group Membership Protocol (IGMP) snooping is enabled on a switch, and a client roams from one access point to another, the multicast session is dropped. Enabling this feature causes the access point to send a general IGMP query to the network infrastructure on behalf of the client every time it associates or reassociates to the access point. By doing so, the multicast stream is maintained for the client as it roams.
Traffic Category
Traffic category identifies a type of traffic in which data processed by the access point is categorized. There are seven categories:
•
Background
•
Spare
•
Best effort
•
Excellent effort
•
Controlled load
•
Interactive video
•
Interactive voice
•
Network control
Each category is assigned a minimum contention window (CWmin) value and a maximum contention window (CWmax) value. Allowed values for CWmin and CWmax are 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63, 127, 255, 511, and 1023.
Note
Cisco recommends that you do not alter these settings without significant testing. If you do alter the values, CWmin must be less than or equal to CWmax.
Applying QoS
You can apply QoS to specific traffic handled by the access point in a number of ways:
•
By station
•
By VLAN
•
By filter
•
By Class of Service (CoS) value
•
By differentiated services code point (DSCP) value
By Station
The access point can prioritize traffic based upon a WLAN client identifying itself as a particular client type that requires a particular traffic classification.
The best example of this is the negotiations between the access point and a Symbol VoIP WLAN handset. A protocol has been defined by Symbol that allows the handset to be identified by the access point and given interactive voice classification. Follow these steps to enable this feature.
Step 1
Browse to the Setup screen on the access point.
Step 2
Click Protocol Filters in the Associations section. The Protocol Filters Setup page appears (Figure 5-10).
Figure 5-10 Protocol Filters Setup Page
Step 3
Click Quality of Service. The AP Radio Quality of Service page appears (Figure 5-11).
Figure 5-11 AP Radio Quality of Service Page
Step 4
Click the yes radio button in the Use Symbol Extensions setting.
By VLAN
The default priority of a VLAN can be set, and the access point uses this setting for all traffic on that VLAN except when overridden by a filter setting. This filter setting is applied through the policy group on the VLAN.
Follow these steps to set up a VLANs QoS default priority.
Step 1
From the Setup page, click VLAN in the Associations section. The VLAN Setup page appears.
Step 2
Choose the VLAN to which you want to apply the priorities by highlighting it in the Existing VLANs field, and click Edit. The VLAN ID page for that VLAN appears (Figure 5-12).
Figure 5-12 VLAN ID page
Step 3
To view the selections in the Default Priority field, click the drop-down menu.
Step 4
Select the default priority you wish the VLAN to use.
Step 5
Click OK to save your settings and return to the VLAN Setup page.
By Filter
Access point and bridge filters already allow the classification of traffic based upon Ethertype, Internet Protocol, or IP Port. An example of a filter classifying traffic is shown on Figure 5-13.
Figure 5-13 Filters Priority Setting
The filters can be applied on interfaces or as a part of a VLAN policy group.
The access point has a default filter to classify all Spectralink voice traffic with voice priority. You do not have to enable this filter, but you can modify the filter and apply it to a specific VLAN or interface.
Note
To set up a filter, see the "Filter Setup" section.
A typical Spectralink filter configuration is shown on Figure 5-14.
Figure 5-14 Spectralink Filter Configuration
Figure 5-15 shows how the Spectralink filter is applied.
Figure 5-15 Applying the Spectralink Filter
By CoS Value
Traffic that comes to the access point over an Ethernet trunk is already classified by its Class of Service (CoS) settings. The classification is applied unless changed by one of the methods described above.
