-
Cisco IOS Voice Command Reference
-
About Cisco IOS Software Documentation
-
Using Cisco IOS Software
-
Commands: A
-
Commands: B
-
Commands:cac master through call application stats
-
Commands: call application voice through call-denial
-
Commands: call fallback through called-number (dial-peer)
-
Commands: caller-id (dial peer) through ccm-manager switchover-to-backup
-
Commands: ccs connect (controller) through clear vsp statistics
-
Commands: clid through cptone
-
Commands: default (MGCP profile) through direct-inward-dial
-
Commands: disable-early-media 180 through dualtone
-
Commands: E
-
Commands: F
-
Commands: G
-
Commands: H
-
Commands: icpif through irq global-request
-
Commands: isdn bind-l3 through ixi transport http
-
Commands: K
-
Commands: L
-
Commands: map q850-cause through mgcp package-capability
-
Commands: mgcp persistent through mmoip aaa send-id secondary
-
Commands: mode (ATM/T1/E1 controller) through mwi-server
-
Commands: N
-
Commands: O
-
Commands: package through pattern
-
Commands: permit hostname through proxy h323
-
Commands: Q
-
Commands: R
-
Commands: sccp through service-type call-check
-
Commands: session through sgcp tse payload
-
Commands: show aal2 profile through show call filter match-list
-
Commands: show call history fax through show debug condition
-
Commands: show dial-peer video through show gatekeeper zone status
-
Commands: show gateway through show modem relay statistics
-
Commands: show mrcp client session active through show sgcp statistics
-
Commands: show sip service through show trunk hdlc
-
Commands: show vdev through show voice statistics memory-usage
-
Commands: show voice translation-profile through shutdown (voice-port)
-
Commands: signal through srv version
-
Commands: ss7 mtp2-variant through switchover method
-
Commands: target carrier-id through threshold noise
-
Commands: timeout (auto-config application) through timing clear-wait
-
Commands:timing delay-duration through type (voice)
-
Commands: U
-
Commands: vad (dial peer) through voice class dualtone-detect-params
-
Commands: voice class h323 through vxml tree memory
-
Commands: W
-
Commands: Z
-
Table Of Contents
call fallback instantaneous-value-weight
call fallback jitter-probe dscp
call fallback jitter-probe num-packets
call fallback jitter-probe precedence
call fallback jitter-probe priority-queue
call fallback map address-list
call fallback reject-cause-code
call fallback threshold delay loss
call leg event-log max-buffer-size
call leg history event-log save-exception-only
call fallback
To enable a call request to fall back to a specific dial peer in case of network congestion, use the call fallback command in dial peer configuration mode. To disable PSTN fallback for a specific dial peer, use the no form of this command.
call fallback
no call fallback
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
This command is enabled by default if the call fallback active command is enabled in global configuration mode
Command Modes
Dial peer configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Disabling the call fallback command for a dial peer causes the call fallback subsystem not to fall back to the specified dial peer. Disabling the command is useful when internetworking fallback capable H.323 gateways with the Cisco CallManager or third-party equipment that does not run fallback. Connected calls are not affected by this feature.
Examples
The following example disables a PSTN fallback for a specific dial peer:
no call fallbackRelated Commands
call fallback active
To enable a call request to fall back to alternate dial peers in case of network congestion, use the call fallback active command in global configuration mode. To disable PSTN fallback, use the no form of this command.
call fallback active
no call fallback active
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
This command is disabled by default.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Enabling the call fallback active command determines whether calls should be accepted or rejected on the basis of probing of network conditions. The call fallback active command checks each H.323 call request and rejects the call if the network congestion parameters are greater than the value of the configured threshold parameters of the destination. If this is the case, alternative dial peers are tried from the session application layer.
Use the call fallback threshold delay loss or call fallback threshold icpif command to set the threshold parameters.
Connected calls are not affected by this command.
Examples
The following example enables the call fallback active command:
Router(config)# call fallback activeRelated Commands
call fallback cache-size
To specify the call fallback cache size for network traffic probe entries, use the call fallback cache-size command in global configuration mode. To restore the default value, use the no form of this command.
call fallback cache-size number
no call fallback cache-size
Syntax Description
Command Default
128 entries
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The cache size can be changed only when the call fallback active command is not enabled.
The overflow process deletes up to one-fourth of the cache entries to allow for additional calls beyond the specified cache size. The cache entries chosen for deletion are the oldest entries in the cache.
If the cache size is left unchanged, it can be changed only when fallback is off. Use the no form of the call fallback command to turn fallback off.
Examples
The following example specifies 120 cache entries:
Router(config)# call fallback cache-size 120Related Commands
call fallback cache-timeout
To specify the time after which the cache entries of network conditions are purged, use the call fallback cache-timeout command in global configuration mode. To disable the call fallback cache-timeout command, use the no form of this command.
call fallback cache-timeout seconds
no call fallback cache-timeout
Syntax Description
Command Default
600 seconds
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Enabling the call fallback cache-timeout command sends a Service Assurance Agent (SAA) probe out to the network to determine the amount of congestion in terms of configured thresholds. The network condition is based upon delay and loss, or Calculated Planning Impairment Factor (ICPIF) thresholds. Use the call fallback threshold delay loss or call fallback threshold icpif command to set the threshold parameters.
The cache keeps entries for every network congestion-checking probe sent and received between timeouts. The cache updates after each probe returns the current condition of network traffic. To set the probe frequency, use the call fallback probe-timeout command.
When a call comes into the router, the router matches a dial peer and obtains the destination information. The router calls the fallback subsystem to look up the specified destination in its network traffic cache. If the delay/loss or ICPIF threshold exists and is current, the router uses that value to decide whether to permit the call into the Voice over IP (VoIP) network. If the router determines that the network congestion is below the configured threshold (by looking at the value in the cache), the call is connected.
After each call request, the timer is reset. Purging of the cache occurs only when the cache has received no call requests during the timeout period (seconds). When the cache timeout expires, the entire cache is deleted, and a probe is sent to start a new cache entry. A call cannot be completed until this probe returns with network traffic information.
The network congestion probes continue in the background as long as the entry for the last call request remains in the cache.
Examples
The following example specifies an elapsed time of 1200 seconds before the cache times out:
Router(config)# call fallback cache-timeout 1200Related Commands
call fallback expect-factor
To set a configurable value by which the call fallback expect factor feature will be activated, use the call fallback expect-factor command in global configuration mode. To disable the expect factor, use the no form of this command.
call fallback expect-factor value
no call fallback expect-factor
Syntax Description
Command Default
No value for the expect-factor is configured.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
12.3(3)
This command was introduced.
12.3(4)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(4)T.
Usage Guidelines
The expect-factor is the level of expected voice quality that the user may have during a call. For example, you expect higher voice quality from a call on your home than on your cell phone. The expect-factor is a subjective value determined by the local administrators.
Call fallback is used by the software to generate a series of probes across an IP network to help make a Impairment/Calculated Impairment Planning Factor (ICPIF) calculation. The value calculated by the probes, ICPIF, is modified by the configured expect factor using the following formula:
ICPIF = Idd + Ie-A
Idd represents the impairment due to end-end delay, Ie, represents the impairment due to packet loss and the impact of the codec being used on the call, and A represents the expect-factor value. The expect-factor is the value to be subtracted from the calculated ICPIF value. This expect factor is known as the Advantage Factor (A) as specified in G.107 and takes into account the user's expected level of voice quality based upon the type of call being made.
