- Preface
- Configuration Management
- Administering the Cisco ME 1200 NID
- Configuring Notifications
- Zero Touch Provisioning
- Configuring Synchronous Ethernet
- Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connections
- Configuring Switch Ports
- Configuring Spanning-Tree Protocol
- Configuring Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
- Provisioning Link Layer Discovery Protocol
- Configuring SNMP
- Configuring PTP
- Configuring ACLs
- Configuring Quality of Service (QoS)
- Configuring Ethernet OAM, Link OAM, and CFM
- Configuring Performance Monitoring
- Configuring EPS
- Configuring ERPS
- Configuring L2CP
- Configuring MAC Security
- Configuring NTP
- Configuring Storm Control
- Configuring Syslog
- Configuring Dedicated Debug Shell
- Configuring SPAN
- Configuring RSPAN
- Configuring RFC 2544
- Configuring sFlow
- Configuring UDLD
- Configuring Flex Links
- Configuring Y.1564
- Configuring LST
- Configuring Security Access Control Lists
- Multicast Vlan Register
- Double-tagged management VLAN using IVID parameter
- Configuring LAG Aggregation
- Prerequisites for Configuring RFC 2544
- Restrictions for Configuring RFC 2544
- Information About RFC 2544
- How to Provision RFC 2544
- Disabling LLDP Port on NID-1
- Creating Layer 2 VLANs on NID-1
- Assigning VLANs to Ports on NID-1
- Disabling Spanning-Tree Protocol on NID-1
- Disabling LLDP Port on NID-2
- Creating Layer 2 VLANs on NID-2
- Assigning VLANs to Ports on NID-2
- Disabling Spanning-Tree Protocol on NID-2
- Creating Port MEP Profile on NID-1
- Creating Traffic Test Loop on Destination Port on NID-2
- Disabling Loop Protection on Destination Port on NID-2
- Setting RFC 2544 Reporting Parameters on NID-1
- Displaying RFC 2544 Profile and Report on NID-1
- Creating VLAN Profile on NID-1
- Getting RFC 2544 Profile for VLAN on NID-1
- Setting RFC 2544 Reporting Parameters for VLAN on NID-1
- Displaying RFC 2544 Report for VLAN on NID-1
- Deleting RFC 2544 Profile on NID-1
- Modifying RFC 2544 with Frameloss and Backtoback
- Getting RFC 2544 Profile after Modifying Frameloss and Backtoback
- Verifying RFC 2544
- Additional References
Configuring RFC 2544
This document describes the RFC 2544 feature and configuration steps to implement RFC 2544.
- Prerequisites for Configuring RFC 2544
- Restrictions for Configuring RFC 2544
- Information About RFC 2544
- How to Provision RFC 2544
- Verifying RFC 2544
- Additional References
Prerequisites for Configuring RFC 2544
Restrictions for Configuring RFC 2544
Information About RFC 2544
RFC 2544 defines a number of tests that can be used to describe the performance characteristics of a network interconnect devices. These tests certify that a Service Level Agreement (SLA) between a customer and a service provider is met.
You can perform RFC 2544 benchmark tests on Carrier Ethernet switch platforms running ME 1200 software without the need for any external test equipment.
-
Throughput—Measures the maximum rate at which none of the offered frames are dropped on the device.
-
Back-to-back—Measures the buffering capacity of a device.
-
Frame loss—Measures the performance of a network device in an overloaded state.
-
Latency—Measures the round-trip time taken by a test frame to travel through a network device or across the network and back to the test port.
 Note | For RFC 2544 to function properly, the Remote Node must support looping of particular frames. |
The RFC 2544 benchmarking can be done either on the Port MEP or Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) MEP. The following figure shows the topology used for provisioning RFC 2544 on two NIDs using a UPE NID Controller.
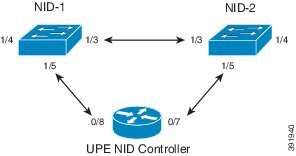
Before executing RFC 2544 test, you must prepare a test profile. The RFC 2544 test profile contains all the parameters associated with one test, where one test may be a combination of one or more sub-tests (Throughput, Latency, and Frame Loss, Back-to-Back).
-
Common Parameters
-
Profile Name— Name of each profile. Name can be up to 32 characters. Default name is New profile.
-
Profile Description—A text description up to 128 characters associated with the profile. Default description is blank.
-
MEG Level— Maintenance Entity Group (MEG) level on which the RFC 2544 test is run. Default MEG level is 7.
-
Egress Port—Egress port of the switch on which the RFC 2544 test frames are generated and checked.
