- Planning Considerations
- Audio Bit Rates for Cisco Jabber Desktop Clients
- Audio Bit Rates for Cisco Jabber Mobile Clients
- Video Bit Rates for Cisco Jabber Desktop Clients
- Video Bit Rates for Cisco Jabber for Android
- Video Bit Rates for Cisco Jabber for iPhone and iPad
- Presentation Video Bit Rates
- Maximum Negotiated Bit Rate
- Bandwidth Performance Expectations for Cisco Jabber for Windows and Cisco Jabber for Mac
- Bandwidth Performance Expectations for Cisco Jabber for Android
- Bandwidth Performance Expectations for Cisco Jabber for iPhone and iPad
- Video Rate Adaptation
Requirements
Planning Considerations
Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access Deployments
Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access for Cisco Unified Communications Manager allows users to access their collaboration tools from outside the corporate firewall without a VPN client. Using Cisco collaboration gateways, the client can connect securely to your corporate network from remote locations such as public Wi-Fi networks or mobile data networks.
-
Set up servers to support Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access using Cisco Expressway-E and Cisco Expressway-C.*
-
See the following documents to set up the Cisco Expressway servers: * If you currently deploy a Cisco TelePresence Video Communications Server (VCS) environment, you can set up Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access. For more information, see Cisco VCS Basic Configuration (Control with Expressway) Deployment Guide and Mobile and Remote Access via Cisco VCS Deployment Guide.
-
Add any relevant servers to the whitelist for your Cisco Expressway-C server to ensure that the client can access services that are located inside the corporate network.
To add a server to the Cisco Expressway-C whitelist, use the HTTP server allow setting.
This list can include the servers on which you host voicemail or contact photos.
-
-
Configure an external DNS server that contains the _collab-edge DNS SRV record to allow the client to locate the Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access server.
-
If you deploy a hybrid cloud-based architecture where the domain of the IM and presence server differs from the domain of the voice server, ensure that you configure the Voice Services Domain.
The Voice Services Domain allows the client to locate the DNS server that contains the _collab-edge record.
You can configure the voice services domain using one of the following methods:
-
If the voice services domain is different from the services domain. In this case, users must be inside the corporate network to get the correct voice services domain from the jabber-config.xml file.
-
If the client needs to complete the CAPF enrollment process, which is required when using a secure or mixed mode cluster.

Supported Services
| Service | Supported | Unsupported | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Directory | |||
| UDS directory search |
X |
||
| LDAP directory search |
X |
||
| Directory photo resolution |
X * Using HTTP white list on Cisco Expressway-C |
||
|
Intradomain federation |
X * Contact search support depends of the format of your contact IDs. For more information, see the note below. |
||
|
Interdomain federation |
X |
||
| Instant Messaging and Presence | |||
| On-premises |
X |
||
| Cloud |
X |
||
| Chat |
X |
||
| Group chat |
X |
||
| High Availability: On-premises deployments |
X |
||
| File transfer: On-premises deployments |
X |
||
| File transfer: Cloud deployments |
X Desktop clients, some file transfer features are supported for mobile clients. |
||
| Video desktop share - BFCP |
X (Cisco Jabber for mobile clients only support BFCP receive.) |
|
|
| Audio and Video | |||
| Audio and video calls |
X * Cisco Unified Communications Manager 9.1(2) and later |
||
| Deskphone control mode (CTI) |
X |
||
| Extend and connect |
X |
||
| Dial via Office - Reverse |
X |
||
| Session persistency |
X |
||
| Early media |
X |
||
| Self Care Portal access |
X |
||
| Voicemail | |||
| Visual voicemail |
X * Using HTTP white list on Cisco Expressway-C |
||
| Cisco WebEx Meetings | |||
| On-premises |
X |
||
| Cloud |
X |
||
| Cisco WebEx desktop share |
X |
||
| Installation | |||
| Installer update |
X * Using HTTP white list on Cisco Expressway-C |
||
| Customization | |||
| Custom HTML tabs |
X * Using HTTP white list on Cisco Expressway-C (Desktop clients only) |
||
| Security | |||
| End-to-end encryption |
X |
||
| CAPF enrollment |
X |
||
| Troubleshooting | |||
| Problem report generation |
X |
||
| Problem report upload |
X |
||
| High Availability (failover) | |||
| Audio and Video services |
X |
||
| Voicemail services |
X |
||
| IM and Presence services |
X |
||
Directory
-
LDAP contact resolution —The client cannot use LDAP for contact resolution when outside of the corporate firewall. Instead, the client must use UDS for contact resolution.
When users are inside the corporate firewall, the client can use either UDS or LDAP for contact resolution. If you deploy LDAP within the corporate firewall, Cisco recommends that you synchronize your LDAP directory server with Cisco Unified Communications Manager to allow the client to connect with UDS when users are outside the corporate firewall.
-
Directory photo resolution — To ensure that the client can download contact photos, you must add the server on which you host contact photos to the white list of your Cisco Expressway-C server. To add a server to Cisco Expressway-C white list, use the HTTP server allow setting. For more information, see the relevant Cisco Expressway documentation.
-
Intradomain federation — When you deploy intradomain federation and the client connects with Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access from outside the firewall, contact search is supported only when the contact ID uses one of the following formats:
Instant Messaging and Presence
When the client connects to services using Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access, it supports instant messaging and presence with the following limitations.
File transfer — The client does not support file transfer including screen capture with Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service deployments. File Transfer is supported only with Cisco WebEx cloud deployments with desktop clients. Managed File Transfer is supported with Cisco Unified Communication IM and Presence when Cisco Jabber is connected to Cisco Unified services using Expressway. Peer-to-Peer files transfer is not supported.
Audio and Video Calling
-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager — Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access supports video and voice calling with Cisco Unified Communications Manager Version 9.1.2 and later. Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access is not supported with Cisco Unified Communications Manager Version 8.x.
-
Deskphone control mode (CTI) — The client does not support deskphone control mode (CTI), including extension mobility.
-
Extend and connect — The client cannot be used to: -
Dial via Office - Reverse — The client cannot make Dial via Office - Reverse calls from outside the firewall.
-
Session Persistency — The client cannot recover from audio and video calls drop when a network transition occurs. For example, if a users start a Cisco Jabber call inside their office and then they walk outside their building and lose Wi-Fi connectivity, the call drops as the client switches to use Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access.
-
Early Media — Early Media allows the client to exchange data between endpoints before a connection is established. For example, if a user makes a call to a party that is not part of the same organization, and the other party declines or does not answer the call, Early Media ensures that the user hears the busy tone or is sent to voicemail.
When using Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access, the user does not hear a busy tone if the other party declines or does not answer the call. Instead, the user hears approximately one minute of silence before the call is terminated.
-
Self care portal access — Users cannot access the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Self Care Portal when outside the firewall. The Cisco Unified Communications Manager user page cannot be accessed externally.
Cisco Expressway-E proxies all communications between the client and unified communications services inside the firewall. However, the Cisco Expressway-E does not proxy services that are accessed from a browser that is not part of the Cisco Jabber application.
Voicemail
Voicemail service is supported when the client connects to services using Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access.
 Note | To ensure that the client can access voicemail services, you must add the voicemail server to the white list of your Cisco Expressway-C server. To add a server to Cisco Expressway-C white list, use the HTTP server allow setting. For more information, see the relevant Cisco Expressway documentation. |
Cisco WebEx Meetings
When the client connects to services using Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access, it supports only cloud-based conferencing using Cisco WebEx Meetings Center.
The client cannot access the Cisco WebEx Meetings Server or join or start on-premises Cisco WebEx meetings.
Installation
When the client connects to services using Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access, it supports installer updates.
 Note | To ensure that the client can download installer updates, you must add the server that hosts the installer updates to the white list of your Cisco Expressway-C server. To add a server to the Cisco Expressway-C white list, use the HTTP server allow setting. For more information, see the relevant Cisco Expressway documentation. |
Customization
When the client connects to services using Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access, it supports custom HTML tab configuration for desktop clients.
 Note | To ensure that the client can download the custom HTML tab configuration, you must add the server that hosts the custom HTML tab configuration to the white list of your Cisco Expressway-C server. To add a server to the Cisco Expressway-C whitelist, use the HTTP server allow setting. For more information, see the relevant Cisco Expressway documentation. |
Security
-
Initial CAPF enrollment — Certificate Authority Proxy Function (CAPF) enrollment is a security service that runs on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Publisher that issues certificates to Cisco Jabber (or other clients). To successfully enrol for CAPF, the client must connect from inside the firewall or using VPN.
-
End-to-end encryption — When users connect through Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access and participate in a call: -
Media is encrypted on the call path between the Cisco Expressway-C and devices that are registered to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager using Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access.
-
Media is not encrypted on the call path between the Cisco Expressway-C and devices that are registered locally to Cisco Unified Communications Manager, if either Cisco Jabber or an internal device is not configured with Encrypted security mode.
-
Media is encrypted on the call path between the Expressway-C and devices that are registered locally to Cisco Unified Communnication Manager, if both Cisco Jabber and internal device are configured with Encypted security mode.
-
Troubleshooting
Problem report upload — When the desktop client connects to services using Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access, it cannot send problem reports because the client uploads problem reports over HTTPS to a specified internal server.
To work around this issue, users can save the report locally and send the report in another manner.
High Availability (failover)
High Availability means that if the client fails to connect to the primary server, it fails over to a secondary server with little or no interruption to the service. In relation to high availability being supported on the Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access, high availability refers to the server for the specific service failing over to a secondary server (such as Instant Messaging and Presence), and not the Cisco Expressway-E server itself failing over.
Some services are available on the Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access that are not supported for high availability. This means that if users are connected to the client from outside the corporate network and the instant messaging and presence server fails over, the services will continue to work as normal. However, if the audio and video server or voicemail server fails over, those services will not work as the relevant servers do not support high availability.
Deployment in a Virtual Environment
You can deploy Cisco Jabber for Windows in virtual environments using the following software:
-
Citrix XenDesktop 7.5
-
Citrix XenDesktop 7.1
-
Citrix XenDesktop 7.0
-
Citrix XenDesktop 5.6
-
Citrix XenApp 7.5 Enterprise Edition for Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard Service Pack 1 64 bit, published desktop
- Citrix XenApp 6.5 Feature Pack 2 Enterprise Edition for Windows Server 2008 Service Pack 2 64 bit, published desktop
-
Citrix XenApp 6.5 Feature Pack 1 Enterprise Edition for Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard Service Pack 1 64 bit, published desktop
-
Citrix XenApp 6.5 Enterprise Edition for Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard Service Pack 1 64 bit, published desktop
-
VMware Horizon View 6.0
- VMware Horizon View 5.3
- VMware Horizon View 5.2
Supported Features
Softphones in Virtual Environments
Use Cisco Virtualization Experience Media Engine (VXME) for softphone calls in a virtual environment.
Roaming Profiles
The client stores user data such as user call history and configuration store cache on the local machine for use when the user next signs in. In virtual environments, users do not always access the same virtual desktop. To guarantee a consistent user experience, these files need to be accessible every time the client is launched.
To preserve the user's personal settings in a virtual environment when roaming between hosted virtual desktops, use dedicated profile management solutions from Citrix and VMware.
Citrix Profile Management is a profile solution for Citrix environments. In deployments with random hosted virtual desktop assignments, Citrix Profile Management synchronizes each user's entire profile between the system it is installed on and the user store.
VMware View Persona Management preserves user profiles and dynamically synchronizes them with a remote profile repository. VMware View Persona Management does not require the configuration of Windows roaming profiles and can bypass Windows Active Directory in the management of View user profiles. Persona Management enhances the functionality of existing roaming profiles.
You can specify which files and folders to omit from synchronization by adding them to an exclusion list. To include a subfolder within an excluded folder, add the subfolder to an inclusion list.
- AppData\Local\Cisco
- AppData\Local\JabberWerxCPP
- AppData\Roaming\Cisco
- AppData\Roaming\JabberWerxCPP
Client Information Storage
The client stores user information in the following locations:
C:\Users\username\AppData\Local\Cisco\Unified Communications\Jabber\CSF| Folder Name | Description |
| Contacts | Contact cache files |
| History | Call history and chat history |
| Photo cache | Caches the directory photos locally |
| Folder Name | Description |
| Config | Maintains users' Jabber configuration files and stores configuration store cache |
| Credentials | Stores encrypted user name and password file |
How the Client Connects to Services
- URL Configuration
Users are sent an email from their administrators. The email contains a URL that will configure the domain needed for service discovery.
- Service Discovery
-
The client automatically locates and connects to services.
- Manual Connection Settings
-
Users manually enter connection settings in the client user interface.
- Recommended Connection Methods
- Sources of Authentication
- About Service Discovery
- Manual Connection Settings
- Installer Switches: Cisco Jabber for Windows
Recommended Connection Methods
The method that you should use to provide the client with the information it needs to connect to services depends on your deployment type, server versions, and product modes. The following tables highlight various deployment methods and how to provide the client with the necessary information.
|
Product Mode |
Server Versions |
Discovery Method |
Non-DNS Method |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Full UC (default mode) |
Release 9.1.2 and later: |
A DNS SRV request against _cisco-uds .<domain> |
Use the following installer switches and values: |
|
Full UC (default mode) |
Release 8.x: |
A DNS SRV request against _cuplogin.<domain> |
Use the following installer switches and values: |
|
IM Only (default mode) |
|
A DNS SRV request against _cisco-uds .<domain> |
Use the following installer switches and values: |
|
IM Only (default mode) |
|
A DNS SRV request against _cuplogin .<domain> |
Use the following installer switches and values: |
|
Phone Mode |
|
A DNS SRV request against _cisco-uds.<domain> |
Use the following installer switches and values: |
|
Phone Mode |
|
Manual connection settings |
Use the following installer switches and values: |
 Note | Cisco Jabber release 9.6 and later can still discover full Unified Communications and IM-only services using the _cuplogin DNS SRV request but a _cisco-uds request will take precedence if it is present. |
Use the SERVICES_DOMAIN installer switch to specify the value of the domain where DNS records reside if you want users to bypass the email screen during the first login of a fresh installation.