Examples
The following example shows the call fallback expect-factor command and the call fallback threshold icpicf command being configured. A calculated ICPIF value of 20 based on Idd and Ie from the probes set on a IP network would not activate the call fallback feature in this configuration. Even though the calculated ICPIF value of 20 exceeds the configured threshold of 10, subtraction of the expect-value of 15 would leave a value of 5, which is below the threshold value.
Router(config)# call fallback expect-factor 15Router(config)# call fallback threshold icpif 10Related Commands
call fallback instantaneous-value-weight
To configure the call fallback subsystem to take an average from the last two probes registered in the cache for call requests, use the call fallback instantaneous-value-weight command in global configuration mode. To return to the default before the average was calculated, use the no form of this command.
call fallback instantaneous-value-weight percent
no call fallback instantaneous-value-weight
Syntax Description
percent
Instantaneous value weight, in expressed as a percentage. Range is from 0 to 100. The default is 66.
Command Default
66 percent
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Probes that return the network congestion information are logged into the cache to determine whether the next call request is granted. When the network is regularly busy, the cache entries reflect the heavy traffic conditions. However, one probe may return with low traffic conditions, which is in contrast to normal conditions. All call requests received between the time of this probe and the next use this entry to determine call acceptance. These calls are allowed through the network, but before the next probe is sent and received, the normal, heavy traffic conditions must have returned. The calls sent through congest the network and cause worsen traffic conditions.
Use the call fallback instantaneous-value-weight command to gradually recover from heavy traffic network conditions. While the system waits for a call, probes update the cache. When a new probe is received, the percentage is set and indicates how much the system is to rely upon the new probe and the previous cache entry. If the percentage is set to 50 percent, the system enters a cache entry based upon an average from the new probe and the most recent entry in the cache. Call requests use this blended entry to determine acceptance. This allows the call fallback subsystem to keep conservative measures of network congestion.
The configured percentate applies to the new probe first. If the call fallback instantaneous-value-weight command is configured with the default percentage of 66 percent, the new probe is given a higher value to calculate the average for the new cache entry.
Examples
The following example specifies a fallback value weight of 50 percent:
Router(config)# call fallback instantaneous-value-weight 50Related Commands
call fallback active
Enables a call request to fall back to alternate dial peers in case of network congestion.
show call fallback config
Displays the call fallback configuration.
call fallback jitter-probe dscp
To specify the differentiated services code point (DSCP) of the jitter-probe transmission, use the call fallback jitter-probe dscp command in global configuration mode. To disable this feature and restore the default value of jitter-probe precedence, use the no form of this command.
call fallback jitter-probe dscp dscp-number
no call fallback jitter-probe dscp
Syntax Description
Command Default
None
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
12.3(8)T
This command was introduced.
12.3(9)
This command was implemented in Cisco IOS Release 12.3(9).
Usage Guidelines
Network devices that support differentiated services (DiffServ) use a DSCP in the IP header to select a per-hop behavior (PHB) for a packet. Cisco implements queuing techniques that can base their PHB on the IP precedence or DSCP value in the IP header of a packet. On the basic of DSCP or IP precedence, traffic can be put into a particular service class. Packets within a service class are treated alike.
The call fallback jitter-probe dscp command allows you to set a DSCP for jitter-probe packets. The specified DSCP is stored, displayed, and passed in probing packets to the Service Assurance Agent (SAA). This command enables the router to reserve some bandwidth so that during network congestion some of the jitter-probe packets do not get dropped. This command avoids the conflict that occurs with traditional precedence bits.
The call fallback jitter-probe dscp command is mutually exclusive with the call fallback jitter-probe precedence command. Only one of these command can be enabled on the router. When the call fallback jitter-probe dscp command is configured, the precedence value is replaced with the DSCP value. The no call fallback jitter-probe dscp command restores the default value for precedence.
Examples
The following example specifies the jitter-probe DSCP as 10. DSCP configuration replaces the set jitter-probe precedence value with the DSCP value.
call fallback jitter-probe dscp 10The following configuration disables the DSCP value and restores the default value for precedence, which is set to 2:
no call fallback jitter-probe dscpRelated Commands
call fallback jitter-probe num-packets
To specify the number of packets in a jitter probe used to determine network conditions, use the call fallback jitter-probe num-packets command in global configuration mode. To restore the default number of packets, use the no form of this command.
call fallback jitter-probe num-packets number-of-packets
no call fallback jitter-probe num-packets
Syntax Description
Command Default
15 packets
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
A jitter probe, consisting of 2 to 50 packets, details the conditions of the network. More than one packet is used by the probe to calculate an average of delay/loss or Calculated Planning Impairment Factor (ICPIF). After the packets return to the probe, the probe delivers the traffic information to the cache where it is logged for call acceptance/denial. Use the call fallback threshold delay loss or call fallback threshold icpif command to set the threshold parameters. The newly specified number of packets take effect only for new probes.
To get a more realistic estimate on the network congestion, increase the number of packets. If more probing packets are sent, better estimates of network conditions are obtained, but the bandwidth for other network operations is negatively affected. Use fewer packets when you need to maximize bandwidth.
Examples
The following example specifies 20 packets in a jitter probe:
Router(config)# call fallback jitter-probe num-packets 20Related Commands
call fallback threshold icpif
Specifies the ICPIF threshold.
call fallback threshold delay loss
Specifies the call fallback threshold delay and loss values.
call fallback jitter-probe precedence
To specify the priority of the jitter-probe transmission, use the call fallback jitter-probe precedence command in global configuration mode. To restore the default priority, use the no form of this command.
call fallback jitter-probe precedence precedence-value
no call fallback jitter-probe precedence
Syntax Description
Defaults
Enabled
Value set to 2Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Every IP packet has a precedence header. Precedence is used by various queueing mechanisms in routers to determine the priority of traffic passing through the system.
Use the call fallback jitter-probe precedence command if there are different queueing mechanisms in your network. Enabling the call fallback jitter-probe precedence command sets the precedence for jitter probes to pass through your network.
If you require your probes to be sent and returned quickly, set the precedence to a low number (0 or 1): the lower the precedence, the higher the priority given.
The call fallback jitter-probe precedence command is mutually exclusive with the call fallback jitter-probe dscp command. Only one of these commands can be enabled on the router. Usually the call fallback jitter-probe precedence command is enabled. When the call fallback jitter-probe dscp command is configured, the precedence value is replaced by the DSCP value. To disable DSCP and restore the default jitter probe precedence value, use the no call fallback jitter-probe dscp command.
Examples
The following example specifies a jitter-probe precedence of 5, or low priority.
call fallback jitter-probe precedence 5The following configuration restores the default value for precedence:
no call fallback jitter-probe precedenceRelated Commands
call fallback jitter-probe priority-queue
To assign a priority queue for jitter-probe transmissions, use the call fallback jitter-probe priority-queue command in global configuration mode. To return to the default state, use the no form of this command.
call fallback jitter-probe priority-queue
no call fallback jitter-probe priority-queue
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
Disabled
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
This command is applicable only if the queueing method used is IP Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) priority. This command is unnecessary when low latency queueing (LLQ) is used because these packets follow the priority queue path (or not) based on the LLQ classification criteria.
