Planning Considerations
Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access Deployments
Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access for Cisco Unified Communications Manager allows users to access their collaboration tools from outside the corporate firewall without a VPN client. Using Cisco collaboration gateways, the client can connect securely to your corporate network from remote locations such as public Wi-Fi networks or mobile data networks.
-
Set up servers to support Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access using Cisco Expressway-E and Cisco Expressway-C.*
-
See the following documents to set up the Cisco Expressway servers: -
Cisco Expressway Basic Configuration Deployment Guide
-
Mobile and Remote Access via Cisco Expressway Deployment Guide
* If you currently deploy a Cisco TelePresence Video Communications Server (VCS) environment, you can set up Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access. For more information, see Cisco VCS Basic Configuration (Control with Expressway) Deployment Guide and Mobile and Remote Access via Cisco VCS Deployment Guide.
-
-
Add any relevant servers to the whitelist for your Cisco Expressway-C server to ensure that the client can access services that are located inside the corporate network.
To add a server to the Cisco Expressway-C whitelist, use the HTTP server allow setting.
This list can include the servers on which you host voicemail or contact photos.
-
-
Configure an external DNS server that contains the
_collab-edgeDNS SRV record to allow the client to locate the Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access server. -
If you deploy a hybrid cloud-based architecture where the domain of the IM and presence server differs from the domain of the voice server, ensure that you configure the Voice Services Domain.
The Voice Services Domain allows the client to locate the DNS server that contains the
_collab-edgerecord.You can configure the voice services domain using one of the following methods: -
Client configuration file (all Cisco Jabber clients)
-
Configuration URL (all Cisco Jabber clients except Cisco Jabber for Windows)
-
Installer options (Cisco Jabber for Windows only)
-
 Important |
|

Supported Services
The following table summarizes the services and functionality that are supported when the client uses Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access to remotely connect to Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
| Service | Supported | Unsupported | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Directory | |||
| UDS directory search |
X |
||
| LDAP directory search |
X |
||
| Directory photo resolution |
X * Using HTTP white list on Cisco Expressway-C |
||
|
Intradomain federation |
X * Contact search support depends of the format of your contact IDs. For more information, see the note below. |
||
|
Interdomain federation |
X |
||
| Instant Messaging and Presence | |||
| On-premises |
X |
||
| Cloud |
X |
||
| Chat |
X |
||
| Group chat |
X |
||
| High Availability: On-premises deployments |
X |
||
| File transfer: On-premises deployments |
X |
||
| File transfer: Cloud deployments |
X Desktop clients, some file transfer features are supported for mobile clients. |
||
| Video desktop share - BFCP |
X (Cisco Jabber for mobile clients only support BFCP receive.) |
||
| Audio and Video | |||
| Audio and video calls |
X * Cisco Unified Communications Manager 9.1(2) and later |
||
| Deskphone control mode (CTI) |
X |
||
|
Remote Desktop Control |
X |
||
| Extend and connect |
X |
||
| Dial via Office - Reverse |
X |
||
| Session persistency |
X |
||
| Early media |
X |
||
| Self Care Portal access |
X |
||
| Voicemail | |||
| Visual voicemail |
X * Using HTTP white list on Cisco Expressway-C |
||
| Cisco WebEx Meetings | |||
| On-premises |
X |
||
| Cloud |
X |
||
| Cisco WebEx desktop share |
X |
||
| Installation | |||
| Installer update |
X * Using HTTP white list on Cisco Expressway-C |
||
| Customization | |||
| Custom HTML tabs |
X * Using HTTP white list on Cisco Expressway-C (Desktop clients only) |
||
| Security | |||
| End-to-end encryption |
X |
||
| CAPF enrollment |
X |
||
| Troubleshooting | |||
| Problem report generation |
X |
||
| Problem report upload |
X |
||
| High Availability (failover) | |||
| Audio and Video services |
X |
||
| Voicemail services |
X |
||
| IM and Presence services |
X |
||
Directory
-
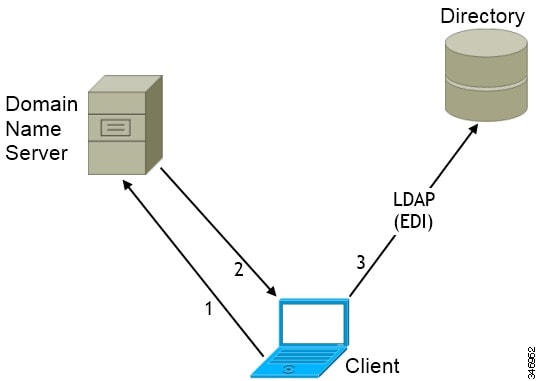
LDAP contact resolution —The client cannot use LDAP for contact resolution when outside of the corporate firewall. Instead, the client must use UDS for contact resolution.
When users are inside the corporate firewall, the client can use either UDS or LDAP for contact resolution. If you deploy LDAP within the corporate firewall, Cisco recommends that you synchronize your LDAP directory server with Cisco Unified Communications Manager to allow the client to connect with UDS when users are outside the corporate firewall.
-
Directory photo resolution — To ensure that the client can download contact photos, you must add the server on which you host contact photos to the white list of your Cisco Expressway-C server. To add a server to Cisco Expressway-C white list, use the HTTP server allow setting. For more information, see the relevant Cisco Expressway documentation.
-
Intradomain federation — When you deploy intradomain federation and the client connects with Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access from outside the firewall, contact search is supported only when the contact ID uses one of the following formats: -
sAMAccountName@domain
-
UserPrincipleName (UPN)@domain
-
EmailAddress@domain
-
employeeNumber@domain
-
telephoneNumber@domain
-
-
Interdomain federation using XMPP — The client does not support interdomain federation with XMPP standard-based environments such as Google Talk when it connects with Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access from outside the firewall.
Instant Messaging and Presence
When the client connects to services using Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access, it supports instant messaging and presence with the following limitations.
File transfer — The client does not support file transfer including screen capture with Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service deployments. File Transfer is supported only with Cisco WebEx cloud deployments with desktop clients. Managed File Transfer is supported with Cisco Unified Communication IM and Presence when Cisco Jabber is connected to Cisco Unified services using Expressway. Peer-to-Peer files transfer is not supported.
Audio and Video Calling
-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager — Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access supports video and voice calling with Cisco Unified Communications Manager Version 9.1.2 and later. Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access is not supported with Cisco Unified Communications Manager Version 8.x.
-
Deskphone control mode (CTI) — The client does not support deskphone control mode (CTI), including extension mobility.
-
Extend and connect — The client cannot be used to: -
Make and receive calls on a Cisco IP Phone in the office.
-
Perform mid-call control such as hold and resume on a home phone, hotel phone, or Cisco IP Phone in the office.
-
-
Dial via Office - Reverse — The client cannot make Dial via Office - Reverse calls from outside the firewall.
-
Session Persistency — The client cannot recover from audio and video calls drop when a network transition occurs. For example, if a users start a Cisco Jabber call inside their office and then they walk outside their building and lose Wi-Fi connectivity, the call drops as the client switches to use Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access.