-
Sequence Number Check—Checks generated frame sequence number. Default is Disabled.
-
Dwell Time—Number of seconds to wait after each trial for the system to settle before reading statistics from the hardware. Default is 2 seconds.
-
Type—Selects between two types of traffic: Port Down_MEP and VLAN-based Down_MEP. With VLAN-based Down_MEP, a configurable VLAN tag is inserted in the generated test frames.
-
VLAN ID—Specifies the VLAN ID if VLAN-based Down_MEP is configured.
-
PCP—Specifies the PCP value if VLAN-basedDown_MEP is configured.
-
DEI—Specifies the DEI value if VLAN-based Down_MEP is configured.
-
DMAC—Specifies the DMAC of the generated frames for both Port-based and VLAN-based Down_MEP.
-
Frame Size—Specifies the frame size each test must be repeated with, such as 64,128,256,512, 1024,1280,1518,2000, and 9600 bytes. Default frame size is all but 9600.
-
Sub-Tests To Run—Specifies the sub-tests to be run in the profile (Throughput, Latency, Frame Loss, Back-to-Back). Default sub-tests to run is Throughput and Latency.
-
-
Throughput Test Parameters
-
Trial Duration—Duration of a trial run in seconds. Valid range is from 1 to 1800 seconds. Default trial duration is 60 seconds.
-
Minimum and Maximum Rate—Specifies the maximum and minimum search rates.
-
Rate Step—Specifies the granularity of search within the minimum and maximum rates define above. All three input parameters are specified in % of the egress port’s actual link speed and must be in the range from 1 to 1000% with a granularity of 1%. Default rate step is Minimum: 800% of link speed, Maximum: 1000% of link speed, and Step size: 20% of link speed.
-
Allowed Frame Loss—Specifies the allowable frame loss. Valid value is in range is from 0 to 100% with a granularity of 1%. Default allowable frame loss is 0.
-
-
Latency Test Parameters
-
Trial Duration—Duration of a trial run in seconds. Valid range is from 10 to 1800 seconds. Default trial duration is 120 seconds.
-
Delay Measurement Interval—Specifies the number of seconds between each delay measurement. Valid range is from 1 to 60 seconds in steps of 1 second. Default delay measurement interval is 10 seconds.
-
Allowed Frame Loss—Specifies the pass criterion of an allowable frame loss. Valid range is from 0 to 10% with a granularity of 0.1%. Default allowed frame loss is 0.
-
-
Frame Loss Test Parameters
-
Trial Duration—Duration of a trial run in seconds. Valid range is from 1 to 1800 seconds. Default trial duration is 60 seconds.
-
Minimum and Maximum Rate—Specifies the maximum and minimum search rates.
-
Rate Step—Specifies the granularity of search within the minimum and maximum rates define above. All three input parameters must be specified in % of the egress port’s actual link speed and must be in the range from 1 to 1000% with a granularity of 1%. Default rate step is Minimum: 800%.
-
-
Back-to-Back Test Parameters
-
Trial duration—Specifies the duration of a burst. Valid range is from 100 to 10000 milliseconds. Default trial duration is 2000 milliseconds.
-
Trial Count—Specifies the number of times the trial is executed. Valid range is from 1 to 100. Default trial count is 50. Up to 16 profiles can be created and saved in the switch flash memory.
-
RFC 2544 Test Report
On executing a RFC 2544 test profile, RFC 2544 test report is generated. The RFC 2544 test report is in clear text format and contains all the input parameters defined by the associated test profile and the measurement results. The RFC 2544 test report can be used to certify if an SLA is met.