 Note | The services domain is read from a cached configuration if you are upgrading from Cisco Jabber for Windows 9.2. |
|
Product Mode |
Server Versions |
Discovery Method |
|---|---|---|
|
Full UC (default mode) |
Release 9 and later: |
A DNS SRV request against _cisco-uds.<domain> |
|
Full UC (default mode) |
Release 8.x: |
A DNS SRV request against _cuplogin.<domain> |
|
Product Mode |
Server Versions |
Discovery Method |
|---|---|---|
|
Full UC (default mode) |
Release 9 and later: |
A DNS SRV request against _cisco-uds .<domain> and _cuplogin.<domain> |
|
Full UC (default mode) |
Release 8.x: |
A DNS SRV request against _cuplogin.<domain> |
|
IM Only (default mode) |
Release 9 and later: Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service |
A DNS SRV request against _cisco-uds .<domain> and _cuplogin.<domain> |
|
IM Only (default mode) |
Release 8.x: Cisco Unified Presence |
A DNS SRV request against _cuplogin .<domain> |
|
Phone mode |
Release 9 and later: Cisco Unified Communications Manager |
A DNS SRV request against _cisco-uds.<domain> |
|
Phone mode |
Release 8.x: Cisco Unified Communications Manager |
Manual connection settings or bootstrap file Manual connection settings |
 Note | Cisco Unified Communications Manager version 9 and later can still discover full Unified Communications and IM-only services using the _cuplogin DNS SRV request but a _cisco-uds request will take precedence if it is present. |
|
Server Versions |
Connection Method |
|---|---|
|
Cisco WebEx Messenger |
HTTPS request against http://loginp.webexconnect.com/cas/FederatedSSO?org=<domain> |
|
Deployment Type |
Connection Method |
|---|---|
|
Enabled for single sign-on (SSO) |
Cisco WebEx Administration Tool Bootstrap file to set the SSO_ORG_DOMAIN argument. |
|
Not enabled for SSO |
Cisco WebEx Administration Tool |
Sources of Authentication
A source of authentication, or an authenticator, enables users to sign in to the client.
Initial Launch Sequence
On the initial launch after installation, Cisco Jabber starts in the default product mode. The client then gets an authenticator and signs the user in. After sign in, the client determines the product mode.
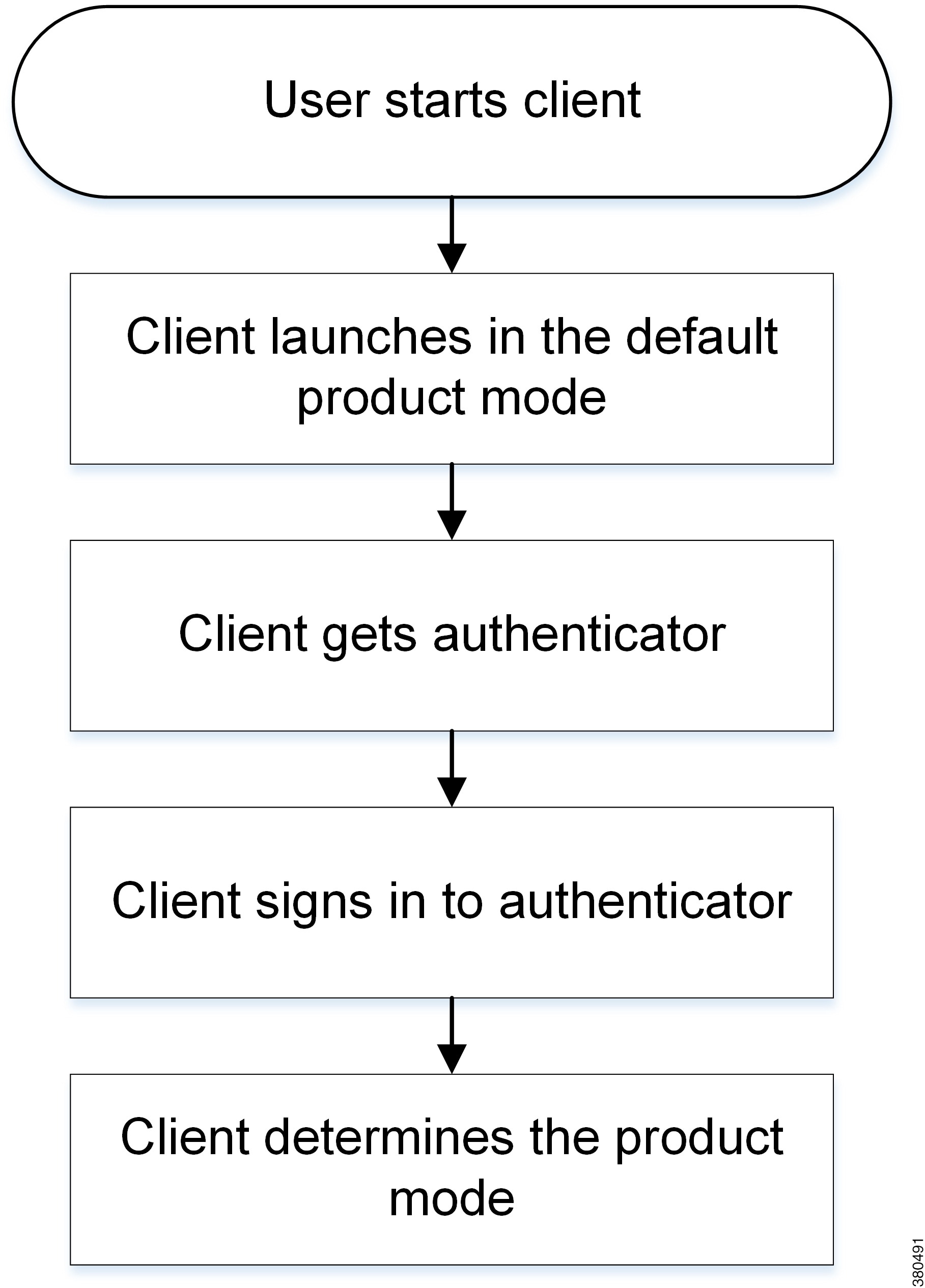
How the Client Gets an Authenticator
-
Client checks cache for manual settings.
Users can manually enter authenticator through the client user interface.
-
Client checks cache to discover if the user's domain is a Webex organisation..
The client chooses Webex as the authenticator.
-
Client makes a Webex cloud service HTTP request to discover if the user's organisation domain is a Webex organisation.
The client chooses Webex as the authenticator.
-
Client checks cache for service discovery.
The client loads settings from previous queries for service (SRV) records.
-
Client queries for SRV records.
The client queries the DNS name server for SRV records to locate services.
If the client finds the _cisco-uds SRV record, it can get the authenticator from the service profile.
About Service Discovery
Service discovery enables clients to automatically detect and locate services on your enterprise network. Clients query domain name servers to retrieve service (SRV) records that provide the location of servers.
If you are migrating from Cisco Unified Presence 8.x to Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service 9.0 or later, you must specify the Cisco Unified Presence server FQDN in the migrated UC service on Cisco Unified Communications Manager. Open Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration interface. Select User Management > User Settings > UC Service.
For UC services with type IM and Presence, when you migrate from Cisco Unified Presence 8.x to Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service the Host Name/IP Address field is populated with a domain name and you must change this to the Cisco Unified Presence server FQDN.
However, the client can retrieve different SRV records that indicate to the client different servers are present and different services are available. In this way, the client derives specific information about your environment when it retrieves each SRV record.
- How the Client Locates Services
- Client Issues HTTP Query
- Cisco UDS SRV Record
- CUP Login SRV Record
- Collaboration Edge SRV Record
- Configuration URL
How the Client Locates Services
-
The client's host computer or device gets a network connection.
When the client's host computer gets a network connection, it also gets the address of a Domain Name System (DNS) name server from the DHCP settings.
-
The user employs one of the following methods to discover the service during the first sign in:
-
Manual—The user starts Cisco Jabber and then inputs an email-like address on the welcome screen.
-
URL configuration—URL configuration allows users to click on a link to cross-launch Cisco Jabber without manually inputting an email.
-
Mobile Configuration Using Enterprise Mobility Management—As an alternative to URL configuration, you can configure Cisco Jabber using Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM) with Android for Work on Cisco Jabber for Android and with Apple Managed App Configuration on Cisco Jabber for iPhone and iPad. You need to configure the same parameters in the EMM console that are used for creating URL configuration link.
To create a URL configuration link, you include the following:
-
ServicesDomain—The domain that Cisco Jabber uses for service discovery.
-
VoiceServicesDomain—For a hybrid deployment, the domain that Cisco Jabber uses to retrieve the DNS SRV records can be different from the ServicesDomain that is used to discover the Cisco Jabber domain.
-
ServiceDiscoveryExcludedServices—In certain deployment scenarios, services can be excluded from the service discovery process. These values can be a combination of the following:

Note
When all three parameters are included, service discovery does not happen and the user is prompted to manually enter connection settings.
Create the link in the following format:
ciscojabber://provision?ServicesDomain=<domain_for_service_discover> &VoiceServicesDomain=<domain_for_voice_services> &ServiceDiscoveryExcludedServices=<services_to_exclude_from_service_discover>
Examples: Provide the link to users using email or a website.

Note
If your organization uses a mail application that supports cross-launching proprietary protocols or custom links, you can provide the link to users using email, otherwise provide the link to users using a website.
-
-
The client gets the address of the DNS name server from the DHCP settings.
-
The client issues an HTTP query to a Central Authentication Service (CAS) URL for the Cisco WebEx Messenger service.
This query enables the client to determine if the domain is a valid Cisco WebEx domain.
-
The client queries the name server for the following SRV records in order of priority:
The following is an example of an SRV record entry:
_cuplogin._tcp.DOMAIN SRV service location: priority = 0 weight = 0 port = 8443 svr hostname=192.168.0.26
Client Issues HTTP Query
When the client gets a domain from the user, it appends that domain to the following HTTP query:
http://loginp.webexconnect.com/cas/FederatedSSO?org=
For example, if the client gets example.com as the domain from the user, it issues the following query:
http://loginp.webexconnect.com/cas/FederatedSSO?org=example.com
That query returns an XML response that the client uses to determine if the domain is a valid Cisco WebEx domain.
If the client determines the domain is a valid Cisco WebEx domain, it prompts users to enter their Cisco WebEx credentials. The client then authenticates to theCisco WebEx Messenger service and retrieves configuration and UC services configured in Cisco WebEx Org Admin.
If the client determines the domain is not a valid Cisco WebEx domain, it uses the results of the query to the name server to locate available services.
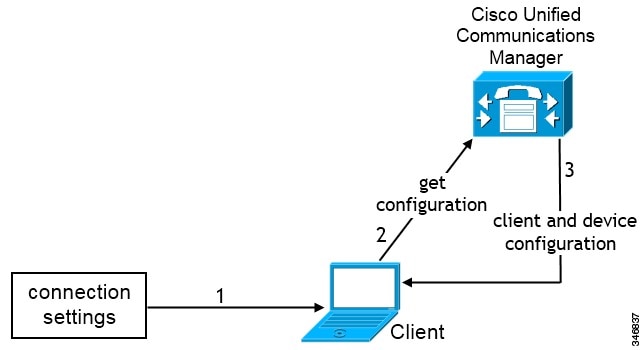
Cisco UDS SRV Record
In deployments with Cisco Unified Communications Manager version 9 and later, the client can automatically discover services and configuration with the _cisco-uds SRV record.
The following figure shows how the client uses the _cisco-uds SRV record.
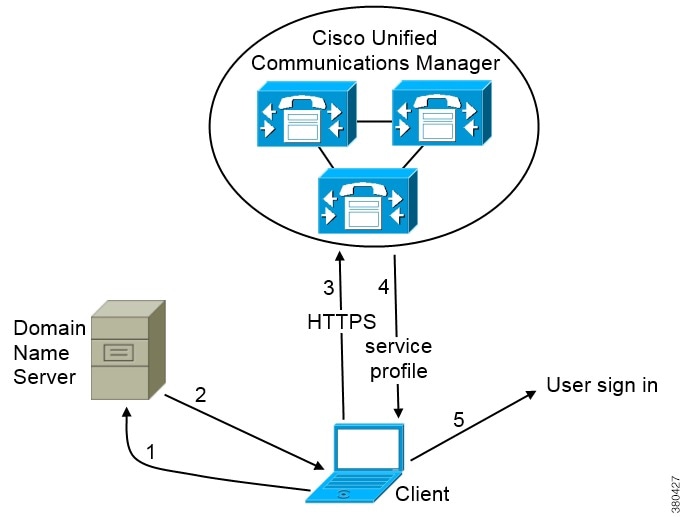
-
The client queries the domain name server for SRV records.
-
The domain name server returns the _cisco-uds SRV record.
-
The client locates the user's home cluster.
As a result, the client can retrieve the device configuration for the user and automatically register telephony services.
Important: In an environment with multiple Cisco Unified Communications Manager clusters, you can configure the Intercluster Lookup Service (ILS). ILS enables the client to find the user's home cluster and discover services.
If you do not configure ILS, you must manually configure remote cluster information, similar to the Extension Mobility Cross Cluster (EMCC) remote cluster setup. For more information on remote cluster configurations, see the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Features and Services Guide.
-
The client retrieves the user's service profile.
The user's service profile contains the addresses and settings for UC services and client configuration.
The client also determines the authenticator from the service profile.
-
The client signs the user in to the authenticator.
_cisco-uds._tcp.example.com SRV service location:
priority = 6
weight = 30
port = 8443
svr hostname = cucm3.example.com
_cisco-uds._tcp.example.com SRV service location:
priority = 2
weight = 20
port = 8443
svr hostname = cucm2.example.com
_cisco-uds._tcp.example.com SRV service location:
priority = 1
weight = 5
port = 8443
svr hostname = cucm1.example.com
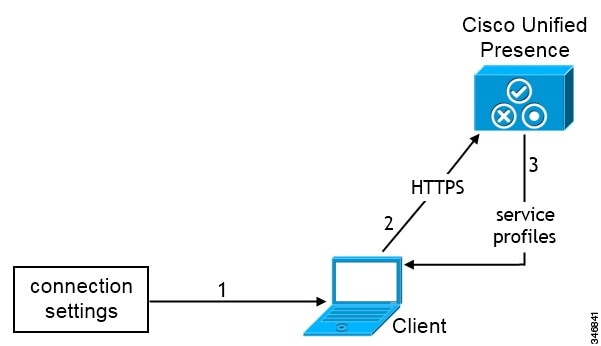
CUP Login SRV Record
Cisco Jabber can automatically discover and connect to Cisco Unified Presence or Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service with the _cuplogin SRV record.
The following figure shows how the client uses the _cuplogin SRV record.
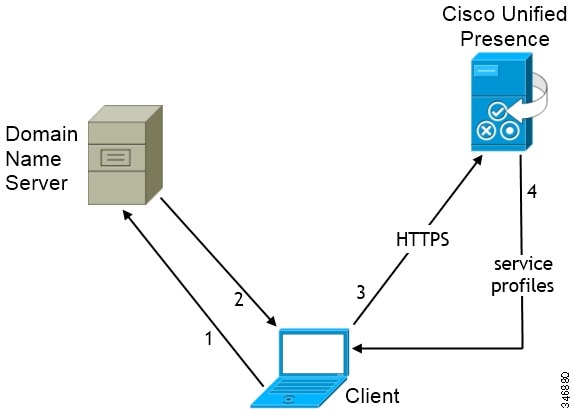
-
The client queries the domain name server for SRV records.
-
The name server returns the _cuplogin SRV record.
As a result, Cisco Jabber can locate the presence server and determine that Cisco Unified Presence is the authenticator.
-
The client prompts the user for credentials and authenticates to the presence server.
-
The client retrieves service profiles from the presence server.
