Shared Expressway
Data Center Configuration Overview
This section provides guidance for configuring the Cisco Expressway for Business-to-Business Communication through the Internet. Use this information with, but not as a replacement for, the Cisco Expressway documentation.
-
Two VLANs (Shared Transit VLAN and Shared outside VLAN) are required to accommodate the deployment of shared Expressway.
-
The DMZ outside VLAN and DMZ inside VLANs may exist if you deployed Expressway for OTT. If OTT is not deployed, then you need two more VLANs (DMZ outside VLAN and DMZ inside VLAN).
-
Configuration is required in the Nexus 7000, vSphere Distributed Switch (VDS) (and, optionally, the Nexus 5000, if deployed), UCS Manager, and ASA.
-
Ensure that the global DMZ inside VLAN, Shared Transit VLAN, and shared outside VLAN extend into the data center. These VLANs are used on the virtualized Cisco Expressway-E and Expressway-C.
-
Cisco Expressway-E hosts the public IP address. The remote businesses access this address by way of the public Internet.
-
In the Service Provider Cisco HCS data center, Cisco Expressway-E runs on UCS behind the ASA.
-
Cisco Expressway-C sits in the shared outside VLAN along with the Session Border Controller.
-
Communication between Cisco Expressway-C and Cisco Expressway-E is through the ASA, which provides the NAT and firewall functions.
-
Create a Shared Cisco Expressway Data Center Network
The diagram DC Deployment for Shared Expressway captures the data center deployment for the Shared Expressway.
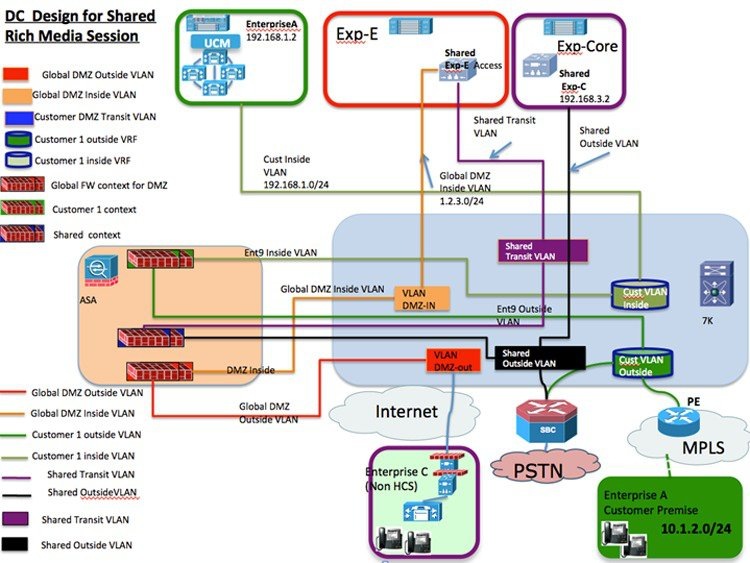
The following diagram captures the network topology for the Shared Expressway.
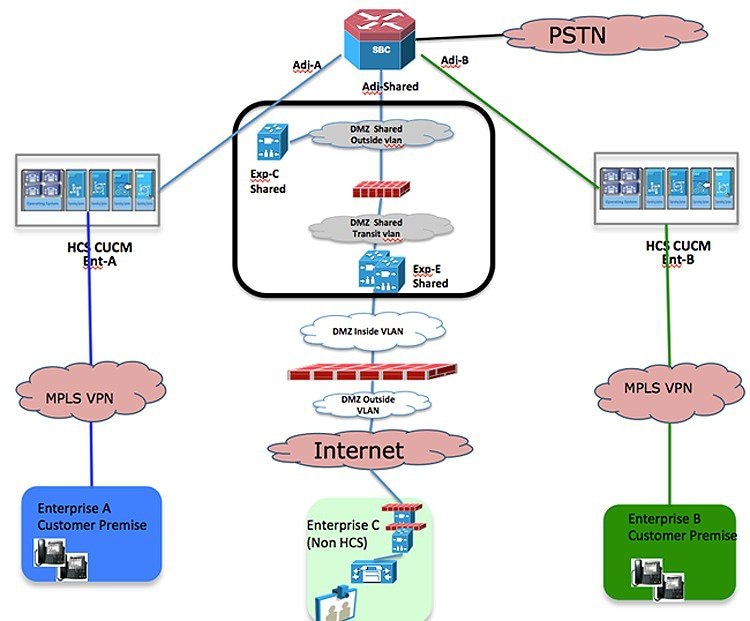
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Create four VLANs (DMZ inside, DMZ outside, Shared Transit, and Shared Outside) on the aggregation device (Nexus 7000). The DMZ inside and DMZ outside may already exist if Expressway based OTT is already deployed. Refer to the OTT deployment. |
| Step 2 |
Extend the Shared outside VLAN, Shared Transit VLAN and DMZ inside VLAN into the vSphere Distributed Switch (VDS) and UCS Manager. (Fabric Interconnect) |
| Step 3 |
In the ASA, create two contexts: Create Context 1 for Internet connectivity and add DMZ inside/DMZ outside interfaces with previously created VLANs. Create Context 2 for SBC traversal between C and E with the Shared Transit VLAN and the Shared Outside VLAN. |
| Step 4 |
In the ASA, configure the inside and outside interfaces according to step 3. |
| Step 5 |
Add any static routes and access lists for inside and outside access. Perform port and protocol filtering as described in the VCS IP Port usage for FirewallTraversal Deployment Guide. See Unified Communications Port Reference for a table that summarizes the ports to open on the firewalls between your internal network (Cisco Expressway-C), DMZ (Cisco Expressway-E), and the DMZ to public internet. |
Configuration Tasks and Concepts
Review the topics outlined in this seciton when configuring Shared Expressway.