This command works by choosing between sending the probe on an odd or even Service Assurance Agent (SAA) port number. The SAA probe packets go out on randomly selected ports chosen from within the top end of the audio User Datagram Protocol (UDP) defined port range (16384 to 32767). The port pair (RTP Control Protocol [RTCP] port) is selected, and by default, SAA probes for call fallback use the RTCP port (odd) to avoid going into the priority queue, if enabled. If call fallback is configured to use the priority queue, the RTP port (even) is selected.
Examples
The following example specifies that a probe be sent to an SAA port:
Router(config)# call fallback jitter-probe priority-queue
Note
In order for this command to have any effect on the probes, the IP priority queueing must be set for UDP voice ports numbered from 16384 to 32767.
Related Commands
call fallback key-chain
To specify the use of message digest algorithm 5 (MD5) authentication for sending and receiving Service Assurance Agents (SAA) probes, use the call fallback key-chain command in global configuration mode. To disable MD5, use the no form of this command.
call fallback key-chain name-of-chain
no call fallback key-chain name-of-chain
Syntax Description
name-of-chain
Name of the chain. This name is alphanumeric and case-sensitive text. There is no default value.
Command Default
MD5 authentication is not used.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
This command is used to enable the SAA probe authentication using MD5. If MD5 authentication is used, the keys on the sender and receiver routers must match.
Examples
The following example specifies "sample" as the fallback key chain:
Router(config)# call fallback key-chain sampleRelated Commands
call fallback map address-list
To specify that the call fallback router keep a cache table by IP addresses of distances for several destination peers, use the call fallback map address-list command in global configuration mode. To restore the default values, use the no form of this command.
call fallback map map target ip-address address-list ip-address1 ... ip-address7
no call fallback map map target ip-address address-list ip-address1 ... ip-address7
Syntax Description
Command Default
No call fallback maps are defined.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use this command when several destination peers are in one common node.
Call fallback map setup allows the decongestion of traffic caused by a high volume of call probes sent across a network to query a large number of dial peers. One router/common node can keep the distances in a cache table of the numerous IP addresses/destination peers in a network. When the fallback is queried for network congestion to a particular IP address (that is, the common node), the map addresses are searched to find the target IP address. If a match is determined, the probes are sent to the target address rather than to the particular IP address.
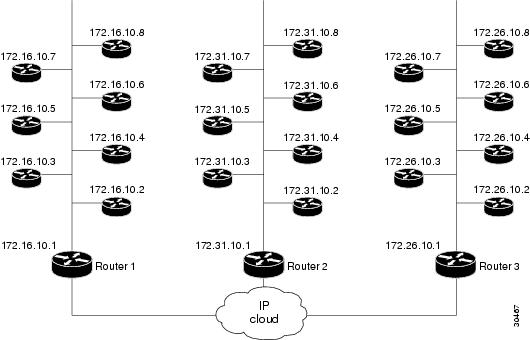
In Figure 1, the three routers (1, 2, and 3) keep the cache tables of distances for the destination peers behind them. When a call probe comes from somewhere in the IP cloud, the cache routers check their distance tables for the IP address/destination peer where the call probe is destined. This distance checking limits congestion on the networks behind these routers by directing the probe to the particular IP address and not to the entire network.
Figure 1 Call Fallback Map with IP Addresses
Examples
The following example specifies call fallback map address-list configurations for 172.32.10.1 and 172.46.10.1:
Router(config)# call fallback map 1 target 172.32.10.1 address-list 172.32.10.2 172.32.10.3 172.32.10.4 172.32.10.5 172.32.10.6 172.32.10.7 172.32.10.8Router(config)# call fallback map 2 target 172.46.10.1 address-list 172.46.10.2 172.46.10.3 172.46.10.4 172.46.10.5 172.46.10.6 172.46.10.7 172.46.10.8Related Commands
call fallback map subnet
To specify that the call fallback router keep a cache table by subnet addresses of distances for several destination peers, use the call fallback map subnet command in global configuration mode. To restore the default values, use the no form of this command.
call fallback map map target ip-address subnet ip-network netmask
no call fallback map map target ip-address subnet ip-network netmask
Syntax Description
map
Fallback map. Range is from 1 to 16. There is no default.
target ip-address
Target IP address.
subnet ip-network
Subnet IP address.
netmask
Network mask number.
Command Default
No call fallback maps are defined.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use this command when several destination peers are in one common node.
Call fallback map setup allows the decongestion of traffic caused by a high volume of call probes sent across a network to query a large number of dial peers. One router/common node can keep the distances in a cache table of the numerous IP addresses within a subnet (destination peers) in a network. When the fallback is queried for network congestion to a particular IP address (that is, the common node), the map addresses are searched to find the target IP address. If a match is determined, the probes are sent to the target address rather than to the particular IP address.
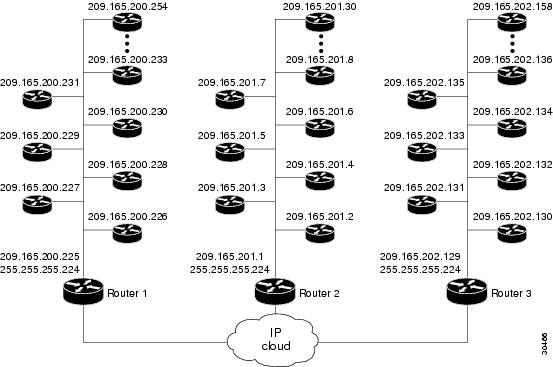
In Figure 2, the three routers (1, 2, and 3) keep the cache tables of distances for the destination peers behind them. When a call probe comes from somewhere in the IP cloud, the cache routers check their distance tables for the subnet address/destination peer where the call probe is destined. This distance checking limits congestion on the networks behind these routers by directing the probe to the particular subnet address and not to the entire network.
Figure 2 Call Fallback Map with Subnet Addresses
Examples
The following examples specify the call fallback map subnet configuration for two different IP addresses:
Router(config)# call fallback map 1 target 209.165.201.225 subnet209.165.201.224 255.255.255.224Router(config)# call fallback map 2 target 209.165.202.225 subnet209.165.202.224 255.255.255.224Related Commands
call fallback monitor
To enable the monitoring of destinations without call fallback to alternate dial peers, use the call fallback monitor command in global configuration mode. To disable monitoring without fallback, use the no form of this command.
call fallback monitor
no call fallback monitor
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
Disabled
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The call fallback monitor command is used as a statistics collector of network conditions based upon probes (detailing network traffic) and connected calls. There is no H.323 call checking/rejecting as with the call fallback active command. All call requests are granted regardless of network traffic conditions.
Configure the call fallback threshold delay loss or call fallback threshold icpif command to set threshold parameters. The thresholds are ignored, but for statistics collecting, configuring one of the thresholds allows you to monitor cache entries for either delay/loss or Calculated Planning Impairment Factor (ICPIF) values.
Examples
The following example enables the call fallback monitor command:
Router(config)# call fallback monitorRelated Commands
call fallback probe-timeout
To set the timeout for a Service Assurance Agent (SAA) probe for call fallback purposes, use the call fallback probe-timeout command in global configuration mode. To restore the default value, use the no form of this command.
call fallback probe-timeout seconds
no call fallback probe-timeout
Syntax Description
Command Default
30 seconds
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
SAA probes collect network traffic information based upon configured delay and loss or Calculated Planning Impairment Factor (ICPIF) values and report this information to the cache for call request determination. Use the call fallback threshold delay loss or call fallback threshold icpif command to set the threshold parameters.