 Tip | The _cuplogin SRV record also sets the default server address on the Advanced Settings window. |
_cuplogin._tcp.example.com SRV service location:
priority = 8
weight = 50
port = 8443
svr hostname = cup3.example.com
_cuplogin._tcp.example.com SRV service location:
priority = 5
weight = 100
port = 8443
svr hostname = cup1.example.com
_cuplogin._tcp.example.com SRV service location:
priority = 7
weight = 4
port = 8443
svr hostname = cup2.example.com
Collaboration Edge SRV Record
Cisco Jabber can attempt to connect to internal servers through Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access to discover services with the following _collab-edge SRV record.
The following figure shows how the client uses the _collab-edge SRV record.
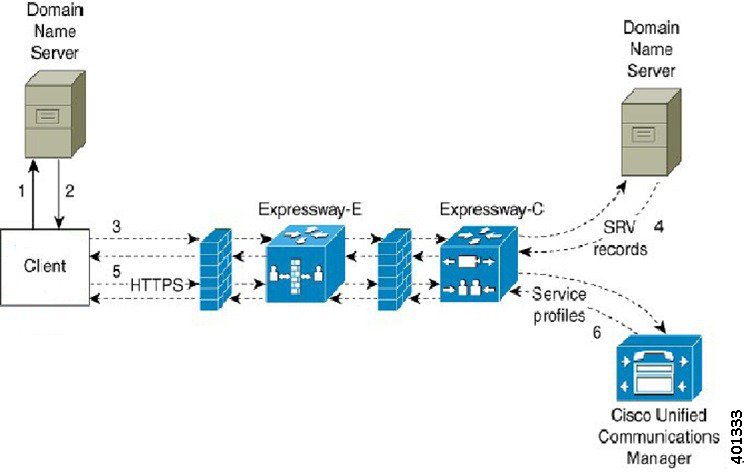
-
The client queries the external domain name server for SRV records.
-
The name server returns the _collab-edge SRV record and does not return the _cuplogin or _cisco-uds SRV records.
As a result, Cisco Jabber can locate the Cisco Expressway-E server.
-
The client requests the internal SRV records (through Expressway) from the internal domain name server.
These SRV records must include the _cisco-uds SRV record.
- The client obtains the
internal SRV records (through Expressway).
As a result, the client can locate the Cisco Unified Communications Manager server.
-
The client requests the service profiles (through Expressway) from Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
-
The client retrieves the service profiles (through Expressway) from Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
The service profile contains the user's home cluster, the primary source of authentication, and the client configuration.
Configuration URL
You can create a configuration URL to make it easier for users to set up the client for the first time. Users can click this link to cross-launch Cisco Jabber without having to manually enter service discovery information.
To use this feature, you must create a URL and then distribute that URL to users.
Create Configuration URL
To enable users to launch Cisco Jabber without having to manually enter service discovery information, create and distribute a configuration URL to users.
You can provide a configuration URL link to users by emailing the link to the user directly, or by posting the link to a website.
You can include and specify the following parameters in the URL:
-
ServicesDomain — Required. Every configuration URL must include the domain of the IM and presence server that Cisco Jabber needs for service discovery.
-
VoiceServiceDomain — Required only if you deploy a hybrid cloud-based architecture where the domain of the IM and presence server differs from the domain of the voice server. You must set this parameter to ensure that Cisco Jabber can discover voice services.
-
ServiceDiscoveryExcludedServices — Optional. You can exclude any of the following services from the service discovery process:
-
WEBEX—When you set this value, the client: -
CUCM—When you set this value, the client: -
CUP—When you set this value, the client:
You can specify multiple, comma-separated values to exclude multiple services.
If you exclude all three services, the client does not perform service discovery and prompts the user to manually enter connection settings.
-
-
ServicesDomainSsoEmailPrompt—Optional. Specifies whether the user is shown the email prompt for the purposes of determining their home cluster.
-
Telephony_Enabled— Specifies whether the user has the phone capability or not. The default is true.
-
ForceLaunchBrowser— Used to force user to use the external browser. 
Note
ForceLaunchBrowser is used for client certificate deployments and for devices with Android OS below 5.0.
Create the configuration URL in the following format:
ciscojabber://provision?ServicesDomain=<domain_for_service_discover> &VoiceServicesDomain=<domain_for_voice_services> &ServiceDiscoveryExcludedServices=<services_to_exclude_from_service_discover> &ServicesDomainSsoEmailPrompt=<ON/OFF>
 Note |
Examples
-
ciscojabber://provision?ServicesDomain=cisco.com
-
ciscojabber://provision?ServicesDomain=cisco.com &VoiceServicesDomain=alphauk.cisco.com
-
ciscojabber://provision?ServicesDomain=service_domain &VoiceServicesDomain=voiceservice_domain&ServiceDiscoveryExcludedServices=WEBEX
-
ciscojabber://provision?ServicesDomain=cisco.com &VoiceServicesDomain=alphauk.cisco.com&ServiceDiscoveryExcludedServices=CUCM,CUP
-
ciscojabber://provision?ServicesDomain=cisco.com &VoiceServicesDomain=alphauk.cisco.com&ServiceDiscoveryExcludedServices=CUCM,CUP &ServicesDomainSsoEmailPrompt=OFF
Provide Users with Configuration URL from a Website
You can provide a configuration URL link to users by emailing the link to the user directly, or by posting the link to a website.
 Note | Due to a limitation of the Android operating system, Cisco Jabber for Android users can encounter an issue if they open the configuration URL directly from an Android application. To work around this issue, we recommend that you distribute your configuration URL link using a website. |
If you want to use the website explore option for URL provisioning, we recommended you to use Mozilla Firefox.
Use the following procedure to distribute the link from a website.
Manual Connection Settings
Manual connection settings provide a fallback mechanism when Service Discovery is not used.
When you start Cisco Jabber, you can specify the authenticator and server address in the Advanced settings window. The client caches the server address to the local application configuration that loads on subsequent starts.
On-Premises with Cisco Unified Communications Manager release 9.x and Later — If the client cannot get the authenticator and server addresses from the service profile.
Cloud-Based or On-Premises with Cisco Unified Communications Manager release 8.x — The client also prompts users to enter server addresses in the Advanced settings window if you do not set server addresses with SRV records.
Settings that you enter in the Advanced settings window take priority over any other sources including SRV records.
- Manual Connection Settings for On-Premises Deployments
- Manual Connection Settings for On-Premises Deployments in Phone Mode
- Manual Connection Settings for Cloud-Based Deployments
- Automatic Connection Setting for Service Discovery
Manual Connection Settings for On-Premises Deployments
Users can set Cisco Unified Presence or Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service as the authenticator and specify the server address in the Advanced settings window.
You can automatically set the default server address with the _cuplogin SRV record.
Manual Connection Settings for On-Premises Deployments in Phone Mode
Manual Connection Settings for Cloud-Based Deployments
Users can set the Cisco WebEx Messenger service as the authenticator and specify the CAS URL for login in the Advanced settings window.
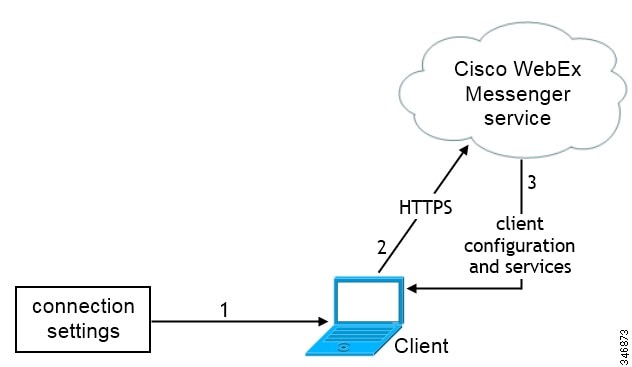
Automatic Connection Setting for Service Discovery
Users can select the Automatic option in the Advanced settings window to discover servers automatically.
This option lets users change from manually setting the service connection details to using service discovery. For example, on the initial launch, you manually set the authenticator and specify a server address in the Advanced settings window.
The client always checks the cache for manual settings. The manual settings also take higher priority over SRV records, and for Cisco Jabber for Windows, the bootstrap file. For this reason, if you decide to deploy SRV records and use service discovery, you must override the manual settings from the initial launch.
Installer Switches: Cisco Jabber for Windows
When you install Cisco Jabber, you can specify the authenticator and server addresses. The installer saves these details to a bootstrap file. When users launch the client for the first time, it reads the bootstrap file. The bootstrap file is ignored if service discovery is deployed.
Bootstrap files provide a fallback mechanism for service discovery in situations where service discovery has not been deployed and where you do not want users to manually specify their connection settings.
The client only reads the bootstrap file on the initial launch. After the initial launch, the client caches the server addresses and configuration, and then loads from the cache on subsequent launches.
We recommend that you do not use a bootstrap file, and instead use service discovery, in on-premises deployments with Cisco Unified Communications Manager release 9.x and later.
- Bootstrap Settings for On-Premises Deployments
- Bootstrap Settings for On-Premises Deployments in Phone Mode
- Bootstrap Settings for Cloud-Based Deployments
Bootstrap Settings for On-Premises Deployments
Product Mode |
Server Releases |
Argument Values |
|---|---|---|
Full UC (Default Mode) |
|
Use the following installer switches and values: |
Full UC (Default Mode) |
|
Use the following installer switches and values: |
IM Only (Default Mode) |
|
Use the following installer switches and values: |
IM Only (Default Mode) |
|
Use the following installer switches and values: |
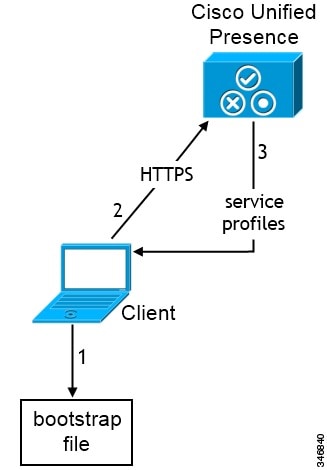
-
The client retrieves settings from the bootstrap file.
The client starts in default mode and determines that Cisco Unified Presence or Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service is the authenticator. The client also gets the address of the presence server, unless Service Discovery results dictate otherwise.
-
The client authenticates to Cisco Unified Presence or Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service .
-
The client retrieves service profiles from the presence server.
Bootstrap Settings for On-Premises Deployments in Phone Mode
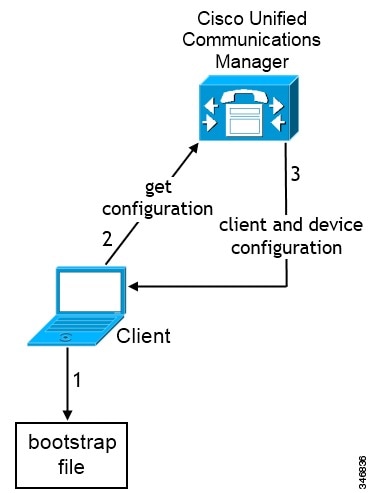
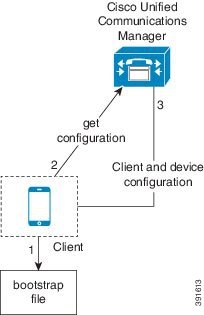
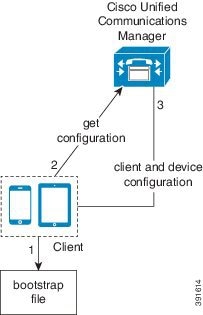
-
The client retrieves settings from the bootstrap file.
The client starts in phone mode and determines that Cisco Unified Communications Manager is the authenticator. The client also gets the addresses for the TFTP and CTI servers, unless Service Discovery results dictate otherwise.
The client starts in phone mode and determines that Cisco Unified Communications Manager is the authenticator. The client also gets the addresses for the TFTP server, unless Service Discovery results dictate otherwise.
-
The client authenticates to Cisco Unified Communications Manager and gets configuration.
-
The client retrieves device and client configuration.
Bootstrap Settings for Cloud-Based Deployments
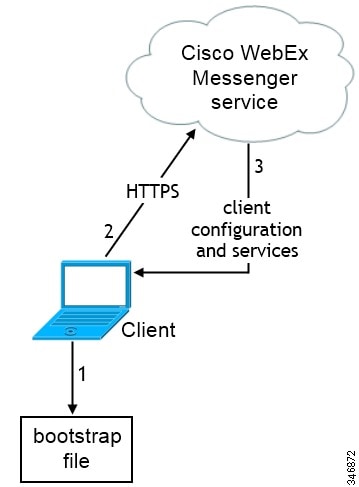
-
The client retrieves settings from the bootstrap file.
The client starts in default mode and determines that the Cisco WebEx Messenger service is the authenticator, unless Service Discovery results dictate otherwise.
-
The client authenticates to the Cisco WebEx Messenger service.
-
The client retrieves configuration and services.
Hardware Requirements
Hardware Requirements for Cisco Jabber for Windows
Installed RAM
- 2 GB RAM on Microsoft Windows 7 and Windows 8
Free Physical Memory
- 128 MB
Free Disk Space
- 256 MB
CPU Speed and Type
- Mobile AMD Sempron Processor 3600+ 2 GHz
- Intel Core2 CPU T7400 @ 2. 16 GHz
GPU
- DirectX11 on Microsoft Windows 7
I/O Ports
- USB 2.0 for USB camera and audio devices.
Hardware Requirements for Cisco Jabber for Mac
Installed RAM
- 2 GB RAM
Free Physical Memory
- 1 GB
Free Disk Space
- 300 MB
CPU Speed and Type
- Intel Core 2 Duo or later processors in any of the following Apple hardware:
I/O Ports
- USB 2.0 for USB camera and audio devices.
Device Requirements for Cisco Jabber for Android
Device Support
Cisco Jabber for Android is available from the Google Play Store.
Cisco specifically supports Cisco Jabber for Android on audio and video for the following Android device and operating system combinations:
-
Samsung Galaxy SII (Android OS 4.1.2 to Android OS 4.4 latest)
-
Samsung Galaxy SIII (Android OS 4.1.2 to Android OS 4.4 latest)
-
Samsung Galaxy S4 (Android OS 4.2.2 to Android OS 4.4 latest)
-
Samsung Galaxy S4 mini (Android OS 4.2.2 to Android OS 4.4 latest)
-
Samsung Galaxy S5 (Android OS 4.4.x)
-
Samsung Galaxy Note II (Android OS 4.2 to Android OS 4.4 latest)
-
Samsung Galaxy Note III (Android OS 4.3 to Android OS 4.4 latest)
-
Samsung Galaxy Rugby Pro (Android OS 4.2.2 to Android OS 4.4 latest)
-
Samsung Galaxy Note Pro 12.2 (Android OS 4.4.x)
-
Google Nexus 5 (Android OS 4.4.x and Android OS 5.0)
-
Google Nexus 10 (Android OS 4.4.x and Android OS 5.0)
-
Sony Xperia Z1 (Android OS 4.2 to Android OS 4.4 latest)
-
Sony Xperia ZR/A (Android OS 4.1.2 to Android OS 4.4 latest)
-
Sony Xperia Z2 (Android OS 4.4.x)
-
Sony Xperia M2 (Android OS 4.3)
-
LG G2 (Android OS 4.2.2 to Android OS 4.4 latest)
-
Motorola Moto G (Android OS 4.4.x)
 Note | Cisco supports Cisco Jabber for Android with tested Android devices. Although other devices are not officially supported, you may be able to use Cisco Jabber for Android with other devices. |
 Note |
|
Bluetooth Device Support
 Note | Cisco supports Cisco Jabber for Android with tested Bluetooth devices. Although other Bluetooth devices are not officially supported, you may be able to use Cisco Jabber for Android with other devices. |
Using a Bluetooth device on a Samsung Galaxy SIII may cause distorted ringtone and distorted call audio.
