- Cisco Analog Video Gateway Module Overview
- Configuring Host Router and Cisco Analog Video Gateway Module Interfaces
- Administering the Cisco Analog Video Gateway
- Configuring Video Ports and Profiles
- Configuring Contact Closure Profiles
- Configuring Alarm Monitor Profiles
- Configuring Camera Controls
- Cisco Analog Video Gateway Command Reference
- Glossary
- Index
Configuring Host Router and Cisco Analog Video Gateway Module Interfaces
To configure the Cisco Analog Video Gateway network module after it is installed in your host Cisco Integrated Services Router (ISR), you need to configure the following:
•![]() Cisco ISR external interface to an external network link using the Cisco IOS CLI for setting standard router settings
Cisco ISR external interface to an external network link using the Cisco IOS CLI for setting standard router settings
•![]() Cisco ISR internal interface to the Cisco Analog Video Gateway module, using the Cisco IOS CLI for setting the network module IP address and default gateway router
Cisco ISR internal interface to the Cisco Analog Video Gateway module, using the Cisco IOS CLI for setting the network module IP address and default gateway router
•![]() Cisco Analog Video Gateway module internal interface to the host router, using network module firmware for setting application settings
Cisco Analog Video Gateway module internal interface to the host router, using network module firmware for setting application settings
•![]() Cisco Analog Video Gateway module external interface to an external link, using the module firmware for servicing external requests
Cisco Analog Video Gateway module external interface to an external link, using the module firmware for servicing external requests
Whenever possible, configuration and management of the Cisco Analog Video Gateway module should be configured using the Video Surveillance Operations Manager (VSOM) graphical user interface.
The following sections describe the tasks required to configure the host router and Cisco Analog Video Gateway module interfaces:
•![]() Before Configuring the Cisco Analog Video Gateway
Before Configuring the Cisco Analog Video Gateway
•![]() Entering and Exiting the Command Environment
Entering and Exiting the Command Environment
•![]() Opening and Closing a Network Module Session
Opening and Closing a Network Module Session
•![]() Configuring the Cisco Analog Video Gateway Profiles
Configuring the Cisco Analog Video Gateway Profiles
Before Configuring the Cisco Analog Video Gateway
Complete the following prerequisites for the ISR, network module, and file server before you attempt to configure the Cisco Analog Video Gateway:
Cisco ISR
•![]() Plan software installations, upgrades, or downgrades for times when you can take out of service or off line all applications that run on the host router.
Plan software installations, upgrades, or downgrades for times when you can take out of service or off line all applications that run on the host router.
•![]() Ensure that your Cisco router serves as your host router, running the appropriate Cisco IOS release. To learn which release your router is currently running, check the output from the show version command.
Ensure that your Cisco router serves as your host router, running the appropriate Cisco IOS release. To learn which release your router is currently running, check the output from the show version command.

Note ![]() When minimum release requirements are met, you can change images on either the host router or on the Cisco Analog Video Gateway module, without affecting the other image.
When minimum release requirements are met, you can change images on either the host router or on the Cisco Analog Video Gateway module, without affecting the other image.
Network Module
•![]() If it is not already installed at the factory, install the Cisco Analog Video Gateway network module into the host router with sufficient physical memory (see Table 1) to accommodate the Cisco Analog Video Gateway application software.
If it is not already installed at the factory, install the Cisco Analog Video Gateway network module into the host router with sufficient physical memory (see Table 1) to accommodate the Cisco Analog Video Gateway application software.
|
|
|
|---|---|
CompactFlash memory |
512 M |
RAM |
512 M |

Note ![]() For detailed information on hardware installation, see Installing Cisco Network Modules in Cisco Access Routers.
For detailed information on hardware installation, see Installing Cisco Network Modules in Cisco Access Routers.
•![]() Before swapping out a Cisco Analog Video Gateway module in an existing system, perform a full backup of all data.
Before swapping out a Cisco Analog Video Gateway module in an existing system, perform a full backup of all data.
•![]() After the swap, restore the data.
After the swap, restore the data.

