Capabilities
Cisco Unified Mobile Agent Description
Mobile Agent enables an agent to use any PSTN phone and a broadband VPN connection (for agent desktop communications). The agent has the same capabilities as an agent in your call center using a Cisco IP Phone.
Unified Mobile Agent supports call center agents using phones that your contact center enterprise solution does not directly control. You can deploy a Mobile Agent as follows:
-
Outside the contact center, by using an analog phone or a mobile phone in the home.
-
On an IP phone connection that is not CTI-controlled by HCS-CC or by an associated Unified Communications Manager.
-
On any voice endpoint of any ACD (including endpoints on other Unified Communication Managers) that the contact center Unified Communication Manager can reach by a SIP trunk.
A Mobile Agent can use different phone numbers at different times; the agent enters the phone number at login time. An agent can access the Mobile Agent functionality using any phone number that is included in the Unified Communications Manager dial plan.
Unified Mobile Agent Extends Unified CCE Capabilities
Before Mobile Agent, Unified CCE used a JTAPI interface to Unified CM to connect customer calls arriving on a voice gateway to an agent's IP phone. Mobile Agent enables the Unified CCE architecture to connect customer calls to an agent phone that Unified CCE does not directly control.
Mobile Agent uses a pair of CTI ports that function as proxies for the Mobile Agent phone and the caller phone. Every logged-in Mobile Agent requires two CTI ports (local and remote). The two CTI ports take the place of the Cisco IP Phone monitored and controlled by Unified CM JTAPI. The agent at login uses the local CTI port DN. When this agent is selected, the router transfers the caller to that CTI port. The remote CTI port calls the agent either at login for a nailed (permanent) connection or upon being selected for a call-by-call connection.
Cisco Unified Contact Center functionality remains intact whether an agent is mobile or local:
-
Mobile Agents have the same capabilities and functionality that local agents have.
-
Mobile Agents do not need any specialized equipment; they can receive calls on an analog or mobile phone.
-
Unified Mobile Agent supports Cisco Finesse.
-
Mobile Agent activity is recorded in the same contact center reports as local agent activity.
-
Mobile Agent CTI and application data uses the same security mechanisms as local agent data.
Unified Mobile Agent Provides Agent Sign-In Flexibility
Agents can be either local agents or Mobile Agents, depending on how they sign in at various times.
Regardless of whether agents sign in as local or Mobile Agents, their skill groups do not change. Because agents are chosen by existing selection rules and not by how they are connected, the same routing applies regardless of how the agents log in. If you want to control routing depending on whether agents are local or mobile, assign the agents to different skill groups and design your scripts accordingly.
Connection Modes
Cisco Unified Mobile Agent allows system administrators to configure agents to use either call by call dialing or a nailed connection, or the administrator can configure agents to choose a connection mode at login time.
Mobile Agents are defined as agents using phones not directly controlled by Unified CC, irrespective of their physical location. (The term local agent refers to an agent who uses a phone that is under control of Unified CC, irrespective of physical location.)
You can configure Mobile Agents using either of two delivery modes:
-
Call by Call—In this mode, the Mobile Agent's phone is dialed for each incoming call. When the call ends, the Mobile Agent's phone is disconnected before being made ready for the next call.
-
Nailed Connection—In this mode, the agent is called at login time and the line stays connected through multiple customer calls.
 Note |
The administrator can select the Agent chooses option, which allows an agent to select a call delivery mode at login. |
Call by Call
In a call by call delivery mode, the Mobile Agent's phone is dialed for each incoming call. When the call ends, the Mobile Agent's phone disconnects before is it made ready for the next call.
The call by call call flow works as follows:
-
At login, the agent specifies an assigned extension for a CTI port.
-
A customer call arrives in the system and, through normal Unified ICM configuration and scripting, is queued for a skill group or an agent. (This is no different than existing processing for local agents.)