If you use a Samsung Galaxy S4 with either Jawbone ICON for Cisco Bluetooth Headset or Plantronics BackBeat 903+, you may experience problems due to compatibility issues between these devices.
Remote Access
 Note | Administrators can configure remote access using either a VPN or Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access. If administrators configure Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access, there is no need to configure VPN access. |
Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client
To connect with VPN, users can use the latest version of Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client, which is available from the Google Play Store.
Device Requirements for Cisco Jabber for iPhone and iPad
Device Support
Cisco Jabber for iPhone and iPad is available from the Apple App Store.
Cisco supports Cisco Jabber for iPhone and iPad on the following iOS devices:
-
iTouch 5
-
iPhone model 4, 4S, 5, 5C, and 5S

Note
Video call is not supported for iPhone model 4 -
iPad second, third, fourth generation, iPad mini with Retina display, and iPad Air
The device must be able to access the corporate network using Wi-Fi or VPN.
Device Operating System Support
iOS support: iOS 7
Bluetooth Headset Support
iTouch: supported (optional)
iPhone: supported (optional)
iPad: Supported (optional)
Software Requirements
For successful deployment, ensure that client workstations meet the software requirements.
- Operating System Requirements
- Software Requirements for On-Premise Servers
- Cloud-Based Servers
- Directory Servers
- Integrate with Microsoft Products
- Calendar Integration
- Local Contacts in Mac Address Book
- Computer Telephony Integration Servitude
- Accessibility
Operating System Requirements
Operating Systems for Cisco Jabber for Windows
 Note | Cisco Jabber for Windows does not require the Microsoft .NET Framework or any Java modules. |
 Note | For Microsoft Windows 7 or 8.x, you can download Cisco Media Services Interface (MSI) 4.1.2 for use with deskphone video. |
Cisco Jabber for Windows supports Microsoft Windows 8 in desktop mode only.
Operating Systems for Cisco Jabber for Mac
Software Requirements for On-Premise Servers
On-Premises Servers for Cisco Jabber for Windows and Cisco Jabber for Mac
-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager, release 8.6(2) or later
-
Cisco Unified Presence, release 8.6(2) or later
-
Cisco Unity Connection, release 8.6(2) or later
-
Cisco WebEx Meetings Server, version 1.5 or later (Windows only)
-
Cisco WebEx Meetings Server, version 2.0 or later (Mac only)
-
Cisco Expressway Series for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
-
Cisco TelePresence Video Communications Server
Cisco Jabber requires an active connection to the presence server to successfully fall back to Cisco Unified Survivable Remote Site Telephony.
Refer to the Cisco Unified SCCP and SIP SRST System Administrator Guide for information about configuring Cisco Unified Survivable Remote Site Telephony at: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/voice_ip_comm/cusrst/admin/sccp_sip_srst/configuration/guide/SCCP_and_SIP_SRST_Admin_Guide.html.
For Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express support details, refer to the Cisco Unified CME documentation: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/voicesw/ps4625/products_device_support_tables_list.html
On-Premises and Cloud Servers for Cisco Jabber for Android and iOS
WebEx Meeting Centre
Cisco Jabber for mobile clients supports the following cloud servers:
WebEx Meeting Centre T28+
Cisco Jabber for mobile clients supports the following on-premises nodes and servers:
Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Cisco Unified Presence
Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service
 Note | Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service is formerly known as Cisco Unified Presence. |
-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service, Release 9.1(1)
-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service, Release 9.1(2)
-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service, Release 10.0(1)
-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service, Release 10.5(1)
-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service, Release 10.5(2)
-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service, Release 11.0
Video Conferencing Bridge
Cisco Unity Connection
Cisco WebEx Meetings Server
Cisco WebEx Meetings Client
 Note | This Cisco WebEx Meetings Server client, version 8.0 supports Collaboration Meeting Room and Personal Meeting Room. |
Cisco Unified Survivable Remote Site Telephony
Cisco Jabber for mobile clients support the following features with Cisco Unified Survivable Remote Site Telephony, version 8.5.
Cisco Expressway Series for Cisco Unified Communications Manager (Optional)
Use the following servers to set up mobile and remote access for the client. The Expressway servers do not provide call control for Cisco Jabber. The client uses Cisco Unified Communications Manager for call control.
-
Cisco Expressway-E, version 8.5
-
Cisco Expressway-C, version 8.5
-
Cisco Expressway, version 8.2
-
Cisco Expressway, version 8.2.1
If you currently deploy a Cisco TelePresence Video Communications Server (VCS) environment, you can set up Cisco Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access. A VCS environment requires Cisco VCS Expressway, version 8.1.1 and Cisco VCS Control, version 8.1.1.
Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (Optional)
-
Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) 5500 Series, version 8.4(1) or later.
-
Cisco Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM), version 6.4 or later.
-
Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client Integration (Optional)—Android devices must run the latest version of Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client, which is available from the Google Play Store.

Note
When you are using AnyConnect with Samsung, the supported version is 4.0.01128.
-
ASA license requirements—Use one of the following combinations:
-
Certificate authority (CA) if using certificate-based authentication—Cisco IOS Certificate Server, Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise Certificate Authority, or Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Certificate Authority.
On-Premises Servers for Cisco Jabber for iPhone and iPad
Cisco Jabber for iPhone and iPad supports the following on-premises servers:
Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Cisco Unified Presence
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Release IM and Presence Service
 Note | Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service is formerly known as Cisco Unified Presence. |
-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service, Release 9.1(1)
-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service, Release 9.1(2)
-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service, Release 10.0(1)
-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service, Release 10.5(1)
-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service, Release 10.5(2)
Cisco Unity Connection
-
Cisco Unity Connection, Release 8.5
-
Cisco Unity Connection, Release 8.6(1)
-
Cisco Unity Connection, Release 8.6(2)
-
Cisco Unity Connection, Release 9.1(1)
-
Cisco Unity Connection, Release 9.1(2)
-
Cisco Unity Connection, Release 10.0(1)
-
Cisco Unity Connection, Release 10.5(1)
-
Cisco Unity Connection, Release 10.5(2)
Cisco WebEx Meetings Server
Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (Optional)
-
VPN On Demand (Optional)—The Apple iOS On-Demand VPN feature requires certificate-only authentication. If you set up an ASA without certificate-only authentication, the user must manually initiate the AnyConnect VPN connection as needed.
The iOS device must be able to access the corporate network, servers, and telephony endpoints using a VPN client, such as Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client.
-
Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client Integration (Optional) - iOS devices must run Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client version 3.0.09115, which is available from the Apple App Store
- Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA), version 8.4(1) or later
- Cisco Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM), version 6.4 or later
- ASA license
requirements—Use one of the following combinations:

Note
For more information about Cisco AnyConnect license requirements, see VPN License and Feature Compatibility. - Certificate authority (CA) if using certificate-based authentication: Cisco IOS Certificate Server, Cisco IOS Certificate Server or Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Certificate Authority
Cisco Jabber supports the following features with Cisco Unified Survivable Remote Site Telephony, version 8.6:
High Availability for Instant Messaging and Presence
High availability refers to an environment in which multiple nodes exist in a subcluster to provide failover capabilities for instant messaging and presence services. If one node in a subcluster becomes unavailable, the instant messaging and presence services from that node failover to another node in the subcluster. In this way, high availability ensures reliable continuity of instant messaging and presence services for Cisco Jabber.
Cisco Jabber supports high availability with the following servers:
Cisco Unified Presence releases 8.5 and 8.6
- Configuration and Administration of Cisco Unified Presence Release 8.6
-
Multi-node Deployment Administration
- Deployment Guide for Cisco Unified Presence Release 8.0 and 8.5
-
Planning a Cisco Unified Presence Multi-Node Deployment
Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service release 9.0 and higher
- Configuration and Administration of IM and Presence Service on Cisco Unified Communications Manager
-
High Availability Client Login Profiles
- Active Calls on Hold During Failover
-
You cannot place an active call on hold if failover occurs from the primary instance of Cisco Unified Communications Manager to the secondary instance.
High Availability in the Client
- Client Behavior During Failover
-
If high availability is configured on the server, then after the primary server fails over to the secondary server, the client temporarily loses presence states for up to one minute. Configure the re-login parameters to define how long the client waits before attempting to re-login to the server.
- Configure Re-Login Parameters
-
In Cisco Unified Presence and Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service, you can configure the maximum and minimum number of seconds that Cisco Jabber waits before attempting to re-login to the server. On the server, you specify the re-login parameters in the following fields:
Client Behavior During a Failover
The following figure shows the client's behavior when the Cisco Unified Presence server during a failover.
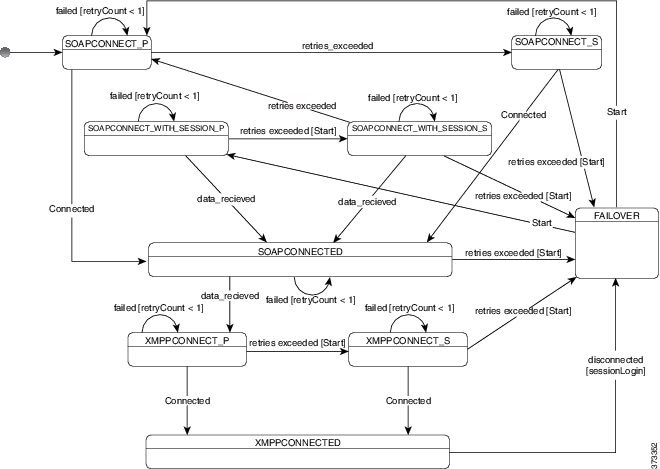
-
When the client is disconnected from its active server, the client goes from XMPPCONNECTED state to a FAILOVER state.
-
From a FAILOVER state, the client tries to attain a SOAPCONNECTED state by attempting SOAPCONNECT_SESSION_P (as the primary server), and if that fails, attempts SOAPCONNECT_SESSION_S (as the secondary server).
- If it is unable to attain SOAPCONNECT_SESSION_P or SOAPCONNECT_SESSION_S, the client re-enters into the FAILOVER state.
-
From a FAILOVER state, the clients attempts to attain a SOAPCONNECT_P state, and if that fails, attempts to reach a SOAPCONNECT_S state.
-
If the client cannot reach the SOAPCONNECT_P or SOAPCONNECT_S state, then the client does not attempt any more automatic connections to the IM&P server until a user initiates a login attempt.
-
From a SOAPCONNECT_SESSION_P, SOAPCONNECT_SESSION_S, SOAPCONNECT_P, or SOAPCONNECT_S state, the client retrieves its current primary secondary XMPP server address. This address changes during a failover.
-
From a SOAPCONNECTED state, the client tries to attain an XMPPCONNECTED state by attempting to connect to the XMPPCONNECT_P state, and if that fails, attempts XMPPCONNECT_S state.
-
After the client is in an XMPPCONNECTED state, then the client has IM&P capability.
Cloud-Based Servers
Directory Servers
 Note | Cisco Jabber for Mac, Cisco Jabber for iPhone and iPad, and Cisco Jabber for Android support the LDAPv3 standard for directory integration. Any directory server that supports this standard should be compatible with these clients. |
-
Active Directory Domain Services for Windows Server 2012 R2
-
Active Directory Domain Services for Windows Server 2008 R2
-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager User Data Server (UDS)
Cisco Jabber supports UDS using the following Cisco Unified Communications Manager versions: - Cisco Unified Communications Manager, version 9.1(2) or later, with the following Cisco Options Package (COP) file: cmterm-cucm-uds-912-5.cop.sgn.
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager, version 10.0(1). No COP file is required.
-
OpenLDAP
-
Active Directory Lightweight Directory Service (AD LDS) or Active Directory Application Mode (ADAM)
Directory integration with OpenLDAP, AD LDS, or ADAM requires that you define specific parameters in a Cisco Jabber configuration file. See LDAP Directory Servers for more information.
Integrate with Microsoft Products
Cisco Jabber for Windows supports a range of Microsoft products that integrate with the application. This section describes the support and integrations for these products.
Internet Explorer
Microsoft Internet Explorer 8 or later is required. Cisco Jabber for Windows uses the Internet Explorer rendering engine to display HTML content.
Cisco Jabber for Windows requires Internet Explorer active scripting to render IMs. See http://windows.microsoft.com/en-US/windows/help/genuine/ie-active-script for instructions on enabling active scripting.
 Note | Internet Explorer 9 users in Cloud-based deployments that use Single Sign On (SSO) get security alerts when they sign in to Cisco Jabber for Windows. Add webexconnect.com to the list of websites in the Compatibility View Settings window of Internet Explorer 9 to stop these alerts. |
Office
Integration with the following versions of Office is supported:
Office 365
Microsoft Office 365 supports different configuration types based on the plan or subscription type. Cisco Jabber for Windows has been tested with small business plan P1 of Microsoft Office 365. This plan requires an on-premises Active Directory server.
Client-side integration with Microsoft Office 365 is supported with the following applications:
SharePoint
Integration with the following versions of SharePoint is supported:
Availability status in Microsoft SharePoint sites is supported only if users access those sites with Microsoft Internet Explorer. You should add the Microsoft SharePoint site to the list of trusted sites in Microsoft Internet Explorer.
Product Integration
See the following topics for information on product integration:
Calendar Integration
Local Contacts in Mac Address Book
Cisco Jabber allows users search for and add local contacts in the Mac Address book.
To enable the Address Book plug-in:
To communicate with local contacts in Mac Address book using the client, local contacts must have the relevant details. To send instant messages to contacts, local contacts must have an instant message address. To call contacts in Mac Address book, local contacts must have phone numbers.
Computer Telephony Integration Servitude
Cisco Jabber for Windows and Cisco Jabber for Mac support CTI servitude of Cisco Jabber from a third party application.
Computer Telephony Integration (CTI) enables you to use computer-processing functions while making, receiving, and managing telephone calls. A CTI application can allow you to retrieve customer information from a database on the basis of information that caller ID provides and can enable you to use information that an interactive voice response (IVR) system captures.
-
Cisco TAPI: http://developer.cisco.com/web/tapi/home
-
Cisco JTAPI: http://developer.cisco.com/web/jtapi/home
Accessibility
Accessibility for Cisco Jabber for Android
Screen Readers
Cisco Jabber for Android is compatible with the TalkBack screen reader. Users who require screen readers should always use the most recent version to ensure the best possible user experience.
Assistive Touch
You can navigate Cisco Jabber for Android using Explore by Touch.
Accessibility for Cisco Jabber for iPhone and iPad
Screen Readers
Cisco Jabber for iPhone and iPad is compatible with the VoiceOver screen reader. Users who require screen readers should always use the most recent version to ensure the best possible user experience.