-
Early Media — Early Media allows the client to exchange data between endpoints before a connection is established. For example, if a user makes a call to a party that is not part of the same organization, and the other party declines or does not answer the call, Early Media ensures that the user hears the busy tone or is sent to voicemail.
When using Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access, the user does not hear a busy tone if the other party declines or does not answer the call. Instead, the user hears approximately one minute of silence before the call is terminated.
-
Self care portal access — Users cannot access the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Self Care Portal when outside the firewall. The Cisco Unified Communications Manager user page cannot be accessed externally.
Cisco Expressway-E proxies all communications between the client and unified communications services inside the firewall. However, the Cisco Expressway-E does not proxy services that are accessed from a browser that is not part of the Cisco Jabber application.
Voicemail
Voicemail service is supported when the client connects to services using Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access.
 Note |
To ensure that the client can access voicemail services, you must add the voicemail server to the white list of your Cisco Expressway-C server. To add a server to Cisco Expressway-C white list, use the HTTP server allow setting. For more information, see the relevant Cisco Expressway documentation. |
Cisco WebEx Meetings
When the client connects to services using Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access, it supports only cloud-based conferencing using Cisco WebEx Meetings Center.
The client cannot access the Cisco WebEx Meetings Server or join or start on-premises Cisco WebEx meetings.
Installation
When the client connects to services using Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access, it supports installer updates.
 Note |
To ensure that the client can download installer updates, you must add the server that hosts the installer updates to the white list of your Cisco Expressway-C server. To add a server to the Cisco Expressway-C white list, use the HTTP server allow setting. For more information, see the relevant Cisco Expressway documentation. |
Customization
When the client connects to services using Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access, it supports custom HTML tab configuration for desktop clients.
 Note |
To ensure that the client can download the custom HTML tab configuration, you must add the server that hosts the custom HTML tab configuration to the white list of your Cisco Expressway-C server. To add a server to the Cisco Expressway-C whitelist, use the HTTP server allow setting. For more information, see the relevant Cisco Expressway documentation. |
Security
-
Initial CAPF enrollment — Certificate Authority Proxy Function (CAPF) enrollment is a security service that runs on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Publisher that issues certificates to Cisco Jabber (or other clients). To successfully enrol for CAPF, the client must connect from inside the firewall or using VPN.
-
End-to-end encryption — When users connect through Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access and participate in a call: -
Media is encrypted on the call path between the Cisco Expressway-C and devices that are registered to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager using Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access.
-
Media is not encrypted on the call path between the Cisco Expressway-C and devices that are registered locally to Cisco Unified Communications Manager, if either Cisco Jabber or an internal device is not configured with Encrypted security mode.
-
Media is encrypted on the call path between the Expressway-C and devices that are registered locally to Cisco Unified Communnication Manager, if both Cisco Jabber and internal device are configured with Encypted security mode.
-
Troubleshooting
Problem report upload — When the desktop client connects to services using Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access, it cannot send problem reports because the client uploads problem reports over HTTPS to a specified internal server.
To work around this issue, users can save the report locally and send the report in another manner.
High Availability (failover)
High Availability means that if the client fails to connect to the primary server, it fails over to a secondary server with little or no interruption to the service. In relation to high availability being supported on the Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access, high availability refers to the server for the specific service failing over to a secondary server (such as Instant Messaging and Presence), and not the Cisco Expressway-E server itself failing over.
Some services are available on the Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access that are not supported for high availability. This means that if users are connected to the client from outside the corporate network and the instant messaging and presence server fails over, the services will continue to work as normal. However, if the audio and video server or voicemail server fails over, those services will not work as the relevant servers do not support high availability.
Deployment in a Virtual Environment
You can deploy Cisco Jabber for Windows in virtual environments using the following software:
-
Citrix XenDesktop 7.5
-
Citrix XenDesktop 7.1
-
Citrix XenDesktop 7.0
-
Citrix XenDesktop 5.6
-
Citrix XenApp 7.5 Enterprise Edition for Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard Service Pack 1 64 bit, published desktop
- Citrix XenApp 6.5 Feature Pack 2 Enterprise Edition for Windows Server 2008 Service Pack 2 64 bit, published desktop
-
Citrix XenApp 6.5 Feature Pack 1 Enterprise Edition for Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard Service Pack 1 64 bit, published desktop
-
Citrix XenApp 6.5 Enterprise Edition for Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard Service Pack 1 64 bit, published desktop
-
VMware Horizon View 6.0
- VMware Horizon View 5.3
- VMware Horizon View 5.2
Supported Features
- Instant messaging and presence with other Cisco Jabber clients
- Desk phone control
- Voicemail
- Presence integration with Microsoft Outlook 2007, 2010 and 2013
 Note |
Cisco Jabber credentials caching is not supported when using Cisco Jabber in non-persistent virtual deployment infrastructure (VDI) mode. |
Softphones in Virtual Environments
Use Cisco Virtualization Experience Media Engine (VXME) for softphone calls in a virtual environment.
Roaming Profiles
The client stores user data such as user call history and configuration store cache on the local machine for use when the user next signs in. In virtual environments, users do not always access the same virtual desktop. To guarantee a consistent user experience, these files need to be accessible every time the client is launched.
To preserve the user's personal settings in a virtual environment when roaming between hosted virtual desktops, use dedicated profile management solutions from Citrix and VMware.
Citrix Profile Management is a profile solution for Citrix environments. In deployments with random hosted virtual desktop assignments, Citrix Profile Management synchronizes each user's entire profile between the system it is installed on and the user store.
VMware View Persona Management preserves user profiles and dynamically synchronizes them with a remote profile repository. VMware View Persona Management does not require the configuration of Windows roaming profiles and can bypass Windows Active Directory in the management of View user profiles. Persona Management enhances the functionality of existing roaming profiles.
You can specify which files and folders to omit from synchronization by adding them to an exclusion list. To include a subfolder within an excluded folder, add the subfolder to an inclusion list.
- AppData\Local\Cisco
- AppData\Local\JabberWerxCPP
- AppData\Roaming\Cisco
- AppData\Roaming\JabberWerxCPP
Client Information Storage
The client stores user information in the following locations:
C:\Users\username\AppData\Local\Cisco\Unified Communications\Jabber\CSF| Folder Name | Description |
| Contacts | Contact cache files |
| History | Call history and chat history |
| Photo cache | Caches the directory photos locally |
| Folder Name | Description |
| Config | Maintains users' Jabber configuration files and stores configuration store cache |
| Credentials | Stores encrypted user name and password file |
How the Client Connects to Services
-
Source of authentication that enables users to sign in to the client.
-
Location of services.
- URL Configuration
-
Users are sent an email from their administrators. The email contains a URL that will configure the domain needed for service discovery.
- Service Discovery
-
The client automatically locates and connects to services.
- Manual Connection Settings
-
Users manually enter connection settings in the client user interface.