-
The system assigns an agent to the call. If the agent's Desk Setting is Unified Mobile Agent-enabled and configured for either call by call or Agent chooses mode, the router uses the extension of the agent's CTI port as a label.
-
The incoming call rings at the agent's CTI port. The JTAPI Gateway and PIM notice this but do not answer the call.
-
A call to the agent is initiated on another CTI port chosen from a preconfigured pool. If this call fails, Redirect on No Answer processing is initiated.

Note
In call by call mode, the Answer Wait Time is 3 to 15 seconds longer than in a local agent inbound call scenario. Specify a Redirect on No Answer setting large enough to accommodate the extra processing time.
-
When the agent takes the remote phone off-hook to answer the call, the system directs the customer call to the agent's call media address and the agent's call to the customer's call media address.
-
When the call ends, both connections are terminated and the agent is ready to accept another call.
 Note |
To configure Mobile Agent in call by call delivery mode, you must set the wrap-up timer to at least one second using the Agent Desktop Settings List tool in the Configuration Manager. In call by call delivery mode, callers often perceive a longer ring time compared to nailed connection delivery mode. This is because callers hear the ringtone during the call flow; ringing stops only after the agent answers. From the Unified CCE reporting perspective, a Mobile Agent in call by call delivery mode has a longer Answer Wait Time for the same reason. |
Nailed Connections
In nailed connection delivery mode, the agent is called once, at login, and the phone line remains connected through multiple customer calls. See the following figure.
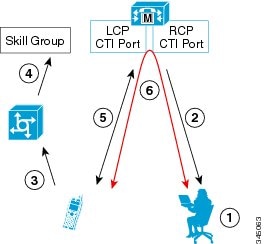
The nailed connection call flow works as follows:
-
At login, the agent enters the directory number of the local CTI port (LCP) in the Instrument Number field and the remote phone number in CTI OS Desktop. The remote phone number can be any phone number reachable by Unified CM.
When the agent clicks the Login button, a call is initiated to the agent's remote CTI port (RCP) and the agent's remote phone rings.
-
When the agent answers the call, the call is then nailed up. This means that the agent will remain on this call until the agent logs out or ends the call.
-
A customer's call arrives in the system , and scripting, is queued for a skill group/precision queue. (This is no different than existing processing for local agents.)
-
When the agent clicks the Answer button, the voice path between the agent and the customer phone is established, and the two parties can talk.
-
When the system assigns an agent to the call, the call is routed to the agent's LCP port. The agent then hears the connect tone on the headset.
-
When the call ends, the customer connection is terminated and the agent state returns to Ready.
Connect Tone
The Connect Tone feature in the nailed connection mode enables the system to play a tone to the Mobile Agent through the agent's headset to let the agent know when a new call is connected.
Connect Tone is particularly useful when Auto Answer is enabled or the agent is an Outbound agent. Here are its features:
-
An audible tone (two beeps) is sent to the Mobile Agent headset when the call to the nailed connection Mobile Agent is connected. It is a DTMF tone played by Unified CM and cannot be modified.
-
The Connect Tone plays only when the nailed connection Mobile Agent receives a call, as in the following examples:
-
The agent receives a consultation call.
-
The agent receives an outbound call.
-
-
The Connect Tone does not play when the Mobile Agent initiates a call, as in the following examples:
-
The agent makes a call.
-
The agent makes the consultation call.
-
Outbound direct preview call is made.
-
Supervisor barge-in call is made.
-
Agent Greeting and Whisper Announcement
The Agent Greeting and Whisper Announcement features are available to Unified Mobile Agents. The following sections explain more about how these features apply to Unified Mobile Agents.
Agent Greeting
You can use the Agent Greeting feature to record a message that plays automatically to callers when they connect to you. Your greeting message can welcome the caller, identify you, and include other useful information.
Limitations
The following limitations apply to the Agent Greeting feature for Mobile Agents.
