Customer Profiles
This chapter describes various configurations and combinations of the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch and the Cisco ITP that are built on top of the basic Shared Point Code and Mated STP-Pair configurations documented in Chapter 1 "SS7 Basic Configurations," to form the following customer profiles:
•![]() Multiple Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Nodes per ITP
Multiple Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Nodes per ITP
•![]() Multiple OPCs on the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch
Multiple OPCs on the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch
•![]() Multiple Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Nodes Sharing the Same OPC
Multiple Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Nodes Sharing the Same OPC
•![]() Geographically Separated Mated STP Pair with SG Priority Routing
Geographically Separated Mated STP Pair with SG Priority Routing
Multiple Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Nodes per ITP
This profile, illustrated in Figure 3-1, is recommended for a customer who is setting up an all-IP telephony network based on Cisco BTS 10200 softswitches and has a long-term plan for network expansion. Each BTS has only one Origination Point Code (OPC), and this profile is appropriate when there is a requirement for high capacity traffic to each OPC.
A pair of high capacity Cisco 73XX or 7507 series ITP nodes are required to provide the necessary throughput. The topology between ITPs and Signal Transfer Point (STPs) forms a typical Signaling System 7 (SS7) STP quad. Global title translation (GTT) is supported on the Cisco ITP.

Note ![]() This profile is only available when connecting to the SS7 network via D-links. Therefore, a mated STP pair must be used.
This profile is only available when connecting to the SS7 network via D-links. Therefore, a mated STP pair must be used.
Figure 3-1 Multiple Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitches per ITP
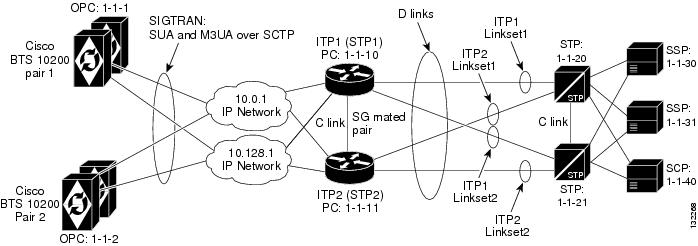
Cisco ITP Configuration Example
The Cisco ITP configuration information for this customer profile is similar to the basic Mated STP-Pair configuration described in Chapter 2 "Provisioning Basic SS7 Configurations." However, in this profile, extra Application Server Process (ASP) configuration information is necessary to communicate with the second Cisco BTS 10200. There is also extra information in the application server (AS) configuration section for routing to each of the BTS nodes based on Destination Point Code (DPC) (BTS OPC value).
The following example provisions ASP and AS configuration elements for ITP1:
ITP1 Configuration — It is important to note that ITP2 will have the same ASP and AS configuration information that is shown below for ITP1.
The ASP configuration for BTS1 Active and Standby Nodes— For ISDN user part (ISUP) - M3UA
cs7 asp PRI_ISUP_BTS1 11146 2905 m3ua
remote-ip 10.0.1.5
remote-ip 10.128.1.2
cs7 asp SEC_ISUP_BTS1 11146 2905 m3ua
remote-ip 10.0.1.6
remote-ip 10.128.1.3
Transaction Capability Application Part (TCAP)/AIN - SUA
cs7 asp PRI_AIN_BTS1 12205 14001 sua
remote-ip 10.0.1.5
remote-ip 10.128.1.2
!
cs7 asp SEC_AIN_BTS1 12205 14001 sua
remote-ip 10.0.1.6
remote-ip 10.128.1.3
TCAP/PTC - SUA
cs7 asp PRI_PTC_BTS1 12235 14001 sua
remote-ip 10.0.1.5
remote-ip 10.128.1.2
!
cs7 asp SEC_PTC_BTS1 12235 14001 sua
remote-ip 10.0.1.6
remote-ip 10.128.1.3
AS configuration for BTS1—The routing context entries are as follows:
routing context = 1, DPC(BTS OPC)=1.1.1 service indicator=ISUP
cs7 as ISUP_BTS1 m3ua
routing-key 1 1.1.1 si isup
asp PRI_ISUP_BTS1
asp SEC_ISUP_BTS1
traffic-mode override
cs7 as LNP_BTS1 sua
routing-key 4402 1.1.1 si sccp ssn 247
asp PRI_AIN_BTS1
asp SEC_AIN_BTS1
traffic-mode override
cs7 as 800T_BTS1 sua
routing-key 4401 1.1.1 si sccp ssn 254
asp PRI_AIN_BTS1
asp SEC_AIN_BTS1
traffic-mode override
!
cs7 as 800A_BTS1 sua
routing-key 4403 1.1.1 si sccp ssn 248
asp PRI_AIN_BTS1
asp SEC_AIN_BTS1
traffic-mode override
!
cs7 as CNAM_BTS1 sua
routing-key 4404 1.1.1 si sccp ssn 232
asp PRI_PTC_BTS1
asp SEC_PTC_BTS1
traffic-mode override
!
cs7 as ACAR_BTS1 sua
routing-key 4405 1.1.1 si sccp ssn 251
asp PRI_PTC_BTS1
asp SEC_PTC_BTS1
traffic-mode override
ASP configuration for BTS2 active and standby modes—ISUP - M3UA
cs7 asp PRI_ISUP_BTS2 11146 2905 m3ua
remote-ip 10.0.1.7
remote-ip 10.128.1.4
cs7 asp SEC_ISUP_BTS2 11146 2905 m3ua
remote-ip 10.0.1.8
remote-ip 10.128.1.5
Transaction Capabilities Application Part (TCAP)/AIN - SUA
cs7 asp PRI_AIN_BTS2 12205 14001 sua
remote-ip 10.0.1.7
remote-ip 10.128.1.4
!
cs7 asp SEC_AIN_BTS2 12205 14001 sua
remote-ip 10.0.1.8
remote-ip 10.128.1.5
TCAP/PTC - SUA
cs7 asp PRI_PTC_BTS2 12235 14001 sua
remote-ip 10.0.1.5
remote-ip 10.128.1.4
!
cs7 asp SEC_PTC_BTS2 12235 14001 sua
remote-ip 10.0.1.6
remote-ip 10.128.1.5
AS configuration for BTS2—The DPC value changes to 1.1.2 for sending messages to BTS2
cs7 as ISUP_BTS2 m3ua
routing-key 2 1.1.2 si isup
asp PRI_ISUP_BTS2
asp SEC_ISUP_BTS2
traffic-mode override
cs7 as LNP_BTS2 sua
routing-key 4502 1.1.1 si sccp ssn 247
asp PRI_AIN_BTS2
asp SEC_AIN_BTS2
traffic-mode override
cs7 as 800T_BTS2 sua
routing-key 4501 1.1.1 si sccp ssn 254
asp PRI_AIN_BTS2
asp SEC_AIN_BTS2
traffic-mode override
!
cs7 as 800A_BTS2 sua
routing-key 4503 1.1.1 si sccp ssn 248
asp PRI_AIN_BTS2
asp SEC_AIN_BTS2
traffic-mode override
!
cs7 as CNAM_BTS2 sua
routing-key 4504 1.1.1 si sccp ssn 232
asp PRI_PTC_BTS2
asp SEC_PTC_BTS2
traffic-mode override
!
cs7 as ACAR_BTS2 sua
routing-key 4505 1.1.1 si sccp ssn 251
asp PRI_PTC_BTS2
asp SEC_PTC_BTS2
traffic-mode override
Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Configuration Example
Provisioning the Cisco BTS 10200 for this profile is essentially the same as the basic Mated STP-Pair profile given in Chapter 1 "SS7 Basic Configurations." However, the following provisioning script is necessary for the secondary BTS:
CA Configuration
add ca-config type=MGCP-INIT-TERMS;value=160;datatype=integer;
add ca-config type=MGCP-INIT-DURATION;value=5;datatype=integer;
add ca-config type=MGCP-ICMP-PING-RETRANSMIT-DURATION;value=5;datatype=integer;
add ca-config type=MGCP-ICMP-PING-RETRY-COUNT;value=5;datatype=integer;
add ca-config type=MGCP-MAX-UNREACH-COUNT;value=5;datatype=integer;
add ca-config type=MGCP-MAX-FAULT-COUNT;value=5;datatype=integer;
add ca-config type=MGCP-ADM-RESP-TIME;value=300;datatype=integer;
add ca-config type=MGCP-SIG-TOS-LOWDELAY;value=Y;datatype=boolean;
add ca-config type=MGCP-SIG-TOS-PRECEDENCE;value=1;datatype=integer;
add ca-config type=MGCP-SIG-TOS-RELIABILITY;value=Y;datatype=boolean;
add ca-config type=MGCP-SIG-TOS-THROUGHPUT;value=Y;datatype=boolean;
CA & FS—The CA147 and FSAIN206 ids are different than on BTS1.
