Troubleshooting
Server Hardware or Software Issues
This chapter includes the following sections:
- Troubleshooting Operating System and Drivers Installation
- Troubleshooting Disk Drive and RAID Issues
- DIMM Memory Issues
- Troubleshooting Server and Memory Issues
- Troubleshooting Communication Issues
Troubleshooting Operating System and Drivers Installation
|
Issue |
Recommended Solution |
|
|
|
The Windows 2003 R2 64-bit install is not starting because the system is not seeing the install CD on the C200 servers. |
|
|
Slow performance (slow mouse and keyboard) on C200 or C210 servers when running Windows 2008 R2. |
There is a known issue with Intel 82576 driver included with Windows 2008 R2. Update to the latest Intel driver for this chipset at the following link: https://downloadcenter.intel.com/product/32261/Intel-82576-Gigabit-Ethernet-Controller |
|
Installation of the Windows 2008 R2 OS failed with error message: The computer restarted unexpectedly or encountered an unexpected error. Windows installation cannot proceed. |
On the C200 server, Windows 2008 R2 install fails with the Intel Quad Port NIC. Start the install without the NIC and put it in after the install is complete. Also, see this forum message: https://supportforums.cisco.com/message/3179297 |
|
VMware ESX/ESXi on C200, C210, or C250 failed. |
|
|
Running Windows 2008 R2, Task Manager shows multiple spikes. |
Go to this URL and update the drivers to the latest version: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/unified_computing/ucs/overview/guide/UCS_rack_roadmap.html |
|
The ESXi installation does not recognize the LOM or NIC Ethernet ports. |
|
|
The ESXi update does not recognize the NICs. |
Update the LOM firmware using the Cisco Host Update Utility. Download the 1.2.x version from this link: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/unified_computing/ucs/c/sw/lomug/install/LOMUG.html Download the 1.3.x version from this link: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/unified_computing/ucs/c/sw/lomug/1.3.x/install/HUUUG.html |
|
Unable to install older OS. |
Different C-Series servers support different versions of OS. Use the following link to see matrix of supported operating systems: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps10477/prod_technical_reference_list.html |
|
Cannot upgrade BIOS on the system with no OS. |
Use the BIOS upgrade instructions for the HW installation and service guide for their server. Go to: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps10493/prod_installation_guides_list.html |
|
With ESXi installed on the drives, unable to boot from the partition. |
Review the documentation at the following link: http://www.VMware.com |
|
CIMC defaults to DHCP and will not retain the IP address. |
Review the documentation at the following link: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps10739/products_installation_and_configuration_guides_list.html |
|
System becomes unresponsive during BIOS POST. |
When the system boots, if the system is hanging at LSI, waiting for user input, follow the instructions on the screen. Possible reasons would be:
|
|
Drives are not detected or the system hangs when the adapter ROM for the ICH10R SATA Software RAID scans the SATA ports. |
|
|
The drives are not detected or the system hangs when the adapter ROM for the LSI RAID Controller scans the SAS/SATA Drives. |
|
|
The Operating System does not boot. |
|
Troubleshooting Disk Drive and RAID Issues
Disk Drive/RAID Configuration Issues
|
Issue |
Recommended Solution |
|
Windows does not detect hard drives. |
LSI drivers may not be bundled with the Windows OS version being installed. These drivers must be installed during the installation process. During the install process, if the hard drives fail to be detected, use the load driver option to point the drives to the correct drivers for the LSI controller in the system. The drivers can be loaded using a USB drive. When loaded, the hard drives are displayed and the hard drive for the OS can be selected. |
|
Installing Windows 2008 64-bit and RAID controller had issues. |
LSI drivers are not bundled in Windows 2008 64-bit. These must be installed during the installation process. During the install process, if the hard drives fail to be detected, use the load driver option to point the drives to the correct drivers for the LSI controller in the system. The drivers can be loaded using a USB drive. When loaded, the hard drives are displayed and the hard drive for the OS can be selected. |
|
Unable to install ESX on server with only the onboard controller. |
The LSI hardware RAID controller is required. |
|
|
|
VMware does not show the local drive during installation. |
VMware supports a maximum of two TB partitions sizes. Resize the partition to not exceed the 2TB partition size limitation. |
|
The RAID controller card is not working. |
Verify that the card installed is supported for this server. If supported, follow the steps listed in Unable to see LSI RAID controller in BOOT environment. (above). |
|
Problem with setup of the RAID6 virtual device and installation of Windows 2003 X64. |
|
|
Unable to see HDD. |
|
|
Problem setting up the RAID configuration. |
|
Configuring Multiple (Redundant) RAID controllers
Cisco does not support multiple (redundant) RAID controllers that automatically fail over if one RAID controllers fails. It is possible to recover from a RAID controller failure. Install a new RAID card of the same type and model.
Configuration data about a RAID array is stored inside the disks being managed by the controller. A new controller can import those configurations from disks to restore proper RAID operation. Each disk has its own copy of the metadata. If there are 16 disks in an array, each disk can contain its own copy of the metadata.