Assistive Touch
You can navigate Cisco Jabber for iPhone and iPad using Assistive Touch.
Network Requirements
If you deploy Phone Services, mobile devices must be able to connect to the corporate network.
When using Cisco Jabber over your corporate Wi-Fi network, we recommend that you do the following:
- Design your Wi-Fi network to eliminate gaps in coverage as much as possible, including in areas such as elevators, stairways, and outside corridors.
- Ensure that all access points assign the same IP address to the mobile device. Calls are dropped if the IP address changes during the call.
- Ensure that all access points have the same service set identifier (SSID). Hand-off may be much slower if the SSIDs do not match.
- Ensure that all access points broadcast their SSID. If the access points do not broadcast their SSID, the mobile device may prompt the user to join another Wi-Fi network, which interrupts the call.
For more information, see the following documentation:
- The "VoWLAN Design Recommendations" section in the Enterprise Mobility Design Guide.
- The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Deployment Guide.
- The Capacity Coverage & Deployment Considerations for IEEE 802.11g white paper.
- The Solutions Reference Network Design (SRND) for your Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
Bluetooth use can cause voice quality and connectivity issues.
If users connect to the network remotely, their mobile devices must be able to connect to the corporate network using a solid, high-bandwidth connection. Video and audio quality depends on connection quality.
Ports and Protocols
Ports and Protocols for Cisco Jabber for Windows and Cisco Jabber for Mac
The following table lists outbound ports and protocols that Cisco Jabber uses.
|
Port |
Protocol |
Description |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
443 |
TCP (Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol [XMPP] and HTTPS) |
XMPP traffic to the WebEx Messenger service. The client sends XMPP through this port in cloud-based deployments only. If port 443 is blocked, the client falls back to port 5222.
|
||
|
389 |
UDP/TCP |
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directory server. |
||
|
636 |
LDAPS |
LDAP directory server (secure). |
||
|
3268 |
TCP |
Global Catalog server. |
||
|
3269 |
LDAPS |
Global Catalog server (secure). |
||
|
5070 |
UDP |
Binary Floor Control Protocol (BFCP) for video desktop sharing capabilities. |
||
|
5222 |
TCP (XMPP) |
XMPP traffic to Cisco Unified Presence or Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service. |
||
|
8443 |
TCP ( HTTPS ) |
Traffic to Cisco Unified Communications Manager and Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service. | ||
|
7080 |
TCP ( HTTPS ) |
Cisco Unity Connection for notifications of voice messages (new message, message update, and message deletion). |
||
|
53 |
UDP/TCP |
Domain Name System (DNS) traffic. |
||
|
37200 |
SOCKS5 Bytestreams |
Peer-to-peer file transfers. In on-premises deployments, the client also uses this port to send screen captures. |
||
|
5060 |
UDP/TCP |
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) call signaling. |
||
|
5061 |
TCP |
Secure SIP call signaling. |
||
|
49152 to 65535 |
TCP |
IM-only screen share. The client randomly selects a port from the range. The actual range may vary. To find the real range, enter the netsh interface ipv4 show dynamicportrange tcp command. You can use the SharePortRangeStart and SharePortRangeSize parameters to narrow the range used for IM screen share. For more information on these parameters, see the section on Common Policies parameters in the Deployment and Installation Guide. |
Ports for Additional Services and Protocols
-
For Cisco Unified Communications Manager, Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service, and Cisco Unified Presence, see the TCP and UDP Port Usage Guide.
-
For Cisco Unity Connection, see the System Administration Guide.
-
For Cisco WebEx Meetings Server, see the Administration Guide.
-
For Cisco WebEx services, see the Administrator's Guide.
- Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access, refer to Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage for Firewall Traversal.
Ports and Protocols for Cisco Jabber for Android, iPhone, and iPad
The client uses the ports and protocols listed in the following table. If you plan to deploy a firewall between the client and a server, you must configure the firewall to allow these ports and protocols.
 Note | No TCP/IP services are enabled in the client. |
|
Port |
Application Layer Protocol |
Transport Layer Protocol |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inbound | |||
|
16384 to 32766 |
RTP |
UDP |
Receives Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) media streams for audio and video. You set these ports in Cisco Unified Communications Manager. |
| Outbound | |||
|
7080 |
HTTPS |
TCP |
Used for Cisco Unity Connection to receive notifications of voice messages (new message, message update, and message deleted). |
|
6970 |
HTTP |
TCP |
Connects to the TFTP server to download client configuration files. |
|
80 |
HTTP |
TCP |
Connects to services such as Cisco WebEx Meeting Center for meetings or Cisco Unity Connection for voicemail. |
|
389 |
LDAP |
TCP (UDP) |
Connects to an LDAP directory service. |
|
3268 |
LDAP |
TCP |
Connects to a Global Catalog server for contact searches. |
|
443 |
HTTPS |
TCP |
Connects to services such as such as Cisco WebEx Meeting Center for meetings or Cisco Unity Connection for voicemail. |
|
636 |
LDAPS |
TCP |
Connects securely to an LDAP directory service. |
|
3269 |
LDAPS |
TCP |
Connects securely to the Global Catalog server. |
|
5060 |
SIP |
TCP |
Provides Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) call signaling. |
|
5061 |
SIP over Transport Layer Security (TLS) |
TCP |
Provides secure SIP call signaling. |
|
5222 |
XMPP |
TCP |
Connects to Cisco Unified Presence or Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service for instant messaging and presence. |
|
5269 |
XMPP |
TCP |
Enables XMPP federation. |
|
8191 |
SOAP |
TCP |
Connects to the local port to provide Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) web services. |
|
8443 |
HTTPS |
TCP |
|
|
16384 to 32766 |
RTP |
UDP |
Sends RTP media streams for audio and video. |
|
53 |
DNS |
UDP |
Provides hostname resolution. |
|
3804 |
CAPF |
TCP |
Issues Locally Significant Certificates (LSC) to IP phones. This port is the listening port for Cisco Unified Communications Manager Certificate Authority Proxy Function (CAPF) enrollment. |
For information about port usage for Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access, see Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage for Firewall Traversal.
For information about file transfer port usage see the Managed File Transfer chapter of the Configuration and Administration of IM and Presence Service on Cisco Unified Communications Manager, Release 10.5(2).
Call Control with Accessories API
Cisco Jabber for Windows includes an API that exposes call control functions to third party accessories. This API lets our vendor partners create software plugins that enable their accessories to use the API call control functions in Cisco Jabber.
Compatible Third Party Accessories
You can use certain Cisco compatible accessories such as headsets, speakers, keyboards, and audio devices to perform call control actions with Cisco Jabber from the device. For example, with some headsets you can use controls to answer incoming calls, end active calls, mute audio, and place calls on hold.
For a list of devices that are compatible with Cisco Jabber, refer to the Unified Communications Endpoint and Client Accessories site at: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/voicesw/uc_endpoints_accessories.html
 Note | You can use certain third party accessories that are not Cisco compatible. However, Cisco cannot guarantee an optimal user experience with such third party accessories. For the best user experience, you should use only Cisco compatible devices with Cisco Jabber. |
Install Vendor Plugins
To use compatible accessories with Cisco Jabber, you must do the following:
Plugin Versions
CTI Supported Devices
To view the list of Computer Telephony Integration (CTI) supported devices: From Cisco Unified Reporting, select Unified CM Phone Feature List. From the Feature drop-down list, select CTI controlled.
Supported Codecs
Supported Codecs for Cisco Jabber for Windows and Cisco Jabber for Mac
Supported Audio Codecs
Supported Video Codec
Supported Codecs for Cisco Jabber for Android, iPhone, and iPad
Supported Audio Codecs
Minimum requirement for low-bandwidth availability: G.729a.
Users can turn low bandwidth mode on and off in the client settings if they experience voice quality issues.
Normal mode supports G.711, G.722.1, and G.729a.
Low bandwidth mode supports G.729a only.
Supported Video Codecs
H.264/AVC
Supported Voicemail Codecs
 Note | Cisco Jabber does not support visual voicemail with G.729. However, you can access voice messages using G.729 and the Call Voicemail feature. |
COP Files
COP Files for Cisco Jabber for Windows and Cisco Jabber for Mac
In certain cases, you might need to apply COP files to Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
| COP File | Description | Cisco Unified Communications Manager Versions |
|---|---|---|
| ciscocm.installcsfdevicetype.cop.sgn | Adds the CSF device type to
Cisco Unified
Communications Manager.
For more information, see Software Requirements. |
7.1.3 |
| cmterm-bfcp-e.8-6-2.cop.sgn | Enables CSF devices to support BFCP video desktop sharing.
For more information, see Apply COP File for BFCP Capabilities. |
8.6.2 only |
| ciscocm.addcsfsupportfield.cop.sgn | Adds the
CSF Support Field field for group configuration
files.
For more information, see Create Group Configurations. |
8.6.1 and earlier |
| cmterm-cupc-dialrule-wizard-0.1.cop.sgn | Publishes application dial rules and directory lookup rules to
Cisco Jabber.
For more information, see Publish Dial Rules. |
8.6.1 and earlier |
Device COP file for Cisco Jabber for Android
You must install the device COP file on Cisco Unified Communications Manager to add the Cisco Dual Mode for Android device type for the first time, or to update your existing Cisco Dual Mode for Android devices with the configuration settings for the latest release of the client. To obtain the device COP file, do the following:
Device COP File for Cisco Jabber for iPhone and iPad
The device COP file adds the TCT/TAB device type to Cisco Unified Communications Manager . To obtain the device COP file, do the following:
-
Go to the software download site: http://www.cisco.com/go/jabber_iphone_cop..
-
Locate cmterm-iphone-install-141105.cop.sgn for TCT device and cmterm-jabberipad-140904.cop.sgn for TAB device..
-
Download the file.
Contact Sources
In on-premises deployments, the client requires a contact source to resolve directory look ups for user information. You can use the following as a contact source:
- Enhanced Directory Integration
-
Enhanced Directory Integration (EDI) is an LDAP-based contact source.
- Basic Directory Integration
-
Basic Directory Integration (BDI) is an LDAP-based contact source.
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager User Data Service
-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager User Data Service (UDS) is a contact source on Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
UDS is used for contact resolution in the following cases: -
If you configure the DirectoryServerType parameter in the client configuration file to use "UDS".
With this configuration, the client uses UDS for contact resolution when it is inside or outside of the corporate firewall.
-
If you deploy Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access.
With this configuration, the client automatically uses UDS for contact resolution when it is outside of the corporate firewall.

NoteCisco Jabber supports UDS using the following Cisco Unified Communications Manager versions: You can deploy approximately 50 percent of the maximum number of Cisco Jabber clients that your Cisco Unified Communications Manager node supports.
For example, if a Cisco Unified Communications Manager node can support 10,000 Cisco Jabber clients using an LDAP-based contact source, that same node can support 5,000 Cisco Jabber clients using UDS as a contact source.
-
- Enhanced Directory Integration
- Basic Directory Integration
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager User Data Service
Enhanced Directory Integration
EDI uses native Microsoft Windows APIs to retrieve contact data from the directory service.
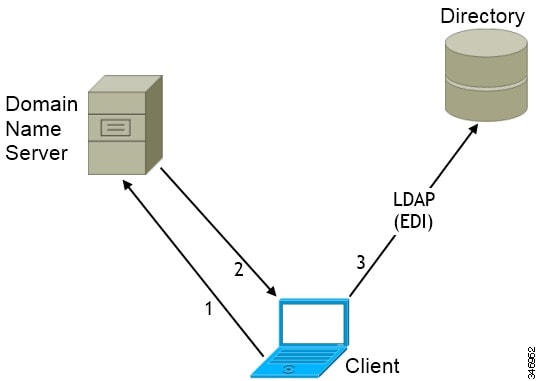
Domain Name Retrieval
Cisco Jabber for Windows retrieves the fully qualified DNS domain from the USERDNSDOMAIN environment variable on the client workstation.
After the client gets the DNS domain, it can locate the Domain Name Server and retrieve SRV records.
In some instances, the value of the USERDNSDOMAIN environment variable does not resolve to the DNS domain that corresponds to the domain of the entire forest. For example, when an organization uses a sub-domain or resource domain. In this case, the USERDNSDOMAIN environment variable resolves to a child domain, not the parent domain. As a result, the client cannot access information for all users in the organization.
If the USERDNSDOMAIN environment variable resolves to a child domain, you can use one of the following options to enable Cisco Jabber for Windows to connect to a service in the parent domain:
-
Ensure that the Global Catalog or LDAP directory server can access all users in the organization.
-
Configure your DNS server to direct the client to a server that can access all users in the organization when Cisco Jabber for Windows requests a Global Catalog or LDAP directory server.
-
Configure Cisco Jabber for Windows to use the FQDN of the parent domain.
Specify the FQDN of the parent domain as the value of the PrimaryServerName parameter in your client configuration as follows: <PrimaryServerName>parent-domain-fqdn</PrimaryServerName>
Directory Server Discovery
Directory Server |
SRV Record |
|---|---|
Global Catalog |
_gc._msdcs._tcp.domain.com |
Domain Controller LDAP-based directory servers |
_ldap._msdcs._tcp.domain.com |
Basic Directory Integration
When using Basic Directory Integration ( BDI), the client retrieves contact data from the directory service as follows.
-
The client connects to the Cisco Unified Presence or Cisco Unified Communication Manager IM and Presence Service node.
-
The client gets the LDAP profile configuration section in the service profile from the Cisco Unified Presence or Cisco Unified Communication Manager IM and Presence Service node.
The service profile contains the location of Cisco Unified Communication Manager (TFTP) node. Depending on your configuration, the service profile can also contain the credentials to authenticate with the directory.
-
The client connects to the Cisco Unified Communication Manager node.
-
The client downloads the client configuration file from the Cisco Unified Communication Manager node.
The client configuration file contains the location of the directory. Depending on your configuration, the client configuration file can also contain the credentials to authenticate with the directory.
-
The client uses the directory location and the authentication credentials to connect to the directory.
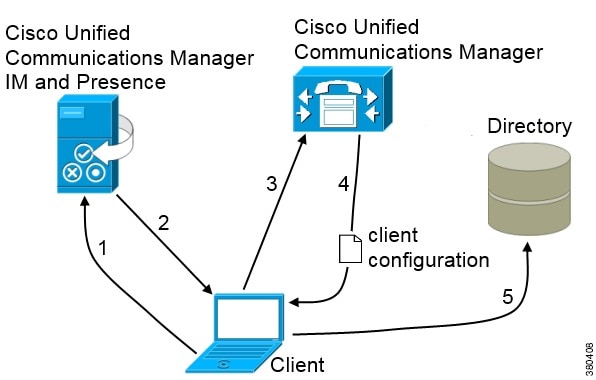
Authentication with Contact Sources
Specify credentials in Cisco Unified Presence or Cisco Unified Communications Manager — Specify credentials in a profile on the server. The client can then retrieve the credentials from the server to authenticate with the directory. This method is the most secure option for storing and transmitting credentials.