add call-agent id=CA147; tsap-addr-sidea=hrn11ca; mgw-monitoring-enabled=N;
add feature-server id=FSAIN206; tsap-addr-sidea=hrn11ca:11205; type=AIN;
SIGTRAN components
add user-part-variant id=ANSISS7_GR317;
add sg id=sg1; description=Signaling gateway 1;
add sg id=sg2; description=Signaling gateway 2;
add sg-grp id=sg-grp1; sg1-id=sg1; sg2-id=sg2 description=SG group 1;
add sgp id=sg1-sgp1 ; sg-id=sg1; description=SG process 1 for sg1;
add sgp id=sg2-sgp1 ; sg-id=sg2; description=SG process 1 for sg2;
OPC value for BTS2 is 1-1-2
add opc id=opc1; point-code=1-1-2; description=OPC; point-code-type=ANSI_CHINA;
add dpc id=dpc1; point-code=1-1-30; description=DPC 1; point-code-type=ANSI_CHINA;
add dpc id=dpc2; point-code=1-1-31; description=DPC 2; point-code-type=ANSI_CHINA;
ISUP routing keys—A unique rc value was needed when defining the routing-key. It must match the rc value that is defined in the associated AS/routing-key definition in the ITPs. This routing key has a different OPC value than defined for BTS1.
add routing-key id=rk1; opc-id=opc1; sg-grp-id=sg-grp1; si=ISUP; rc=2; platform-id=CA147;
add call-ctrl-route id=dpc1-route1; dpc-id=dpc1; routing-key-id=rk1; si=isup; user-part-variant-id= ANSISS7_GR317
add call-ctrl-route id=dpc2-route1; dpc-id=dpc2; routing-key-id=rk1; si=isup; user-part-variant-id= ANSISS7_GR317;
add sctp-assoc-profile id=sctp-prof;
SCTP associations
add sctp-assoc id=sg1-sgp1-sctp; sgp-id=sg1-sgp1; sctp-assoc-profile-id=sctp-prof; platform-id=CA147; remote-port=2905; remote-tsap-addr1=10.0.1.54; remote-tsap-addr2=10.128.1.239; ip-tos-precedence=ROUTINE;
add sctp-assoc id=sg2-sgp1-sctp; sgp-id=sg2-sgp1; sctp-assoc-profile-id=sctp-prof; platform-id=CA147; remote-port=2905; remote-tsap-addr1=10.0.1.55; remote-tsap-addr2=10.128.1.240; ip-tos-precedence=ROUTINE;
Dial plan profile
add digman-profile id=pretrans;
add digman id=pretrans; rule=1; match-string=^*; replace-string=&; match-noa=any; replace-noa=VSC;
add digman id=pretrans; rule=2; match-string=^#; replace-string=&; match-noa=any; replace-noa=VSC;
add digman-profile id=ani_20;
add digman id=ani_20; rule=1; match-string=^20; replace-string=none;
add dial-plan-profile id=dp-1; nanp-dial-plan=Y; description=NA dial plan profile; dnis-digman-id=pretrans; ani-digman-id=ani_20;
SS7 TG
add ss7-ansi-tg-profile ID=ansi-tg-prof;
add trunk-grp ID=1; call_agent_id=CA147; tg_type=SS7; direction=BOTH; tg_profile_id=ansi-tg-prof; call-ctrl-route-id=dpc1-route1; dial-plan-id=dp-1; description=TG to DPC 1; MGCP_PKG_TYPE=T;
add trunk-grp ID=2; call_agent_id=CA147; tg_type=SS7; direction=BOTH; tg_profile_id=ansi-tg-prof; call-ctrl-route-id=dpc2-route1; dial-plan-id=dp-1; description=TG to DPC 2; MGCP_PKG_TYPE=T;
MGW
add mgw-profile id=as5300-prof; vendor=Cisco; mgcp-hairpin-supp=n; MGCP_RSIPSTAR_SUPP=N; MGCP_TERM_INIT_LEVEL=0; RBK_ON_CONN_SUPP=N; MGCP_VERSION=MGCP_1_0; mgcp-max2-retries=3; fax-t38-camode-supp=Y; mgcp-keepalive-interval=60; mgcp-keepalive-retries=10; mgcp-t-tran=400; mgcp-max1-retries=2; mgcp-t-longtran=5; mgcp-default-pkg=NONE; MGCP_3WAY_HSHAKE_SUPP=N; mgw_type=AS5300; PC_MPTIME_SUPP=N;
MGCP_VERSION=MGCP_1_0; PC_MPTIME_SUPP=N;
add mgw id=va-5350-23; tsap-addr=va-5350-23.hrndevtest.cisco.com; call-agent-id=CA147; mgw-profile-id=as5300-prof; type=TGW;
SS7 terminations and trunks
add termination prefix=S3/DS1-4/; port-start=1; port-end=31; type=trunk; mgw-id=va-5350-23;
add termination prefix=S3/DS1-5/; port-start=1; port-end=31; type=trunk; mgw-id=va-5350-23;
add trunk cic-start=1; cic-end=31; tgn-id=1; mgw-id=va-5350-23; termination-prefix=S3/DS1-4/; termination-port-start=1; termination-port-end=31;
add trunk cic-start=1; cic-end=31; tgn-id=2; mgw-id=va-5350-23; termination-prefix=S3/DS1-5/; termination-port-start=1; termination-port-end=31;
SS7 routes, route guides and destinations
add route id=dpc1-route; tg_selection=RR; tgn1_id=1;
add route id=dpc2-route; tg_selection=RR; tgn1_id=2;
add route-guide id=dpc1-rg; policy-type=ROUTE; policy-id=dpc1-route;
add route-guide id=dpc2-rg; policy-type=ROUTE; policy-id=dpc2-route;
add destination dest-id=dpc1-dest; call-type=LOCAL; route-type=ROUTE; route-guide-id=dpc1-rg;
add destination dest-id=dpc2-dest; call-type=LOCAL; route-type=ROUTE; route-guide-id=dpc2-rg;
TCAP/SUA provisioning for LNP
add sctp-assoc id=sg1-sgp1-sctp-ain; sgp-id=sg1-sgp1; sctp-assoc-profile-id=sctp-prof; platform-id=FSAIN205; remote-port=14001; remote-tsap-addr1=10.0.1.54; remote-tsap-addr2=10.128.1.239; ip-tos-precedence=ROUTINE;
add sctp-assoc id=sg2-sgp1-sctp-ain; sgp-id=sg2-sgp1; sctp-assoc-profile-id=sctp-prof; platform-id=FSAIN205; remote-port=14001; remote-tsap-addr1=10.0.1.55; remote-tsap-addr2=10.128.1.240; ip-tos-precedence=ROUTINE;
add sctp-assoc id=sg1-sgp1-sctp-ptc; sgp-id=sg1-sgp1; sctp-assoc-profile-id=sctp-prof; platform-id=FSPTC235; remote-port=14001; remote-tsap-addr1=10.0.1.54; remote-tsap-addr2=10.128.1.239; ip-tos-precedence=ROUTINE;
add sctp-assoc id=sg2-sgp1-sctp-ptc; sgp-id=sg2-sgp1; sctp-assoc-profile-id=sctp-prof; platform-id=FSPTC235; remote-port=14001; remote-tsap-addr1=10.0.1.55; remote-tsap-addr2=10.128.1.240; ip-tos-precedence=ROUTINE;
add sccp-nw id=1;NET_IND=NATIONAL;SUB_SVC=NATIONAL;HOP_COUNT=3;
add subsystem-profile id=SS_LNP; platform-id=FSAIN205; description=LNP subsystem;
add subsystem-profile id=SS_800A; platform-id=FSAIN205; description=AIN 800 subsystem;
add subsystem-profile id=SS_800T; platform-id=FSAIN205; description=IN1 800 subsystem;
add subsystem-profile id=SS_CNAM; platform-id=FSAIN205; description=CNAM subsystem;