The last 10 RFC 2544 test reports are stored in the Flash memory of the UPE NID controller.How to Provision RFC 2544
Disabling LLDP Port on NID-1
Configuration Example
The example shows how to disable LLDP port on NID-1:
Switch(config)# controller nid 1/1 Switch(config-controller)# ProvisionLldpPortType Switch(config-controller-ProvisionLldpPortType)# setLldpPortConfig lldpPortConfiguration port_number 3 Switch(config-controller-ProvisionLldpPortType)# setLldpPortConfig lldpPortConfiguration lldp_receive_enable disable Switch(config-controller-ProvisionLldpPortType)# setLldpPortConfig lldpPortConfiguration lldp_transmit_enable disable Switch(config-controller-ProvisionLldpPortType)# setLldpPortConfig review Switch(config-controller-ProvisionLldpPortType)# setLldpPortConfig commit Switch(config-controller-ProvisionLldpPortType)# exit
Creating Layer 2 VLANs on NID-1
Configuration Example
The example shows how to create Layer 2 VLANs on NID-1:
Switch(config)# controller nid 1/1 Switch(config-controller)# ProvisionPortVlanPortType Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# createVlanCommand createVlanReq vlan_list 2-4095 Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# createVlanCommand review Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# createVlanCommand commit Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# exit
Assigning VLANs to Ports on NID-1
Configuration Example
The example shows how to assign VLANs to ports on NID-1:
Switch(config)# controller nid 1/1 Switch(config-controller)# ProvisionPortVlanPortType Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# modifySwPort modifySWPortConfig interaface 3 Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# modifySwPort modifySWPortConfig mode trunk native vlan 3 Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# modifySwPort modifySWPortConfig mode trunk allowed vlan add vlan_list 2-4095 Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# modifySwPort review Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# modifySwPort commit Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# exit
Disabling Spanning-Tree Protocol on NID-1
Configuration Example
The example shows how to disable Spanning-Tree Protocol on NID-1:
Switch(config)# controller nid 1/1 Switch(config-controller)# ProvisionStpPortType Switch(config-controller-ProvisionStpPortType)# setStpGlobalConfig stpGlobalConfig port-number 3 disable Switch(config-controller-ProvisionStpPortType)# setStpGlobalConfig review Switch(config-controller-ProvisionStpPortType)# setStpGlobalConfig commit Switch(config-controller-ProvisionStpPortType)# exit
Disabling LLDP Port on NID-2
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | controller nid
1/NID_ID
Example: Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 |
Enters the controller configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | controller nid
1/NID_ID
Example: Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 |
Enters the controller configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | ProvisionLldpPortType
Example: Switch(config-controller)# ProvisionLldpPortType | Enters the ProvisionLldpPortType mode. |
| Step 4 | setLldpportconfig
lldpPortConfiguration {lldp_receive_enable {disable |
enable} |
lldp_transmit_enable
{disable |
enable} |
port_number
port_number}
Example: Switch(config-controller-ProvisionLldpPortType)# setLldpPortConfig lldpPortConfiguration port_number 3 Switch(config-controller-ProvisionLldpPortType)# setLldpPortConfig lldpPortConfiguration lldp_receive_enable disable Switch(config-controller-ProvisionLldpPortType)# setLldpPortConfig lldpPortConfiguration lldp_transmit_enable disable |
Sets the Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) port configuration. |
| Step 5 | setLldpPortConfig review
Example: Switch(config-controller-ProvisionLldpPortType)# setLldpPortConfig review
| Displays the setLldpPortConfig configuration. |
| Step 6 | setLldpPortConfig commit
Example: Switch(config-controller-ProvisionLldpPortType)# setLldpPortConfig commit
| Sends the setLldpConfig configuration to the ME 1200 NID. |
| Step 7 | exit
Example: Switch(config-controller-ProvisionLldpPortType)# exit
| Exits to the config-controller mode. |
Configuration Example
The example shows how to disable LLDP port on NID-2:
Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 Switch(config-controller)# ProvisionLldpPortType Switch(config-controller-ProvisionLldpPortType)# setLldpPortConfig lldpPortConfiguration port_number 3 Switch(config-controller-ProvisionLldpPortType)# setLldpPortConfig lldpPortConfiguration lldp_receive_enable disable Switch(config-controller-ProvisionLldpPortType)# setLldpPortConfig lldpPortConfiguration lldp_transmit_enable disable Switch(config-controller-ProvisionLldpPortType)# setLldpPortConfig review Switch(config-controller-ProvisionLldpPortType)# setLldpPortConfig commit Switch(config-controller-ProvisionLldpPortType)# exit
Creating Layer 2 VLANs on NID-2
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure
terminal
Example: Switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | controller nid
1/NID_ID
Example: Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 |
Enters the controller configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | ProvisionPortVlanPortType
Example: Switch(config-controller)# ProvisionPortVlanPortType
| Enters the ProvisionPortVlanPortType mode. |
| Step 4 | createVlanCommand
createVlanReq
vlan_list
vlan_list
Example: Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# createVlanCommand createVlanReq vlan_list 2-4095 | Creates the VLAN list. The valid values are from 1 to 4095. |
| Step 5 | createVlanCommand
review
Example: Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# createVlanCommand review
|
Displays the createVlanCommand configuration. |
| Step 6 | createVlanCommand
commit
Example: Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# createVlanCommand commit
| Sends the createVlanCommand configuration to the ME 1200 NID. |
| Step 7 | exit
Example: Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# exit
