Getting Started
Sign In
You must do post installation configurations to sign in to the Unified CCE Administration. For more information, see Post Installation Configuration .
Sign in to Unified CCE Administration at https://<IP Address>/cceadmin. <IP Address> is the address of the Side A or B Unified CCE AW or optional external HDS.
 Note |
Users are logged out of the Unified CCE Administration console automatically after 30 minutes of inactivity. |
Administrators
Administrators sign in using their Active Directory credentials. For username, use the user@domain.com format.
Supervisors
Supervisors on an IPv6 network sign in to Unified CCE Administration at https://<FQDN>/cceadmin. <FQDN> is the fully qualified domain name of the Side A or B CCE AW or optional external HDS.
Supervisors sign in using their Active Directory (user@domain.com) or single sign-on credentials. If supervisors are enabled for single sign-on, after entering their username they are redirected to the Identity Provider sign-in screen to enter their credentials. Supervisors are redirected to Unified CCE Administration after successfully signing in.
Languages
If the Language Pack is installed, the Sign-In window includes a Language drop-down menu, showing more than a dozen languages. English is the initial and the default language. Select any other language to see the user interface and the online help in that language. The system retains your choice for subsequent sign-ins until you change it again.
Single Sign-On Log Out
For a complete logout from all applications, sign out of the applications and close the browser window. In a Windows desktop, log out of the Windows account. In a Mac desktop, quit the browser application.
 Note |
Users enabled for single sign-on are at risk of having their accounts misused by others if the browser is not closed completely. If the browser is left open, a different user can access the application from the browser page without entering credentials. |
System Interface
Packaged CCE user interface enables you to configure the application through one window. The landing page has a left navigation bar and a card view which contains all the configuration options. What you see after a successful sign-in depends on your role.
The left navigation bar consists of the following menus:
-
Overview
-
Infrastructure
-
Organization
-
Users
-
Desktop
-
Capacity
The following menus appear as cards:
-
Infrastructure Settings
-
Call Settings
-
User Setup
-
Organization Setup
-
Bulk Import
-
Desktop Settings
-
Features
-
Email and Chat
(Available only when ECE Web Server is added to the page on the Unified CCE Administration.)
 Note |
The Unified CCE Administration interface also provides access to HTML-based online help for users and administrators. Click on the help button (?) on any page (except the Overview page) in the Unified CCE Administration interface and the online help specific to that page is displayed in a pop-over window. You can navigate to the previous or next page in the online help using the following keys:
|
Lists
List Windows
Most tools open to a List window that has rows for all currently configured objects. For example, the Teams tool has a list with a row for each team, and the Call Types tool has a list with a row for each call type. List windows allow you to search, sort, edit, and delete from the list.
Permissions on List windows vary for administrators and supervisors and are noted in the topic for each tool.
Search a List
There is a Search field on the List window for most tools. The search interface is similar, with small variations, depending on the tool.
Search and Administrators
If you sign in as a global administrator, a search returns all objects.
If you sign in as a departmental administrator, a search returns all objects in the departments you administer, as well as all global objects (objects that are in no departments).
Basic Search
Some tools offer a basic search on the Name (or name-equivalent) and Description fields.
Enter all or part of either value to find matches. Clear the search by deleting text from the Search field.
Search for Tools with Department IDs
For objects that can be associated with a department, you can click the + icon to the right of the Search field to open a popup window, where you can:
-
Enter a name or description ( for call types and precision queues add id).
-
Select departments, with options for Globals and Departments, Globals only, or Departments only.
Selecting Globals and Departments or Departments only enables an input field where you can enter a space-separated list of department names. (Departments is an OR search.)

Note
Search by department is enabled only when departments are configured.
Agent Advanced Search
The Search field in the Agents tool offers an advanced and flexible search.Click the + icon at the far right of the Search field to open a popup window, where you can:
-
Select to search for agents only, supervisors only, or both.
-
Enter a username, agent ID, first or last name, or description to search for that string.
-
Enter one or more team names separated by spaces. (Team is an OR search--the agent or supervisor must be a member of one of the teams.)
-
Enter one or more attribute names separated by spaces. (Attributes is an AND search--the agent or supervisor must have all attributes.)
-
Enter one or more skill group names separated by spaces. (Skill Groups is an AND search.)
-
Select departments, with options for Globals and Departments, Globals only, or Departments only.
Selecting Globals and Departments or Departments only enables an input field where you can enter a space-separated list of department names. (Departments is an OR search.)
Sort a List
If a column in a List window has an arrow icon in the column header, click the arrow to sort in ascending or descending order.
Add Objects
Click New in a List window to open an Add window where you can complete fields to create and save a new object.