add subsystem-profile id=SS_ACAR; platform-id=FSPTC235; description=ACAR subsystem;
add subsystem id=SS_LNP; opc-id=opc1; local-ssn=247; remote-ssn=247; sccp-nw-id=1; SCCP_VERSION=ANS92; TCAP_VERSION=ANS92; APPLICATION_VERSION=AIN01;
add subsystem id=SS_800A; opc-id=opc1; local-ssn=248; remote-ssn=248; sccp-nw-id=1; SCCP_VERSION=ANS92; TCAP_VERSION=ANS92; APPLICATION_VERSION=AIN01;
add subsystem id=SS_CNAM; opc-id=opc1; local-ssn=232; remote-ssn=232; sccp-nw-id=1; SCCP_VERSION=ANS92; TCAP_VERSION=ANS92; APPLICATION_VERSION=IN1;
add subsystem id=SS_800T; opc-id=opc1; local-ssn=254; remote-ssn=254; sccp-nw-id=1; SCCP_VERSION=ANS92; TCAP_VERSION=ANS92; APPLICATION_VERSION=IN1;
add subsystem id=SS_ACAR; opc-id=opc1; local-ssn=251; remote-ssn=251; sccp-nw-id=1; SCCP_VERSION=ANS92; TCAP_VERSION=ANS92; APPLICATION_VERSION=IN1;
This routing key differs from the one on BTS1
add routing-key id=rk_lnp; opc-id=opc1; sg-grp-id=sg_grp1; si=SCCP; rc=4502; PLATFORM_ID=FSAIN205; ssn-id=SS_LNP;
add routing-key id=rk_800a; opc-id=opc1; sg-grp-id=sg_grp1; si=SCCP; rc=4503; PLATFORM_ID=FSAIN205; ssn-id=SS_800A;
add routing-key id=rk_cnam; opc-id=opc1; sg-grp-id=sg_grp1; si=SCCP; rc=4504; PLATFORM_ID=FSAIN205; ssn-id=SS_CNAM;
add routing-key id=rk_800t; opc-id=opc1; sg-grp-id=sg_grp1; si=SCCP; rc=4501; PLATFORM_ID=FSAIN205; ssn-id=SS_800T;
add routing-key id=rk_acar; opc-id=opc1; sg-grp-id=sg_grp1; si=SCCP; rc=4505; PLATFORM_ID=FSPTC235; ssn-id=SS_ACAR;
Provisioned DPC is the STP capabilty point code
add dpc id=stp_cap_pc; point-code=1-1-22; point-code-type=ANSI_CHINA; description=Capability Point Code of STPs
add feature fname=LNP; feature-server-id=FSAIN206; description=Local number portability; tdp1=COLLECTED_INFORMATION; tid1=LNP_TRIGGER; ttype1=R;
add ported-office-code digit-string=301-612; in-call-agent=n;
add CA-Config type=DEFAULT-LNP-SLHR-ID; datatype=string; value=slhr_lnp;
add slhr-profile id=slhr_lnp;
add slhr id=slhr_lnp; gtt-req=Y; tt=11; GTT_ADDR_TYPE=CDPN; GTT_ADDR=3; opc-id=opc1; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; ssn_id=SSN_LNP1;
add sccp-route opc-id=opc1; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; rk-id=itp-grp-rk2; ssn-id=SSN_LNP1; description=LNP for opc1;
add pop ID=50901; STATE=tx; COUNTRY=US; TIMEZONE=CDT; LOCAL_7D_DIALING=Y; ITP=N; ZERO_MINUS=LEC; BLOCK_EAWOPIC=Y; CNAM_OPTION=EXT_LIDB; PIC2_REQD=N; MY_LRN=4692559999; TREAT_IMS_ANONYMOUS=N; OPC_ID=opc1; ZERO_PLUS_LOCAL=N
Multiple OPCs on the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch
This customer profile, illustrated in Figure 3-2, is based on the Mated STP-Pair profile. It is recommended for the customer who wants to emulate multiple legacy SS7 switches with one high-capacity Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch.
A similar A-link profile can also be implemented. However, the A-link profile requires a separate ITP-Group for each OPC on the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch.
Figure 3-2 Multiple OPCs on the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch
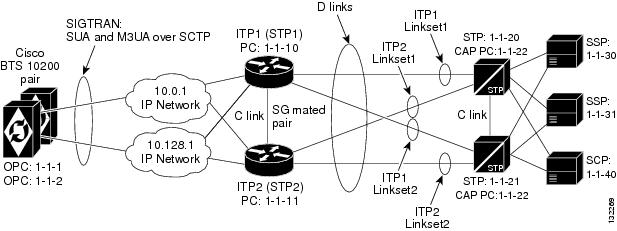
The Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch also supports up to 30 OPCs when the SIGTRAN signaling gateway supports Single User Account (SUA) and MTP3 User Adaptation Layer (M3UA) in a D-link configuration.
Configuration Requirements for Supporting 30 OPCs
The user must complete the following tasks to configure the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch to support 30 OPCs:
The following tasks include examples of CLI commands that illustrate how to configure the feature. Most of these tables have additional tokens that are not included in the examples.
•![]() Subsystem_grp Table:
Subsystem_grp Table:
add subsystem_grp id=CNAM; platform_id=FSPTC235; tcap_version=ANS-92;
•![]() Subsystem Table:
Subsystem Table:
add subsystem id=CNAM; opc-id=opc_tx; local-ssn=232; remote-ssn=232; sccp-nw-id=1; SCCP_VERSION=ANS92; application-version=IN1;
add subsystem id=CNAM; opc-id=opc_nc; local-ssn=232; remote-ssn=232; sccp-nw-id=1; SCCP_VERSION=ANS92; application-version=IN1;
•![]() SLHR Table:
SLHR Table:
add slhr id=slhr_cnam; opc-id=opc_tx; dpc-id=stp1; subsystem-grp-id=CNAM; gtt-req=Y; tt=5; GTT_ADDR_TYPE=CLGN; GTT_ADDR=3;
•![]() SCCP_Route Table
SCCP_Route Table
add sccp-route opc-id=opc_tx; dpc-id=stp1; subsystem-grp-id=CNAM; rk-id=rk_cnam_tx;
•![]() Routing_Key Table
Routing_Key Table
add routing-key id=rk_cnam_tx; opc-id=opc_tx; sg-grp-id=sg_grp; si=SCCP; rc=204; PLATFORM_ID=FSPTC325; subsystem-grp-id=CNAM;
•![]() Controlling the Subsystem Group In or Out of Service
Controlling the Subsystem Group In or Out of Service
The Subsystem Group table has a status associated with it. The operator can control a subsystem group in or out of service. Controlling the subsystem group out of service has the same affect as controlling all the subsystems in the subsystem group out of service. Controlling the subsystem group in service puts all subsystems in the group in service.
The following CLI command controls both subsystem/OPC combinations out of service:
control subsystem_grp id=CNAM; mode=forced; target_state=UOS;
SUBSYSTEM GRP ID -> CNAM
INITIAL STATE -> User in service
RESULT STATE -> User out of service
REQUEST STATE -> User out of service
FAIL REASON -> ADM found no failure
REASON -> ADM executed successfully
RESULT -> ADM configure result in success
Reply : Success: CLI change successful

Note ![]() For a complete list of all CLI tables and tokens, refer to the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch CLI Database.