By DSCP Value
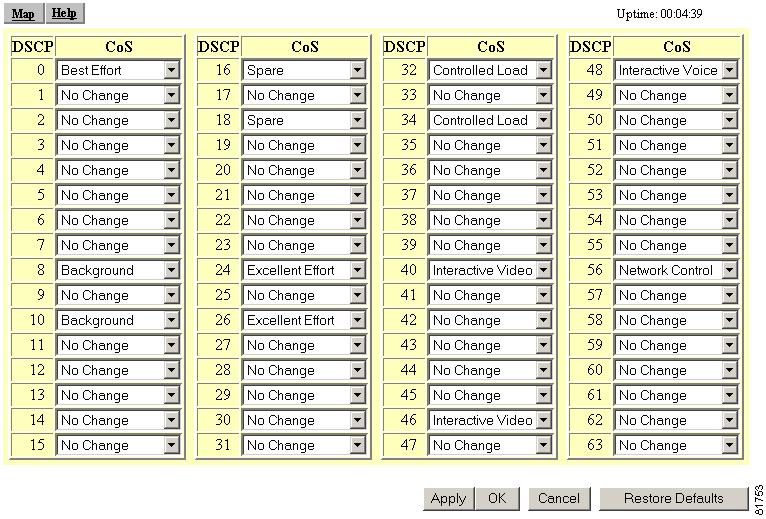
The differentiated services code point (DSCP) values in the IP packets can be used to classify the traffic based on the DSCP-to-CoS mappings shown in Figure 5-16.
Figure 5-16 DSCP-to-CoS Conversion
Follow these steps to access the DSCP-to-CoS Conversion page.
Step 1
From the Summary Status page, click Setup. The Setup page appears.
Step 2
In the Associations section, click Protocol Filters. The Protocol Filters Setup page appears.
Step 3
Click DSCP-to-CoS Conversion.
A Wireless QoS Deployment Example
This section outlines a typical use for deploying QoS on a wireless LAN: configuring the access point to properly prioritize an 802.11b wireless phone using a VLAN.
Before discussing the steps involved to configure this QoS scenario, it is assumed that you have configured and enabled VLANs on the access point and that all downstream interactive voice configurations are made to other infrastructure devices and applicable applications on the wired LAN, such as switches, routers, DHCP servers, Call Manager, etc.
In this example, we create a VLAN dedicated to interactive voice. Its ID is 12 and its name is Voice. An SSID called Voice is created to handle the interactive voice traffic on the access point.
Note
The example shows how to configure QoS on a root access point. Screens will differ slightly for repeater access points and bridged applications.
Follow these steps to configure the access point:
Step 1
Browse to the Setup screen on the access point.
Step 2
In the Associations section, click VLAN. The VLAN Setup page appears.
Step 3
Enter a VLAN ID in the VLAN ID field.
Step 4
Enter a VLAN name in the VLAN Name field (Figure 5-17).
Figure 5-17 VLAN Setup page
Step 5
Click Add New. The VLAN ID #xx page appears.
Step 6
Set VLAN Enable setting to Enable.
Step 7
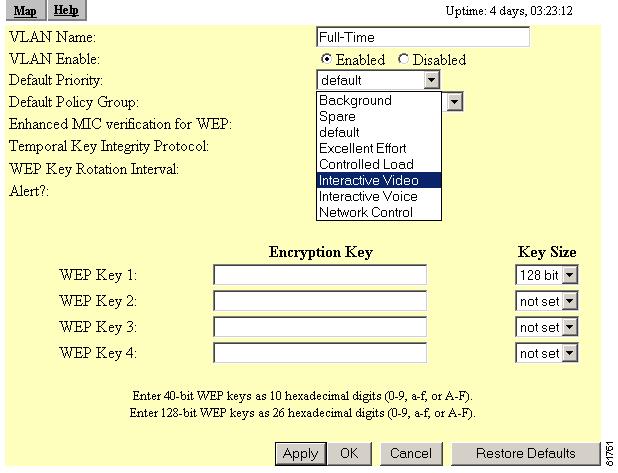
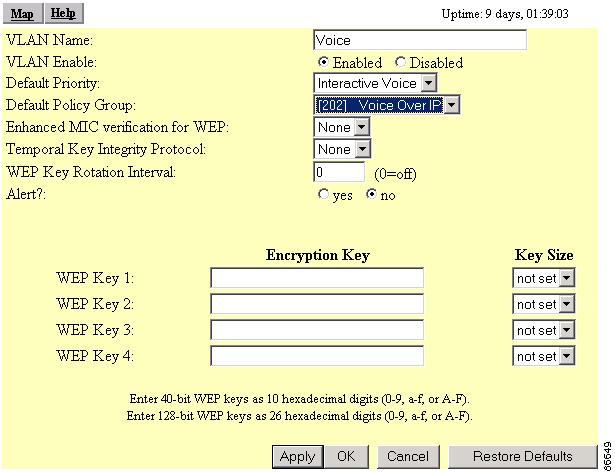
In the Default Priority Group drop-down menu, select Interactive Voice. (Figure 5-18).