-
A supervisor cannot barge in when an Agent Greeting is playing.
-
If a Peripheral Gateway (PG), JTAPI Gateway (JGW), or PIM failover occurs when an Agent Greeting plays for a Mobile Agent, the call fails.
-
If a Mobile Agent ends the call when an Agent Greeting plays, the customer still hears the complete Agent Greeting before the call ends.

Note
In the Agent Greeting Call Type Report, this call does not appear as a failed agent greeting call.
For more information about Agent Greeting, see Capabilities.
Whisper Announcement
With Whisper Announcement, agents can hear a brief prerecorded message just before they connect with each caller. The announcement plays only to the agent; the caller hears ringing (based on existing ringtone patterns) while the announcement plays. The announcement can contain information about the caller, such as language preference or customer status. This information helps the agent prepare for the call.
Configuration Requirement
For the Whisper Announcement feature for Unified Mobile Agents, you require a Media Termination Point (MTP) resource on an incoming SIP device.
Feature Requirements
Hardware and Software Requirements
Hardware and software requirements for the Unified Mobile Agent are identical to those of Unified CCE. For more information on feature requirements, consult these documents:
-
Solution Design Guide for Cisco Unified Contact Center Enterprise at https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/customer-collaboration/unified-contact-center-enterprise/products-implementation-design-guides-list.html
-
Virtualization for Unified Contact Center Enterprise at https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/en/us/td/docs/voice_ip_comm/uc_system/virtualization/cisco-collaboration-virtualization.html
-
Contact Center Enterprise Compatibility Matrix at https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/customer-collaboration/unified-contact-center-enterprise/products-device-support-tables-list.html
Phone Requirements
A Unified Mobile Agent can use an analog, digital, or IP phone to handle calls.
Conference Requirements
To use Agent Greeting for Mobile Agents, you must configure external conference-bridge (hardware) resources. To estimate the number of required resources, you can use the following formula:
Number of conference bridge resources = Mobile Agent call rate × Average greeting time (in seconds)
For information about configuring external conference-bridge resources, see the dspfarm profile 1 for conference configuration section in the sample configuration gateway, listed in Media Termination Points Configuration.
CTI Port Requirements
You need two CTI ports (local and remote) for every logged-in Mobile Agent.
Unified Mobile Agent uses Unified CM CTI Port as a proxy for the agent's phone. When this proxy is set up, whenever a Mobile Agent is selected to handle a customer call, the following happens:
-
The call is directed to the CTI port extension.
-
intercepts the call arriving on the CTI Port and directs Unified CM to connect the call to the Mobile Agent.
For Unified Mobile Agent to work properly, you must configure two CTI ports:
-
One port to serve as the agent's virtual extension.
-
The other port to initiate calls to the agent.
You must assign these CTI ports to the application. The ports are recognized by when receiving the Unified CM configuration.
For these CTI ports in IPv6 enabled deployments, you have to set IP Addressing Mode to IPv4 Only. You do this by creating a Common Device Configuration and referencing it to these CTI ports.
Supported Unified CCE/Unified CCH Features
The following features are supported:
-
Unified CCE supports temporary uninstallation while preserving Mobile Agent data.
For more information about temporary uninstallation, see the Cisco Unified Contact Center Enterprise Installation and Upgrade Guide.
-
Mobile Agents can participate in outbound campaigns, but they must use a nailed-up connection for all outbound dialing modes.
-
Unified Mobile Agent supports Redirect on No Answer (RONA). If the Mobile Agent fails to answer, the agent is made Not Ready, and the call is redirected to a RANA DN route point.
-
Unified Mobile Agent supports G.711A-law, G.711u-law, and G.729 codecs.
-
There is no direct interaction between Unified Mobile Agent and multichannel applications. Email and Chat are IP applications that continue to operate, assuming the Mobile Agent has a desktop with enough bandwidth on the broadband connection to support them.