Set common credentials in the client configuration file — Specify a shared username and password in the client configuration file. The client can then authenticate with the directory server. Important: The client transmits and stores these credentials as plain text.
Use a well-known or public set of credentials for an account that has read-only permissions.
Use anonymous binds — Configure the client to connect to the directory source with anonymous binds.
- Specify LDAP Directory Configuration on Cisco Unified Presence
- Specify LDAP Directory Configuration on Cisco Unified Communications Manager
- Set Credentials in the Client Configuration
- Use Anonymous Binds
Specify LDAP Directory Configuration on Cisco Unified Presence
If your environment includes Cisco Unified Presence release 8.x, you can specify directory configuration in the LDAP profile. The client can then get the directory configuration from the server to authenticate with the directory source.
Complete the steps to create an LDAP profile that contains authentication credentials, and then assign that profile to users.
What to Do Next
Specify any additional BDI information in the client configuration file.
Specify LDAP Directory Configuration on Cisco Unified Communications Manager
If your environment includes Cisco Unified Communications Manager release 9.x and later, you can specify credentials when you add a directory service. The client can then get the configuration from the server to authenticate with the directory source.
Complete the steps to add a directory service, apply the directory service to the service profile, and specify the LDAP authentication configuration for the directory service.
Set Credentials in the Client Configuration
The client transmits and stores these credentials as plain text.
Use a well-known or public set of credentials for an account that has read-only permissions.
The following is an example configuration:
<Directory> <BDIConnectionUsername>admin@example.com</BDIConnectionUsername> <BDIConnectionPassword>password</BDIConnectionPassword> </Directory>
Use Anonymous Binds
To use anonymous binds, you set the following parameters in the client configuration file:
Parameter |
Value |
|---|---|
DirectoryServerType |
BDI |
| BDIPrimaryServerName |
IP address FQDN |
BDIEnableTLS |
True |
| BDISearchBase1 |
Searchable organizational unit (OU) in the directory tree |
| BDIBaseFilter | Object class that your directory service uses; for example, inetOrgPerson |
| BDIPredictiveSearchFilter | UID or other search filter A search filter is optional. |
The following is an example configuration:
<Directory> <DirectoryServerType>BDI</DirectoryServerType> <BDIPrimaryServerName>11.22.33.456</BDIPrimaryServerName> <BDIEnableTLS>True</BDIEnableTLS> <BDISearchBase1>ou=people,dc=cisco,dc=com</BDISearchBase1> <BDIBaseFilter>(&(objectClass=inetOrgPerson)</BDIBaseFilter> <BDIPredictiveSearchFilter>uid</BDIPredictiveSearchFilter> </Directory>
Cisco Unified Communications Manager User Data Service
User Data Service (UDS) is a REST interface on Cisco Unified Communications Manager that provides contact resolution.
-
If you set the DirectoryServerType parameter to use a value of UDS in the client configuration file.
With this configuration, the client uses UDS for contact resolution when it is inside or outside of the corporate firewall.
-
If you deploy Expressway for Remote and Mobile Access.
With this configuration, the client automatically uses UDS for contact resolution when it is outside of the corporate firewall.
You synchronize contact data into Cisco Unified Communications Manager from a directory server. Cisco Jabber then automatically retrieves that contact data from UDS.
Enable Integration with UDS
To enable integration with UDS, perform the following steps:
Contact Resolution with Multiple Clusters
For contact resolution with multiple Cisco Unified Communications Manager clusters, synchronize all users on the corporate directory to each cluster. Provision a subset of those users on the appropriate cluster.
When users in Europe call users in North America, Cisco Jabber retrieves the contact details for the user in Europe from cucm-cluster-na.
When users in North America call users in Europe, Cisco Jabber retrieves the contact details for the user in North America from cucm-cluster-eu.
Client Availability
Users can define whether their availability reflects their calendar events by setting an option to let others know they are in a meeting from the Status tab of the Options window from the client. This option synchronizes events in your calendar with your availability. The client only displays In a meeting availability for supported integrated calendars.
 Note | In Cisco Jabber for Android and Cisco Jabber for iPod or iPad, we do not support this meeting integration. But we do support In a meeting status in Cisco Jabber for Mac and Cisco Jabber for Windows. |
Microsoft Exchange and Cisco Unified Presence Integration — Applies to on-premises deployments. The Include Calendar information in my Presence Status field in Cisco Unified Presence is the same as the In a meeting option in the client. Both fields update the same value in the Cisco Unified Presence database.
If users set both fields to different values, then the last field that the user sets takes priority. If users change the value of the Include Calendar information in my Presence Status field while the client is running, the users must restart the client for those changes to apply.
Cisco Jabber Client — Applies to on-premises and cloud-based deployments. You must disable Cisco Unified Presence and Microsoft Exchange integration for the client to set the In a meeting availability. The client checks if integration between Cisco Unified Presence and Microsoft Exchange is on or off. The client can only set availability if integration is off.
Deployment Scenario |
You select In a meeting (according to my calendar) |
You do not select In a meeting (according to my calendar) |
|---|---|---|
|
You enable integration between Cisco Unified Presence and Microsoft Exchange. |
Cisco Unified Presence sets availability status |
Availability status does not change |
|
You do not enable integration between Cisco Unified Presence and Microsoft Exchange. |
Client sets availability status |
Availability status does not change |
Cloud-based deployments |
Client sets availability status |
Availability status does not change |
Availability Enabled in the Client |
Availability Enabled by Integrating Cisco Unified Presence with Microsoft Exchange |
||
|---|---|---|---|
Offline in a meeting availability is not supported. |
Offline in a meeting availability is supported. |
||
In a meeting availability is supported for non-calendar events. |
In a meeting availability is not supported for non-calendar events. |
||
|
|||
Multiple Resource Login
All Cisco Jabber clients register with a central IM and Presence Service node when a user logs into the system. This is Cisco Unified Presence or Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service node in on-premise deployments or Cisco WebEx in cloud-based deployments. This node tracks availability, contact lists, and other aspects of the IM and Presence Service environment.
This IM and Presence Service node tracks all of the registered clients associated with each unique network user. When a new IM session is initiated between two users, the first incoming message is broadcast to all of the registered clients of the receiving user. The IM and Presence Service node then waits for the first response from one of the registered clients. The first client to respond subsequently receives the remainder of the incoming messages until the user starts responded using another registered client. The node then reroutes subsequent messages to this new client.
Adam wishes to initiate an IM conversation with Anita. Anita has previously logged into Cisco Jabber for Windows and Cisco Jabber for Android. Anita has registered two clients with the central IM and Presence Service node. Adam initiates the conversation by sending the message, "Hi Anita. Are you free?"
The node identifies that Anita has two registered clients and broadcasts Adam's message to both.
Anita is sitting at her desk and observes Adam's message appearing on both her laptop and phone. She chooses to respond using her laptop and responds with the message, "I have a meeting in a few moments but I can chat briefly right now."
The IM and Presence Service node identifies that Anita has responded using Cisco Jabber for Windows and marks this as the client to route all subsequent messages to in the conversation. When Adam responds with "This will only take a minute," it is routed directly to Cisco Jabber for Windows. If Anita starts responding to Adam using her phone at some point in the conversation, the IM and Presence Service node then routes subsequent messages there instead of to Cisco Jabber for Windows.
Instant Message Encryption
Cisco Jabber uses Transport Layer Security (TLS) to secure Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP) traffic over the network between the client and server. Cisco Jabber encrypts point to point instant messages.
On-Premises Encryption
|
Connection |
Protocol |
Negotiation Certificate |
Expected Encryption Algorithm |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Client to server |
XMPP over TLS v2 |
X.509 public key infrastructure certificate |
AES 256 bit |
Server and Client Negotiation
After the server and client negotiate TLS encryption, both the client and server generate and exchange session keys to encrypt instant messaging traffic.
|
Version |
Key Length |
|---|---|
|
Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service versions 9.0.1 and higher |
2048 bit |
|
Cisco Unified Presence version 8.6.4 |
2048 bit |
|
Cisco Unified Presence versions lower than 8.6.4 |
1024 bit |
XMPP Encryption
Cisco Unified Presence and Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service both use 256-bit length session keys that are encrypted with the AES algorithm to secure instant message traffic between Cisco Jabber and the presence server.
Instant Message Logging
You can log and archive instant messages for compliance with regulatory guidelines. To log instant messages, you either configure an external database or integrate with a third-party compliance server. Cisco Unified Presence and Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service do not encrypt instant messages that you log in external databases or in third party compliance servers. You must configure your external database or third party compliance server as appropriate to protect the instant messages that you log.
For more information about encryption levels and cryptographic algorithms, including symmetric key algorithms such as AES or public key algorithms such as RSA, see Next Generation Encryption.
For more information about X.509 public key infrastructure certificates, see the Internet X.509 Public Key Infrastructure Certificate and CRL Profile document.
Cloud-Based Encryption
|
Connection |
Protocol |
Negotiation Certificate |
Expected Encryption Algorithm |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Client to server |
XMPP within TLS |
X.509 public key infrastructure certificate |
AES 128 bit |
|
Client to client |
XMPP within TLS |
X.509 public key infrastructure certificate |
AES 256 bit |
Server and Client Negotiation
The following servers negotiate TLS encryption with Cisco Jabber using X.509 public key infrastructure (PKI) certificates with the Cisco WebEx Messenger service.
After the server and client negotiate TLS encryption, both the client and server generate and exchange session keys to encrypt instant messaging traffic.
XMPP Encryption
The Cisco WebEx Messenger service uses 128-bit session keys that are encrypted with the AES algorithm to secure instant message traffic between Cisco Jabber and the Cisco WebEx Messenger service.
You can optionally enable 256-bit client-to-client AES encryption to secure the traffic between clients.
Instant Message Logging
The Cisco WebEx Messenger service can log instant messages, but it does not archive those instant messages in an encrypted format. However, the Cisco WebEx Messenger service uses stringent data center security, including SAE-16 and ISO-27001 audits, to protect the instant messages that it logs.
The Cisco WebEx Messenger service cannot log instant messages if you enable AES 256 bit client-to-client encryption.
For more information about encryption levels and cryptographic algorithms, including symmetric key algorithms such as AES or public key algorithms such as RSA, see Next Generation Encryption.
For more information about X509 public key infrastructure certificates, see the Internet X.509 Public Key Infrastructure Certificate and CRL Profile document.
Client-to-Client Encryption
By default, instant messaging traffic between the client and the Cisco WebEx Messenger service is secure. You can optionally specify policies in the Cisco WebEx Administration Tool to secure instant messaging traffic between clients.
|
Policy Combination |
Client-to-Client Encryption |
When the Remote Client Supports AES Encryption |
When the Remote Client Does not Support AES Encryption |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Support AES Encoding For IM = false Support No Encoding For IM = true |
No |
Cisco Jabber sends unencrypted instant messages. Cisco Jabber does not negotiate a key exchange. As a result, other clients do not send Cisco Jabber encrypted instant messages. |
Cisco Jabber sends and receives unencrypted instant messages. |
|
Support AES Encoding For IM = true Support No Encoding For IM = true |
Yes |
Cisco Jabber sends and receives encrypted instant messages. Cisco Jabber displays an icon to indicate instant messages are encrypted. |
Cisco Jabber sends encrypted instant messages. Cisco Jabber receives unencrypted instant messages. |
|
Support AES Encoding For IM = true Support No Encoding For IM = false |
Yes |
Cisco Jabber sends and receives encrypted instant messages. Cisco Jabber displays an icon to indicate instant messages are encrypted. |
Cisco Jabber does not send or receive instant messages to the remote client. Cisco Jabber displays an error message when users attempt to send instant messages to the remote client. |
 Note | Cisco Jabber does not support client-to-client encryption with group chats. Cisco Jabber uses client-to-client encryption for point-to-point chats only. |
For more information about encryption and Cisco WebEx policies, see About Encryption Levels in the Cisco WebEx documentation.
Encryption Icons
Review the icons that the client displays to indicate encryption levels.
Lock Icon for Client to Server Encryption
Padlock Icon for Client to Client Encryption
Local Chat History
Cisco Jabber for iPhone and iPad does not encrypt archived instant message stored locally on a mobile device when local chat history is enabled. Disable local chat history if you do not want unencrypted instant messages to be stored locally.
Cisco Jabber for Android does not encrypt archived instant message stored locally on a mobile device when local chat history is enabled. Disable local chat history if you do not want unencrypted instant messages to be stored locally.
If you enable local chat history, Cisco Jabber for Windows does not archive instant messages in an encrypted format. In order to restrict access to chat history, the client saves archives to the following directory: %USERPROFILE%\AppData\Local\Cisco\Unified Communications\Jabber\CSF\History\uri.db.
If you enable local chat history, Cisco Jabber for Mac does not archive instant messages in an encrypted format. In order to restrict access to chat history, Cisco Jabber saves archives to the following directory: ~/Library/Application Support/Cisco/Unified Communications/Jabber/CSF/History/uri.db.
For on-premises deployment, if you select the Save chat archives to: option in the Chat Preferences window of Cisco Jabber for Mac, chat history is stored locally in the Mac file system and can be searched using Spotlight.
Chat history is retained after participants close the chat window and until participants sign out. If you do not want to retain chat history after participants close the chat window, set the Disable_IM_History parameter to true. This parameter is available to all clients except IM-only users.
Quality of Service Configuration
Set DSCP Values
Set Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) values in RTP media packet headers to prioritize Cisco Jabber traffic as it traverses the network.
Port Ranges on Cisco Unified Communications Manager
You define the port range that the client uses on the SIP profile in Cisco Unified Communications Manager. The client then uses this port range to send RTP traffic across the network.
Port Ranges on Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Cisco Unified Communications Manager lets you define one port range for the client. The client divides this port range equally and uses the lower half for audio calls and the upper half for video calls. For example, you define a port range of 1000 to 3000 in Cisco Unified Communications Manager. The client uses a port range of 1000 to 2000 for audio calls and a port range of 2000 to 3000 for video calls.
You set port ranges on the SIP Profile Configuration window for the Cisco Jabber for iPhone SIP profile on Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
You set port ranges on the SIP Profile Configuration window for the Cisco Jabber for Android SIP profile on Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
To access the SIP Profile Configuration window, select .
The Start Media Port field defines the lowest port available to the client. The Stop Media Port field defines the highest port available. See the SIP Profile Configuration topic in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager documentation for more information.
Define a Port Range on the SIP Profile
The client uses the port range to send RTP traffic across the network. The client divides the port range equally and uses the lower half for audio calls and the upper half for video calls. As a result of splitting the port range for audio media and video media, the client creates identifiable media streams. You can then classify and prioritize those media streams by setting DSCP values in the IP packet headers.
How the Client Uses Port Ranges
As a result of splitting the port range for audio media and video media, the client creates identifiable media streams. You can then classify and prioritize those media streams by setting DSCP values in the IP packet headers.