Configuring the Nexus 7000
Two new VRFs and two new VLANs, Shared Transit VLAN (916) and Shared Outside VLAN (917), are added as part of the Shared Expressway deployment. The configuration provided in this seciton is from the Nexus 7000.
N7K side A configuration
Shared Transit VRF
interface Vlan916
vrf member shd-expy-inside
vrf context shd-expy-inside
description Shared Transit Vlan
!
interface Vlan916
description Shared Transit Vlan
no shutdown
vrf member shd-expy-inside
ip address 199.91.6.4/28
hsrp version 2
hsrp 916
ip 199.91.6.5
Shared Outside VRF
interface Vlan917
vrf member shd-expy-outside
vrf context shd-expy-outside
description Shared Outside Vlan
!
interface Vlan917
description Shared Outside Vlan
no shutdown
vrf member shd-expy-outside
ip address 199.91.7.4/28
hsrp version 2
hsrp 917
ip 199.91.7.5
N7K side B configuration
Shared Transit VRF
!
interface Vlan916
vrf member shd-expy-inside
vrf context shd-expy-inside
description Shared Transit Vlan
!
interface Vlan916
description Shared Transit Vlan
no shutdown
vrf member shd-expy-inside
ip address 199.91.6.3/28
hsrp version 2
hsrp 916
preempt
priority 150
ip 199.91.6.5
!
Shared Outside VRF
interface Vlan917
vrf member shd-expy-outside
vrf context shd-expy-outside
description Shared Outside Vlan
interface Vlan917
description Shared Outside Vlan
no shutdown
vrf member shd-expy-outside
ip address 199.91.7.3/28
hsrp version 2
hsrp 917
preempt
priority 150
ip 199.91.7.5
Configuring the ASA
In a shared Expressway deployment, a call from a non-Cisco HCS customer is routed through the external DMZ interface of Expressway-E to Expressway-C. From there, the call is routed to Session Border Controller, and then to the respective customer's Unified Communications server. The IP address of the Expressway-E is discovered through the DNS SRV lookup as detailed in the DNS configuration section.
 Note |
Reverse DNS lookup fails if you use a common DNS instance for all the tenant VRFs. For reverse DNS lookup to work, manually reconfigure DNS providing the local instance for each tenant. Configure the DNS entries on each box using the host file. |
DMZ context config
DMZ context config
DMZ inside interface
interface Port-channel21.906
nameif inside
security-level 0
ip address 199.90.6.1 255.255.255.240 standby 199.90.6.2
!
DMZ outside interface
interface Port-channel21.907
nameif outside
security-level 100
ip address 199.90.7.1 255.255.255.240 standby 199.90.7.2
External interface address of shared expressway E
object-group network SHD-EXPY-E
network-object 199.90.6.3 255.255.255.255
Natted IP address of external interface
object-group network SHD-EXPY-E-Outside
network-object 199.90.7.9 255.255.255.255
nat (inside,outside) source static SHD-EXPY-E SHD-EXPY-E-Outside
access-list incoming_traffic extended permit udp any gt 16384 object-group SHD-EXPY-E range 36002 59999
access-list incoming_traffic extended permit tcp any gt 1023 object-group SHD-EXPY-E eq 5061
access-list outgoing_traffic extended permit tcp object-group SHD-EXPY-E any eq 5061
access-list outgoing_traffic extended permit udp object-group SHD-EXPY-E any gt 1023
access-list outgoing_traffic extended permit udp object-group SHD-EXPY-E any eq domain
access-group incoming_traffic in interface outside
access-group outgoing_traffic out interface outsideShared Expressway Context on ASA
The inside interface of Shared Expressway-E and Shared Expressway-C is in a new context.
Inside interface - Shared Expressway E
interface Port-channel21.916
description Shared Transit Vlan
nameif outside
security-level 100
ip address 199.91.6.1 255.255.255.240 standby 199.91.6.2
!Outside interface Shared Expressway-C
interface Port-channel21.917
description Shared Outside Vlan
nameif inside
security-level 0
ip address 199.91.7.1 255.255.255.240 standby 199.91.7.2
!
object-group network SHD-EXPY-E
network-object 199.91.6.13 255.255.255.255
object-group network SHD-EXPY-C
network-object 199.91.7.13 255.255.255.255
access-list incoming_traffic extended permit udp object-group SHD-EXPY-C host 192.6.1.3 eq domain
access-list incoming_traffic extended permit tcp object-group SHD-EXPY-C object-group SHD-EXPY-E eq 7002
access-list incoming_traffic extended permit udp object-group SHD-EXPY-C gt 1023 object-group SHD-EXPY-E gt 1023
!
access-group outgoing_traffic in interface inside
access-group incoming_traffic in interface outside Note |
More configuration can allow management access to Expressway servers. |
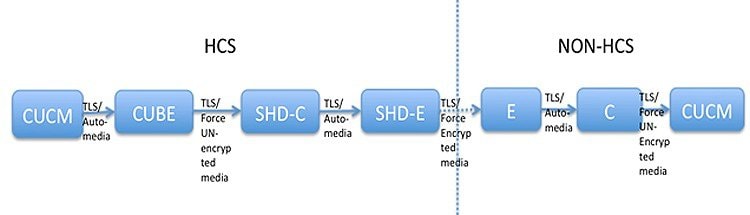
 Feedback
Feedback