When the probe timeout expires, a new probe is sent to collect network statistics. To reduce the bandwidth taken up by the probes, increase the probe-timeout interval (seconds). Probes do not have a great effect upon bandwidth unless several thousand destinations are involved. If this is the case in your network, use a longer timeout. If you need more network traffic information, and bandwidth is not an issue, use a lower timeout. The default interval, 30 seconds, is a low timeout.
When the call fallback cache-timeout command is configured or expires, new probes are initiated for data collection.
Examples
The following example configures a 120-second interval:
Router(config)# call fallback probe-timeout 120Related Commands
call fallback reject-cause-code
To enable a specific call fallback reject cause code in case of network congestion, use the call fallback reject-cause-code command in global configuration mode. To reset the code to the default of 49, use the no form of this command.
call fallback reject-cause-code number
no call fallback reject-cause-code
Syntax Description
number
Specifies the cause code as defined in the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) standard Q.850 except the code for normal call clearing, which is code 16. The default is 49. See Table 10 for ITU cause-code numbers.
Command Default
49 (quality of service is unavailable)
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Enabling the call fallback reject-cause-code command determines the code to display when calls are rejected because of probing of network conditions.
Note
Connected calls are not affected by this command.
Examples
The following example enables the call fallback reject-cause-code command and specifies cause code 34:
call fallback reject-cause-code 34Related Commands
call fallback threshold delay loss
To specify that the call fallback threshold use only packet delay and loss values, use the call fallback threshold delay loss command in global configuration mode. To restore the default value, use the no form of this command.
call fallback threshold delay milliseconds loss percent
no call fallback threshold delay milliseconds loss percent
Syntax Description
Command Default
None
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
During times of heavy voice traffic, two parties in a conversation may notice a significant delay in transmission or hear only part of a conversation because of voice-packet loss.
Use the call fallback threshold delay loss command to configure parameters for voice quality. Lower values of delay and loss allow higher quality of voice. Call requests match the network information in the cache with the configured thresholds of delay and loss.
The amount of delay set by the call fallback threshold delay loss command should not be more than half the amount of the time-to-wait value set by the call fallback wait-timeout command; otherwise the threshold delay will not work correctly. Because the default value of the call fallback wait-timeout command is set to 300 ms, the user can configure a delay of up to 150 ms for the call fallback threshold delay loss command. If the user wants to configure a higher threshold, the time-to-wait delay has to be increased from its default (300 ms) using the call fallback wait-timeout command.
Note
The delay configured by the call fallback threshold delay loss command corresponds to a one-way delay, whereas the time-to-wait period configured by the call fallback wait-timeout command corresponds to a round-trip delay.
If you enable the call fallback active command, the call fallback subsystem uses the last cache entry compared with the configured delay/loss threshold to determine whether the call is connected or denied. If you enable the call fallback monitor command, all calls are connected, regardless of the configured threshold or voice quality. In this case, configuring the call fallback threshold delay loss command allows you to collect network statistics for further tracking.
Note
The call fallback threshold delay loss command differs from the call fallback threshold icpif command because the call fallback threshold delay loss command uses only packet delay and loss parameters, and the call fallback threshold icpif command uses packet delay and loss parameters plus other International Telecommunication Union (ITU) G.113 factors to gather impairment information.
Setting this command does not affect bandwidth. Available bandwidth for call requests is determined by the call fallback subsystem using probes. The number of probes on the network affects bandwidth.
Examples
The following example configures a threshold delay of 20 ms and a threshold loss of 50 percent:
Router(config)# call fallback threshold delay 20 loss 50Related Commands
call fallback threshold icpif
To specify that call fallback use the Calculated Planning Impairment Factor (ICPIF) threshold, use the call fallback threshold icpif command in global configuration mode. To restore the default value, use the no form of this command.
call fallback threshold icpif threshold-value
no call fallback threshold icpif
Syntax Description
Command Default
5
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
During times of heavy voice traffic, the parties in a conversation may notice a significant delay in transmission or hear only part of a conversation because of voice-packet loss.
Use the call fallback threshold icpif command to configure parameters for voice quality. A low ICPIF value allows for higher quality of voice. Call requests match the network information in the cache with the configured ICPIF threshold. If you enable the call fallback active command, the call fallback subsystem uses the last cache entry compared with the configured ICPIF threshold to determine whether the call is connected or denied. If you enable the call fallback monitor command, all calls are connected regardless of the configured threshold or voice quality. In this case, configuring the call fallback threshold icpif command allows you to collect network statistics for further tracking.
A lower ICPIF value tolerates less delay and loss of voice packets (according to ICPIF calculations). Use lower values for higher quality of voice. Configuring a value of 34 equates to 100 percent packet loss.
The ICPIF is calculated and used according to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) G.113 specification.
Note
The call fallback threshold delay loss command differs from the call fallback threshold icpif command because the call fallback threshold delay loss command uses only packet delay and loss parameters, while the call fallback threshold icpif command uses packet delay and loss parameters plus other ITU G.113 factors to gather impairment information.
Setting this command does not affect bandwidth. Available bandwidth for call requests is determined by the call fallback subsystem using probes. The number of probes on the network affects bandwidth.
Examples
The following example sets the ICPIF threshold to 20:
Router(config)# call fallback threshold icpif 20Related Commands
call fallback wait-timeout
To modify the time to wait for a response to a probe, use the call fallback wait-timeout command in global configuration mode. To return to the default value, use the no form of this command.
call fallback wait-timeout milliseconds
no call fallback wait-timeout milliseconds
Syntax Description
Command Default
300 milliseconds
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
This command is enabled by default. The time to wait for a response to a probe is set to 300 ms. This command allows the user to modify the amount of time to wait for a response to a probe. The milliseconds argument allows the user to configure a time-to-wait value from 100 ms and 3000 ms. A user that has a higher-latency network may want to increase the value of the default timer.
The time-to-wait period set by the call fallback wait-timeout command should always be greater than or equal to twice the amount of the threshold delay time set by the call fallback threshold delay loss command; otherwise the probe will fail.
Note
The delay configured by the call fallback threshold delay loss command corresponds to a one-way delay, whereas the time-to-wait period configured by call fallback wait-timeout command corresponds to a round-trip delay. The threshold delay time should be set at half the value of the time-to-wait value.
Examples
The following example sets the amount of time to wait for a response to a probe to 200 ms:
call fallback wait-timeout 200Related Commands
call fallback threshold delay loss
Specifies the call fallback threshold delay and loss values.
call filter match-list voice
To enter the call filter match list configuration mode and create a call filter match list for debugging voice calls, use the call filter match-list voice command in global configuration mode. To remove the filter, use the no form of this command.
call filter match-list number voice
no call filter match-list number voice
Syntax Description
Command Default
None
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Configure the call filter match-list voice command to set the conditions for filtering voice call debugging. After the conditions are set with this command, use the debug condition match-list command in privileged EXEC mode to get the filtered debug output.
Examples
The following example shows that the call filter match list designated as list 1 filters the debug output for an incoming calling number matching 8288807, an incoming called number matching 6560729, and on incoming port 7/0:D:
call filter match-list 1 voiceincoming calling-number 8288807incoming called-number 6560729incoming port 7/0:DRelated Commands
debug condition match-list
Runs a filtered debug on a voice call.
show call filter match-list
Displays call filter match lists.
call forward all
To designate an SCCP telephony control (STC) feature access code for setting call forward all on an analog phone, use the call forward all command in STC application feature access-code configuration mode. To return the code to its default, use the no form of this command.
call forward all keypad-character
no call forward all
Syntax Description
Command Default
The default code for forwarding all calls is 1.