Recommended Connection Methods
The method that you should use to provide the client with the information it needs to connect to services depends on your deployment type, server versions, and product modes. The following tables highlight various deployment methods and how to provide the client with the necessary information.
|
Product Mode |
Server Versions |
Discovery Method |
Non DNS SRV Record Method |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Full UC (default mode) |
Release 9.1.2 and later:
|
A DNS SRV request against _cisco-uds .<domain> |
Use the following installer switches and values:
|
|
Full UC (default mode) |
Release 8.x:
|
A DNS SRV request against _cuplogin.<domain> |
Use the following installer switches and values:
|
|
IM Only (default mode) |
|
A DNS SRV request against _cisco-uds .<domain> |
Use the following installer switches and values:
|
|
IM Only (default mode) |
|
A DNS SRV request against _cuplogin .<domain> |
Use the following installer switches and values:
|
|
Phone Mode |
|
A DNS SRV request against _cisco-uds.<domain> |
Use the following installer switches and values:
High availability is not supported using this method of deployment. |
|
Phone Mode |
|
Manual connection settings |
Use the following installer switches and values:
High availability is not supported using this method of deployment. |
Cisco Unified
Communications Manager release 9.x and earlier—If you enable Cisco Extension
Mobility, the
Cisco
Extension Mobility service must be activated on the Cisco Unified
Communications Manager nodes that are used for CCMCIP. For information about
Cisco Extension Mobility, see the
Feature and
Services guide for your Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
 Note |
Cisco Jabber release 9.6 and later can still discover full Unified Communications and IM-only services using the _cuplogin DNS SRV request but a _cisco-uds request will take precedence if it is present. |
Use the SERVICES_DOMAIN installer switch to specify the value of the domain where DNS records reside if you want users to bypass the email screen during the first login of a fresh installation.
 Note |
The services domain is read from a cached configuration if you are upgrading from Cisco Jabber for Windows 9.2. |
|
Product Mode |
Server Versions |
Discovery Method |
|---|---|---|
|
Full UC (default mode) |
Release 9 and later:
|
A DNS SRV request against _cisco-uds.<domain> |
|
Full UC (default mode) |
Release 8.x:
|
A DNS SRV request against _cuplogin.<domain> |
|
Product Mode |
Server Versions |
Discovery Method |
|---|---|---|
|
Full UC (default mode) |
Release 9 and later:
|
A DNS SRV request against _cisco-uds .<domain> and _cuplogin.<domain> |
|
Full UC (default mode) |
Release 8.x:
|
A DNS SRV request against _cuplogin.<domain> |
|
IM Only (default mode) |
Release 9 and later: Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service |
A DNS SRV request against _cisco-uds .<domain> and _cuplogin.<domain> |
|
IM Only (default mode) |
Release 8.x: Cisco Unified Presence |
A DNS SRV request against _cuplogin .<domain> |
|
Phone mode |
Release 9 and later: Cisco Unified Communications Manager |
A DNS SRV request against _cisco-uds.<domain> |
|
Phone mode |
Release 8.x: Cisco Unified Communications Manager |
Manual connection settings or bootstrap file Manual connection settings |
 Note |
Cisco Unified Communications Manager version 9 and later can still discover full Unified Communications and IM-only services using the _cuplogin DNS SRV request but a _cisco-uds request will take precedence if it is present. |
|
Server Versions |