Note ![]() For more information, see the "Backing Up and Restoring Configurations" section on page 19.
For more information, see the "Backing Up and Restoring Configurations" section on page 19.
•![]() Note the Cisco Analog Video Gateway module location in the host router:
Note the Cisco Analog Video Gateway module location in the host router:
–![]() slot: Number of the host router chassis slot for the module. After you install the module, you can obtain this information by using the router show running-config command.
slot: Number of the host router chassis slot for the module. After you install the module, you can obtain this information by using the router show running-config command.
–![]() unit: Number of the daughter card on the module. This value should be 0.
unit: Number of the daughter card on the module. This value should be 0.

Note ![]() You need this information for the "Interface Configuration Tasks" section and the "Opening and Closing a Network Module Session" section.
You need this information for the "Interface Configuration Tasks" section and the "Opening and Closing a Network Module Session" section.
File Server
•![]() Verify that your download File Transfer Protocol (FTP) or Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) file server is accessible:
Verify that your download File Transfer Protocol (FTP) or Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) file server is accessible:
–![]() FTP file server: Use for installations, backups, and data restores.
FTP file server: Use for installations, backups, and data restores.
–![]() TFTP file server: Use for boot helper operations to recover from a failed installation.
TFTP file server: Use for boot helper operations to recover from a failed installation.
•![]() Configure the Cisco Analog Video Gateway module software only from a console that connects to a serial console port on the host router.
Configure the Cisco Analog Video Gateway module software only from a console that connects to a serial console port on the host router.

Note ![]() See the Cisco Analog Video Gateway Installation and Upgrade Guide for more information.
See the Cisco Analog Video Gateway Installation and Upgrade Guide for more information.
•![]() Access the Cisco Analog Video Gateway module software only by first accessing one of the following:
Access the Cisco Analog Video Gateway module software only by first accessing one of the following:
–![]() Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI)
Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI)
–![]() Cisco Analog Video Gateway XML application programming interface (API)
Cisco Analog Video Gateway XML application programming interface (API)
Entering and Exiting the Command Environment
This section describes the procedures for entering and exiting the command environment, in which the Cisco Analog Video Gateway configuration commands are executed. The following sections describe these procedures:
•![]() Entering the Command Environment
Entering the Command Environment
•![]() Exiting the Command Environment
Exiting the Command Environment
EXEC and Configuration Modes
The Cisco Analog Video Gateway user EXEC, privileged EXEC, and configuration command modes are similar to the user EXEC, privilege EXEC, and configuration modes for Cisco IOS CLI commands. The description for each command of this section indicates the command mode.
Entering the Command Environment
When the Cisco Analog Video Gateway module has been installed and is active, use the following procedure to enter the command environment.
Prerequisites
The following information is required to enter the command environment:
•![]() IP address of the Cisco ISR that contains the Cisco Analog Video Gateway module
IP address of the Cisco ISR that contains the Cisco Analog Video Gateway module
•![]() Username and password for logging in to the router
Username and password for logging in to the router
•![]() Slot number of the module
Slot number of the module
SUMMARY STEPS
1. ![]() Open a Telnet session.
Open a Telnet session.
2. ![]() telnet ip-address
telnet ip-address
3. ![]() Enter the user ID and password of the router.
Enter the user ID and password of the router.
4. ![]() service-module video-service-engine slot/port session
service-module video-service-engine slot/port session
5. ![]() (Optional) enable
(Optional) enable
DETAILED STEPS
Exiting the Command Environment
To leave the Cisco Analog Video Gateway module command environment and return to the router command environment, return to the Cisco Analog Video Gateway EXEC mode and enter the exit command twice.
The following example shows the exit procedure:
se-10-0-0-0# exit
se-10-0-0-0> exit
Router#
Configuring Interfaces
The host router and the Cisco Analog Video Gateway network module use several interfaces for internal and external communication (see Figure 2). Each interface is configurable—for the router by using the Cisco IOS CLI, and for the module by using the module firmware Linux-based CLI or XML API.
Figure 2 Router and Cisco Analog Video Gateway Module Interfaces
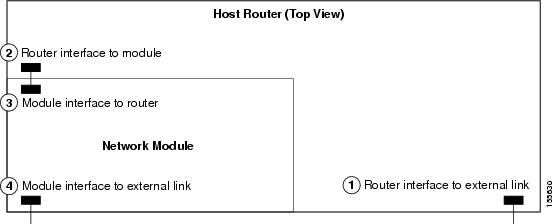
The following sections describe the tasks that are necessary for configuring the host router and network module interfaces:
•![]() Interface Configuration Tasks
Interface Configuration Tasks
•![]() Opening and Closing a Network Module Session
Opening and Closing a Network Module Session
Interface Configuration Tasks
The first configuration task is to set up the Cisco Analog Video Gateway module interface to the host router and to its external links. This enables you to access the module so that you can install and configure the Cisco Analog Video Gateway software application.
Steps 1 and 2 open the host router CLI and accesses the router interface to the Cisco Analog Video Gateway module. The remaining steps configure the interface.