-
Unified Mobile Agent supports Cisco Unified Customer Voice Portal (Unified CVP) and Cisco Unified IP-IVR (Unified IP IVR).
Fault Tolerance Support
Fault tolerance for the Unified Mobile Agent follows the behavior of Unified CCE:
-
The JTAPI Gateway, Unified CCE PIM, and CTI components record key events related to Unified Mobile Agent as part of the logging process.
-
As with standard Unified CCE calls, if a Peripheral Gateway (PG) component such as the JTAPI Gateway fails, the phone call is not lost, but subsequent call control (transfer, conference, or hold) might not be possible after a failover. The Mobile Agent is notified of a failure (on the desktop), but they must log in again after a Unified CM or Unified ICM failure occurs.
-
Where CTI data is delivered for screen pops, CTI data is preserved.
Unified Mobile Agent can experience many of the same failure cases as Unified CCE:
-
Side A/B failure
-
VRU failure
-
Unified CM failure
-
CTI server failure
There are also some failure cases that are unique to Unified Mobile Agent:
-
A situation where a Mobile Agent is using a cellular phone and the connection is dropped due to non-availability of a signal, is deemed as external failure. The agent must call back and log-in again.
-
If a Mobile Agent's phone line disconnects while using nailed connection mode, the agent must log in again to receive new calls.
Important Considerations
Before you proceed, consider the following Unified Mobile Agent limitations and considerations:
Failover
-
During a failover, if an agent in call by call mode answers an alerting call, the call can drop. This occurs because the media cannot be bridged when there is no active PG.
-
During a prolonged Peripheral Gateway (PG) failover, if an agent takes call control action for a Unified Mobile Agent-to-Unified Mobile Agent call, the call can drop. This occurs because the activating PG may not have information for all agents and calls at that point.
-
Unified Communications Manager failover causes a Mobile Agent call to be lost.
-
If a call by call Mobile Agent initiates a call (including a supervisor call) and does not answer the remote leg of the call before PG failover, the call fails. The agent must disconnect the remote agent call leg and reinitiate the call.
Performance
-
Because Unified Mobile Agent adds processing steps to Unified CCE default functionality, Mobile Agents may experience some delay in screen popup windows.
-
From a caller's perspective, the call by call delivery mode has a longer ring time compared with the nailed connection delivery mode. This is because Unified CCE does not start to dial the Mobile Agent's phone number until after the call information is routed to the agent desktop. In addition, the customer call media stream is not connected to the agent until after the agent answers the phone.
The caller hears a repeated ringtone while Unified CCE makes these connections.
Codec
The codec settings on the Peripheral Gateway and Voice Gateway must match. Perform the following procedure:
-
Launch the Peripheral Gateway Setup.
-
In the Peripheral Gateway Component Properties, select the UCM PIM and click Edit.
-
In the CallManager Parameters section, select the appropriate codec from the Mobile Agent Codec drop down list.
Figure 2. Mobile Agent Codec Selection 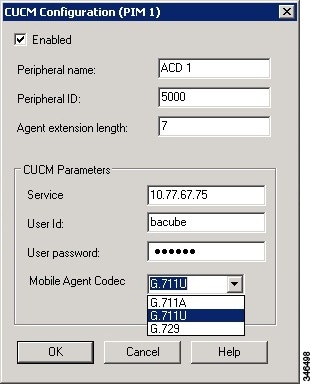
Silent Monitoring
Unified Mobile Agent provides the following silent monitoring support:
-
Unified Mobile Agent requires that caller and agent voice gateways be on separate devices if silent monitoring is to be used.
-
Unified Mobile Agent does not support desktop monitoring.
-
Whenever silent monitoring is used on Unified Mobile Agent, caller and agent voice gateways must be on separate devices. Similarly, if MTP is enabled when silent monitoring is used, MTP resources for caller and agent must also be on separate devices.