Update Objects
To edit an object in a List window, click in the row for that object. This opens a window where you can make and save modifications. This table explains which fields are editable for each tool.
In the List window for the Agent tool, you can edit descriptions, desk settings, and teams for multiple agents at once (see Edit Description, Desk Settings, and Teams for Multiple Agents).
In the List window of the Dialed Number tool, you can edit the ringtone media file for multiple Dialed Numbers at once (see Add and Update Ringtone Media File for Multiple Dialed Numbers).
 Remember |
Not all tools are available for all Deployment Types. |
| Tool | Editable Fields | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Administrators | All fields | ||
| Agents |
All fields except Site and Peripheral Set. If an agent is not enabled for single sign-on, you can check Change Password to reset the agent's password.
|
||
| Attributes |
All fields except Type. |
||
| Bucket Intervals |
Name You cannot edit the built-in bucket interval. |
||
| Bulk Jobs | No fields | ||
| Business Hours |
General tab: All fields. Regular Hours tab: All fields. Special Hours & Holidays tab: All fields. Status Reasons: The Status Reason field is editable. |
||
| Call Types |
All fields except the system-generated ID. |
||
|
Campaigns |
General tab: All fields except Type field. Skill Group tab: You can add and delete the Skill Groups using Add and Delete buttons. Advanced tab: All fields. |
||
| Desk Settings | All fields | ||
| Dialed Numbers | All fields except Site, Routing Type , Peripheral Setand Media Routing Domain. | ||
| Expanded Call Variables |
For user-defined array and scalar expanded call variables, Name, Description, Maximum Length, Enabled, and Persistent are editable. For built-in expanded call variables, Enabled and Persistent are the only editable fields. |
||
| Media Routing Domains |
All fields You cannot edit the built-in Cisco_Voice MRD or Multichannel MRDs for Enterprise Chat and Email. |
||
| Network VRU Scripts | All fields | ||
| Precision Queues | All fields | ||
|
Reason Labels |
Label, Description , Global , and Team Specific | ||
| Roles |
For custom roles, except for the Administrators, Departments and Roles fields in the Access category, all fields on both tabs are editable. You cannot edit the built-in roles. |
||
| Routing Pattern |
All fields except Routing Pattern, Site and Pattern Type. |
||
|
Location |
All fields except Location Name. |
||
|
SIP Server Group |
All fields except Domain Name FQDN, Site, and Type. |
||
| Teams | All fields except Site
and Peripheral Set.
|
||
| Skill Groups |
All fields except Site, Media Routing Domain , Peripheral Set and Peripheral Number.
|
Delete Objects
To delete an object from a List window, hover over the row for that object to see the x icon at the end of the row. Click the x icon and confirm your intention to delete.
Departmental administrators cannot delete global objects. Objects are identified as global in the Department column in the List window.
When you delete an object from Unified CCE Administration, the system does one of the following:
-
Immediately deletes the object.
-
Marks the object for deletion and enables permanent deletion. (You delete the object permanently using the Deleted Objects tool in Configuration Manager.)
-
Shows an error message explaining why the object cannot be deleted in its current state.
You cannot delete certain objects, including:
-
Objects set as system defaults, such as the default desk settings.
-
Objects referenced by other objects, such as a call type that is referenced by a dialed number.
-
Most built-in objects, such as built-in expanded call variables.
This table lists the delete types for all Unified CCE Administration objects. Available objects depend on your role and deployment type.