For a complete list of all CLI tables and tokens, refer to the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch CLI Database.
Alternate Base Profiles
Although this profile is based on the Mated STP-Pair configuration, a similar Shared Point Code configuration can be implemented. However, it requires a separate ITP Group for each OPC on the Cisco BTS 10200.
ITP Configuration
The ITP configuration for this profile is essentially identical to the one for the Mated STP-Pair configuration documented in Chapter 1 "SS7 Basic Configurations." However, there is an extra AS configuration for the added OPC on BTS1. This additional AS configuration information is shown here:
cs7 as BtsIsupAs2 m3ua
routing-key 2 1.1.2 si isup
asp PrimaryBtsIsupAsp
asp SecondaryBtsIsupAsp
traffic-mode override
cs7 as LNP2_BTS1 sua
routing-key 4412 1.1.2 si sccp ssn 247
asp PRI_AIN_BTS1
asp SEC_AIN_BTS1
traffic-mode override
cs7 as 800T2_BTS1 sua
routing-key 4411 1.1.2 si sccp ssn 254
asp PRI_AIN_BTS1
asp SEC_AIN_BTS1
traffic-mode override
cs7 as 800A2_BTS1 sua
routing-key 4413 1.1.2 si sccp ssn 248
asp PRI_AIN_BTS1
asp SEC_AIN_BTS1
traffic-mode override
cs7 as CNAM2_BTS1 sua
routing-key 4414 1.1.2 si sccp ssn 232
asp PRI_PTC_BTS1
asp SEC_PTC_BTS1
traffic-mode override
cs7 as ACAR2_BTS1 sua
routing-key 4415 1.1.2 si sccp ssn 251
asp PRI_PTC_BTS1
asp SEC_PTC_BTS1
traffic-mode override
Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Configuration Example
The Cisco BTS 10200 provisioning information is the same as the basic Mated STP-Pair configuration given in Chapter 1 "SS7 Basic Configurations," with additional objects based on the provisioning of a second OPC, OPC 1.1.2. The BTS configuration is shown here.
CA configuration
add ca-config type=MGCP-INIT-TERMS;value=160;datatype=integer;
add ca-config type=MGCP-INIT-DURATION;value=5;datatype=integer;
add ca-config type=MGCP-ICMP-PING-RETRANSMIT-DURATION;value=5;datatype=integer;
add ca-config type=MGCP-ICMP-PING-RETRY-COUNT;value=5;datatype=integer;
add ca-config type=MGCP-MAX-UNREACH-COUNT;value=5;datatype=integer;
add ca-config type=MGCP-MAX-FAULT-COUNT;value=5;datatype=integer;
add ca-config type=MGCP-ADM-RESP-TIME;value=300;datatype=integer;
add ca-config type=MGCP-SIG-TOS-LOWDELAY;value=Y;datatype=boolean;
add ca-config type=MGCP-SIG-TOS-PRECEDENCE;value=1;datatype=integer;
add ca-config type=MGCP-SIG-TOS-RELIABILITY;value=Y;datatype=boolean;
add ca-config type=MGCP-SIG-TOS-THROUGHPUT;value=Y;datatype=boolean;
CA & FS
add call-agent id=CA146; tsap-addr-sidea=hrn11ca; mgw-monitoring-enabled=N;
add feature-server id=FSAIN205; tsap-addr-sidea=hrn11ca:11205; type=AIN;
SIGTRAN and SS7 components
add user-part-variant id=ANSISS7_GR317;
add sg id=sg1; description=Signaling gateway 1;
add sg id=sg2; description=Signaling gateway 2;
add sg-grp id=sg-grp1; sg1-id=sg1; sg2-id=sg2 description=SG group 1;
add sgp id=sg1-sgp1 ; sg-id=sg1; description=SG process 1 for sg1;
add sgp id=sg2-sgp1 ; sg-id=sg2; description=SG process 1 for sg2;
add opc id=opc1; point-code=1-1-1; description=OPC1; point-code-type=ANSI_CHINA;
Second OPC
add opc id=opc2; point-code=1-1-2; description=OPC2; point-code-type=ANSI_CHINA;
add dpc id=dpc1; point-code=1-1-30; description=DPC 1; point-code-type=ANSI_CHINA;
add dpc id=dpc2; point-code=1-1-31; description=DPC 2; point-code-type=ANSI_CHINA;
ISUP routing keys
add routing-key id=rk1; opc-id=opc1; sg-grp-id=sg-grp1; si=ISUP; rc=1; platform-id=CA146;
The new ISUP routing key is added for OPC2
add routing-key id=rk2; opc-id=opc2; sg-grp-id=sg-grp1; si=ISUP; rc=2; platform-id=CA146;
add call-ctrl-route id=dpc1-route1; dpc-id=dpc1; routing-key-id=rk1; si=isup; user-part-variant-id= ANSISS7_GR317
add call-ctrl-route id=dpc2-route1; dpc-id=dpc2; routing-key-id=rk1; si=isup; user-part-variant-id= ANSISS7_GR317;
Two new routes are added for OPC2
add call-ctrl-route id=dpc1-route2; dpc-id=dpc1; routing-key-id=rk2; si=isup; user-part-variant-id= ANSISS7_GR317
add call-ctrl-route id=dpc2-route2; dpc-id=dpc2; routing-key-id=rk2; si=isup; user-part-variant-id= ANSISS7_GR317;
add sctp-assoc-profile id=sctp-prof;
SCTP associations
add sctp-assoc id=sg1-sgp1-sctp; sgp-id=sg1-sgp1; sctp-assoc-profile-id=sctp-prof; platform-id=CA146; remote-port=2905; remote-tsap-addr1=10.0.1.54; remote-tsap-addr2=10.128.1.239; ip-tos-precedence=ROUTINE;
add sctp-assoc id=sg2-sgp1-sctp; sgp-id=sg2-sgp1; sctp-assoc-profile-id=sctp-prof; platform-id=CA146; remote-port=2905; remote-tsap-addr1=10.0.1.55; remote-tsap-addr2=10.128.1.240; ip-tos-precedence=ROUTINE;
Dial plan profile
add digman-profile id=pretrans;
add digman id=pretrans; rule=1; match-string=^*; replace-string=&; match-noa=any; replace-noa=VSC;
add digman id=pretrans; rule=2; match-string=^#; replace-string=&; match-noa=any; replace-noa=VSC;
add digman-profile id=ani_20;
add digman id=ani_20; rule=1; match-string=^20; replace-string=none;
add dial-plan-profile id=dp-1; nanp-dial-plan=Y; description=NA dial plan profile; dnis-digman-id=pretrans; ani-digman-id=ani_20;
SS7 TG
add ss7-ansi-tg-profile ID=ansi-tg-prof;
add trunk-grp ID=1; call_agent_id=CA146; tg_type=SS7; direction=BOTH; tg_profile_id=ansi-tg-prof; call-ctrl-route-id=dpc1-route1; dial-plan-id=dp-1; description=TG to DPC 1; MGCP_PKG_TYPE=T;
add trunk-grp ID=2; call_agent_id=CA146; tg_type=SS7; direction=BOTH; tg_profile_id=ansi-tg-prof; call-ctrl-route-id=dpc2-route1; dial-plan-id=dp-1; description=TG to DPC 2; MGCP_PKG_TYPE=T;
Two new trunk groups are added for OPC2
add trunk-grp ID=3; call_agent_id=CA146; tg_type=SS7; direction=BOTH; tg_profile_id=ansi-tg-prof; call-ctrl-route-id=dpc1-route2; dial-plan-id=dp-1; description=TG2 to DPC 1; MGCP_PKG_TYPE=T;
add trunk-grp ID=4; call_agent_id=CA146; tg_type=SS7; direction=BOTH; tg_profile_id=ansi-tg-prof; call-ctrl-route-id=dpc2-route2; dial-plan-id=dp-1; description=TG2 to DPC 2; MGCP_PKG_TYPE=T;
