IPv6 Capabilities of Collaboration Endpoints
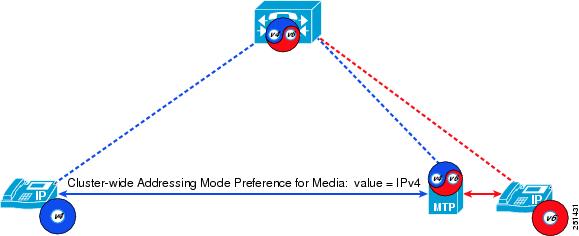
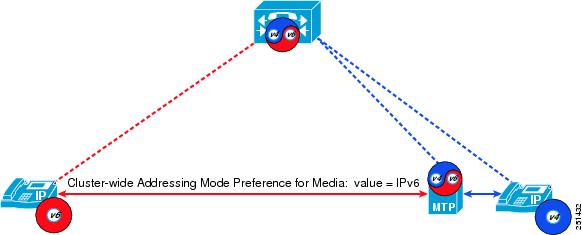
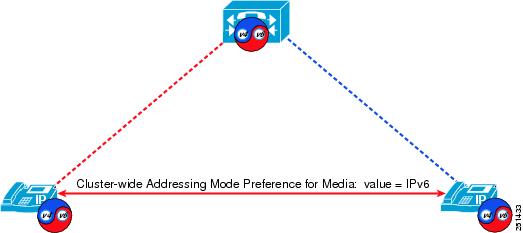
This chapter describes a subset of the Cisco Collaboration endpoints and their IPv6 capabilities. The following table lists the endpoint types and summarizes their IPv6 capabilities. IPv6 support extends to only a subset of the Cisco analog gateways and IP phones. The following sections discuss these devices in more detail.
|
Endpoint Type |
IPv6 Capability |
|---|---|
|
Analog gateways |
Does not support Cisco VG Series Gateways for IPv6-only. |
|
Cisco IP Phones |
Cisco Unified IP Phones 78xx and 88xx Series support IPv6-only. |
|
Software-based endpoints |
Jabber software-based endpoints support IPv6. |
|
Wireless endpoints |
No wireless endpoints support IPv6. |
|
Cisco Unified IP Conference Station |
Conference stations support IPv6. |
|
Cisco TelePresence video endpoints (CE software) |
- |
|
Third-party SIP IP phones |
Third-party IPv6-capable phones are not supported. |
 Feedback
Feedback