| Tool | Delete Type | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Administrators | Permanent | — | ||
| Agents | Marked |
|
||
| Attributes | Marked | — | ||
| Bucket Intervals | Marked | — | ||
| Bulk Jobs | Permanent |
Deletes the bulk job, its content file, and its log file from the host computer that created it. You can delete a bulk job that is in queue, has completed, or has failed. You cannot delete a bulk job that is in process. If your deployment includes two AW server hosts, you must delete a bulk job from the Unified CCE AW host on which it was created. |
||
|
Business Hours |
Permanent |
You cannot delete a business hour associated with a script. You must first dissociate the business hour from the script. |
||
|
Status Reasons |
Permanent |
— |
||
| Call Types | Marked | — | ||
| Campaigns | Marked | — | ||
| Desk Settings | Permanent | — | ||
| Dialed Numbers | Marked | — | ||
|
SIP Server Group |
Permanent |
You cannot delete the SIP Server Group associated with a Routing Pattern. You must first remove the SIP Server Group from the Routing Pattern. | ||
| Expanded Call Variables | Marked | — | ||
| Media Routing Domains | Permanent |
You cannot delete the built-in Cisco_Voice MRD or Multichannel MRDs for Enterprise Chat and Email (ECE). |
||
| Network VRU Scripts | Permanent | — | ||
|
File Transfer Job |
Permanent |
Deletes the file transfer job, its job details file, and its log file from the host computer where it is created. You cannot delete a file transfer job that is in processing state. |
||
| Precision Queues | Marked | Depends on whether the precision queue is referenced statically or dynamically in a script. . | ||
| Reason Labels | Marked | — | ||
| Roles | Permanent | — | ||
| Routing Pattern | Permanent | — | ||
| Location | Permanent | — | ||
| Teams | Permanent |
|
||
| Skill Groups | Marked | — |
Popup Windows
Popup window selection
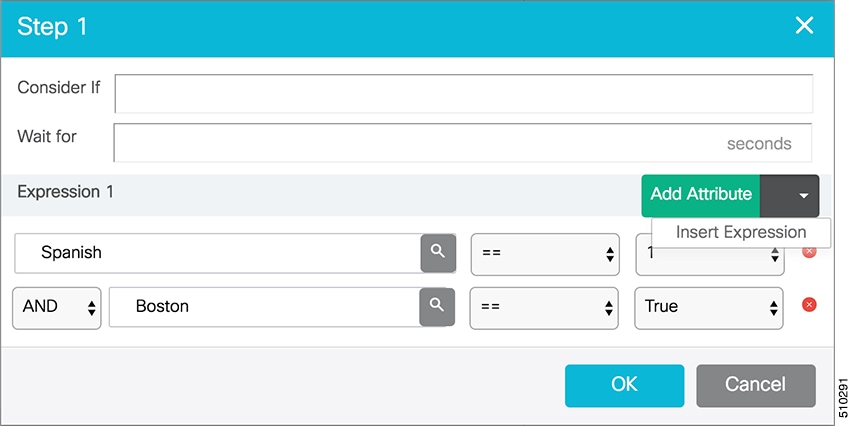
Many Add and Edit windows have popup windows for searching and choosing objects that are relevant to that tool.
Some popup windows allow you to chose one object. Other popup windows allow you to select multiple objects. For example, because an agent can be on only one team, the popup window for adding an agent to a team allows only one selection, while the Skill Group Members popup window allows you to select one or more agents to add to the skill group.
Click the + icon to open the popup window, where you can locate and select items that are configured.
Keyboard Shortcuts
Press the question mark (?) key to open a window that shows the keyboard shortcuts that are applicable for that tool and for your status (Supervisor or Administrator).
 Tip |
The keyboard shortcuts window does not open when you press the (?) key in a text field. Press the esc key to remove focus from the text field and then press the (?) key. |
System and Device Sync Alerts
Unified CCE Administration includes icons to notify users of any system alerts and device out-of-sync alert.
System Alerts
In Unified CCE Administration, you can monitor the status of the systems. The Alerts icon on the page includes alert count.
To view the alert and validation rule of a machine, click the Alerts icon. The Inventory page opens where you can view more details on the errors. For more information on server status rules, see Monitor Server Status Rules for Packaged CCE 2000 Agents Deployment
Device Out of Sync Alerts
In Unified CCE Administration, the configured data is synchronized with respective devices deployed in the inventory. If configured data synchronization fails with any device, the device is marked as out-of-sync and the Out of Sync device alert icon appears at the top of the page.
You can click the icon to open the Inventory page, and view data synchronization status of:
-
Cisco Unified Customer Voice Portal (CVP)
-
Cisco Finesse Primary
-
Cisco Unified Intelligence Center (CUIC) Publisher
-
Enterprise Email and Chat (ECE) Web Server
-
Cisco Virtualized Voice Browser (VVB) and
-
Cloud Connect Publisher
You can perform manual synchronization of data on each In Sync and Out of Sync device in the Inventory. See Manual Synchronization of Configured Data.
Manual Synchronization of Configured Data
Full Sync: This option is enabled for all CVPs (Main site and remote site) and VVBs (Main site and remote site).
-
CVP: reinitializes the device (CVP redeploy) and synchronizes all configuration data from the time when the initial configuration was done. Use this option after you reimage or reinstall the CVP Server.
-
VVB: synchronizes all configuration data from the time when the initial configuration was done. Use this option after you reimage, reinstall, or readd the VVB Server.
-
Cloud Connect: synchronizes all configuration data from the time when the initial configuration was done. Use this option after you reimage, reinstall, or read the Cloud Connect Publisher.
Differential Sync: This option synchronizes the configured data from the time the device was out of sync.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Navigate to . |
||
|
Step 2 |
If the device Sync Status is In Sync, click the Sync icon and select Full Sync. |
||
|
Step 3 |
If the device Sync Status is Out of Sync, click the Sync icon and select one of the following options
|
||
|
Step 4 |
Click the Sync button.
|




 Feedback
Feedback