Command Modes
STC application feature access-code configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
This command is used on a voice gateway with the STC application, which enables certain features on analog FXS endpoints that use Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP) for call control.
Use this command to set the STC application feature access code (FAC) for phone users to dial to enable call forwarding for all calls. Use this command only if you want to change the FAC from its default (1). The call forward cancel command can be used to change the value of the FAC that cancels call forwarding from its default.
To enable a call-forward-all condition on a phone, dial the FAC prefix, the FAC that has been configured with this command (or the default if this command has not been used), and, following the beep prompt, a target extension to which calls will be forwarded. Note that this feature can also be activated using the call-forward all (ephone-dn) command on the Cisco CME router. If you activate CFA from the Cisco CME router and also from the phone, whichever took place later takes precedence.
The call-forward max-length command can be used on the Cisco CME router to limit the number of digits that can be dialed for the target forwarding number.
If you set this FAC to a value that is already in use for another FAC, you receive a warning message. If you configure a duplicate code, the system implements the first matching feature in the order of precedence shown in the output of the show stcapp feature codes command.
The show running-config command displays nondefault FACs only. The show stcapp feature codes command displays all FACs.
Examples
The following example sets two nondefault values: a FAC prefix of two pound signs (##) and a call-forward-all FAC of 2. After these values are configured, a phone user presses ##2, 3333 on the keypad to forward all calls to extension 3333.
Router(config)# stcapp feature access-codeRouter(stcapp-fac)# prefix ##Router(stcapp-fac)# call forward all 2Router(stcapp-fac)# exitRelated Commands
call forward cancel
To designate an SCCP telephony control (STC) feature access code for canceling call forwarding, use the call forward cancel command in STC application feature access-code configuration mode. To return the code to its default, use the no form of this command.
call forward cancel keypad-character
no call forward cancel
Syntax Description
Command Default
The default code for canceling call forwarding is 2.
Command Modes
STC application feature access-code configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
This command is used on a voice gateway with the STC application, which enables certain features on analog FXS endpoints that use Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP) for call control.
Use this command to set the STC application feature access code (FAC) for phone users to dial to cancel call forwarding for all calls. Use this command only if you want to change the FAC from its default (2). The call forward all command can be used to change the code to initiate call forwarding from its default.
To cancel a call-forward-all condition on a phone, dial the FAC prefix and the FAC that has been configured with this command (or the default if this command has not been used). You can also use the no call-forward all (ephone-dn) command on the Cisco CME router to cancel a call-forward-all condition.
If you set this FAC to a value that is already in use for another FAC, you receive a warning message. If you configure a duplicate code, the system implements the first matching feature in the order of precedence shown in the output of the show stcapp feature codes command.
The show running-config command displays nondefault FACs only. The show stcapp feature codes command displays all FACs.
Examples
The following example sets a FAC prefix of two pound signs (##) and a call-forward-cancel FAC of 3. After these values are configured, a phone user presses ##3 on the keypad to cancel all-call forwarding for that phone extension.
Router(config)# stcapp feature access-codeRouter(stcapp-fac)# prefix ##Router(stcapp-fac)# call forward cancel 3Router(stcapp-fac)# exitRelated Commands
call history max
To retain call history information and to specify the number of call records to be retained, use the call history max command in global configuration mode.
call history max number
Syntax Description
number
The maximum number of call history records to be retained in the history table. Values are from 0 to 1200. The default is 15.
Command Default
If this command is not configured, no call history is maintained for disconnected calls. If the command is configured, the default value for number of records is 15.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The number of disconnected calls displayed is the number specified in the number argument. This maximum number helps to reduce CPU usage in the storage and reporting of this information.
Examples
The following example configures the history table on the gatekeeper to retain 25 records:
Router# call history max 25Related Commands
call language voice
To configure an external Tool Command Language (Tcl) module for use with an interactive voice response (IVR) application, use the call language voice command in global configuration mode.
call language voice language url
Syntax Description
language
Two-character abbreviation for the language; for example, "en" for English or "ru" for Russian.
url
URL that points to the Tcl module.
Command Default
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
12.2(2)T
This command was introduced.
12.3(14)T
This is obsolete in Cisco IOS Release 12.3(14)T. Use the param language command in application parameter configuration mode.
Usage Guidelines
The built-in languages are English (en), Chinese (ch), and Spanish (sp). If you specify "en", "ch", or sp", the new Tcl module replaces the built-in language functionality. When you add a new Tcl module, you create your own prefix to identify the language. When you configure and load the new languages, any upper-layer application (Tcl IVR) can use the language.
You can use the language abbreviation in the language argument of any call application voice command. The language and the text-to-speech (TTS) notations are available for the IVR application to use after they are defined by the Tcl module.
Examples
The following example adds Russian (ru) as a Tcl module:
call language voice ru tftp://box/unix/scripts/multi-lang/ru_translate.tclRelated Commands
call language voice load
To load or reload a Tool Command Language (TCL) module from the configured URL location, use the call language voice load command in EXEC mode.
call language voice load language
Syntax Description
language
The two-character prefix configured with the call language voice command in global configuration mode; for example, "en" for English or "ru" for Russian.
Defaults
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
You cannot use this command if the interactive voice response (IVR) application using the language that you want to configure has an active call. A language that is configured under an IVR application is not necessarily in use. To determine if a call is active, use the show call application voice command.
Examples
The following example loads French (fr) into memory:
call language voice load frRelated Commands
call leg dump event-log
To flush the event log buffer for call legs to an external file, use the call leg dump event-log command in privileged EXEC mode.
call leg dump event-log
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
This command immediately writes the event log buffer to the external file whose location is defined with the call leg event-log dump ftp command in global configuration mode.
Note
The call leg dump event-log command and the call leg event-log dump ftp command are two different commands.
Examples
The following example writes the event log buffer to an external file named leg_elogs:
Router(config)# call leg event-log dump ftp ftp-server/elogs/leg_elogs.log username myname password 0 mypassRouter(config)# exitRouter# call leg dump event-logRelated Commands
call leg event-log
To enable event logging for voice, fax, and modem call legs, use the call leg event-log command in global configuration mode. To reset to the default, use the no form of this command.
call leg event-log
no call leg event-log
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
Event logging for call legs is disabled.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
This command enables event logging for telephony call legs. IP call legs are not supported.
Note
To prevent event logging from adversely impacting system performance for production traffic, the system includes a throttling mechanism. When free processor memory drops below 20%, the gateway automatically disables all event logging. It resumes event logging when free memory rises above 30%. While throttling is occurring, the gateway does not capture any new event logs even if event logging is enabled. You should monitor free memory on the gateway and enable event logging only when necessary to isolate faults.
Examples
The following example enables event logging for all telephony call legs:
call leg event-logRelated Commands
call leg event-log dump ftp
To enable the gateway to write the contents of the call-leg event log buffer to an external file, use the call leg event-log dump ftp command in global configuration mode. To reset to the default, use the no form of this command.
call leg event-log dump ftp server[:port]/file username username password [encryption-type] password
no call leg event-log dump ftp
Syntax Description
Command Default
Event logs are not written to an external file.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
This command enables the gateway to automatically write the event log buffer to the named file either after an active call leg terminates or when the event log buffer becomes full. The default buffer size is 4 KB. To modify the size of the buffer, use the call leg event-log max-buffer-size command. To manually flush the event log buffer, use the call leg dump event-log command in privileged EXEC mode.