| Exits to the config-controller mode. |
Configuration Example
The example shows how to create Layer 2 VLANs on NID-2:
Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 Switch(config-controller)# ProvisionPortVlanPortType Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# createVlanCommand createVlanReq vlan_list 2-4095 Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# createVlanCommand review Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# createVlanCommand commit Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# exit
Assigning VLANs to Ports on NID-2
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure
terminal
Example: Switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | controller nid
1/NID_ID
Example: Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 |
Enters the controller configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | ProvisionPortVlanPortType
Example: Switch(config-controller)# ProvisionPortVlanPortType
| Enters the ProvisionPortVlanPortType mode. |
| Step 4 | modifySwPort
modifySWPortConfig
interface
interface_id
Example: Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# modifySwPort modifySWPortConfig interaface 3
| Modifies the switchport configuration on the defined interface. |
| Step 5 | modifySwPort
modifySWPortConfig
mode
access
vlan
vlan_id
Example: Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# modifySwPort modifySWPortConfig mode trunk native vlan 3
| Sets the mode to ACCESS, and assigns a VLAN. |
| Step 6 | modifySwPort
modifySWPortConfig mode trunk {allowed vlan {add {all |
vlan_list
vlan_list
} |
remove
{all |
vlan_list
vlan_list
}} | {native vlan
vlan_list
}
Example: Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# modifySwPort modifySWPortConfig mode trunk allowed vlan add vlan_list 2-4095 | Sets the mode to TRUNK. |
| Step 7 | modifySwPort
review
Example: Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# modifySwPort review
|
Displays the modifySwPort configuration. |
| Step 8 | modifySwPort
commit
Example: Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# modifySwPort commit
| Sends the modifySwPort configuration to the ME 1200 NID. |
| Step 9 | exit
Example: Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# exit
| Exits to the config-controller mode. |
Configuration Example
The example shows how to assign VLANs to ports on NID-2:
Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 Switch(config-controller)# ProvisionPortVlanPortType Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# modifySwPort modifySWPortConfig interaface 3 Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# modifySwPort modifySWPortConfig mode trunk native vlan 3 Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# modifySwPort modifySWPortConfig mode trunk allowed vlan add vlan_list 2-4095 Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# modifySwPort review Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# modifySwPort commit Switch(config-controller-ProvisionPortVlanPortType)# exit
Disabling Spanning-Tree Protocol on NID-2
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure
terminal
Example: Switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 2 | controller nid
1/NID_ID
Example: Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 |
Enters the controller configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 | ProvisionStpPortType
Example: Switch (config-controller)# ProvisionStpPortType
| Enters the ProvisionStpPortType mode. | ||
| Step 4 | setStpglobalConfig
stpGlobalConfig {edge {bpdu-filter |
bpdu-guard} {enable |
disable} |
mode
{mstp |
rstp |
stp}
{enable |
disable} |
mst
{forward-time
Fwdtime |
instance
instance {active {enable |
disable} |
priority
Prio
|
vlan
WORD}
|
max-age
Maxage
|
max-hops
Maxhops |
name
Name |
revision
Revision } |
port-number
Port
number {enable |
disable} |
recovery
Interval
|
transmit
hold-count }
Example: Switch(config-controller-ProvisionStpPortType)# setStpGlobalConfig stpGlobalConfig port-number 3 disable
|
| ||
| Step 5 | setStpGlobalConfig review
Example: Switch(config-controller-ProvisionStpPortType)# setStpGlobalConfig review
| Displays the setStpGlobalConfig. | ||
| Step 6 | setStpGlobalConfig commit
Example: Switch(config-controller-ProvisionStpPortType)# setStpGlobalConfig commit
| Sends the setStpGlobalConfig configuration to the ME 1200 NID. | ||
| Step 7 | exit
Example: Switch(config-controller-ProvisionStpPortType)# exit
| Exits to the config-controller mode. |
Configuration Example
The example shows how to disable Spanning-Tree Protocol on NID-2:
Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 Switch(config-controller)# ProvisionStpPortType Switch(config-controller-ProvisionStpPortType)# setStpGlobalConfig stpGlobalConfig port-number 3 disable Switch(config-controller-ProvisionStpPortType)# setStpGlobalConfig review Switch(config-controller-ProvisionStpPortType)# setStpGlobalConfig commit Switch(config-controller-ProvisionStpPortType)# exit
Creating Port MEP Profile on NID-1
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure terminal
Example: Switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 2 | controller nid
1/NID_ID
Example: Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 |
Enters the controller configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 | RFC2544PortType
Example: Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType
| Enters the RFC2544PortType mode. | ||
| Step 4 | setRfc2544Profile
Rfc2544Profile {profileName
|
description
|
megLevel
|
egressPort
|
seqNoCheck {enable
|
disable}
|
dwellTime
|
mepType {portDownMep
|
vlanDownMep}
|
vlanId
|
pcp
|
dei
|
dMac}
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile profileName profile1 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile description profile1 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile egressPort 3 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile megLevel 5 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile mepType portDownMep Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile seqNoCheck disable |
Creates Port MEP profile.