Detailed steps are available in the LSI document 80-00156-01_RevH_SAS_SW_UG.pdf.
This document is available from the Documents & Downloads section of the LSI support site at this URL: http://www.lsi.com
When configuring the RAID card for the first time, the step “Import foreign config” in the file provides details on how to import the RAID configuration from previously configured disks.
RHEL 5.4 64-bit Recommended Installation with RAID (C200)
To ensure that the RAID drives are properly recognized, complete the following steps:
DIMM Memory Issues
Types of DIMM Errors
Cisco UCS Servers can detect and report correctable and uncorrectable DIMM errors.
- Correctable DIMM Errors
-
DIMMs with correctable errors are not disabled and are available for the OS to use. The total memory and effective memory are the same (memory mirroring is taken into account). These correctable errors are reported in Cisco IMC as degraded once they exceed pre-determined error thresholds.
- Uncorrectable DIMM Errors
-
Uncorrectable errors generally cannot be fixed, and may make it impossible for the application or operating system to continue execution. The DIMMs with uncorrectable error will be disabled if DIMM blacklisting is enabled or if the DIMM fails upon reboot during BIOS POST and OS will not see that memory. Cisco IMC operState will be inoperable for this DIMM in this case.
A problem with the DIMM memory can cause a server to fail to boot or cause the server to run below its capabilities. If DIMM issues are suspected, consider the following:
-
DIMMs tested, qualified, and sold by Cisco are the only DIMMs supported on your system. Third-party DIMMs are not supported, and if they are present, Cisco technical support will ask you to replace them with Cisco DIMMs before continuing to troubleshoot a problem.
-
Check if the malfunctioning DIMM is supported on that model of server. Refer to the server’s installation guide and technical specifications to verify whether you are using the correct combination of server, CPU and DIMMs.
-
Check if the malfunctioning DIMM seated correctly in the slot. Remove and reseat the DIMMs.
-
All Cisco servers have either a required or recommended order for installing DIMMs. Refer to the server’s installation guide and technical specifications to verify that you are adding the DIMMs appropriately for a given server type.
-
If the replacement DIMMs have a maximum speed lower than those previously installed, all DIMMs in a server run at the slower speed or not work at all. All of the DIMMs in a server should be of the same type. All of the DIMMs in a server should be of the same type for optimal performance.
-
The number and size of DIMMs should be the same for all CPUs in a server. Mismatching DIMM configurations can degrade system performance.
Memory Terms and Acronyms
Acronym |
Meaning |
DIMM |
Dual In-line Memory Module |
DRAM |
Dynamic Random Access Memory |
ECC |
Error Correction Code |
LVDIMM |
Low voltage DIMM |
MCA |
Machine Check Architecture |
MEMBIST |
Memory Built-In Self Test |
MRC |
Memory Reference Code |
POST |
Power On Self Test |
SPD |
Serial Presence Detect |
DDR |
Double Data Rate |
CAS |
Column Address Strobe |
RAS |
Row Address Strobe |
Troubleshooting DIMM Errors
Correct Installation of DIMMs
Verify that the DIMMs are installed correctly.
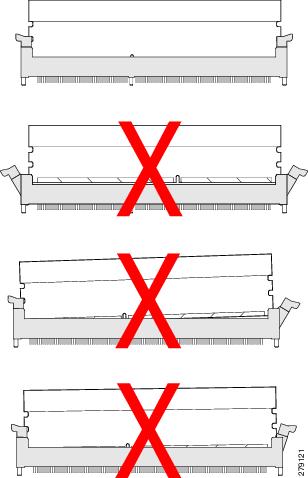
In the first example in the following figure, a DIMM is correctly inserted and latched. Unless there is a small bit of dust blocking one of the contacts, this DIMM should function correctly. The second example shows a DIMM that is mismatched with the key for its slot. That DIMM cannot be inserted in this orientation and must be rotated to fit into the slot. In the third example, the left side of the DIMM seems to be correctly seated and the latch is fully connected, but the right side is just barely touching the slot and the latch is not seated into the notch on the DIMM. In the fourth example, the left side is again fully inserted and seated, and the right side is partially inserted and incompletely latched.
Troubleshooting DIMM Errors Using Cisco IMC CLI
You can check memory information to identify possible DIMM errors in the Cisco IMC CLI.
| Command or Action | Purpose |
|---|
The following example shows how to check memory information using the Cisco IMC CLI:
Server# scope chassis
Server /chassis# show dimm detail
Name DIMM_A1:
Capacity: Failed
Channel Speed (MHz): NA
Channel Type: NA
Memory Type Detail: NA
Bank Locator: NA
Visibility: NA
Operability: NA
Manufacturer: NA
Part Number: NA
Serial Number: NA
Asset Tag: NA
Data Width: NA
Name DIMM_A2:
Capacity: Not Installed
Channel Speed (MHz): NA
Channel Type: NA
Memory Type Detail: NA
Bank Locator: NA
Visibility: NA
Operability: NA
Manufacturer: NA
Part Number: NA
Serial Number: NA
Asset Tag: NA
Data Width: NA
...