Mobile Agent Scalability
Mobile Agent scalability may be contingent on specific Unified CM versions. For more information, see the Solution Design Guide for Cisco Unified Contact Center Enterprise at https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/customer-collaboration/unified-contact-center-enterprise/products-implementation-design-guides-list.html.
Unsupported Features
The following is a list of unsupported features for Mobile Agent:
-
Web Callback
-
Blended Collaboration
-
Unified CM-based Silent Monitoring
-
Agent Request
Unified Mobile Agent Call Flows
This section provides sample Unified Mobile Agent call flows for:
-
Inbound calls
-
Local consultation calls
-
Remote consultation calls
-
Remote conference calls
In all Unified Mobile Agent call flows, the JTAPI Gateway maintains the signaling association between the inbound and outbound calls and, if necessary, performs further operations on the call. JTAPI Gateway, however, does not terminate media; it uses CTI to deliver the customer call from the inbound gateway port to the outbound gateway port.
This means that a Mobile Agent must use an agent desktop application to log in, change agent state, log out, send dual-tone multifrequency (DTMF) digits, and perform call control.
About Figures in This Section
The figures in this section:
-
Show a caller and a Mobile Agent in a cellular network. However, the same concepts apply whether the Mobile Agent is using an enterprise desk phone, an IP Phone spanning another Unified CM cluster, standard analog phone, or a third-party ACD phone.
-
Focus solely on call media flow; a Mobile Agent must use a CTI Desktop with broadband access to perform agent state and call control.
-
Show only a sampling of the call flows possible with Unified Mobile Agent.
Inbound Call Flow
The following figure shows an inbound call flow.
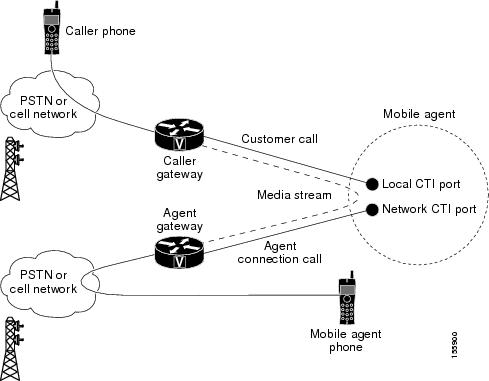
 Note |
Caller and Agent voice gateways can coreside on one device, except in deployments where Silent Monitoring is required. |
The following describes an inbound call flow:
-
The Mobile Agent becomes available to answer calls by:
-
Logging in to the corporate domain using VPN over the ADSL/Cable connection
-
Launching the agent desktop interface and logging in with their remote phone information
-
Entering the Ready mode
-
-
A customer call arrives at the Unified CC.
-
The JTAPI Gateway creates a Mobile Agent class to manage local and network CTI ports for a Mobile Agent.
-
The Router passes the call to the local CTI Port of a Mobile Agent.
-
The JTAPI Gateway places a call on a network CTI port to the agent's cell phone.
-
The JTAPI Gateway uses local and network CTI ports of the Mobile Agent to stream the media for the call from the inbound (caller) gateway port to the outbound (agent) gateway port.
Local Consult Calls
The following figure shows a consult call flow between a Mobile Agent and a local agent.
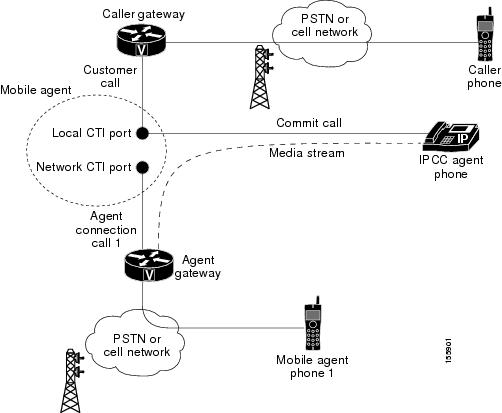
 Note |
Caller and Agent voice gateways can coreside on one device, except in deployments where Silent Monitoring is required. |
The following describes a local consult call flow:
-
The Mobile Agent becomes available to answer calls by:
-
Logging in to the corporate domain using VPN over the ADSL/Cable connection
-
Launching the agent desktop interface and logging in with their remote phone information
-
Entering the Ready mode
-
-
A customer call arrives at the Unified CC.