MGW
add mgw-profile id=as5300-prof; vendor=Cisco; mgcp-hairpin-supp=n; MGCP_RSIPSTAR_SUPP=N; MGCP_TERM_INIT_LEVEL=0; RBK_ON_CONN_SUPP=N; MGCP_VERSION=MGCP_1_0; mgcp-max2-retries=3; fax-t38-camode-supp=Y; mgcp-keepalive-interval=60; mgcp-keepalive-retries=10; mgcp-t-tran=400; mgcp-max1-retries=2; mgcp-t-longtran=5; mgcp-default-pkg=NONE; MGCP_3WAY_HSHAKE_SUPP=N; mgw_type=AS5300; PC_MPTIME_SUPP=N;
MGCP_VERSION=MGCP_1_0; PC_MPTIME_SUPP=N;
add mgw id=va-5350-23; tsap-addr=va-5350-23.hrndevtest.cisco.com; call-agent-id=CA146; mgw-profile-id=as5300-prof; type=TGW;
SS7 terminations and trunks
add termination prefix=S3/DS1-4/; port-start=1; port-end=31; type=trunk; mgw-id=va-5350-23;
add termination prefix=S3/DS1-5/; port-start=1; port-end=31; type=trunk; mgw-id=va-5350-23;
add trunk cic-start=1; cic-end=31; tgn-id=1; mgw-id=va-5350-23; termination-prefix=S3/DS1-4/; termination-port-start=1; termination-port-end=31;
add trunk cic-start=1; cic-end=31; tgn-id=2; mgw-id=va-5350-23; termination-prefix=S3/DS1-5/; termination-port-start=1; termination-port-end=31;
New termination and trunk information for OPC2
add termination prefix=S3/DS1-6/; port-start=1; port-end=31; type=trunk; mgw-id=va-5350-23;
add termination prefix=S3/DS1-7/; port-start=1; port-end=31; type=trunk; mgw-id=va-5350-23;
add trunk cic-start=1; cic-end=31; tgn-id=3; mgw-id=va-5350-23; termination-prefix=S3/DS1-6/; termination-port-start=1; termination-port-end=31;
add trunk cic-start=1; cic-end=31; tgn-id=4; mgw-id=va-5350-23; termination-prefix=S3/DS1-7/; termination-port-start=1; termination-port-end=31;
SS7 routes, route guides and destinations
add route id=dpc1-route; tg_selection=RR; tgn1_id=1;
add route id=dpc2-route; tg_selection=RR; tgn1_id=2;
add route-guide id=dpc1-rg; policy-type=ROUTE; policy-id=dpc1-route;
add route-guide id=dpc2-rg; policy-type=ROUTE; policy-id=dpc2-route;
add destination dest-id=dpc1-dest; call-type=LOCAL; route-type=ROUTE; route-guide-id=dpc1-rg;
add destination dest-id=dpc2-dest; call-type=LOCAL; route-type=ROUTE; route-guide-id=dpc2-rg;
New route, route guide and destination information for OPC2
add route id=dpc1-route2; tg_selection=RR; tgn1_id=3;
add route id=dpc2-route2; tg_selection=RR; tgn1_id=4;
add route-guide id=dpc1-rg2; policy-type=ROUTE; policy-id=dpc1-route2;
add route-guide id=dpc2-rg2; policy-type=ROUTE; policy-id=dpc2-route2;
add destination dest-id=dpc1-dest2; call-type=LOCAL; route-type=ROUTE; route-guide-id=dpc1-rg2;
add destination dest-id=dpc2-dest2; call-type=LOCAL; route-type=ROUTE; route-guide-id=dpc2-rg2;
TCAP/SUA Provisioning for LNP
add sctp-assoc id=sg1-sgp1-sctp-ain; sgp-id=sg1-sgp1; sctp-assoc-profile-id=sctp-prof; platform-id=FSAIN205; remote-port=14001; remote-tsap-addr1=10.0.1.54; remote-tsap-addr2=10.128.1.239; ip-tos-precedence=ROUTINE;
add sctp-assoc id=sg2-sgp1-sctp-ain; sgp-id=sg2-sgp1; sctp-assoc-profile-id=sctp-prof; platform-id=FSAIN205; remote-port=14001; remote-tsap-addr1=10.0.1.55; remote-tsap-addr2=10.128.1.240; ip-tos-precedence=ROUTINE;
add sctp-assoc id=sg1-sgp1-sctp-ptc; sgp-id=sg1-sgp1; sctp-assoc-profile-id=sctp-prof; platform-id=FSPTC235; remote-port=14001; remote-tsap-addr1=10.0.1.54; remote-tsap-addr2=10.128.1.239; ip-tos-precedence=ROUTINE;
add sctp-assoc id=sg2-sgp1-sctp-ptc; sgp-id=sg2-sgp1; sctp-assoc-profile-id=sctp-prof; platform-id=FSPTC235; remote-port=14001; remote-tsap-addr1=10.0.1.55; remote-tsap-addr2=10.128.1.240; ip-tos-precedence=ROUTINE;
add sccp-nw id=1;NET_IND=NATIONAL;SUB_SVC=NATIONAL;HOP_COUNT=3;
add subsystem-profile id=SS_LNP; platform-id=FSAIN205; description=LNP subsystem;
add subsystem-profile id=SS_800A; platform-id=FSAIN205; description=AIN 800 subsystem;
add subsystem-profile id=SS_800T; platform-id=FSAIN205; description=IN1 800 subsystem;
add subsystem-profile id=SS_CNAM; platform-id=FSAIN205; description=CNAM subsystem;
add subsystem-profile id=SS_ACAR; platform-id=FSPTC235; description=ACAR subsystem;
add subsystem id=SS_LNP; opc-id=opc1; local-ssn=247; remote-ssn=247; sccp-nw-id=1; SCCP_VERSION=ANS92; TCAP_VERSION=ANS92; APPLICATION_VERSION=AIN01;
add subsystem id=SS_800A; opc-id=opc1; local-ssn=248; remote-ssn=248; sccp-nw-id=1; SCCP_VERSION=ANS92; TCAP_VERSION=ANS92; APPLICATION_VERSION=AIN01;
add subsystem id=SS_CNAM; opc-id=opc1; local-ssn=232; remote-ssn=232; sccp-nw-id=1; SCCP_VERSION=ANS92; TCAP_VERSION=ANS92; APPLICATION_VERSION=IN1;
add subsystem id=SS_800T; opc-id=opc1; local-ssn=254; remote-ssn=254; sccp-nw-id=1; SCCP_VERSION=ANS92; TCAP_VERSION=ANS92; APPLICATION_VERSION=IN1;
add subsystem id=SS_ACAR; opc-id=opc1; local-ssn=251; remote-ssn=251; sccp-nw-id=1; SCCP_VERSION=ANS92; TCAP_VERSION=ANS92; APPLICATION_VERSION=IN1;
New subsystem ID for OPC2
add subsystem id=SS_LNP; opc-id=opc2; local-ssn=247; remote-ssn=247; sccp-nw-id=1; SCCP_VERSION=ANS92; TCAP_VERSION=ANS92; APPLICATION_VERSION=AIN01;
add subsystem id=SS_800A; opc-id=opc2; local-ssn=248; remote-ssn=248; sccp-nw-id=1; SCCP_VERSION=ANS92; TCAP_VERSION=ANS92; APPLICATION_VERSION=AIN01;
add subsystem id=SS_CNAM; opc-id=opc2; local-ssn=232; remote-ssn=232; sccp-nw-id=1; SCCP_VERSION=ANS92; TCAP_VERSION=ANS92; APPLICATION_VERSION=IN1;
add subsystem id=SS_800T; opc-id=opc2; local-ssn=254; remote-ssn=254; sccp-nw-id=1; SCCP_VERSION=ANS92; TCAP_VERSION=ANS92; APPLICATION_VERSION=IN1;
add subsystem id=SS_ACAR; opc-id=opc2; local-ssn=251; remote-ssn=251; sccp-nw-id=1; SCCP_VERSION=ANS92; TCAP_VERSION=ANS92; APPLICATION_VERSION=IN1;
add routing-key id=rk_lnp; opc-id=opc1; sg-grp-id=sg_grp1; si=SCCP; rc=4402; PLATFORM_ID=FSAIN205; ssn-id=SS_LNP;
add routing-key id=rk_800a; opc-id=opc1; sg-grp-id=sg_grp1; si=SCCP; rc=4403; PLATFORM_ID=FSAIN205; ssn-id=SS_800A;
add routing-key id=rk_cnam; opc-id=opc1; sg-grp-id=sg_grp1; si=SCCP; rc=4404; PLATFORM_ID=FSAIN205; ssn-id=SS_CNAM;