Troubleshooting DIMM errors using Cisco IMC GUI
You can determine the type of DIMM errors being experienced using the Cisco IMC GUI.
Troubleshooting Degraded DIMM Errors
DIMMs with correctable errors are not disabled and are available for the OS to use. The total memory and effective memory are the same (memory mirroring is taken into account). These correctable errors are reported in Cisco IMC as degraded.
If you see a correctable error reported in Cisco IMC, the problem can be corrected by resetting the BMC. Resetting the BMC just hides the DIMM with correctable error. However, to troubleshoot the DIMM physically, see Troubleshooting Inoperable DIMMs Errors
Use the following Cisco IMC CLI commands to reset BMC:
The following example shows how to view and reset the DIMM error flag:
Server/ scope chassis Server /chassis # show dimm Name Capacity Channel Speed (MHz) Channel Type -------------------- --------------- ------------------- --------------- DIMM_A1 Failed NA NA DIMM_A2 Ignored/Disa... NA NA DIMM_B1 16384 MB 1866 DDR3 DIMM_B2 16384 MB 1866 DDR3 DIMM_C1 16384 MB 1866 DDR3 DIMM_C2 16384 MB 1866 DDR3 DIMM_D1 16384 MB 1866 DDR3 DIMM_D2 16384 MB 1866 DDR3 DIMM_E1 16384 MB 1866 DDR3 DIMM_E2 16384 MB 1866 DDR3 DIMM_F1 16384 MB 1866 DDR3 DIMM_F2 16384 MB 1866 DDR3 DIMM_G1 16384 MB 1866 DDR3 DIMM_G2 16384 MB 1866 DDR3 DIMM_H1 16384 MB 1866 DDR3 DIMM_H2 16384 MB 1866 DDR3 Clear DIMM Error flag: Server/chassis# top Server/chassis# scope reset-ecc Server/chassis /reset-ecc # set enabled yes Server/chassis /reset-ecc *# commit
Troubleshooting Inoperable DIMMs Errors
DIMMs with uncorrectable errors are disabled and the OS on the server does not see that memory. If a DIMM or DIMMs fail while the system is up, the OS could crash unexpectedly. Cisco IMC shows the DIMMs as inoperable in the case of uncorrectable DIMM errors. These errors are not correctable using the software. You can identify a bad DIMM and remove it to allow the server to boot. For example, the BIOS fails to pass the POST due to one or more bad DIMMs.
To view and identify a bad DIMM using the Cisco IMC GUI, see Troubleshooting DIMM errors using Cisco IMC GUI
Recommended Solutions for DIMM Issues
The following table lists guidelines and recommended solutions for troubleshooting DIMM issues.
|
Issue |
Recommended Solution |
|---|---|
|
DIMM is not recognized. |
Verify that the DIMM is in a slot that supports an active CPU. Verify that the DIMM is sourced from Cisco. Third-party memory is not supported in Cisco UCS. |
|
DIMM does not fit in slot. |
Verify that the DIMM is supported on that server model. Verify that the DIMM is oriented correctly in the slot. DIMMs and their slots are keyed and only seat in one of the two possible orientations. |
|
The DIMM is reported as bad in the SEL, POST, or LEDs, or the DIMM is reported as inoperable in Cisco IMC. |
Verify that the DIMM is supported on that server model. Verify that the DIMM is populated in its slot according to the population rules for that server model. Verify that the DIMM is seated fully and correctly in its slot. Reseat it to assure a good contact and rerun POST. Verify that the DIMM is the problem by trying it in a slot that is known to be functioning correctly. Verify that the slot for the DIMM is not damaged by trying a DIMM that is known to be functioning correctly in the slot. Reset the BMC. |
|
The DIMM is reported as degraded in the GUI or CLI, or is running slower than expected. |
Reset the BMC. Reseat the rack server in the chassis. |
|
The DIMM is reported as overheating. |
Verify that the DIMM is seated fully and correctly in its slot. Reseat it to assure a good contact and rerun POST. Verify that all empty HDD bays, server slots, and power supply bays use blanking covers to assure that the air is flowing as designed. Verify that the server air baffles are installed to assure that the air is flowing as designed. Verify that any needed CPU air blockers are installed to assure that the air is flowing as designed. |
Troubleshooting Server and Memory Issues
|
Issue |
Recommended Solution |
| Server Related Issues | |
|
Every several days, the server requires a hard boot. |
|
|
Host is unreachable via IP, the CIMC works but KVM shows a blank screen. |
Upgrade the CIMC firmware and BIOS. |
| Memory Configuration Issues | |
|
Memory fault LED is amber on a new server. |
Upgrade the CIMC and BIOS. |
|
Memory errors on a previously working server. |
|
Troubleshooting Communication Issues
“No Signal” on vKVM and Physical Video Connection
If immediately at boot you receive a “No Signal” message from the vKVM and physical video connection, the PCI riser card might not be properly seated to the motherboard. To resolve the issue, complete these steps:
| Step 1 | Power off the server and disconnect the power cord. |
| Step 2 | Confirm that all cards are properly seated. |
| Step 3 | Connect the power cord and power on the server. |
 Feedback
Feedback