Self-Service Provisioning
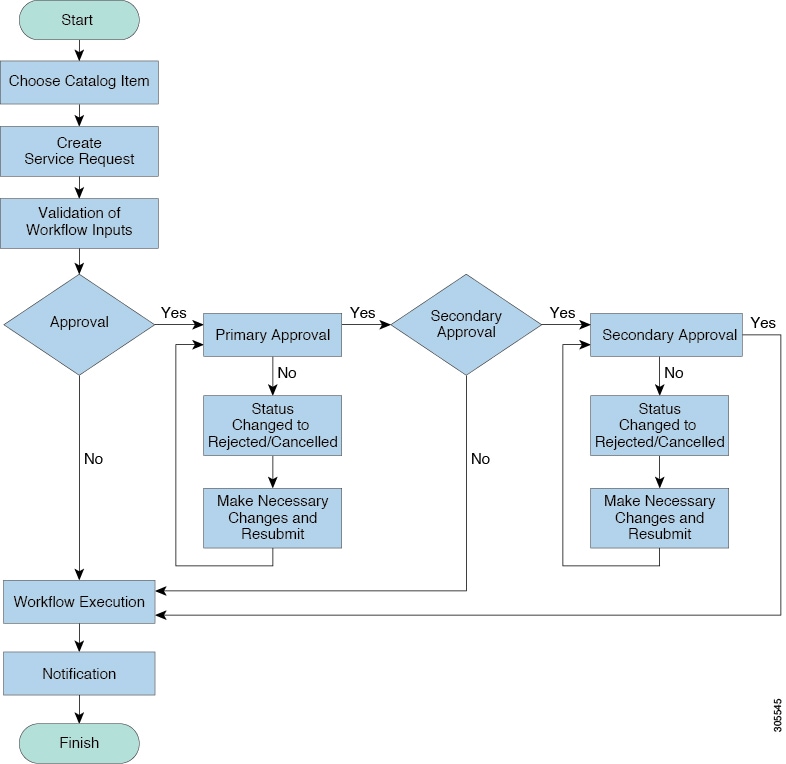
You can provision virtual machines (VMs) or applications through self-service provisioning. To provision a VM or an application using self-service provisioning, you must first create a service request. This action initiates a VM-creation workflow that includes the following:
-
Budget validation
-
Dynamic resource allocation
-
Approval
-
Provisioning
-
Lifecycle setup
-
Notification about the status of service requests

 Feedback
Feedback