Note ![]() If you lose power or connection during any of the following procedures, the system usually detects the interruption and tries to recover. If it fails to do so, fully reinstall the system using the boot helper.
If you lose power or connection during any of the following procedures, the system usually detects the interruption and tries to recover. If it fails to do so, fully reinstall the system using the boot helper.
SUMMARY STEPS
From the Host-Router CLI
1. ![]() enable
enable
2. ![]() configure terminal
configure terminal
3. ![]() interface video-service-engine slot/0
interface video-service-engine slot/0
4. ![]() ip address router-side-ip-address subnet-mask
ip address router-side-ip-address subnet-mask
or
ip unnumbered type number
5. ![]() service-module ip address module-side-ip-address subnet-mask
service-module ip address module-side-ip-address subnet-mask
6. ![]() service-module external ip address external-ip-address subnet-mask
service-module external ip address external-ip-address subnet-mask
7. ![]() service-module ip default-gateway gateway-ip-address
service-module ip default-gateway gateway-ip-address
8. ![]() If ip unnumbered type number is used in step 4, then set ip route
If ip unnumbered type number is used in step 4, then set ip route
9. ![]() end
end
10. ![]() copy running-config startup-config
copy running-config startup-config
11. ![]() show running-config
show running-config
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
||
Step 1 |
enable Router> enable |
Enters privileged EXEC mode on the host router. Enter your password if prompted. |
Step 2 |
configure terminal Router# config t |
Enters global configuration mode on the host router. |
Step 3 |
interface video-service-engine slot/0 Router(config)# interface video-service-engine 1/0 |
Enters interface configuration mode for the slot and port where the Cisco Analog Video Gateway module resides. • • |
Step 4 |
ip address router-side-ip-address subnet-mask or ip unnumbered type number Router(config-if)# ip address 10.0.0.20 255.255.255.0 or Router(config-if)# ip unnumbered ethernet 0 |
Specifies the router interface to the module. • • |
Step 5 |
service-module ip address module-side-ip-address subnet-mask Router(config-if)# service-module ip address 172.0.0.20 255.255.255.0 |
Specifies the IP address for the Cisco Analog Video Gateway module interface to the router. • • |
Step 6 |
service-module external ip address external-ip-address subnet-mask Router(config-if)# service-module external ip address 172.0.0.30 255.255.255.0 |
Specifies the IP address for the external LAN interface on the module. • • |
Step 7 |
service-module ip default-gateway gateway-ip-address Router(config-if)# service-module ip default-gateway 10.0.0.40 |
Specifies the IP address for the default gateway router for the module. The argument is as follows: • |
Step 8 |
(Optional) If the ip unnumbered type number command is used in step 4, then set: ip route service-module-ip-address subnet-mask video-service-engine 1/0 Router(config-if)# ip route 172.0.0.20 255.255.255.255 video-service-engine 1/0 |
Sets the ip route command if the ip unnumbered type number command is used in Step 4. |
Step 9 |
end Router(config-if)# end |
Returns to global configuration mode on the host router. |
Step 10 |
copy running-config startup-config Router# copy running-config startup-config |
Saves the new running configuration of the host router. |
Step 11 |
show running-config Router# show running-config |
Displays the running configuration of the host router. Use this command to verify address configurations. |
Examples
The following partial sample output from the show running-config command shows how the interfaces are configured.
interface video-service-engine1/0
ip address 10.0.0.20 255.255.255.0
service-module external ip address 172.0.0.30 255.255.0.0
service-module ip address 172.0.0.20 255.255.255.0
service-module ip default-gateway 10.0.0.40
Opening and Closing a Network Module Session
This section describes how to open and close a session on the Cisco Analog Video Gateway module.