-
The JTAPI Gateway creates a Mobile Agent class to manage local and network CTI ports for a Mobile Agent.
-
The Router passes the call to the local CTI Port of a Mobile Agent.
-
The JTAPI Gateway places Agent Connection Call 1 on a network CTI port to the agent's cell phone.
-
The Mobile Agent places the customer call on hold and consults a local Unified CCE/Unified CCH agent.
-
The JTAPI Gateway uses local and network CTI ports of the Mobile Agent to stream the media for the call from the IP hard phone to the outbound gateway port.
Remote Consult Calls
The following figure shows a remote consult call flow between two Mobile Agents.
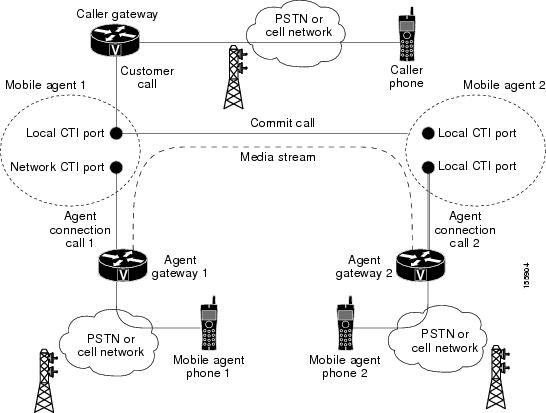
 Note |
Caller and Agent voice gateways can coreside on one device, except in deployments where Silent Monitoring is required. |
The following describes a remote consult call flow:
-
The Mobile Agent becomes available to answer calls by:
-
Logging in to the corporate domain using VPN over the ADSL/Cable connection
-
Launching the agent desktop interface and logging in with their remote phone information
-
Entering the Ready mode
-
-
A customer call arrives at the Unified CC.
-
The JTAPI Gateway creates a Mobile Agent class to manage local and network CTI ports for a Mobile Agent.
-
The Router passes the call to the local CTI Port of a Mobile Agent.
-
The JTAPI Gateway places Agent Connection Call 1 on a network CTI port to the agent's cell phone.
-
Mobile Agent 1 puts the customer call on hold and consults Mobile Agent 2.
-
The JTAPI Gateway uses the network CTI port of Mobile Agent 1 and the network CTI port of Mobile Agent 2 to stream the media for the call from the outbound gateway port on Agent Gateway 1 to the outbound gateway port on Agent Gateway 2.
Remote Conference Calls
The following figure shows a remote conference call flow between two Mobile Agents.
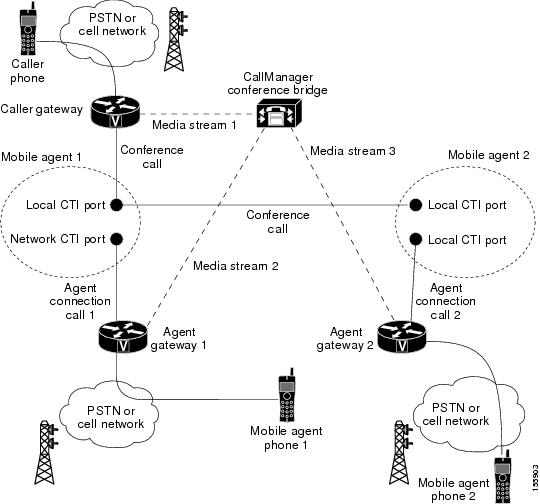
 Note |
Caller and Agent voice gateways can coreside on one device, except in deployments where Silent Monitoring is required. |
The following describes a remote conference call flow:
-
The Mobile Agent becomes available to answer calls by:
-
Logging in to the corporate domain using VPN over the ADSL/Cable connection
-
Launching the agent desktop interface and logging in with their remote phone information
-
Entering the Ready mode
-
-
A customer call arrives at the Unified CC.