Connection Method |
|---|---|
|
Cisco Webex Messenger |
HTTPS request against https://loginp.webexconnect.com/cas/FederatedSSO?org=<domain> |
|
Deployment Type |
Connection Method |
|---|---|
|
Enabled for single sign-on (SSO) |
Cisco Webex Administration Tool Bootstrap file to set the SSO_ORG_DOMAIN argument. |
|
Not enabled for SSO |
Cisco Webex Administration Tool |
Sources of Authentication
A source of authentication, or an authenticator, enables users to sign in to the client.
-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence—On-premises deployments in either full UC or IM only.
-
Cisco Unified Communications Manager—On-premises deployments in phone mode.
-
Cisco Webex Messenger Service—Cloud-based or hybrid cloud-based deployments.
Initial Launch Sequence
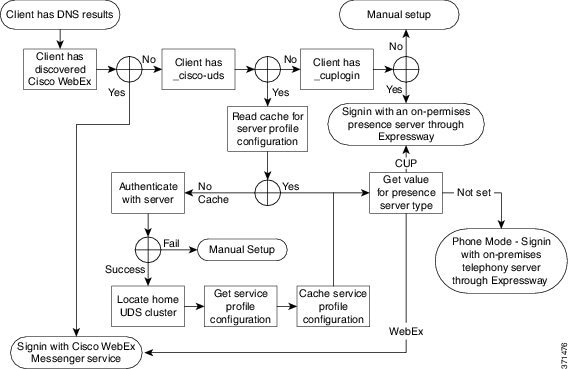
On the initial launch after installation, Cisco Jabber starts in the default product mode. The client then gets an authenticator and signs the user in. After sign in, the client determines the product mode.
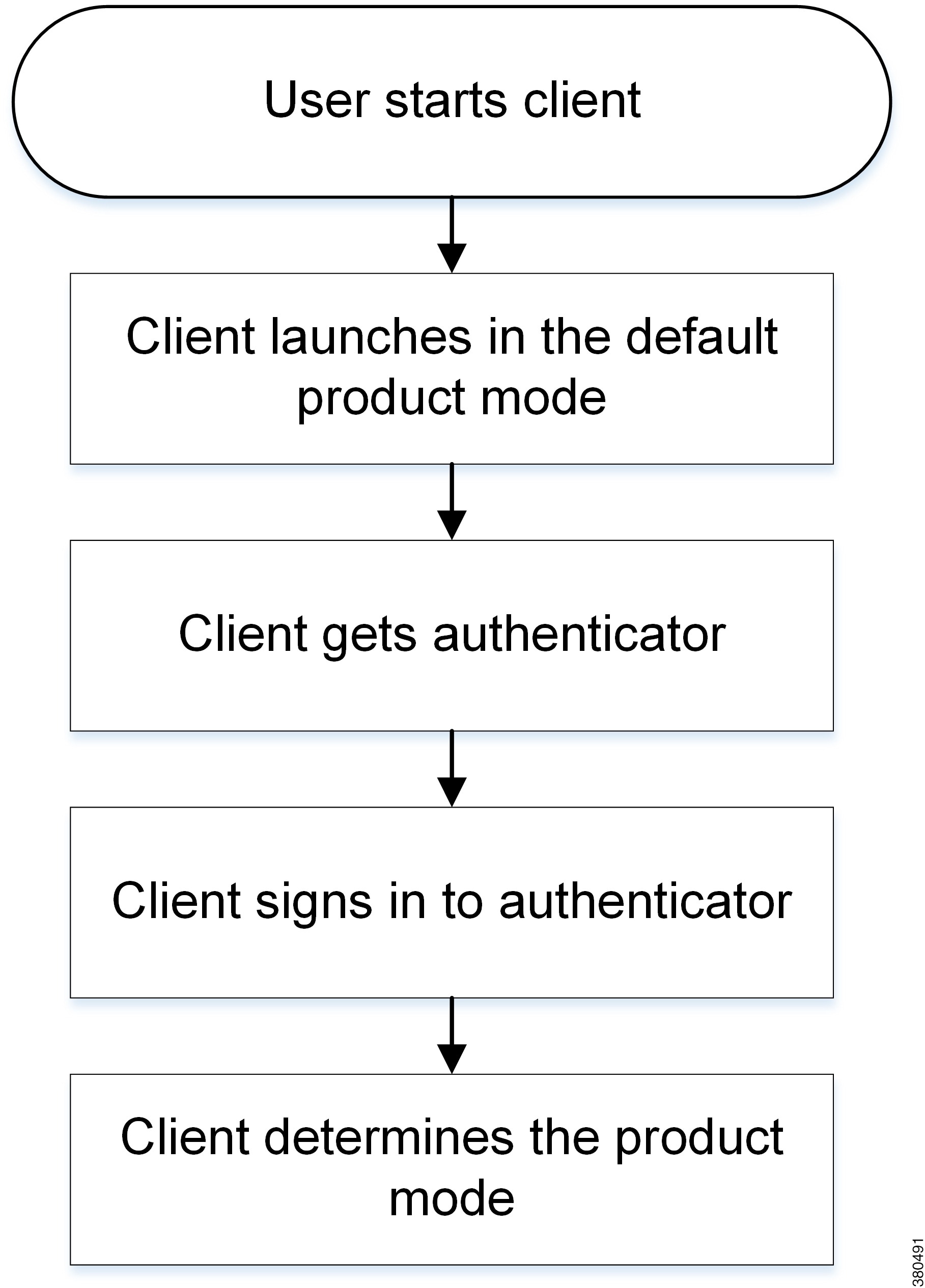
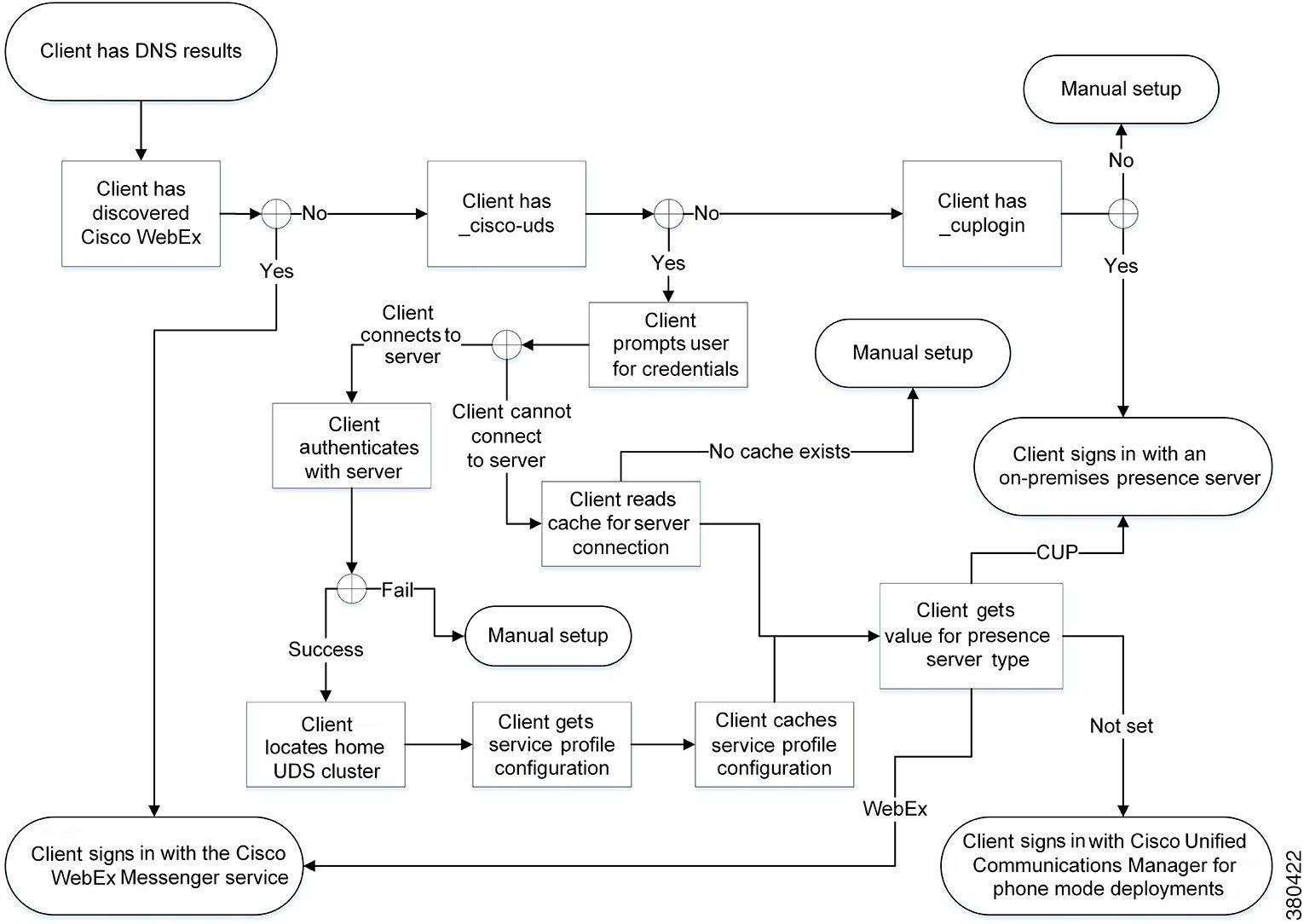
How the Client Gets an Authenticator
-
Client checks cache for manual settings.
Users can manually enter authenticator through the client user interface.
-
Client checks cache to discover if the user's domain is a Webex organisation..
The client chooses Webex as the authenticator.
-
Client makes a Webex cloud service HTTP request to discover if the user's organisation domain is a Webex organisation.
The client chooses Webex as the authenticator.
-
Client checks cache for service discovery.
The client loads settings from previous queries for service (SRV) records.
-
Client queries for SRV records.
The client queries the DNS name server for SRV records to locate services.
If the client finds the _cisco-uds SRV record, it can get the authenticator from the service profile.
About Service Discovery
Service discovery enables clients to automatically detect and locate services on your enterprise network. Clients query domain name servers to retrieve service (SRV) records that provide the location of servers.
-
Speeds time to deployment.
-
Allows you to centrally manage server locations.
 Important |
If you are migrating from Cisco Unified Presence 8.x to Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service 9.0 or later, you must specify the Cisco Unified Presence server FQDN in the migrated UC service on Cisco Unified Communications Manager. Open Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration interface. Select User Management > User Settings > UC Service. For UC services with type IM and Presence, when you migrate from Cisco Unified Presence 8.x to Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service the Host Name/IP Address field is populated with a domain name and you must change this to the Cisco Unified Presence server FQDN. |
However, the client can retrieve different SRV records that indicate to the client different servers are present and different services are available. In this way, the client derives specific information about your environment when it retrieves each SRV record.
|
SRV Record |
Purpose |
Why You Deploy |
|---|---|---|
| _cisco-uds |
Provides the location of Cisco Unified Communications Manager version 9.0 and later. The client can retrieve service profiles from Cisco Unified Communications Manager to determine the authenticator. |
|
| _cuplogin |
Provides the location of Cisco Unified Presence. Sets Cisco Unified Presence as the authenticator. |
|
| _collab-edge | Provides the location of Cisco VCS Expressway or Cisco
Expressway-E.