Note![]() •
•![]() Before you install your application software, opening a session brings up the boot loader. The boot loader is a small set of system software that runs when the system first powers up. It loads the operating system from the disk (external CompactFlash memory) or network, which loads and runs the Cisco Analog Video Gateway application. The boot loader may optionally load and run the boot helper. After you install the software, opening a session brings up the application.
Before you install your application software, opening a session brings up the boot loader. The boot loader is a small set of system software that runs when the system first powers up. It loads the operating system from the disk (external CompactFlash memory) or network, which loads and runs the Cisco Analog Video Gateway application. The boot loader may optionally load and run the boot helper. After you install the software, opening a session brings up the application.
•![]() You can conduct only one session at a time.
You can conduct only one session at a time.
•![]() The Steps 1 and 2 open the host-router CLI and access the module. The remaining steps configure the module and return you to the host-router CLI.
The Steps 1 and 2 open the host-router CLI and access the module. The remaining steps configure the module and return you to the host-router CLI.
SUMMARY STEPS
From the Host-Router CLI
1. ![]() enable
enable
2. ![]() service-module video-service-engine slot/0 status
service-module video-service-engine slot/0 status
3. ![]() service-module video-service-engine slot/0 session
service-module video-service-engine slot/0 session
From the Service-Module Interface
4. ![]() Network module configuration commands
Network module configuration commands
5. ![]() Control-Shift-6 x
Control-Shift-6 x
From the Host-Router CLI
6. ![]() service-module video-service-engine slot/0 session clear
service-module video-service-engine slot/0 session clear
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
||
Step 1 |
enable Router> enable |
Enters privileged EXEC mode on the host router. Enter your password if prompted. |
Step 2 |
service-module video-service-engine slot/0 status Router# service-module video-service-engine 2/0 status |
Displays the status of the specified module, so that you can ensure that the module is running (that is, in steady state). Note |
Step 3 |
service-module video-service-engine slot/0 session Router# service-module video-service-engine 1/0 session Trying 10.10.10.1, 2065 ... Open |
Begins a module session on the specified module. Do one of the following: • Note • |
|
|
||
Step 4 |
. . . Example (boot loader): VSE-Module bootloader> config OR Example (Configuration): VSE-Module> configure terminal VSE-Module(config)> . . . VSE-Module(config)> exit VSE-Module> write |
Enters boot loader or configuration commands on the module as needed. • OR • |
Step 5 |
Press Control-Shift-6 x. |
Closes the module session and returns to the router CLI. Note |
|
|
||
Step 6 |
service-module video-service-engine slot/0 session clear Router# service-module video-service-engine 1/0 session clear |
Clears the module session for the specified module. When prompted to confirm this command, press Enter. |
Configuring the Cisco Analog Video Gateway Profiles
After you configure the host router and the Cisco Analog Video Gateway network module, you can begin to configure the video (see Configuring Video Parameters), contact-closure (see Configuring Contact Closure Profiles), and alarm-monitor (see Configuring Alarm Monitor Profiles) profiles.
 Feedback
Feedback