-
The JTAPI Gateway creates a Mobile Agent class to manage local and network CTI ports for a Mobile Agent.
-
The Router passes the call to the local CTI Port of a Mobile Agent.
-
Unified CM redirects the media stream 1 from inbound gateway on the Caller Gateway to the conference bridge during call merging process.
-
The JTAPI Gateway uses local and network CTI ports of Mobile Agent 1 to loop the Media Stream 2 for the call from the outbound gateway port on the Agent Gateway 1 to the conference bridge.
-
The JTAPI Gateway uses local and network CTI ports of Mobile Agent 2 to loop the Media Stream 3 for the call from the outbound gateway port on the Agent Gateway 2 to the conference bridge.
Outbound Option Call Flow
The following figure shows a Outbound Option call flow between a customer and a Mobile Agent.
 Note |
Unified Mobile Agent supports Outbound Option calls in nailed connection delivery mode only. |
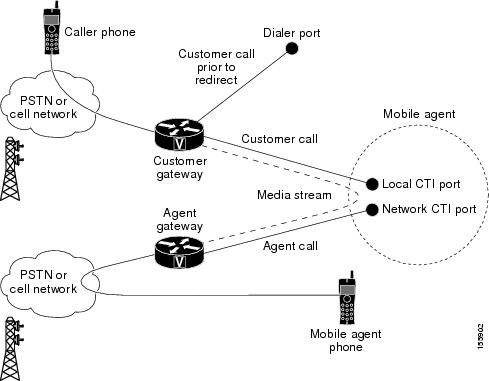
 Note |
Caller and Agent voice gateways can coreside on one device, except in deployments where Silent Monitoring is required. |
The following describes an Outbound Option call flow:
-
The Mobile Agent becomes available to answer calls by:
-
Logging in to the corporate domain using VPN over the ADSL/Cable connection
-
Launching the agent desktop interface and logging in with their remote phone information
-
Entering the Ready mode
-
-
The JTAPI Gateway creates a Mobile Agent class to manage local and network CTI ports for a Mobile Agent.
-
Outbound Option dials the customer number and, after reaching a live customer, the Dialer redirects the customer call to the local CTI Port of an Outbound Option Mobile Agent.
-
The JTAPI Gateway places a call on a network CTI port to the agent's cell phone.
-
The JTAPI Gateway uses local and network CTI ports of the Mobile Agent to stream the media for the call from the inbound gateway port to the outbound gateway port.
Unified Mobile Agent Reporting
Unified Mobile Agent-specific call data is contained in the following Cisco Unified Intelligence Center reports: Agent Team Historical, Agent Real Time, and Agent Skill Group Historical. These “All Field” reports contain information in multiple fields that show what kind of call the agent is on (nonmobile, call by call, nailed connection) and the Unified Mobile Agent phone number.
Notes about Mobile Agents and reporting:
-
The Mobile Agent must be logged in through the agent desktop for call data to be recorded in Unified CC reports.
-
Service level for Mobile Agent calls might be different than local agent calls, because it takes longer to connect the call to the agent.
For example, a call by call Mobile Agent might have a longer Answer Wait Time Average than a local agent. This is because Unified CCE/Unified CCH does not start to dial the Mobile Agent phone number until after the call information is routed to the agent desktop. In addition, the customer call media stream is not connected to the agent until after the agent answers the phone.
For more information about Unified Mobile Agent fields in the database schema, see Database Schema Handbook for Cisco Unified Contact Center Enterprise.
 Feedback
Feedback