Note
The call leg dump event-log command and the call leg event-log dump ftp command are two different commands.
Note
Enabling the gateway to write event logs to FTP could adversely impact gateway memory resources in some scenarios, for example, when:
•
The gateway is consuming high processor resources and FTP does not have enough processor resources to flush the logged buffers to the FTP server.
•
The designated FTP server is not powerful enough to perform FTP transfers quickly
•
Bandwidth on the link between the gateway and the FTP server is not large enough
•
The gateway is receiving a high volume of short-duration calls or calls that are failing
You should enable FTP dumping only when necessary and not enable it in situations where it might adversely impact system performance.
Examples
The following example enables the gateway to write call leg event logs to an external file named leg_elogs.log on a server named ftp-server:
call leg event-log dump ftp ftp-server/elogs/leg_elogs.log username myname password 0 mypassThe following example specifies that call leg event logs are written to an external file named leg_elogs.log on a server with the IP address 10.10.10.101:
call leg event-log dump ftp 10.10.10.101/elogs/leg_elogs.log username myname password 0 mypassRelated Commands
call legevent-log error-only
To restrict event logging to error events only for voice call legs, use the call leg event-log error-only command in global configuration mode. To reset to the default, use the no form of this command.
call leg event-log error-only
no call leg event-log error-only
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
All call leg events are logged.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
This command limits the severity level of the events that are logged; it does not enable logging. You must use this command with the call leg event-log command, which enables event logging for call legs.
Examples
The following example captures event logs only for call legs with errors:
call leg event-logcall leg event-log error-onlyRelated Commands
call leg event-log max-buffer-size
To set the maximum size of the event log buffer for each call leg, use the call leg event-log max-buffer-size command in global configuration mode. To reset to the default, use the no form of this command.
call leg event-log max-buffer-size kbytes
no call leg event-log max-buffer-size
Syntax Description
Command Default
4 KB
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
If the event log buffer reaches the limit set by this command, the gateway allocates a second buffer of equal size. The contents of both buffers is displayed when you use the show call leg command. When the first event log buffer becomes full, the gateway automatically appends its contents to an external FTP location if the call leg event-log dump ftp command is used.
A maximum of two buffers are allocated for an event log. If both buffers are filled, the first buffer is deleted and another buffer is allocated for new events (buffer wraps around). If the call leg event-log dump ftp command is configured and the second buffer becomes full before the first buffer is dumped, event messages are dropped and are not recorded in the buffer.
Examples
The following example sets the maximum buffer size to 8 KB:
call leg event-log max-buffer-size 8Related Commands
call leg history event-log save-exception-only
To save to history only event logs for call legs that had at least one error, use the call leg history event-log save-exception-only command in global configuration mode. To reset to the default, use the no form of this command.
call leg history event-log save-exception-only
no call leg history event-log save-exception-only
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
By default all the events will be logged.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Call leg event logs move from the active to the history table after the call leg terminates. If you use this command, event logs are saved only for those legs that had errors. Event logs for normal legs that do not contain any errors are not saved.
Note
This command does not affect records saved to an FTP server by using the call leg dump event-log command.
Examples
The following example saves to history only call leg records that have errors:
call leg history event-log save-exception-onlyRelated Commands
callmonitor
To enable call monitoring messaging functionality on a SIP endpoint in a VoIP network, use the callmonitor command in voice-service configuration mode. To return to the default, use the no form of this command.
callmonitor
no callmonitor
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
Monitoring service is disabled.
Command Modes
Voice-service configuration (config-voi-serv)
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use this command in voice service configuration mode to allow a SIP endpoint, such as an external feature server, to watch call activity on a VoIP network.
To view call activity, use the show callmon command.
Examples
The following partial output shows the configuration for the callmonitor command:
router# show running-configuration!!!voice service voipgcidcallmonitorallow-connections h323 to h323allow-connections h323 to sipallow-connections sip to h323allow-connections sip to sipno supplementary-service sip moved-temporarilysipregistrar server expires max 120 min 60!!!Related Commands
call preserve
To enable the preservation of H.323 VoIP calls, use the call preserve command in h323, voice-class h323, and voice service voip configuration modes. To reset to the default, use the no form of this command.
call preserve [limit-media-detection]
no call preserve [limit-media-detection]
Syntax Description
limit-media-detection
Limits RTP and RTCP inactivity detection and bidirectional silence detection (if configured) to H.323 VoIP preserved calls only.
Command Default
H.323 VoIP call preservation is disabled.
Command Modes
h323, voice-class h323, or voice service voip
Command History
12.4(4)XC
This command was introduced.
12.4(9)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(9)T.
Usage Guidelines
The call preserve command activates H.323 VoIP call preservation for following types of failures and connections:
Failure Types
•
WAN failures that include WAN links flapping or degraded WAN links
•
Cisco Unified CallManager software failure, such as when the ccm.exe service crashes on a Cisco Unified CallManager server.
•
LAN connectivity failure, except when a failure occurs at the local branch
Connection Types
•
Calls between two Cisco Unified CallManager controlled endpoints
–
During Cisco Unified CallManager reloads
–
When a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) connection between one or both endpoints and Cisco Unified CallManager used for signaling H.225.0 or H.245 messages is lost or flapping
–
Between endpoints that are registered to different Cisco Unified CallManagers in a cluster and the TCP connection between the two Cisco Unified CallManagers is lost
–
Between IP phones and the PSTN at the same site
•
Calls between Cisco IOS gateway and an endpoint controlled by a softswitch where the signaling (H.225.0, H.245 or both) flows between the gateway and the softswitch and media flows between the gateway and the endpoint.
–
When the softswitch reloads.
–
When the H.225.0 or H.245 TCP connection between the gateway and the softswitch is lost, and the softswitch does not clear the call on the endpoint
–
When the H.225.0 or H.245 TCP connection between softswitch and the endpoint is lost, and the soft-switch does not clear the call on the gateway
•
Call flows that involve a Cisco IP in IP (IPIP) gateway running in media flow-around mode that reload or lose connection with the rest of the network
When bidirectional silence and RTP and RTCP inactivity detection are configured, they are enabled for all calls by default. To enable them for H.323 VoIP preserved calls only, you must use the call preserve command's limit-media-detection keyword.
H.323 VoIP call preservation can be applied globally to all calls and to a dial peer.
Examples
The following example enables H.323 VoIP call preservation for all calls.
voice service voiph323call preserveThe following configuration example enables H.323 VoIP call preservation for dial peer 1.
voice-class h323 4call preservedial-peer voice 1 voipvoice-class h323 4The following example enables H.323 VoIP call preservation and enables RTP and RTCP inactivity detection and bidirectional silence detection for preserved calls only:
voice service voiph323call preserve limit-media-detectionThe following example enables RTP and RTCP inactivity detection. Note that for H.323 VoIP call preservation VAD must be set to off (no vad command).
dial-peer voice 10 voipno vadgatewaytimer receive-rtcpip rtcp report-intervalThe following configuration example enables bidirectional silence detection:
gatewaytimer media-inactiveip rtcp report intervalRelated Commands
call-routing hunt-scheme
To enable capacity based load-balancing, use the call-routing hunt-scheme command in gatekeeper configuration mode. To disable this function, use the no form of this command.
call-routing hunt-scheme percentage-capacity-util
no call-routing hunt-scheme
Syntax Description
percentage-capacity-util
Selects the one with least percentage capacity utilized among the gateways.