The client can retrieve service profiles from Cisco Unified Communications Manager to determine the authenticator. |
|
How the Client Locates Services
-
The client's host computer or device gets a network connection.
When the client's host computer gets a network connection, it also gets the address of a Domain Name System (DNS) name server from the DHCP settings.
-
The user employs one of the following methods to discover the service during the first sign in:
-
Manual—The user starts Cisco Jabber and then inputs an email-like address on the welcome screen.
-
URL configuration—URL configuration allows users to click on a link to cross-launch Cisco Jabber without manually inputting an email.
-
Mobile Configuration Using Enterprise Mobility Management—As an alternative to URL configuration, you can configure Cisco Jabber using Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM) with Android for Work on Cisco Jabber for Android and with Apple Managed App Configuration on Cisco Jabber for iPhone and iPad. You need to configure the same parameters in the EMM console that are used for creating URL configuration link.
To create a URL configuration link, you include the following:
-
ServicesDomain—The domain that Cisco Jabber uses for service discovery.
-
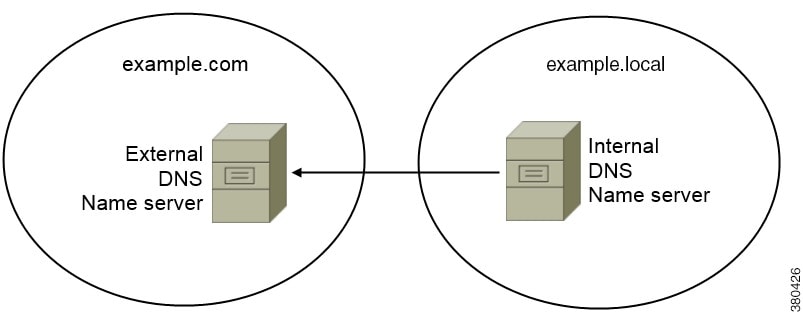
VoiceServicesDomain—For a hybrid deployment, the domain that Cisco Jabber uses to retrieve the DNS SRV records can be different from the ServicesDomain that is used to discover the Cisco Jabber domain.
-
ServiceDiscoveryExcludedServices—In certain deployment scenarios, services can be excluded from the service discovery process. These values can be a combination of the following: -
WEBEX
-
CUCM
-
CUP
-

Note
When all three parameters are included, service discovery does not happen and the user is prompted to manually enter connection settings.
Create the link in the following format:
ciscojabber://provision?ServicesDomain=<domain_for_service_discover> &VoiceServicesDomain=<domain_for_voice_services> &ServiceDiscoveryExcludedServices=<services_to_exclude_from_service_discover>Examples: -
ciscojabber://provision?servicesdomain=example.com -
ciscojabber://provision?servicesdomain=example.com &VoiceServicesDomain=VoiceServices.example.com -
ciscojabber://provision?servicesdomain=example.com &ServiceDiscoveryExcludedServices=WEBEX,CUCM
Provide the link to users using email or a website.

Note
If your organization uses a mail application that supports cross-launching proprietary protocols or custom links, you can provide the link to users using email, otherwise provide the link to users using a website.
-
-
The client gets the address of the DNS name server from the DHCP settings.
-
The client issues an HTTP query to a Central Authentication Service (CAS) URL for the Cisco Webex Messenger service.
This query enables the client to determine if the domain is a valid Cisco Webex domain.
-
The client queries the name server for the following SRV records in order of priority: -
_cisco-uds
-
_cuplogin
-
_collab-edge
-
The following is an example of an SRV record entry:
_cisco_uds._tcp.DOMAIN SRV service location:
priority = 0
weight = 0
port = 8443
svr hostname=192.168.0.26Client Issues HTTP Query
When the client gets a domain from the user, it appends that domain to the following HTTP query:
http://loginp.webexconnect.com/cas/FederatedSSO?org=For example, if the client gets example.com as the domain from the user, it issues the following query:
http://loginp.webexconnect.com/cas/FederatedSSO?org=example.comThat query returns an XML response that the client uses to determine if the domain is a valid Cisco WebEx domain.
If the client determines the domain is a valid Cisco WebEx domain, it prompts users to enter their Cisco WebEx credentials. The client then authenticates to theCisco WebEx Messenger service and retrieves configuration and UC services configured in Cisco WebEx Org Admin.
If the client determines the domain is not a valid Cisco WebEx domain, it uses the results of the query to the name server to locate available services.
 Note |
The client will use any configured system proxies when sending the HTTP request to the CAS URL. Proxy support for this request has the following limitations :
|
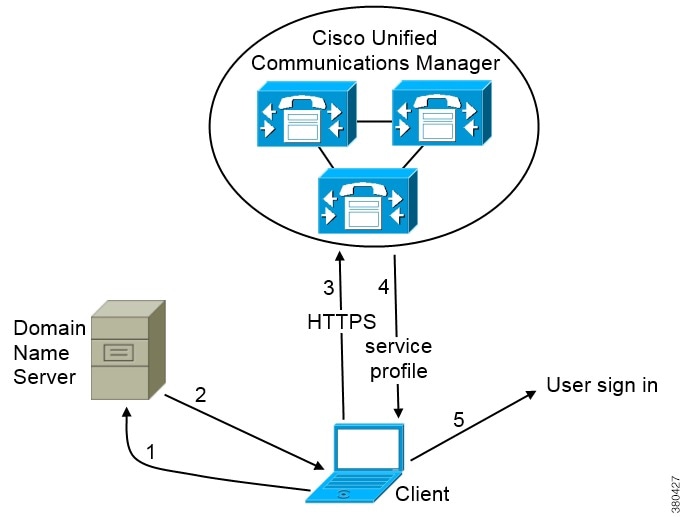
Cisco UDS SRV Record
In deployments with Cisco Unified Communications Manager version 9 and later, the client can automatically discover services and configuration with the _cisco-uds SRV record.
The following figure shows how the client uses the _cisco-uds SRV record.
-
The client queries the domain name server for SRV records.
-
The domain name server returns the _cisco-uds SRV record.
-
The client locates the user's home cluster.
As a result, the client can retrieve the device configuration for the user and automatically register telephony services.

Important
In an environment with multiple Cisco Unified Communications Manager clusters, you can configure the Intercluster Lookup Service (ILS). ILS enables the client to find the user's home cluster and discover services.
If you do not configure ILS, you must manually configure remote cluster information, similar to the Extension Mobility Cross Cluster (EMCC) remote cluster setup. For more information on remote cluster configurations, see the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Features and Services Guide.
-
The client retrieves the user's service profile.
The user's service profile contains the addresses and settings for UC services and client configuration.
The client also determines the authenticator from the service profile.
-
The client signs the user in to the authenticator.