Options for Setting DSCP Values
The following table describes the options for setting DSCP values:
| Method for Setting DSCP Values | Microsoft Windows 7 |
|---|---|
| Set DSCP values with Microsoft Group Policy | Yes |
| Set DSCP values on network switches and routers | Yes |
| Set DSCP values on Cisco Unified Communications Manager | No |
- Set DSCP Values on Cisco Unified Communications Manager
- Set DSCP Values with Group Policy
- Set DSCP Values on the Client
- Set DSCP Values on the Network
Set DSCP Values on Cisco Unified Communications Manager
You can set DSCP values for audio media and video media on Cisco Unified Communications Manager. Cisco Jabber can then retrieve the DSCP values from the device configuration and apply them directly to the IP headers of RTP media packets.
For later operating systems such as Microsoft Windows 7, Microsoft implements a security feature that prevents applications from setting DSCP values on IP packet headers. For this reason, you should use an alternate method for marking DSCP values, such as Microsoft Group Policy.
For more information on configuring flexible DSCP values, refer to Configure Flexible DSCP Marking and Video Promotion Service Parameters
Set DSCP Values with Group Policy
If you deploy Cisco Jabber for Windows on a later operating system such as Microsoft Windows 7, you can use Microsoft Group Policy to apply DSCP values.
Complete the steps in the following Microsoft support article to create a group policy: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc771283%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
Attributes |
Audio Policy |
Video Policy |
Signaling Policy |
|---|---|---|---|
Application name |
CiscoJabber.exe |
CiscoJabber.exe |
CiscoJabber.exe |
Protocol |
UDP |
UDP |
TCP |
Port number or range |
Corresponding port number or range from the SIP profile on Cisco Unified Communications Manager. |
Corresponding port number or range from the SIP profile on Cisco Unified Communications Manager. |
5060 for SIP 5061 for secure SIP |
DSCP value |
46 |
34 |
24 |
Set DSCP Values on the Client
For some configurations there is an option to enable differentiated services for calls in the Cisco Jabber for Mac client.
-
You can hear or see other parties, but you cannot be heard or seen
-
You are experiencing unexpected Wi-Fi disconnection issues
Disabling differentiated service for calls may degrade voice and video quality.
Set DSCP Values on the Network
You can configure switches and routers to mark DSCP values in the IP headers of RTP media.
Media Streams — Because the client uses different port ranges for audio streams and video streams, you can differentiate audio media and video media based on those port range. Using the default port ranges in the SIP profile, you should mark media packets as follows: Signaling Streams — You can identify signaling between the client and servers based on the various ports required for SIP, CTI QBE, and XMPP. For example, SIP signaling between Cisco Jabber and Cisco Unified Communications Manager occurs through port 5060.
You should mark signaling packets as AF31.
Protocol Handlers
-
XMPP:
Starts an instant message and opens a chat window in Cisco Jabber.
-
IM:
Starts an instant message and opens a chat window in Cisco Jabber.
-
TEL:
Starts an audio or video call with Cisco Jabber.

Note
TEL is registered by Apple native phone. It cannot be used to cross launch Cisco Jabber for iPhone and iPad.
- CISCOTEL:
Starts an audio or video call with Cisco Jabber.
- SIP:
Starts an audio or video call with Cisco Jabber.
Registry Entries for Protocol Handlers
Protocol Handlers on HTML Pages
You can add protocol handlers on HTML pages as part of the href attribute. When users click the hyperlinks that your HTML pages expose, the client performs the appropriate action for the protocol.
TEL and IM Protocol Handlers
Example of the TEL: and IM: protocol handlers on an HTML page:
<html>
<body>
<a href="TEL:1234">Call 1234</a><br/>
<a href="IM:msmith@domain">Send an instant message to Mary Smith</a>
</body>
</html>
In the preceding example, when users click the hyperlink to call 1234, the client starts an audio call to that phone number. When users click the hyperlink to send an instant message to Mary Smith, the client opens a chat window with Mary.
CISCOTEL and SIP Protocol Handlers
Example of the CISCOTEL and SIP protocol handlers on an HTML page:
<html>
<body>
<a href="CISCOTEL:1234">Call 1234</a><br/>
<a href="SIP:msmith@domain">Call Mary</a><br/>
<a href="CISCOTELCONF:msmith@domain;amckenzi@domain">Weekly conference call</a>
</body>
</html>
In the preceding example, when users click the Call 1234 or Call Mary hyperlinks, the client starts an audio call to that phone number.
XMPP Protocol Handlers
Example of a group chat using the XMPP: protocol handler on an HTML page:
<html>
<body>
<a href="XMPP:msmith@domain;amckenzi@domain">Create a group chat with Mary Smith and Adam McKenzie</a>
</body>
</html>
In the preceding example, when users click the hyperlink to create a group chat with Mary Smith and Adam McKenzie, the client opens a group chat window with Mary and Adam.
Add Subject Lines and Body Text
You can add subject lines and body text to any of the protocol handlers so that when users click on the hyperlink to create a person-to-person or group chat, the client opens a chat window with pre-populated subject line and body text.
xmpp:msmith@domain?message;subject=I.T.%20Desk
im:user_a@domain.com;user_b@domain.com;user_c@domain.com?message;subject=I.T%20Desk;body=Jabber%2010.5%20Query
Audio and Video Performance Reference
The following data is based on testing in a lab environment. This data is intended to provide an idea of what you can expect in terms of bandwidth usage. The content in this topic is not intended to be exhaustive or to reflect all media scenarios that might affect bandwidth usage.
- Audio Bit Rates for Cisco Jabber Desktop Clients
- Audio Bit Rates for Cisco Jabber Mobile Clients
- Video Bit Rates for Cisco Jabber Desktop Clients
- Video Bit Rates for Cisco Jabber for Android
- Video Bit Rates for Cisco Jabber for iPhone and iPad
- Presentation Video Bit Rates
- Maximum Negotiated Bit Rate
- Bandwidth Performance Expectations for Cisco Jabber for Windows and Cisco Jabber for Mac
- Bandwidth Performance Expectations for Cisco Jabber for Android
- Bandwidth Performance Expectations for Cisco Jabber for iPhone and iPad
- Video Rate Adaptation
Audio Bit Rates for Cisco Jabber Desktop Clients
The following audio bit rates apply to Cisco Jabber for Windows and Cisco Jabber for Mac.
Codec |
RTP (kbits/second) |
Actual bitrate (kbits/second) |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
g.722.1 |
24/32 |
54/62 |
High quality compressed |
g.711 |
64 |
80 |
Standard uncompressed |
g.729a |
8 |
38 |
Low quality compressed |
Audio Bit Rates for Cisco Jabber Mobile Clients
The following audio bit rates apply to Cisco Jabber for iPad and iPhone and Cisco Jabber for Android.
Codec |
Codec bit rate (kbits/second) |
Network Bandwidth Utilized (kbits/second) |
|---|---|---|
g.711 |
64 |
80 |
g.722.1 |
32 |
48 |
g.722.1 |
24 |
40 |
g.729a |
8 |
24 |
Video Bit Rates for Cisco Jabber Desktop Clients
The following video bit rates (with g.711 audio) apply to Cisco Jabber for Windows and Cisco Jabber for Mac. This table does not list all possible resolutions.
Resolution |
Pixels |
Measured bit rate (kbits per second) with g.711 audio |
|---|---|---|
w144p |
256 x 144 |
156 |
w288p This is the default size of the video rendering window for Cisco Jabber. |
512 x 288 |
320 |
w448p |
768 x 448 |
570 |
w576p |
1024 x 576 |
890 |
720p |
1280 x 720 |
1300 |
 Note | The measured bit rate is the actual bandwidth used (RTP payload + IP packet overhead). |
Video Bit Rates for Cisco Jabber for Android
The client captures and transmits video at 15 fps.
|
Resolution |
Pixels |
Bit Rate (kbits per second) with g.711 audio |
|---|---|---|
|
w144p |
256 x 144 |
235 |
w288p |
512 x 288 |
275 |
|
w360p |
640 x 360 |
330 |
w720p |
1080 x 720 |
768 |
w1080p |
1920 x 1080 |
768 |
Video Bit Rates for Cisco Jabber for iPhone and iPad
The client captures and transmits at 20 fps.
Resolution |
Pixels |
Bit rate (kbits/second) with g.711 audio |
|---|---|---|
w144p |
256 x 144 |
290 |
w288p |
512 x 288 |
340 |
w360p |
640 x 360 |
415 |
Presentation Video Bit Rates
Cisco Jabber captures at 8 fps and transmits at 2 to 8 fps.
The values in this table do not include audio.
Pixels |
Estimated wire bit rate at 2 fps (kbits per second) |
Estimated wire bit rate at 8 fps (kbits per second) |
|---|---|---|
720 x 480 |
41 |
164 |
704 x 576 |
47 |
188 |
1024 x 768 |
80 |
320 |
1280 x 720 |
91 |
364 |
1280 x 800 |
100 |
400 |
Maximum Negotiated Bit Rate
You specify the maximum payload bit rate in Cisco Unified Communications Manager in the Region Configuration window. This maximum payload bit rate does not include packet overhead, so the actual bit rate used is higher than the maximum payload bit rate you specify.
Audio |
Interactive video (Main video) |
|---|---|
Cisco Jabber uses the maximum audio bit rate |
Cisco Jabber allocates the remaining bit rate as follows: The maximum video call bit rate minus the audio bit rate. |
Bandwidth Performance Expectations for Cisco Jabber for Windows and Cisco Jabber for Mac
Upload speed |
Audio |
Audio + Interactive video (Main video) |
|---|---|---|
125 kbps under VPN |
At bandwidth threshold for g.711. Sufficient bandwidth for g.729a and g.722.1. |
Insufficient bandwidth for video. |
384 kbps under VPN |
Sufficient bandwidth for any audio codec. |
w288p (512 x 288) at 30 fps |
384 kbps in an enterprise network |
Sufficient bandwidth for any audio codec. |
w288p (512 x 288) at 30 fps |
1000 kbps |
Sufficient bandwidth for any audio codec. |
w576p (1024 x 576) at 30 fps |
2000 kbps |
Sufficient bandwidth for any audio codec. |
w720p30 (1280 x 720) at 30 fps |
Upload speed |
Audio |
Audio + Interactive video (Main video) |
Audio + Presentation video (Desktop sharing video) |
Audio + Interactive video + Presentation video |
|---|---|---|---|---|
125 kbps under VPN |
At bandwidth threshold for g.711. Sufficient bandwidth for g.729a and g.722.1 . |
Insufficient bandwidth for video. |
Insufficient bandwidth for video. |
Insufficient bandwidth for video. |
384 kbps under VPN |
Sufficient bandwidth for any audio codec. |
w288p (512 x 288) at 30 fps |
1280 x 800 at 2+ fps |
w144p (256 x 144) at 30 fps + 1280 x 720 at 2+ fps |
384 kbps in an enterprise network |
Sufficient bandwidth for any audio codec. |
w288p (512 x 288) at 30 fps |
1280 x 800 at 2+ fps |
w144p (256 x 144) at 30 fps + 1280 x 800 at 2+ fps |
1000 kbps |
Sufficient bandwidth for any audio codec. |
w576p (1024 x 576) at 30 fps |
1280 x 800 at 8 fps |
w288p (512 x 288) at 30 fps + 1280 x 800 at 8 fps |
2000 kbps |
Sufficient bandwidth for any audio codec. |
w720p30 (1280 x 720) at 30 fps |
1280 x 800 at 8 fps |
w288p (1024 x 576) at 30 fps + 1280 x 800 at 8 fps |
Note that VPN increases the size of the payload, which increases the bandwidth consumption.
Bandwidth Performance Expectations for Cisco Jabber for Android
Note that VPN increases the size of the payload, which increases the bandwidth consumption.
Upload speed |
Audio |
Audio + Interactive Video (Main Video) |
|---|---|---|
| 125 kbps under VPN |
At bandwidth threshold for g.711. Insufficient bandwidth for video. Sufficient bandwidth for g.729a and g.722.1. |
Insufficient bandwidth for video. |
| 256 kbps |
Sufficient bandwidth for any audio codec. |
Transmission rate (Tx) — 256 x 144 at 15 fps Reception rate (Rx) — 256 x 144 at 30 fps |
| 384 kbps under VPN |
Sufficient bandwidth for any audio codec. |
Tx — 640 x 360 at 15 fps Rx — 640 x 360 at 30 fps |
| 384 kbps in an enterprise network |
Sufficient bandwidth for any audio codec. |
Tx — 640 x 360 at 15 fps Rx — 640 x 360 at 30 fps |
 Note | Due to device limitations, the Samsung Galaxy SII and Samsung Galaxy SIII devices cannot achieve the maximum resolution listed in this table. |
Bandwidth Performance Expectations for Cisco Jabber for iPhone and iPad
The client separates the bit rate for audio and then divides the remaining bandwidth equally between interactive video and presentation video. The following table provides information to help you understand what performance you should be able to achieve per bandwidth.
Note that VPN increases the size of the payload, which increases the bandwidth consumption.
Upload speed |
Audio |
Audio + Interactive Video (Main Video) |
|---|---|---|
|
125 kbps under VPN |
At bandwidth threshold for g.711. Insufficient bandwidth for video. Sufficient bandwidth for g.729a and g.722.1. |
Insufficient bandwidth for video. |
|
290 kbps |
Sufficient bandwidth for any audio codec. |
256 x144 at 20 fps |
|
415 kbps |
Sufficient bandwidth for any audio codec. |
640 x 360 at 20 fps |
Video Rate Adaptation
Cisco Jabber uses video rate adaptation to negotiate optimum video quality. Video rate adaptation dynamically increases or decreases video bit rate throughput to handle real-time variations on available IP path bandwidth.
Cisco Jabber users should expect video calls to begin at lower resolution and scale upwards to higher resolution over a short period of time. Cisco Jabber saves history so that subsequent video calls should begin at the optimal resolution.
DNS Configuration
How the Client Uses DNS
- How the Client Finds a Name Server
- How the Client Gets a Services Domain
- How the Client Discovers Available Services
How the Client Finds a Name Server
When the client’s host computer or device gets a network connection, the host computer or device also gets the address of a DNS name server from the DHCP settings. Depending on the network connection, that name server might be internal or external to the corporate network.
Cisco Jabber queries the name server that the host computer or device gets from the DHCP settings.
How the Client Gets a Services Domain
The services domain is discovered by the Cisco Jabber client in different ways.
-
User enters an address in the format username@example.com in the client user interface.
-
User clicks on a configuration URL that includes the service domain. This option is only available in the following versions of the client: -
The client uses installation switches in bootstrap files. This option is only available in the following version of the client:
-
The client uses the VoiceServicesDomain parameter in the configuration file. This option is available in clients that support the jabber-config.xml file.
-
User clicks on a configuration URL that includes the VoiceServicesDomain. This option is available in the following clients:
-
The client uses the Voice_Services_Domain installation switch in the bootstrap files. This option is only available in the following version of the client:
After Cisco Jabber gets the services domain, it queries the name server that is configured to the client computer or device.