Command Default
This command is disabled.
Command Modes
Gatekeeper configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use the call-routing hunt-scheme command to turn on load balancing based on capacity of gateway and verify that the gateway capacity reporting is enabled.
Examples
The following example shows the gateway with the with least percentage capacity being selected:
Router(gk-config)# call-routing hunt-scheme percentage-capacity-utilRelated Commands
timer cluster-element
Sets the time between resource update messages to gatekeepers in local cluster.
call rscmon update-timer
To change the value of the resource monitor throttle timer, use the call rscmon update-timer command in privileged EXEC mode. To revert to the default value, use the no form of this command.
call rscmon update-timer milliseconds
no call rscmon update-timer
Syntax Description
milliseconds
Duration of the resource monitor throttle timer, in milliseconds (ms). Range is from 20 to 3500. The default is 2000.
Command Default
2000 ms
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
This command specifies the duration of the resource monitor throttle timer. When events are delivered to the resource monitor process, the throttle timer is started and the event is processed after the timer expires (unless the event is a high-priority event). The timer ultimately affects the time it takes the gateway to send Resource Availability Indicator (RAI) messages to the gatekeeper. This command allows you to vary the timer according to your needs.
Examples
The following example shows how the timer is to be configured:
Router(config)# call rscmon update-timer 1000Related Commands
resource threshold
Configures a gateway to report H.323 resource availability to its gatekeeper.
call rsvp-sync
To enable synchronization between Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) signaling and the voice signaling protocol, use the call rsvp-sync command in global configuration mode. To disable synchronization, use the no form of this command.
call rsvp-sync
no call rsvp-sync
Syntax Description
This command has no keywords or arguments.
Command Default
Synchronization is enabled between RSVP and the voice signaling protocol (for example, H.323).
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The call rsvp-sync command is enabled by default.
Examples
The following example enables synchronization between RSVP and the voice signaling protocol:
call rsvp-syncRelated Commands
call rsvp-sync resv-timer
To set the timer on the terminating VoIP gateway for completing RSVP reservation setups, use the call rsvp-sync resv-timer command in global configuration mode. To restore the default value, use the no form of this command.
call rsvp-sync resv-timer seconds
no call rsvp-sync resv-timer
Syntax Description
seconds
Number of seconds in which the reservation setup must be completed, in both directions. Range is from 1 to 60. The default is 10.
Command Default
10 seconds
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The reservation timer is started on the terminating gateway when the session protocol receives an indication of the incoming call. This timer is not set on the originating gateway because the resource reservation is confirmed at the terminating gateway. If the reservation timer expires before the RSVP setup is complete, the outcome of the call depends on the acceptable quality of service (QoS) level configured in the dial peer; either the call proceeds without any bandwidth reservation or it is released. The timer must be set long enough to allow calls to complete but short enough to free up resources. The optimum number of seconds depends on the number of hops between the participating gateways and the delay characteristics of the network.
Examples
The following example sets the reservation timer to 30 seconds:
call rsvp-sync resv-timer 30Related Commands
call service stop
To shut down VoIP call service under the H.323 or SIP submode on a gateway, use the call service stop command in voice service configuration mode. To enable VoIP call service, use the no form of this command.
call service stop [forced] [maintain-registration]
no call service stop
Syntax Description
forced
(Optional) Forces the gateway to immediately terminate all in-progress calls.
maintain-registration
(Optional) Forces the gateway to remain registered with the gatekeeper.
Command Default
Call service is enabled.
Command Modes
Voice service configuration
Command History
Examples
The following example shows SIP call service being shut down on a Cisco gateway:
enableconfigure terminalvoice service voipsipcall service stopThe following example shows H.323 call service being enabled on a Cisco gateway:
enableconfigure terminalvoice service voiph323no call service stopcall spike
To configure limit on the number of incoming calls received in a short period of time, use the call spike command in global configuration mode. To disable this command, use the no form of this command.
call spike call-number [steps number-of-steps size milliseconds]
no call spike
Syntax Description
Defaults
steps—Default is 5.
size—Default is 200.Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
A call spike occurs when a large number of incoming calls arrive from the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) in a short period of time (for example, 100 incoming calls in 10 milliseconds). Setting this command allows you to control the number of call requests that can be received in a configured time period. The sliding window buffers the number of calls that get through. The counter resets according to the specified step size.
Examples
The following configuration of the call spike command has a call number of 30, a sliding window of 10 steps, and a step size of 2000 milliseconds.
call spike 30 steps 10 size 2000Related Commands
call start
To force an H.323 Version 2 gateway to use either fast connect or slow connect procedures for a dial peer, use the call start command in H.323 voice-service configuration mode. To restore the default setting, use the no form of this command.
call start {fast | slow | system | interwork} [sync-rsvp slow-start]
no call start
Syntax Description
Command Default
system
Command Modes
H.323 voice-service configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
In Cisco IOS Release 12.1(3)XI and later releases, H.323 VoIP gateways by default use H.323 Version 2 (fast connect) for all calls, including those initiating RSVP. Previously, gateways used only slow-connect procedures for RSVP calls. To enable Cisco IOS Release 12.1(3)XI gateways to be backward compatible with earlier releases of Cisco IOS Release 12.1T, the call start command allows the originating gateway to initiate calls using slow connect.
The call start command is configured as part of the voice class assigned to an individual VoIP dial peer. It takes precedence over the h323 call start command that is enabled globally to all VoIP calls, unless the system keyword is used, in which case the gateway defaults to Version 2.
The sync-rsvp slow-start keyword, when used in H.323 voice-class configuration mode, controls RSVP synchronization for all slow-start calls handled by the gateway. When the sync-rsvp slow-start keyword is used in an H.323 voice-class definition, the behavior can be specified for individual dial peers by invoking the voice class in dial peer voice configuration mode. This command is enabled by default in some Cisco IOS images, and in this situation the show running-config command displays this information only when the no form of the command is used.
Note
The call start command supports only H.323 to H.323 calls.
The interwork keyword is only used with IP-to-IP gateways connecting fast connect from one side to slow connect on the other for basic audio calls. Configure the interwork keyword in voice-class H.323 configuration mode or on both the incoming and outgoing dial peers. Codecs must be specified on both dial peers for interworking to function. When the interwork keyword is configured, codecs need to be specified on both dial-peers and the codec transparent command should not be configured.
Examples
The following example shows slow connect for the voice class 1000 being selected:
voice service class h323 1000call start slow!dial-peer voice 210 voipvoice-class h323 1000The following example shows the gateway configured to use the H.323 Version 1 (slow connect) procedures:
h323call start slowRelated Commands
call threshold global
To enable the global resources of a gateway, use the call threshold global command in global configuration mode. To disable the global resources of the gateway, use the no form of this command.
call threshold global trigger-name low value high value [busyout] [treatment]
no call threshold global trigger-name
Syntax Description
Command Default
The default is busyout and treatment for global resource triggers.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to enable a trigger and define associated parameters to allow or disallow new calls on the router. Action is enabled when the trigger value goes above the value specified by the high keyword and is disabled when the trigger drops below the value specified by the low keyword.