_cisco-uds._tcp.example.com SRV service location:
priority = 6
weight = 30
port = 8443
svr hostname = cucm3.example.com
_cisco-uds._tcp.example.com SRV service location:
priority = 2
weight = 20
port = 8443
svr hostname = cucm2.example.com
_cisco-uds._tcp.example.com SRV service location:
priority = 1
weight = 5
port = 8443
svr hostname = cucm1.example.com
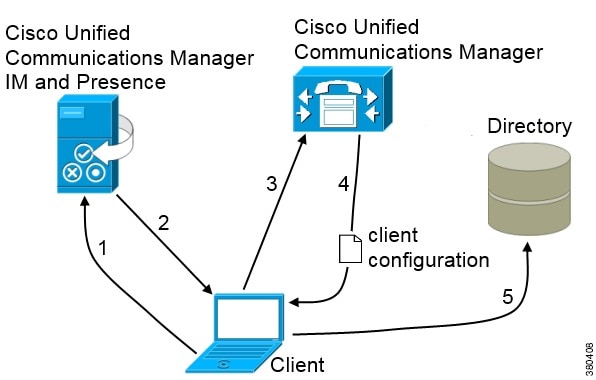
CUP Login SRV Record
Cisco Jabber can automatically discover and connect to Cisco Unified Presence or Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service with the _cuplogin SRV record.
The following figure shows how the client uses the _cuplogin SRV record.
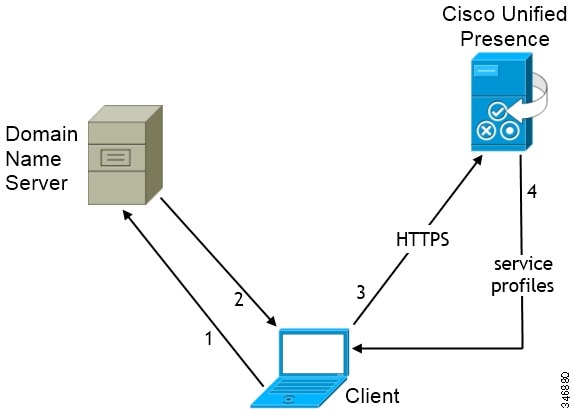
-
The client queries the domain name server for SRV records.
-
The name server returns the _cuplogin SRV record.
As a result, Cisco Jabber can locate the presence server and determine that Cisco Unified Presence is the authenticator.
-
The client prompts the user for credentials and authenticates to the presence server.
-
The client retrieves service profiles from the presence server.
 Tip |
The _cuplogin SRV record also sets the default server address on the Advanced Settings window. |
_cuplogin._tcp.example.com SRV service location:
priority = 8
weight = 50
port = 8443
svr hostname = cup3.example.com
_cuplogin._tcp.example.com SRV service location:
priority = 5
weight = 100
port = 8443
svr hostname = cup1.example.com
_cuplogin._tcp.example.com SRV service location:
priority = 7
weight = 4
port = 8443
svr hostname = cup2.example.com
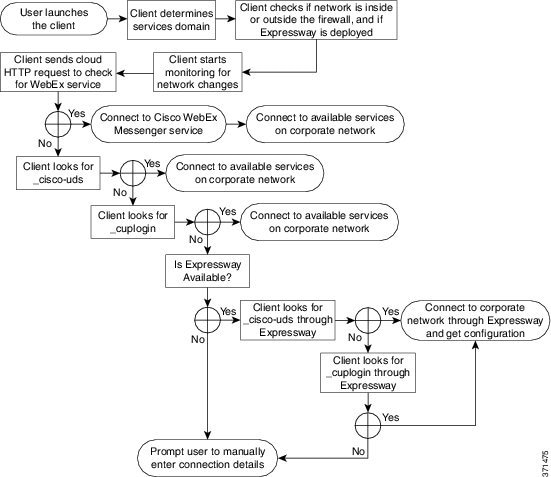
Collaboration Edge SRV Record
Cisco Jabber can attempt to connect to internal servers through Expressway for Mobile and Remote Access to discover services with the following _collab-edge SRV record.
The following figure shows how the client uses the _collab-edge SRV record.
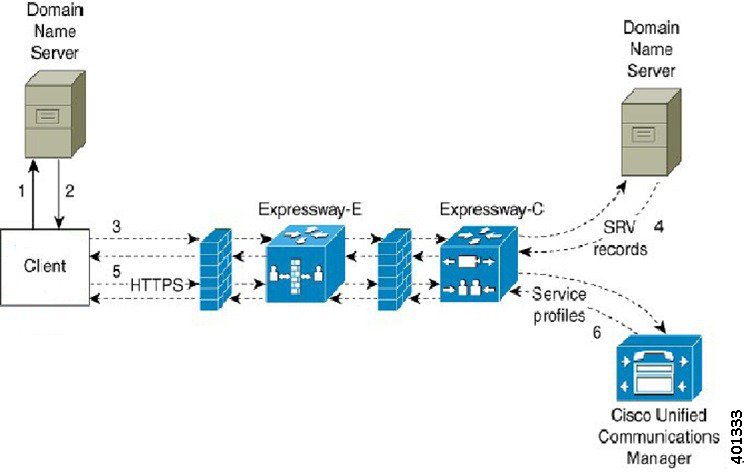
-
The client queries the external domain name server for SRV records.
-
The name server returns the _collab-edge SRV record and does not return the _cuplogin or _cisco-uds SRV records.
As a result, Cisco Jabber can locate the Cisco Expressway-E server.
-
The client requests the internal SRV records (through Expressway) from the internal domain name server.
These SRV records must include the _cisco-uds SRV record.
- The client obtains the internal SRV records (through Expressway).
As a result, the client can locate the Cisco Unified Communications Manager server.
-
The client requests the service profiles (through Expressway) from Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
-
The client retrieves the service profiles (through Expressway) from Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
The service profile contains the user's home cluster, the primary source of authentication, and the client configuration.
Configuration URL
You can create a configuration URL to make it easier for users to set up the client for the first time. Users can click this link to cross-launch Cisco Jabber without having to manually enter service discovery information.
To use this feature, you must create a URL and then distribute that URL to users.
Configuration URL
To enable users to launch Cisco Jabber without having to manually enter service discovery information, create and distribute a configuration URL to users.
You can provide a configuration URL link to users by emailing the link to the user directly, or by posting the link to a website.
-
ServicesDomain—Required. Every configuration URL must include the domain of the IM and presence server that Cisco Jabber needs for service discovery.
-
VoiceServiceDomain—Required only if you deploy a hybrid cloud-based architecture where the domain of the IM and presence server differs from the domain of the voice server. Set this parameter to ensure that Cisco Jabber can discover voice services.
-
ServiceDiscoveryExcludedServices—Optional. You can exclude any of the following services from the service discovery process:
-
Webex—When you set this value, the client: -
Does not perform CAS lookup
-
Looks for:
-
_cisco-uds
-
_cuplogin
-
_collab-edge
-
-
-
CUCM—When you set this value, the client: -
Does not look for _cisco-uds
-
Looks for:
-
_cuplogin
-
_collab-edge
-
-
-
CUP—When you set this value, the client: -
Does not look for _cuplogin
-
Looks for:
-
_cisco-uds
-
_collab-edge
-
-
You can specify multiple, comma-separated values to exclude multiple services.
If you exclude all three services, the client does not perform service discovery and prompts the user to manually enter connection settings.
