Cisco UCS B420 M4 High Performance Blade Server
This document describes how to install and service the Cisco UCS B420 M4 high performance blade server, a full-width, high-density blade server that supports the following features:
-
Up to four Intel Xeon E5-4600 v4 or v3 CPUs, interconnected with Intel QuickPath Interconnect (QPI) links. Two- and four-CPU configurations are supported.
-
48 DDR4 DIMMs, either RDIMMs, LRDIMMs, or TSV-RDIMMs.
-
3 mezzanine adapter slots.
-
Up to 4 SAS or SATA hard disk drives (HDDs) or solid state drives (SSDs).
Up to four Cisco UCS B420 M4 blade servers can reside in a Cisco UCS 5108 Blade Server chassis.
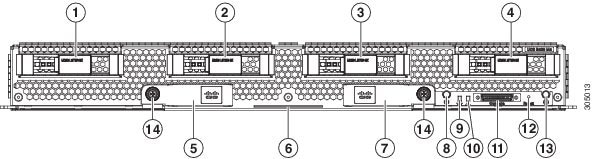
|
1 |
Hard drive bay 1 |
8 |
Power button and LED |
|
2 |
Hard drive bay 2 |
9 |
Network link status LED |
|
3 |
Hard drive bay 3 |
10 |
Blade health LED |
|
4 |
Hard drive bay 4 |
11 |
Local console connector |
|
5 |
Left ejector handle |
12 |
Reset button access |
|
6 |
Asset pull tab |
13 |
Locator button LED |
|
7 |
Right ejector handle |
14 |
Ejector captive screw |
LEDs
Server LEDs indicate whether the blade server is in active or standby mode, the status of the network link, the overall health of the blade server, and whether the server is set to give a flashing blue locator light from the locator button.
The removable drives also have LEDs indicating hard disk access activity and disk health.
|
LED |
Color |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Power |
Off |
Power off. |
|
|
Green |
Main power state. Power is supplied to all server components and the server is operating normally. |
||
|
Amber |
Standby power state. Power is supplied only to the service processor of the server so that the server can still be managed.
|
||
|
Link |
Off |
None of the network links are up. |
|
|
Green |
At least one network link is up. |
||
|
Health |
Off |
Power off. |
|
|
Green |
Normal operation. |
||
|
Amber |
Minor error. |
||
|
Blinking Amber |
Critical error. |
||
|
Blue locator button and LED |
Off |
Blinking is not enabled. |
|
|
Blinking blue 1 Hz |
Blinking to locate a selected blade—If the LED is not blinking, the blade is not selected. You can control the blinking in UCS Manager or by using the blue locator button/LED. |
||
|
Activity (Disk Drive) |
Off |
Inactive. |
|
|
Green |
Outstanding I/O to disk drive. |
||
|
Flashing Green 1 Hz |
Rebuild in progress. Health LED will flash in unison. |
||
|
Flashing Green 4 Hz |
Identify drive as active. |
||
|
Health (Disk Drive) |
Off |
Either no fault is detected or the drive is not installed. |
|
|
Amber |
Fault detected. |
||
|
Flashing Amber 4 Hz |
Rebuild drive active. If the Activity LED is also flashing green, a drive rebuild is in progress. |
Buttons
The Reset button is recessed in the front panel of the server. You can press the button with the tip of a paper clip or a similar item. Hold the button down for five seconds, and then release it to restart the server if other methods of restarting do not work.
The locator function for an individual server may get turned on or off by pressing the locator button/LED.
The power button allows you to manually take a server temporarily out of service but leave it in a state where it can be restarted quickly. If the desired power state for a service profile associated with a blade server is set to "off," using the power button or Cisco UCS Manager to reset the server will cause the desired power state of the server to become out-of-sync with the actual power state and the server may unexpectedly shut down at a later time. To safely reboot a server from a power-down state, use the Boot Server action in Cisco UCS Manager.





 Feedback
Feedback