You can configure these triggers to calculate Resource Availability Indicator (RAI) information. An RAI is forwarded to a gatekeeper so that it can make call admission decisions. You can configure a trigger that is global to a router or is specific to an interface.
Examples
The following example shows how to busy out the total calls when a low of 5 or a high of 5,000 is reached:
call threshold global total-calls low 5 high 5000 busyoutThe following example shows how to busy out the average CPU utilization if a low of 5 percent or a high of 65 percent is reached:
call threshold global cpu-avg low 5 high 65 busyoutRelated Commands
call threshold interface
To enable the interface resources of a gateway, use the call threshold interface command in global configuration mode. To disable the interface resources of the gateway, use the no form of this command.
call threshold interface interface-name interface-number int-calls low value high value
no call threshold interface interface-name interface-number int-calls
Syntax Description
Command Default
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to specify thresholds that allow or disallow new calls on the router.
Examples
The following example enables thresholds as low as 5 and as high as 2500 for interface calls on interface Ethernet 0/1:
call threshold interface Ethernet 0/1 int-calls low 5 high 2500Related Commands
call threshold poll-interval
To enable a polling interval threshold for assessing CPU or memory thresholds, use the call threshold poll-interval command in global configuration mode. To disable this command, use the no form of this command.
call threshold poll-interval {cpu-average | memory} seconds
no call threshold poll-interval {cpu-average | memory}
Syntax Description
Command Default
cpu-average: 60 seconds
memory: 5 secondsCommand Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Examples
The following example shows how to specify that memory thresholds be polled every 10 seconds:
call threshold poll-interval memory 10Related Commands
call treatment action
To configure the action that the router takes when local resources are unavailable, use the call treatment action command in global configuration mode. To disable call treatment action, use the no form of this command.
call treatment action{ hairpin | playmsg value | reject }
no call treatment action
Syntax Description
Command Default
No treatment is applied.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to define parameters to disconnect (with cause code), or hairpin, or whether a message or busy tone is played to the user.
Examples
The following example shows how to enable the call treatment feature with a "hairpin" action:
call treatment oncall treatment action hairpinThe following example shows how to enable the call treatment feature with a "playmsg" action. The file "congestion.au"plays to the caller when local resources are not available to handle the call.
call treatment oncall treatment action playmsg tftp://keyer/prompts/conjestion.auRelated Commands
call treatment cause-code
To specify the reason for the disconnection to the caller when local resources are unavailable, use the call treatment cause-code command in global configuration mode. To disable the call treatment cause-code specification, use the no form of this command.
call treatment cause-code {busy | no-QoS | no-resource}
no call treatment cause-code
Syntax Description
busy
Indicates that the gateway is busy.
no-QoS
Indicates that the gateway cannot provide quality of service (QoS).
no-resource
Indicates that the gateway has no resources available.
Command Default
Disconnect reason is not specified to the caller.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to associate a cause-code with a disconnect event.
Examples
The following example shows how to configure a call treatment cause code to reply with "no-Qos" when local resources are unavailable to process a call:
call treatment oncall treatment cause-code no-QosRelated Commands
call treatment isdn-reject
To specify the rejection cause code for ISDN calls when all ISDN trunks are busied out and the switch ignores the busyout trunks and still sends ISDN calls into the gateway, use the call treatment isdn-reject command in global configuration mode. (Under any other conditions, the command has no effect.) To disable call treatment, use the no form of this command.
call treatment isdn-reject value
no call treatment isdn-reject
Syntax Description
Command Default
No value is specified.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use this command only when all ISDN trunks are busied out and the switch ignores the busyout trunks and still sends ISDN calls into the gateway. The gateway should reject the call in the ISDN stack using the configured cause code.
Under any other conditions, the command has no effect.
Examples
The following example shows how to configure the call treatment to reply to an ISDN call with an ISDN rejection code for "temporary failure" when local resources are unavailable to process a call:
call treatment oncall treatment isdn-reject 41Related Commands
call treatment on
To enable call treatment to process calls when local resources are unavailable, use the call treatment on command in global configuration mode. To disable call treatment, use the no form of this command.
call treatment on
no call treatment on
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
Treatment is inactive
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to enable a trigger and define associated parameters to disconnect (with cause code), or hairpin, or whether a message, or busy tone is played to the user.
Examples
The following example shows how to enable the call treatment feature with a "hairpin" action:
call treatment oncall treatment action hairpinThe following example shows how to enable the call treatment feature with a "playmsg" action. The file "congestion.au"plays to the caller when local resources are not available to handle the call.
call treatment oncall treatment action playmsg tftp://keyer/prompts/conjestion.auThe following example shows how to configure a call treatment cause code to reply with "no-QoS" when local resources are unavailable to process a call:
call treatment oncall treatment cause-code no-QoSRelated Commands
call-router h323-annexg
To enable the Annex G border element (BE) configuration commands by invoking H.323 Annex G configuration mode, use the call-router command in global configuration mode. To remove the definition of a BE, use the no form of this command.
call-router h323-annexg border-element-id
no call-router h323-annexg
Syntax Description
Command Default
No default behaviors or values
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to enter Annex G configuration mode and to identify BEs.
Examples
The following example shows that Annex G configuration mode is being entered for a BE named "be20".
Router(config)# call-router h323-annexg be20Related Commands
show call history
Displays the fax call history table for a fax transmission.
show call-router status
Displays the Annex G BE status.
call-waiting
To enable call waiting, use the call-waiting command in interface configuration mode. To disable call waiting, use the no form of this command.
call-waiting
no call-waiting
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
Call waiting is enabled
Command Modes
Interface configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
This command is applicable to Cisco 800 series routers.
You must specify this command when creating a dial peer. This command does not work if it is not specified within the context of a dial peer. For information on creating a dial peer, refer to the Cisco 800 Series Routers Software Configuration Guide.
Examples
The following example disables call waiting:
no call-waitingRelated Commands
called-number (dial peer)
To enable an incoming Voice over Frame Relay (VoFR) call leg to get bridged to the correct plain old telephone service (POTS) call leg when a static FRF.11 trunk connection is used, use the called-number command in dial peer configuration mode. To disable a static trunk connection, use the no form of this command.
called-number string
no called-number
Syntax Description
string
A string of digits, including wildcards, that specifies the telephone number of the voice port dial peer.
Command Default
This command is disabled
Command Modes
Dial peer configuration
Command History
12.0(4)T
This command was introduced on the Cisco 2600 series and Cisco 3600 series.
Usage Guidelines
The called-number command is used only when the dial peer type is VoFR and you are using the frf11-trunk (FRF.11) session protocol. It is ignored at all times on all other platforms when using the Cisco-switched session protocol.
Because FRF.11 does not provide any end-to-end messaging to manage a trunk, the called-number command is necessary to allow the router to establish an incoming trunk connection. The E.164 number is used to find a matching dial peer during call setup.
Examples
The following example shows how to configure a static FRF.11 trunk connection to a specific telephone number (555-2150), beginning in global configuration mode:
voice-port 1/0/0connection trunk 55Router0exitdial-peer voice 100 potsdestination pattern 5552150exitdial-peer voice 200 vofrsession protocol frf11-trunkcalled-number 5552150destination pattern 55Router0Related Commands

 Feedback
Feedback