add routing-key id=rk_800t; opc-id=opc1; sg-grp-id=sg_grp1; si=SCCP; rc=4401; PLATFORM_ID=FSAIN205; ssn-id=SS_800T;
add routing-key id=rk_acar; opc-id=opc1; sg-grp-id=sg_grp1; si=SCCP; rc=4405; PLATFORM_ID=FSPTC235; ssn-id=SS_ACAR;
New routing-key for OPC2
add routing-key id=rk_lnp2; opc-id=opc2; sg-grp-id=sg_grp1; si=SCCP; rc=4412; PLATFORM_ID=FSAIN205; ssn-id=SS_LNP;
add routing-key id=rk_800a2; opc-id=opc2; sg-grp-id=sg_grp1; si=SCCP; rc=4413; PLATFORM_ID=FSAIN205; ssn-id=SS_800A;
add routing-key id=rk_cnam2; opc-id=opc2; sg-grp-id=sg_grp1; si=SCCP; rc=4414; PLATFORM_ID=FSAIN205; ssn-id=SS_CNAM;
add routing-key id=rk_800t2; opc-id=opc2; sg-grp-id=sg_grp1; si=SCCP; rc=4411; PLATFORM_ID=FSAIN205; ssn-id=SS_800T;
add routing-key id=rk_acar2; opc-id=opc2; sg-grp-id=sg_grp1; si=SCCP; rc=4415; PLATFORM_ID=FSPTC235; ssn-id=SS_ACAR;
Provisioned DPC is the STP capabilty point code
add dpc id=stp_cap_pc; point-code=1-1-22; point-code-type=ANSI_CHINA; description=Capability Point Code of STPs
add feature fname=LNP; feature-server-id=FSAIN205; description=Local number portability; tdp1=COLLECTED_INFORMATION; tid1=LNP_TRIGGER; ttype1=R;
add ported-office-code digit-string=301-612; in-call-agent=n;
add CA-Config type=DEFAULT-LNP-SLHR-ID; datatype=string; value=slhr_lnp;
add slhr-profile id=slhr_800t; description=Service Logic Host Routing Table for IN1 800 Service;
add slhr-profile id=slhr_lnp; description=Service Logic Host Routing Table for AIN LNP Service;
add slhr-profile id=slhr_800a; description=Service Logic Host Routing Table for AIN 800 Service;
add slhr-profile id=slhr_cnam; description=Service Logic Host Routing Table for IN1 CNAM Service;
add slhr-profile id=slhr_acar; description=Service Logic Host Routing Table for ACAR Service;
add slhr id=slhr_800t; opc-id=opc1; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; ssn-id=SS_800T; gtt-req=Y; tt=254; GTT_ADDR_TYPE=CDPN; GTT_ADDR=3;
add slhr id=slhr_lnp; opc-id=opc1; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; ssn-id=SS_LNP; gtt-req=Y; tt=11; GTT_ADDR_TYPE=CDPN; GTT_ADDR=3;
add slhr id=slhr_800a; opc-id=opc1; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; ssn-id=SS_800A; gtt-req=Y; tt=8; GTT_ADDR_TYPE=CDPN; GTT_ADDR=3;
add slhr id=slhr_cnam; opc-id=opc1; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; ssn-id=SS_CNAM; gtt-req=Y; tt=5; GTT_ADDR_TYPE=CLGN; GTT_ADDR=3;
add slhr id=slhr_acar; opc-id=opc1; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; ssn-id=SS_ACAR; gtt-req=Y; tt=251; GTT_ADDR_TYPE=CDPN; GTT_ADDR=10;
New slhr for OPC2
add slhr id=slhr_800t; opc-id=opc2; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; ssn-id=SS_800T; gtt-req=Y; tt=254; GTT_ADDR_TYPE=CDPN; GTT_ADDR=3;
add slhr id=slhr_lnp; opc-id=opc2; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; ssn-id=SS_LNP; gtt-req=Y; tt=11; GTT_ADDR_TYPE=CDPN; GTT_ADDR=3;
add slhr id=slhr_800a; opc-id=opc2; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; ssn-id=SS_800A; gtt-req=Y; tt=8; GTT_ADDR_TYPE=CDPN; GTT_ADDR=3;
add slhr id=slhr_cnam; opc-id=opc2; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; ssn-id=SS_CNAM; gtt-req=Y; tt=5; GTT_ADDR_TYPE=CLGN; GTT_ADDR=3;
add slhr id=slhr_acar; opc-id=opc2; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; ssn-id=SS_ACAR; gtt-req=Y; tt=251; GTT_ADDR_TYPE=CDPN; GTT_ADDR=10;
add sccp-route opc-id=opc1; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; ssn-id=SS_800T; rk-id=rk_800t;
add sccp-route opc-id=opc1; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; ssn-id=SS_800A; rk-id=rk_800a;
add sccp-route opc-id=opc1; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; ssn-id=SS_LNP; rk-id=rk_lnp;
add sccp-route opc-id=opc1; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; ssn-id=SS_CNAM; rk-id=rk_cnam;
add sccp-route opc-id=opc1; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; ssn-id=SS_ACAR; rk-id=rk_acar;
add sccp-route SSN_ID=SS_ACAR; OPC_ID=opc1; DPC_ID=dpc1; RK_ID=rk_acar
add sccp-route SSN_ID=SS_ACAR; OPC_ID=opc1; DPC_ID=dpc2; RK_ID=rk_acar
New sccp-route for OPC2
add sccp-route opc-id=opc2; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; ssn-id=SS_800T; rk-id=rk_800t2;
add sccp-route opc-id=opc2; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; ssn-id=SS_800A; rk-id=rk_800a2;
add sccp-route opc-id=opc2; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; ssn-id=SS_LNP; rk-id=rk_lnp2;
add sccp-route opc-id=opc2; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; ssn-id=SS_CNAM; rk-id=rk_cnam2;
add sccp-route opc-id=opc2; dpc-id=stp_cap_pc; ssn-id=SS_ACAR; rk-id=rk_acar2;
add sccp-route SSN_ID=SS_ACAR; OPC_ID=opc2; DPC_ID=dpc1; RK_ID=rk_acar2
add sccp-route SSN_ID=SS_ACAR; OPC_ID=opc2; DPC_ID=dpc2; RK_ID=rk_acar2
_PLUS_LOCAL=N
New pop for OPC2
add pop ID=50902; STATE=tx; COUNTRY=US; TIMEZONE=CDT; LOCAL_7D_DIALING=Y; ITP=N; ZERO_MINUS=LEC; BLOCK_EAWOPIC=Y; CNAM_OPTION=EXT_LIDB; PIC2_REQD=N; MY_LRN=4692559991; TREAT_IMS_ANONYMOUS=N; OPC_ID=opc2; ZERO_PLUS_LOCAL=N
Multiple Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Nodes Sharing the Same OPC
This profile, illustrated in Figure 3-3, is used when a customer wants to share a single OPC among multiple BTS nodes. When this feature is utilized, traffic is divided in one of two ways:
1. ![]() Traffic can be split between the BTS nodes based on a per call control route basis. In this case, the BTS nodes will not be provisioned with the same DPC. This means that only one of the BTS nodes will send traffic to and receive traffic from the associated DPC in the service provider network.
Traffic can be split between the BTS nodes based on a per call control route basis. In this case, the BTS nodes will not be provisioned with the same DPC. This means that only one of the BTS nodes will send traffic to and receive traffic from the associated DPC in the service provider network.
