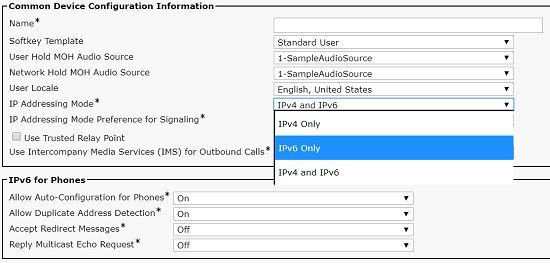
IP Addressing Modes
IP addressing modes specify the types of addresses that a device can communicate with and understand. The following IP addressing modes are used as part of the Cisco Collaboration Systems Release.
|
IP Addressing Mode |
Description |
Notes |
|
|---|---|---|---|
 |
IPv4-only stack |
Used for some endpoints and gateways. |
|
 |
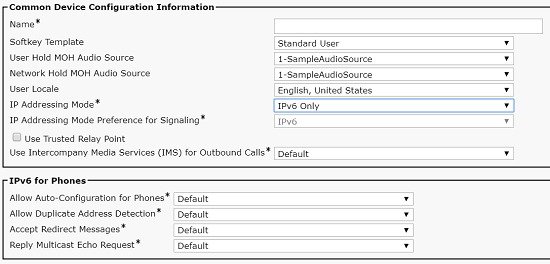
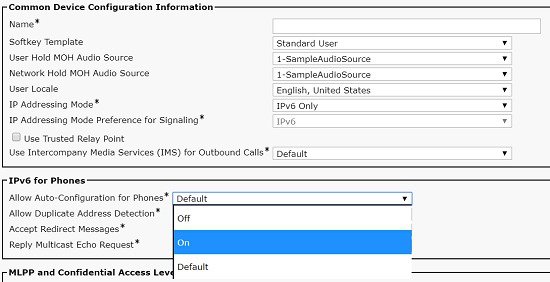
IPv6-only stack |
Used for some endpoints and gateways. |
|
 |
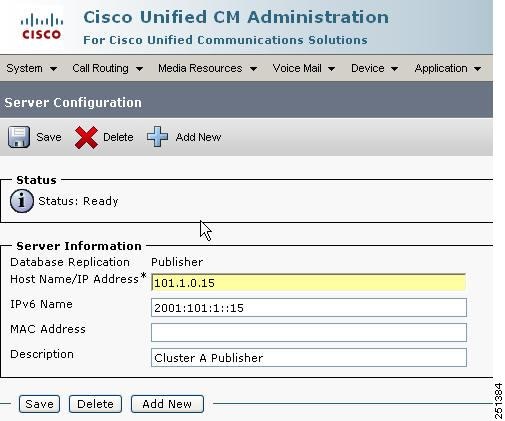
Dual-stacks: IPv4-only and IPv6-only |
Used for applications servers, such as Cisco Unified Communications Manager, Cisco Unity Connection, Cisco Emergency Responder, and Cisco Unified Survivable Remote Site Telephony (Unified SRST). |
The session initiation protocol (SIP) session description protocol (SDP) attribute should not be configured to transition to IPv6-only. |
 |
IPv6 Aware |
Used for applications servers that use IPv4 to transport IPv6 application information, such as the Cisco Prime Collaboration Provisioning module, Cisco Emergency Responder, and Unified CM. |
IPv6 aware devices communicate with IPv4 addresses, but can receive and understand IPv6 addresses embedded in application protocol data units (PDUs). |
 |
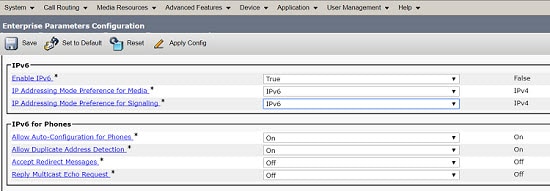
Dual-stack |
Used for applications servers, such as Cisco Unified Communications Manager, Cisco Unity Connection, Cisco Emergency Responder, and Cisco Unified Survivable Remote Site Telephony (Unified SRST). |
- |


 Feedback
Feedback