-
-
ServicesDomainSsoEmailPrompt—Optional. Specifies whether the user is shown the email prompt for the purposes of determining their home cluster.
-
ON
-
OFF
-
-
Telephony_Enabled—Specifies whether the user has phone capability or not. The default is true. -
True
-
False
-
-
ForceLaunchBrowser—Used to force user to use the external browser. Applies to Cisco Jabber mobile clients. -
True
-
False

Note
ForceLaunchBrowser is used for client certificate deployments and for devices with Android OS below 5.0.
-
ciscojabber://provision?ServicesDomain=<domain_for_service_discover>
&VoiceServicesDomain=<domain_for_voice_services>
&ServiceDiscoveryExcludedServices=<services_to_exclude_from_service_discover>
&ServicesDomainSsoEmailPrompt=<ON/OFF> Note |
|
-
ciscojabber://provision?ServicesDomain=cisco.com -
ciscojabber://provision?ServicesDomain=cisco.com &VoiceServicesDomain=alphauk.cisco.com -
ciscojabber://provision?ServicesDomain=service_domain &VoiceServicesDomain=voiceservice_domain&ServiceDiscoveryExcludedServices=WEBEX -
ciscojabber://provision?ServicesDomain=cisco.com &VoiceServicesDomain=alphauk.cisco.com&ServiceDiscoveryExcludedServices=CUCM,CUP -
ciscojabber://provision?ServicesDomain=cisco.com &VoiceServicesDomain=alphauk.cisco.com&ServiceDiscoveryExcludedServices=CUCM,CUP &ServicesDomainSsoEmailPrompt=OFF
Provide Users with Configuration URL from a Website
You can provide a configuration URL link to users by emailing the link to the user directly, or by posting the link to a website.
 Note |
Due to a limitation of the Android operating system, Cisco Jabber for Android users can encounter an issue if they open the configuration URL directly from an Android application. To work around this issue, we recommend that you distribute your configuration URL link using a website. |
If you want to use the website explore option for URL provisioning, we recommended you to use Mozilla Firefox.
Use the following procedure to distribute the link from a website.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Create an internal web page that includes the configuration URL as an HTML hyperlink. |
| Step 2 |
Email the link to the internal web page to users.
|
Manual Connection Settings
Manual connection settings provide a fallback mechanism when Service Discovery is not used.
When you start Cisco Jabber, you can specify the authenticator and server address in the Advanced settings window. The client caches the server address to the local application configuration that loads on subsequent starts.
-
On-Premises with Cisco Unified Communications Manager release 9.x and Later — If the client cannot get the authenticator and server addresses from the service profile.
-
Cloud-Based or On-Premises with Cisco Unified Communications Manager release 8.x — If you do not set the authenticator in the bootstrap file. The client also prompts users to enter server addresses in the Advanced settings window if you do not set server addresses in the bootstrap file or with SRV records.
Settings that you enter in the Advanced settings window take priority over any other sources including SRV records and bootstrap settings.
If you select either Cisco IM & Presence or Cisco Communications Manager 8.xoptions, the client retrieves UC services from Cisco Unified Presence or Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service. The client does not use service profiles or SSO discovery.
 Note |
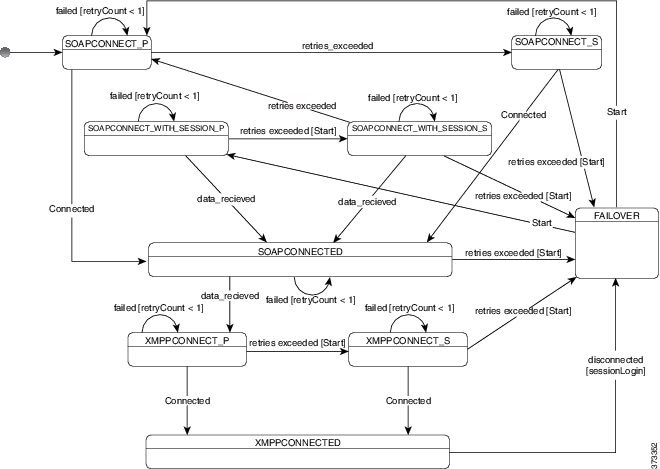
For Cisco Jabber for Windows, service discovery stops after 20 seconds regardless of the number of servers the SRV record resolves to. During service discovery, once Cisco Jabber finds _cisco-uds, it attempts to connect to the first 2 servers within 20 seconds. Cisco Jabber doesn't attempt to connect to any servers after it's attempted service discovery for the highest 2 priority servers. Users can manually point to the working server or re-order SRV priorities to at least one of the top two priority servers available for service discovery. |
Manual Connection Settings for On-Premises Deployments
Users can set Cisco Unified Presence or Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service as the authenticator and specify the server address in the Advanced settings window.
 Remember |
You can automatically set the default server address with the _cuplogin SRV record. |
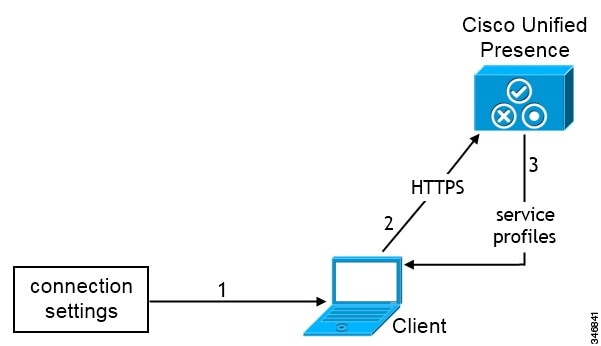
-
Users manually enter connection settings in the Advanced settings window.
-
The client authenticates to Cisco Unified Presence or Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service.
-
The client retrieves service profiles from the presence server.
Manual Connection Settings for On-Premises Deployments in Phone Mode
-
TFTP server
-
CCMCIP server
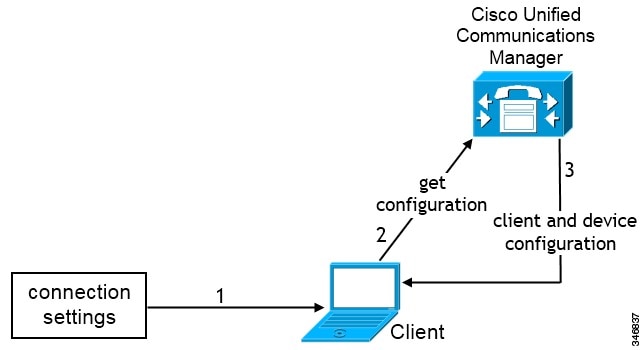
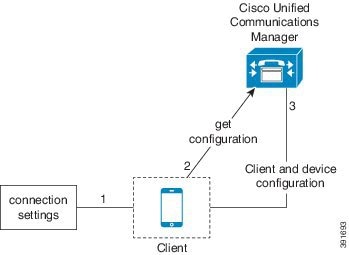
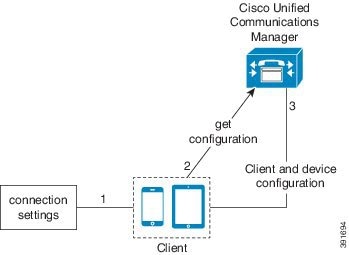
-
Users manually enter connection settings in the Advanced settings window.