2. ![]() Traffic can also be split on a per call control route/Carrier Identification Code (CIC) range basis. In this case, the same DPC (and call control route) can be provisioned for multiple BTS nodes, but the associated trunk group will be provisioned with a CIC range that differs on each BTS node.
Traffic can also be split on a per call control route/Carrier Identification Code (CIC) range basis. In this case, the same DPC (and call control route) can be provisioned for multiple BTS nodes, but the associated trunk group will be provisioned with a CIC range that differs on each BTS node.
This customer profile is subject to the following limitations:
•![]() Multiple Cisco BTS 10200 nodes sharing a single point code is only valid for ISUP. If TCAP queries are needed, a separate TCAP OPC will be needed for each Cisco BTS 10200.
Multiple Cisco BTS 10200 nodes sharing a single point code is only valid for ISUP. If TCAP queries are needed, a separate TCAP OPC will be needed for each Cisco BTS 10200.
•![]() If a provisioned DPC on one BTS is also provisioned on any other BTS, then load must be divided between the BTS nodes based on CIC range.
If a provisioned DPC on one BTS is also provisioned on any other BTS, then load must be divided between the BTS nodes based on CIC range.
•![]() When provisioning call control routes on the BTS, you cannot provision two different call control routes that have the same routing key and DPC information.
When provisioning call control routes on the BTS, you cannot provision two different call control routes that have the same routing key and DPC information.

Note ![]() This customer profile is valid for Mated STP Pair and Shared Point Code topologies. For the Shared Point Code topologies that connect via A, F, and E-links, the point code of the ITP Group is shared by the BTS.
This customer profile is valid for Mated STP Pair and Shared Point Code topologies. For the Shared Point Code topologies that connect via A, F, and E-links, the point code of the ITP Group is shared by the BTS.
Figure 3-3 Multiple BTS Nodes Sharing the Same Point Code
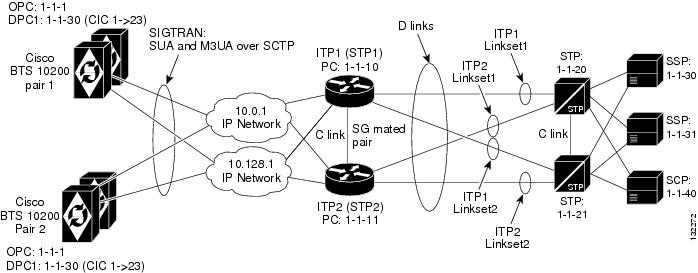
Cisco ITP Configuration Example
This example shows an AS and ASP configuration and is only for M3UA. For a default Mated STP-Pair configuration, which includes SUA, refer to Chapter 1 "SS7 Basic Configurations."
For additional ITP configuration information, refer to the Cisco ITP Configuration Guide

Note ![]() When debugging the ITP, the version of the ITP should be noted so the associated ITP manual can be consulted.
When debugging the ITP, the version of the ITP should be noted so the associated ITP manual can be consulted.
This configuration information is similar to a basic Mated STP-Pair configuration, except that in this example there will be extra ASP configuration information for communicating to the second (CA)(BTS2). Also, there is extra information in the AS configuration section for routing to each of the Cisco BTS 10200 nodes, based on CIC range. Shown below are the ASP and AS configuration elements for ITP1.

Note ![]() ITP2 will have the same ASP and AS configuration information that is shown below for ITP1.
ITP2 will have the same ASP and AS configuration information that is shown below for ITP1.
ASP configuration for BTS1
cs7 asp PRI_ISUP_BTS1 11146 2905 m3ua
remote-ip 10.0.1.5
remote-ip 10.128.1.2
cs7 asp SEC_ISUP_BTS1 11146 2905 m3ua
remote-ip 10.0.1.6
remote-ip 10.128.1.3
ASP configuration for BTS2
cs7 asp PRI_ISUP_BTS2 11146 2905 m3ua
remote-ip 10.0.1.7
remote-ip 10.128.1.4
cs7 asp SEC_ISUP_BTS2 11146 2905 m3ua
remote-ip 10.0.1.8
remote-ip 10.128.1.5
AS configuration for BTS1—The routing context entries are as follows:
routing context = 1, DPC(BTS OPC)=1.1.1, opc=1.1.30, mask is 255.255.255, service indicator=ISUP, CIC range=1->23
cs7 as ISUP_BTS1 m3ua
routing-key 1 1.1.1 opc 1.1.30 255.255.255 si isup cic 1 23
asp PRI_ISUP_BTS1
asp SEC_ISUP_BTS1
traffic-mode override
AS configuration for BTS2—The CIC range changes to 24->46 for sending messages to BTS2
cs7 as ISUP_BTS1 m3ua
routing-key 2 1.1.1 opc 1.1.30 255.255.255 si isup cic 24 46
asp PRI_ISUP_BTS2
asp SEC_ISUP_BTS2
traffic-mode override
Note that additional AS configurations will be needed for other DPCs (such as 1-1-31).
Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Provisioning Example
BTS1 Provisioning
The following example documents BTS1 provisioning for routing key/CIC based routing. It is important to note that, unlike the ITP, the BTS does not configure CIC ranges within the routing key. Instead, the CIC ranges on the BTS are provisioned as part of the trunk object.
add opc id=opc1; point-code=1-1-1; point-code-type=ANSI_CHINA;
add dpc id=dpc1; point-code=1-1-30; point-code-type=ANSI_CHINA;
add dpc id=dpc2; point-code=1-1-31; point-code-type=ANSI_CHINA;
add sg id=sg1; priority=1;
add sg id=sg2; priority=1;
add sg-grp id=sg-grp1; sg1-id=sg1; sg2-id=sg2;
add sgp id=sg1-sgp1; sg-id=sg1;
add sgp id=sg2-sgp2; sg-id=sg2;
add sctp-assoc-profile id=sctp-prof1;
add sctp-assoc id=sg1-sgp1-sctp; sgp-id=sgp1; sctp-assoc-profile-id=sctp-prof1; platform-id=CA146; remote-port=2905; remote-tsap-addr1=10.89.225.235; remote-tsap-addr2=10.89.226.235; dip-tos-precedence=ROUTINE;
add sctp-assoc id=sg2-sgp2-sctp; sgp-id=sgp2; sctp-assoc-profile-id=sctp-prof1; platform-id=CA146; remote-port=2905; remote-tsap-addr1=10.89.225.236; remote-tsap-addr2=10.89.226.236; ip-tos-precedence=ROUTINE;
add user-part-variant id=ANSISS7_GR317;
The RC VALUE IN BTS CONFIG MATCHES RC VALUE IN ITP CONFIG
add routing-key id=rk1; opc-id=opc1; sg-grp-id=sg-grp1; si=ISUP; rc=1; platform-id=CA146;
add call-ctrl-route id=dpc1-route; dpc-id=dpc1; routing-key-id=rk1; si=ISUP; user-part-variant-id=ANSISS7_GR317;
add call-ctrl-route id=dpc2-route; dpc-id=dpc2; routing-key-id=rk2; si=ISUP; user-part-variant-id=ANSISS7_GR317;
add mgw-profile id=as5300-prof; mgw-type=AS5300; mgcp-version=MGCP_1_0;
add mgw id=as5300-1; mgw-profile-id=as5300-prof; call-agent-id=CA146; tsap-addr=as5300-1.cisco.com; type=TGW;
add termination prefix=S1/DS1-0/; port-start=1; port-end=23 or 31; type=trunk; mgw-id=as5300-1;
add ss7-ansi-tg-profile id=ss7-prof1;
add trunk-grp id=1; call-agent-id=CA146; tg-type=SS7; tg-profile=ss7-prof1; call-ctrl-route-id=dpc1-route;
The CIC range in the BTS trunk matches the one in the ITP as rkey configuration. Also the CIC range is not defined in the routing-key for the BTS. It is defined as part of the trunk object. It is however possible to define the DPC in this routing key, but it is not necessary and was not done here.