How the Client Discovers Available Services
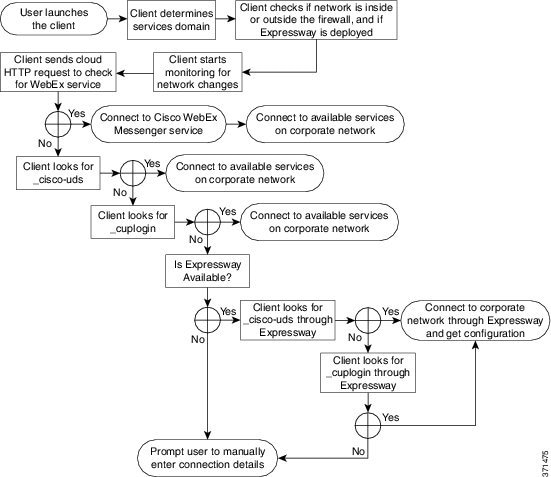
-
Checks if the network is inside or outside the firewall and if Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access is deployed. The client sends a query to the name server to get DNS Service (SRV) records.
-
Starts monitoring for network changes.
When Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access is deployed, the client monitors the network to ensure that it can reconnect if the network changes from inside or outside the firewall.
-
Issues an HTTP query to a CAS URL for the Cisco WebEx Messenger service.
This query enables the client to determine if the domain is a valid Cisco WebEx domain.
-
Queries the name server to get DNS Service (SRV) records, unless the records exist in the cache from a previous query.
This query enables the client to do the following:
- Client Issues an HTTP Query
- Client Queries the Name Server
- Client Connects to Internal Services
- Client Connects through Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access
Client Issues an HTTP Query
In addition to querying the name server for SRV records to locate available services, Cisco Jabber sends an HTTP query to the CAS URL for the Cisco WebEx Messenger service. This request enables the client to determine cloud-based deployments and authenticate users to the Cisco WebEx Messenger service.
When the client gets a services domain from the user, it appends that domain to the following HTTP query:
http://loginp.webexconnect.com/cas/FederatedSSO?org=
For example, if the client gets example.com as the services domain from the user, it issues the following query:
http://loginp.webexconnect.com/cas/FederatedSSO?org=example.com
That query returns an XML response that the client uses to determine if the services domain is a valid Cisco WebEx domain.
If the client determines the services domain is a valid Cisco WebEx domain, it prompts users to enter their Cisco WebEx credentials. The client then authenticates to the Cisco WebEx Messenger service and retrieves the configuration and UC services that are configured in Cisco WebEx Org Admin.
If the client determines the services domain is not a valid Cisco WebEx domain, it uses the results of the query to the name server to locate available services.
When the client sends the HTTP request to the CAS URL, it uses configured system proxies.
For the desktop clients, to configure a proxy in the LAN Settings of Internet Explorer, you must specify a .pac file URL as the automatic configuration script or specify an explicit proxy address under Proxy server.
- Proxy Authentication is not supported.
- Wildcards in the bypass list are not supported. Use example.com instead of *.example.com, for example.
- Web Proxy Auto-Discovery (WPAD) protocol lookup is only supported for iOS devices.
-
Cisco Jabber supports proxy for HTTP request using HTTP CONNECT, but does not support proxy when using HTTPS CONNECT.
Client Queries the Name Server
When the client queries a name server, it sends separate, simultaneous requests to the name server for SRV records.
-
_cisco-uds—The client detects it is inside the corporate network and connects to Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
-
_cuplogin—The client detects it is inside the corporate network and connects to Cisco Unified Presence.
-
_collab-edge—The client attempts to connect to the internal network through Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access and discover services
-
None of the SRV records—The client prompts users to manually enter setup and sign-in details.
Client Connects to Internal Services
The following figure shows how the client connects to internal services:
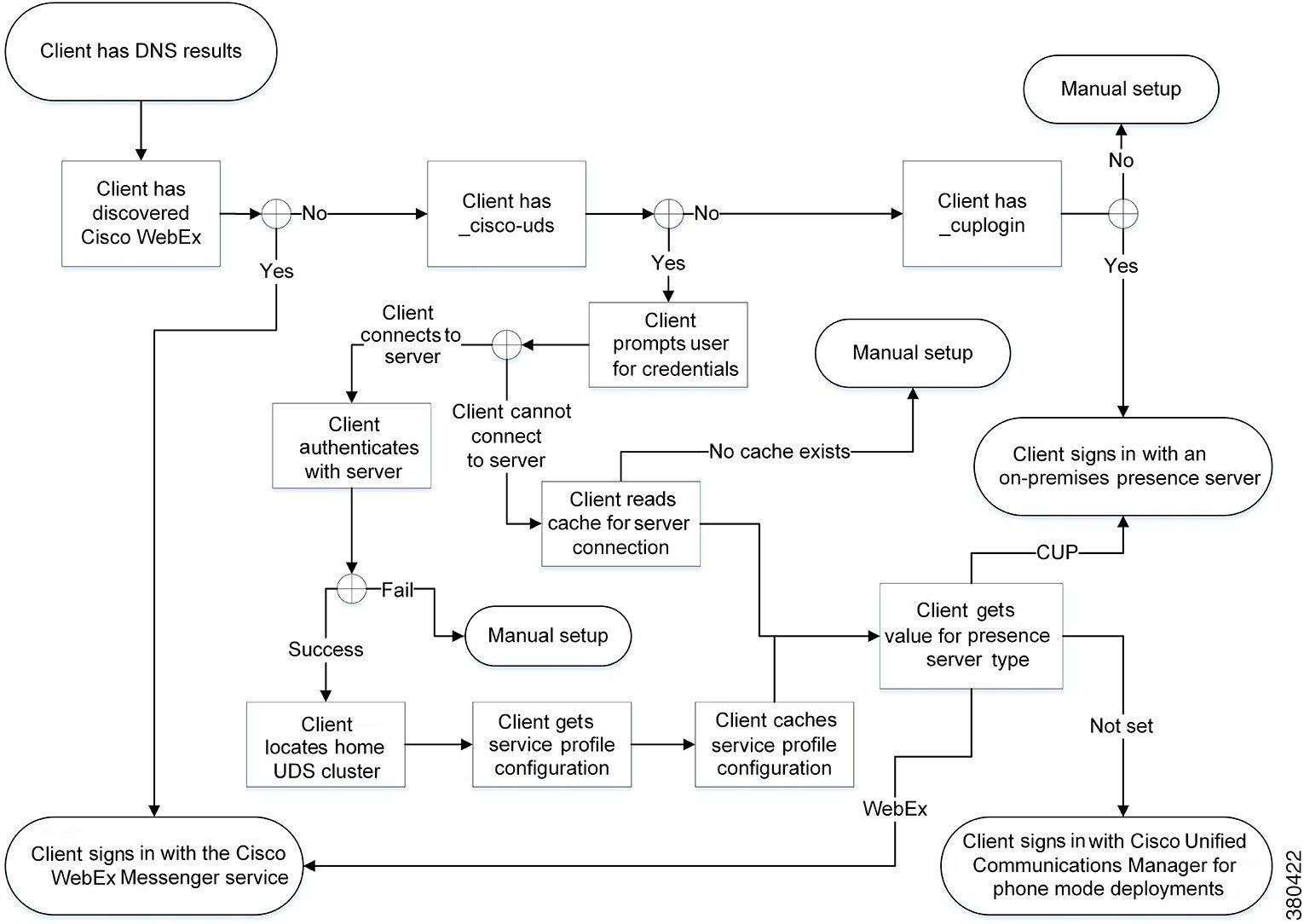
When connecting to internal services, the goals are to determine the authenticator, sign users in, and connect to available services.
-
If the client discovers that the CAS URL lookup indicates a Cisco WebEx user, the client does the following:
-
If the client discovers a _cisco-uds SRV record, the client does the following:
-
Prompts the user for credentials to authenticate with Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
-
Locates the user's home cluster.
Locating the home cluster enables the client to automatically get the user's device list and register with Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
Important: In an environment with multiple Cisco Unified Communications Manager clusters, you must configure the Intercluster Lookup Service (ILS). ILS enables the client to find the user's home cluster.
See the appropriate version of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Features and Services Guide to learn how to configure ILS.
-
Retrieves the service profile.
The service profile provides the client with the authenticator as well as client and UC service configuration.
The client determines the authenticator from the value of the Product type field in the IM and presence profile, as follows: -
Cisco Unified Communications Manager —Cisco Unified Presence or Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service is the authenticator.
-
WebEx (IM and Presence)—Cisco WebEx Messenger service is the authenticator. 
Note
As of this release, the client issues an HTTP query in addition to the query for SRV records. The HTTP query allows the client to determine if it should authenticate to the Cisco WebEx Messenger service.
As a result of the HTTP query, the client connects to the Cisco WebEx Messenger service in cloud-based deployments. Setting the value of the Product type field to WebEx does not effect if the client has already discovered the WebEx service using a CAS lookup.
-
Not set—If the service profile does not contain an IM and Presence Service configuration, the authenticator is Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
-
-
Sign in to the authenticator.
After the client signs in, it can determine the product mode.
-
-
If the client discovers a _cuplogin SRV record, the client does the following:
Client Connects through Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access
If the name server returns the _collab-edge SRV record, the client attempts to connect to internal servers through Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access.
The following figure shows how the client connects to internal services when the client is connected to the network through Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access:
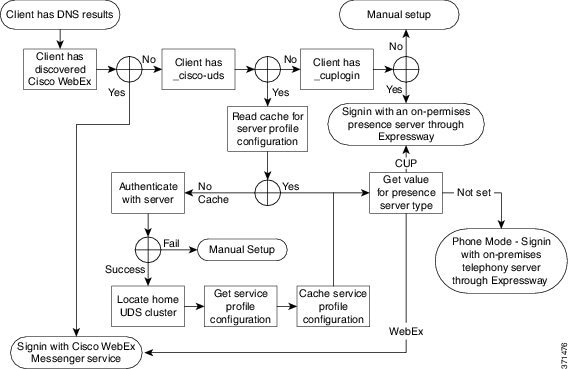
 Note | The Cisco Expressway-C server looks up the internal SRV records and provides the records to the Cisco Expressway-E server. |
After the client gets the internal SRV records, which must include the _cisco-udsSRV record, it retrieves service profiles from Cisco Unified Communications Manager. The service profiles then provide the client with the user's home cluster, the primary source of authentication, and configuration.
Domain Name System Designs
Separate Domain Design
The following figure shows a separate domain design:
An example of a separate domain design is one where your organization registers the following external domain with an Internet name authority: example.com.
-
The internal name server has zones that contain resource records for internal domains. The internal name server is authoritative for the internal domains.
-
The internal name server forwards requests to the external name server when a DNS client queries for external domains.
-
The external name server has a zone that contains resource records for your organization’s external domain. The external name server is authoritative for that domain.
-
The external name server can forward requests to other external name servers. However, the external name server cannot forward requests to the internal name server.
Same Domain Design
An example of a same domain design is one where your organization registers example.com as an external domain with an Internet name authority. Your organization also uses example.com as the name of the internal domain.
Single Domain, Split-Brain
The following figure shows a single domain with a split-brain domain design.
Two DNS zones represent the single domain; one DNS zone in the internal name server and one DNS zone in the external name server.
Single Domain, Not Split-Brain
The following figure shows a single domain that does not have a split-brain domain design.
In the single domain, not split-brain design, internal and external hosts are served by one set of name servers and can access the same DNS information.
This design is not common because it exposes more information about the internal network to potential attackers.
Deploy SRV Records
The client queries name servers for records in the services domain. The services domain is determined as described in How the Client Discovers Available Services.
You must deploy SRV records in each DNS zone for those service domains if your organization has multiple subsets of users who use different service domains.
Deploy SRV Records in a Separate Domain Structure
In a separate name design there are two domains, an internal domain and an external domain. The client queries for SRV records in the services domain. The internal name server must serve records for the services domain. However in a separate name design, a zone for the services domain might not exist on the internal name server.
Use an Internal Zone for a Services Domain
If you do not already have a zone for the services domain on the internal name server, you can create one. This method makes the internal name server authoritative for the services domain. Because it is authoritative, the internal name server does not forward queries to any other name server.
This method changes the forwarding relationship for the entire domain and has the potential to disrupt your internal DNS structure. If you cannot create an internal zone for the services domain, you can create a pinpoint subdomain zone on the internal name server.
Use a Pinpoint Subdomain Zone
Support of the fixed pinpoint subdomain has been replaced in later versions of Cisco Jabber by the support of the new VoiceServicesDomain configuration key.
Set VoiceServicesDomain=cisco-uc.example.com
Create a zone on both the internal and external DNS server for cisco-uc.example.com.
You can create a pinpoint subdomain and zone on the internal name server. The pinpoint zone provides a dedicated location to serve specific records for the pinpoint subdomain. As a result, the internal name server becomes authoritative for that subdomain. The internal name server does not become authoritative for the parent domain, so the behavior of queries for records in the parent domain does not change.
The following diagram illustrates configuration created by the procedure.

In this configuration, the following SRV records are deployed with the internal DNS name server:
When the client queries the name server for SRV records, it issues additional queries if the name server does not return _cisco-uds or _cuplogin.
The additional queries check for the cisco-internal.domain-name pinpoint subdomain zone.
- _cisco-uds._tcp.example.com
- _cuplogin._tcp.example.com
- _collab-edge._tls.example.com
- _cisco-uds._tcp.cisco-internal.example.com
- _cuplogin._tcp.cisco-internal.example.com
SRV Records
Understand which SRV records you should deploy and review examples of each SRV record.
External Records
Service Record |
Description |
||
|---|---|---|---|
_collab-edge |
Provides the location of the Cisco Expressway-E server.
|
_collab-edge._tls.example.com SRV service location:
priority = 3
weight = 7
port = 8443
svr hostname = xpre1.example.com
_collab-edge._tls.example.com SRV service location:
priority = 4
weight = 8
port = 8443
svr hostname = xpre2.example.com
_collab-edge._tls.example.com SRV service location:
priority = 5
weight = 0
port = 8443
svr hostname = xpre3.example.com
Internal Records
Service Record |
Description |
|---|---|
_cisco-uds |
Provides the location of Cisco Unified Communications Manager release 9 and later. In an environment with multiple Cisco Unified Communications Manager clusters, you must configure the Intercluster Lookup Service (ILS). ILS enables the client to find the user's home cluster and discover services. |
_cuplogin |
Provides the location of Cisco Unified Presence. |
 Note | You should use the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) as the hostname in the SRV record. |
_cisco-uds._tcp.example.com SRV service location:
priority = 6
weight = 30
port = 8443
svr hostname = cucm3.example.com
_cisco-uds._tcp.example.com SRV service location:
priority = 2
weight = 20
port = 8443
svr hostname = cucm2.example.com
_cisco-uds._tcp.example.com SRV service location:
priority = 1
weight = 5
port = 8443
svr hostname = cucm1.example.com
_cuplogin._tcp.example.com SRV service location:
priority = 8
weight = 50
port = 8443
svr hostname = cup3.example.com
_cuplogin._tcp.example.com SRV service location:
priority = 5
weight = 100
port = 8443
svr hostname = cup1.example.com
_cuplogin._tcp.example.com SRV service location:
priority = 7
weight = 4
port = 8443
svr hostname = cup2.example.com
 Feedback
Feedback