Figure 5-18 VLAN ID #xx page
Note
Wireless phones do not support Enhanced MIC verification for WEP or TKIP. No changes are required for these settings.
If your wireless phone has a WEP key set, go the next section. If a WEP key is not set, go to the "WEP Not Set on the Wireless Phone" section.
WEP Set on the Wireless Phone
If WEP is set on your wireless phone, you must set an identical WEP key for the interactive voice VLAN. Follow these steps to set the WEP key.
Step 1
Enter the phone's WEP key in the WEP Key 1 Encryption Key field.
Step 2
In the Key Size drop-down menu, select the WEP key size set on the phone.
Step 3
Click Apply or OK. The configuration is complete.
WEP Not Set on the Wireless Phone
If a WEP key is not set on the wireless phone, you must complete the configuration by following these steps:
Step 1
Browse to the VLAN Setup page.
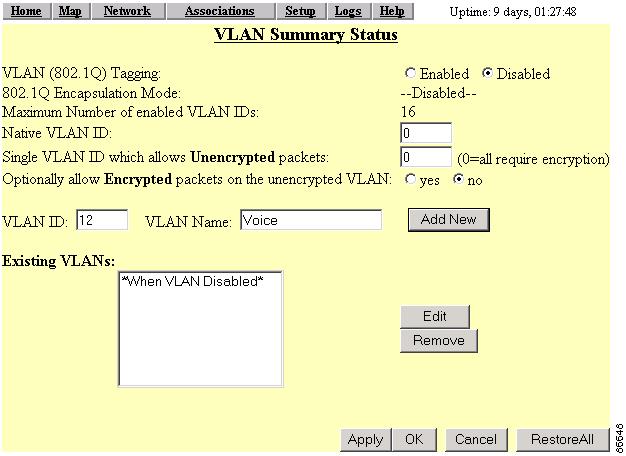
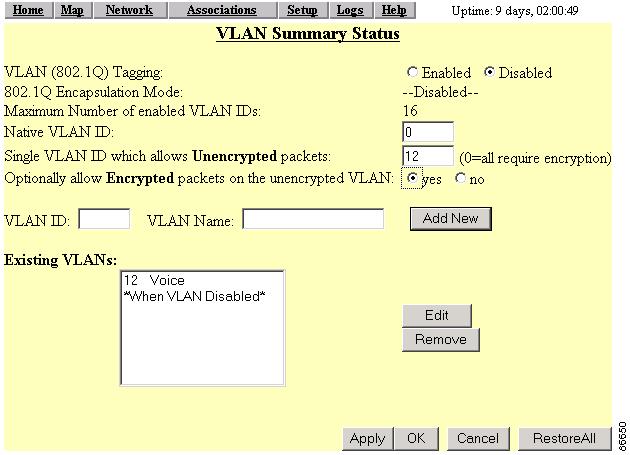
Step 2
In the Single VLAN ID which allows Unencrypted packets field, enter the Voice VLAN ID.
Step 3
Set the Optionally allow Encrypted packets on the unencrypted VLAN to yes (Figure 5-19).
Figure 5-19 VLAN Setup page
Step 4
Click OK. You are returned to the Setup page.
Step 5
In the Associations section, click SSIDs: Int. The AP Radio: Internal Service Sets page appears.
Step 6
Enter a valid SSID in the Service Set ID (SSID) field (Figure 5-20).
Figure 5-20 AP Radio: Internal Service Sets page
Step 7
Click Add New. The AP Radio: Internal SSID #x page appears.
Step 8
In the Default VLAN ID drop-down menu, select [12] Voice (Figure 5-21).
Figure 5-21 AP Radio: Internal Service Sets page
Step 9
Leave all other settings at the default settings and click OK. You are returned to the AP Radio: Internal Service Sets page.
Step 10
Click OK again to return to the Setup page.
Your configuration is complete.

 Feedback
Feedback