-
The client authenticates to Cisco Unified Communications Manager and gets configuration.
-
The client retrieves device and client configuration.
Manual Connection Settings for Cloud-Based Deployments
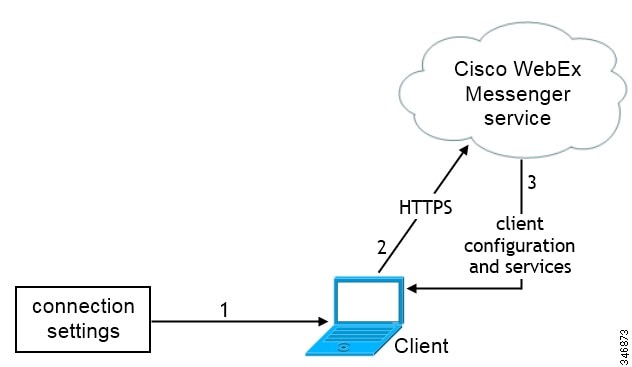
Users can set the Cisco WebEx Messenger service as the authenticator and specify the CAS URL for login in the Advanced settings window.
-
Users manually enter connection settings in the Advanced settings window.
-
The client authenticates to the Cisco WebEx Messenger service.
-
The client retrieves configuration and services.
Automatic Connection Setting for Service Discovery
Users can select the Automatic option in the Advanced settings window to discover servers automatically.
The Automatic option allows users change from manually setting the service connection details to using service discovery. For example, on the initial launch, you manually set the authenticator and specify a server address in the Advanced settings window.
The client always checks the cache for manual settings. The manual settings take higher priority over SRV records, and for Cisco Jabber for Windows, the bootstrap file. For this reason, if you decide to deploy SRV records and use service discovery, you override the manual settings from the initial launch.
Installer Switches: Cisco Jabber for Windows
When you install Cisco Jabber, you can specify the authenticator and server addresses. The installer saves these details to a bootstrap file. When users launch the client for the first time, it reads the bootstrap file. The bootstrap file takes priority if service discovery is deployed.
Bootstrap files provide a fallback mechanism for service discovery in situations where service discovery has not been deployed and where you do not want users to manually specify their connection settings.
The client only reads the bootstrap file on the initial launch. After the initial launch, the client caches the server addresses and configuration, and then loads from the cache on subsequent launches.
We recommend that you do not use a bootstrap file, and instead use service discovery, in on-premises deployments with Cisco Unified Communications Manager release 9.x and later.
Bootstrap Settings for On-Premises Deployments
|
Product Mode |
Server Releases |
Argument Values |
|---|---|---|
|
Full UC (Default Mode) |
|
Use the following installer switches and values:
|
|
Full UC (Default Mode) |
|
Use the following installer switches and values:
|
|
IM Only (Default Mode) |
|
Use the following installer switches and values:
|
|
IM Only (Default Mode) |
|
Use the following installer switches and values:
|
-
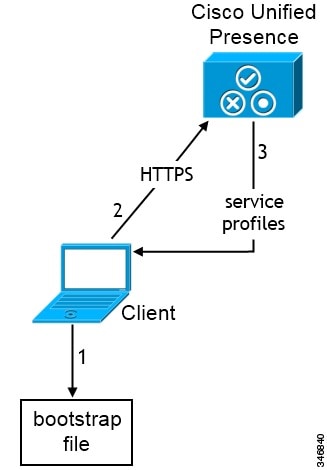
The client retrieves settings from the bootstrap file.
The client starts in default mode and determines that Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service is the authenticator. The client also gets the address of the presence server, unless Service Discovery results dictate otherwise.
-
The client authenticates to Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service .
-
The client retrieves service profiles from the presence server.
Bootstrap Settings for On-Premises Deployments in Phone Mode
-
Set CUCM as the value for AUTHENTICATOR.
-
Set phone_mode as the value for PRODUCT_MODE.
-
Set the TFTP server address as the value for TFTP.
-
Set the CTI server address as the value for CTI.
-
Set the CCMCIP server address as the value for CCMCIP.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager release 9.x and earlier—If you enable Cisco Extension Mobility, the
Cisco Extension Mobilityservice must be activated on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager nodes that are used for CCMCIP. For information about Cisco Extension Mobility, see the Feature and Services guide for your Cisco Unified Communications Manager release.
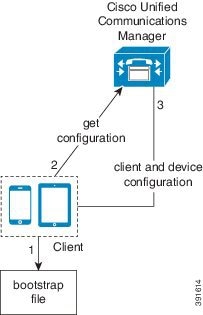
-
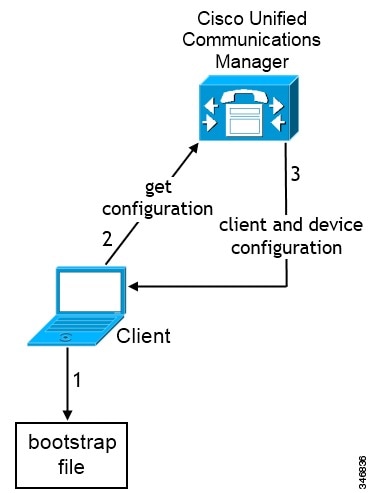
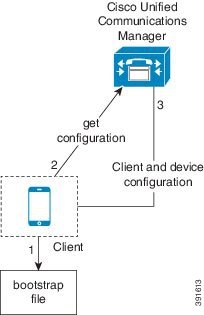
The client retrieves settings from the bootstrap file.
The client starts in phone mode and determines that Cisco Unified Communications Manager is the authenticator. The client also gets the addresses for the TFTP and CTI servers, unless Service Discovery results dictate otherwise.
The client starts in phone mode and determines that Cisco Unified Communications Manager is the authenticator. The client also gets the addresses for the TFTP server, unless Service Discovery results dictate otherwise.
-
The client authenticates to Cisco Unified Communications Manager and gets configuration.
-
The client retrieves device and client configuration.
Bootstrap Settings for Cloud-Based Deployments
-
Set WEBEX as the value for AUTHENTICATOR.
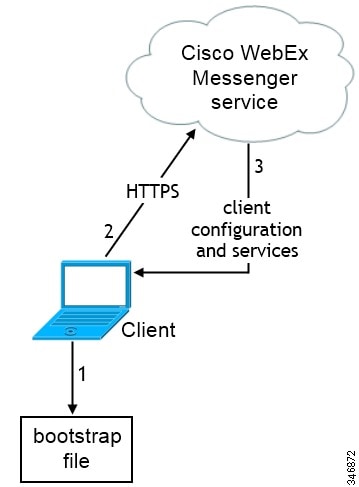
-
The client retrieves settings from the bootstrap file.
The client starts in default mode and determines that the Cisco WebEx Messenger service is the authenticator, unless Service Discovery results dictate otherwise.
-
The client authenticates to the Cisco WebEx Messenger service.
-
The client retrieves configuration and services.


 Feedback
Feedback