add trunk cic-start=1; cic-end=23; type=trunk; mgw-id=as5300-1; termination-prefix=S1/DS1-0/; tgn-id=1; termination-port-start=1; termination-port-end=23;
add route id=dpc1-route; tg-selection=RR; tgn1-id=1;
add route-guide id=dpc1-rg; policy-type=ROUTE; policy-id=dpc1-route;
add destination id=dpc1-dest; route-type=ROUTE; route-guide-id=dpc1-rg;
BTS2 Provisioning
The following example documents BTS2 provisioning for routing key/CIC based routing.
add opc id=opc1; point-code=3-10-3; point-code-type=ANSI_CHINA;
add dpc id=dpc1; point-code=3-50-3; point-code-type=ANSI_CHINA;
add dpc id=dpc2; point-code=3-51-3; point-code-type=ANSI_CHINA;
add sg id=sg1; priority=1;
add sg id=sg2; priority=1;
add sg-grp id=sg-grp1; sg1-id=sg1; sg2-id=sg2;
add sgp id=sgp1; sg-id=sg1;
add sgp id=sgp2; sg-id=sg2;
add sctp-assoc-profile id=sctp-prof1;
add sctp-assoc id=ca-sgp1-sctp; sgp-id=sgp1; sctp-assoc-profile-id=sctp-prof1; platform-id=CA147; remote-port=2905; remote-tsap-addr1=10.89.225.235; remote-tsap-addr2=10.89.226.235; ip-tos-precedence=ROUTINE;
add sctp-assoc id=ca-sgp2-sctp; sgp-id=sgp2; sctp-assoc-profile-id=sctp-prof1; platform-id=CA147; remote-port=2905; remote-tsap-addr1=10.89.225.236; remote-tsap-addr2=10.89.226.236; ip-tos-precedence=ROUTINE;
add user-part-variant id=ANSISS7_GR317;
The RC value in the BTS configuration matches the RC value in the ITP configuration. Also the CIC range is not defined in the routing key for the BTS. It is defined as part of the trunk object. It is, however, possible to define the DPC in this routing key, but it is not necessary and was not done here.
add routing-key id=rk3; opc-id=opc1; sg-grp-id=sg-grp1; si=ISUP; rc=2; platform-id=CA146;
add call-ctrl-route id=dpc1-route; dpc-id=dpc1; routing-key-id=rk3; si=ISUP; user-part-variant-id=ANSISS7_GR317;
add call-ctrl-route id=dpc2-route; dpc-id=dpc2; routing-key-id=rk4; si=ISUP; user-part-variant-id=ANSISS7_GR317;
add mgw-profile id=as5300-prof; mgw-type=AS5300; mgcp-version=MGCP_1_0;
add mgw id=as5300-1; mgw-profile-id=as5300-prof; call-agent-id=CA146; tsap-addr=as5300-1.cisco.com; type=TGW;
add termination prefix=S1/DS1-0/; port-start=1; port-end=23 ; type=trunk; mgw-id=as5300-2;
add ss7-ansi-tg-profile id=ss7-prof1;
add trunk-grp id=1; call-agent-id=CA147; tg-type=SS7; tg-profile=ss7-prof1; call-ctrl-route-id=dpc1-route;
The CIC range in the BTS trunk matches the one in the ITP AS routing key configuration.
add trunk cic-start=24; cic-end=46; type=trunk; mgw-id=as5300-2; termination-prefix=S1/DS1-0/; tgn-id=1; termination-port-start=1; termination-port-end=23;
add route id=dpc1-route; tg-selection=RR; tgn1-id=1;
add route-guide id=dpc1-rg; policy-type=ROUTE; policy-id=dpc1-route;
add destination id=dpc1-dest; route-type=ROUTE; route-guide-id=dpc1-rg;
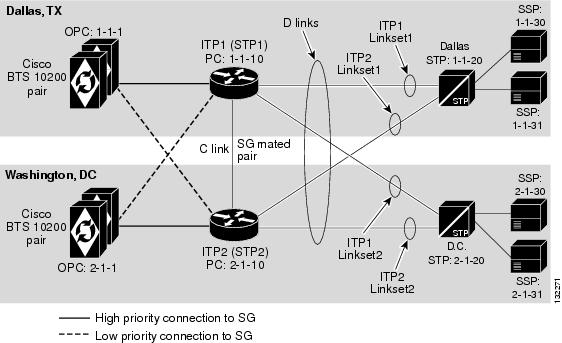
Geographically Separated Mated STP Pair with SG Priority Routing
This customer profile, illustrated in Figure 3-4, is recommended for the customer who operates two different geographically separated telephony networks using geographically separated BTS and ITP nodes. In this example, BTS1 and ITP1 are located in Dallas, and BTS2 and ITP2 are in Washington, DC.
The topology between ITPs and STPs is an SS7 STP quad. The SG Mated Pair could be connected to an STP, a service provider's STP mated pair, or the gateway STPs provided by the local service provider. The ITP pair can be collocated with the BTS in the customer's network or collocated with the STP pair in the service provider's network.
A key component of this profile is the use of SG priority routing, which provides the ability to choose which SG in the SG-Group has priority when sending towards the destinations. In this example, BTS1 will primarily send toward the DPCs (Switching Systems Protocol [SSP]) in the Dallas network via ITP1, and it will only route through ITP2 for these endpoints at a lower priority. This is useful for cost reduction if, for example, BTS1 has a point of presence (POP) in Dallas and BTS2 has a POP in Washington, DC.
This customer profile is valid only for the D-link configuration.

Note ![]() Figure 3-4 only shows one STP in each city. However, each city would probably contain two network STPs.
Figure 3-4 only shows one STP in each city. However, each city would probably contain two network STPs.
Figure 3-4 Geographically Distributed Mated STP Pair Configuration with SG Priority Routing
Cisco ITP Configuration Example
The ITP configuration in this example is similar to the one in the ITP1 Configuration, with the following exceptions:
•![]() In Figure 3-4, only one STP is shown as a route towards each SSP.
In Figure 3-4, only one STP is shown as a route towards each SSP.
•![]() The routes through STP1 and STP2 lead towards different endpoints.
The routes through STP1 and STP2 lead towards different endpoints.
The following is the configuration example for the cs7 linksets and routes:
SS7 Linkset definitions—The number after 'link' represents SLC.
cs7 linkset lset1chn 1.1.20
link 0 Serial0/0:0
!
cs7 linkset lset2chn 2.1.20
link 0 Serial0/1:0
SS7 Route definitions
cs7 route-table system
update route 1.1.30 255.255.255 linkset lset1chn priority 1
update route 1.1.31 255.255.255 linkset lset1chn priority 1
update route 2.1.30 255.255.255 linkset lset2chn priority 1
update route 2.1.31 255.255.255 linkset lset2chn priority 1
Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch Provisioning Example
In this BTS provisioning script, each BTS assigns one of the SGs of the SG-Group as a priority 1 SG route while the other BTS assigns it as a priority 2 SG route. In the BTS1 provisioning script, SG1 has a priority of 1 while SG2 has a priority of 2. In the BTS2 provisioning script, SG2 has a priority of 1 while SG1 has a priority of 2.
The following is a provisioning example for configuring SG priorities.
BTS1 Provisioning
SG configuration for BTS1. The priority is provisioned opposite of what will be done on BTS2 (as shown in the following subsection).
add sg id=sg1; description=Signaling gateway 1 of SG GRP 1; priority 1
add sg id=sg2; description=Signaling gateway 2 of SG GRP 1; priority 2
SG-GRP configuration for BTS1
add sg-grp id=sg-grp1; sg1-id=sg1; sg2-id=sg2 description=SG group 1;
BTS2 Provisioning
SG configuration for BTS2—The priority is provisioned opposite of what it is for BTS1.
add sg id=sg1; description=Signaling gateway 1 of SG GRP 1; priority 2
add sg id=sg2; description=Signaling gateway 2 of SG GRP 1; priority 1
SG-GRP configuration for BTS2
add sg-grp id=sg-grp1; sg1-id=sg1; sg2-id=sg2 description=SG group 1;
 Feedback
Feedback