| ||
| Step 5 | setRfc2544Profile review
Example: Switch((config-controller)RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile review
| Displays the setRfc2544Profile. | ||
| Step 6 | setRfc2544Profile commit
Example: Switch((config-controller)RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile commit
| Sends the setRfc2544Profile configuration to the Cisco ME 1200 NID. | ||
| Step 7 | exit
Example: Switch((config-controller)RFC2544PortType)# exit
| Exits to the config-controller mode. |
Configuration Example
The example shows how to create Port MEP profile on NID-1:
Switch(config)# controller nid 1/1 Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile profileName profile1 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile description profile1 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile egressPort 3 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile megLevel 5 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile mepType portDownMep Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile seqNoCheck disable Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile review Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setrfc2544profile commit Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# exit
Creating Traffic Test Loop on Destination Port on NID-2
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure terminal
Example: Switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 2 | controller nid
1/NID_ID
Example: Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 |
Enters the controller configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 | RFC2544PortType
Example: Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType
|
Enters the RFC2544PortType configuration mode. | ||
| Step 4 |
setTrafficTestLoop
trafficTestLoopConfig {instNum
|
adminState {enable
|
disable}
|
custVID
|
name
|
type
{macLoop
|
oamLoop}
|
interface
|
direction {facility
|
terminal}
|
domain {evc
|
port
|
vlan}
|
flowld
|
level}
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setTrafficTestLoop trafficTestLoopConfig interface 3 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setTrafficTestLoop trafficTestLoopConfig type macLoop Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setTrafficTestLoop trafficTestLoopConfig direction facility Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setTrafficTestLoop trafficTestLoopConfig domain port Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setTrafficTestLoop trafficTestLoopConfig adminState enable Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setTrafficTestLoop trafficTestLoopConfig instNum 1 | Creates traffic
test loop on destination port on NID-2.
| ||
| Step 5 | setTrafficTestLoop
review
Example: Switch((config-controller)RFC2544PortType)# setTrafficTestLoop review
|
Displays the setTrafficTestLoop configuration. | ||
| Step 6 | setTrafficTestLoop
commit
Example: Switch((config-controller)RFC2544PortType)# setTrafficTestLoop commit
| Sends the setTrafficTestLoop configuration to the ME 1200 NID. | ||
| Step 7 | exit
Example: Switch((config-controller)RFC2544PortType)# exit
| Exits to the config-controller mode. |
Configuration Example
The example shows how to create traffic test loop on destination port on NID-2:
Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setTrafficTestLoop trafficTestLoopConfig interface 3 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setTrafficTestLoop trafficTestLoopConfig type macLoop Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setTrafficTestLoop trafficTestLoopConfig direction facility Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setTrafficTestLoop trafficTestLoopConfig domain port Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setTrafficTestLoop trafficTestLoopConfig adminState enable Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setTrafficTestLoop trafficTestLoopConfig instNum 1 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setTrafficTestLoop review Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setTrafficTestLoop commit Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# exit
Disabling Loop Protection on Destination Port on NID-2
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure terminal
Example: Switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | controller nid
1/NID_ID
Example: Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 |
Enters the controller configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | RFC2544PortType
Example: Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType
|
Enters the RFC2544PortType configuration mode. |
| Step 4 |
deleteTrafficTestLoop
deleteLoopConfig {trafficLoop
instNum
|loopPotect
interface}
Example: Switch((config-controller)RFC2544PortType)# deleteTrafficTestLoop deleteLoopConfig loopPotect interface 3
| Disables loop protection on destination port on NID-2. |
| Step 5 | deleteTrafficTestLoop
review
Example: Switch((config-controller)RFC2544PortType)# deleteTrafficTestLoop review
|
Displays the deleteTrafficTestLoop configuration. |
| Step 6 | deleteTrafficTestLoop
commit
Example: Switch((config-controller)RFC2544PortType)# deleteTrafficTestLoop commit
| Sends the deleteTrafficTestLoop configuration to the ME 1200 NID. |
| Step 7 | exit
Example: Switch((config-controller)RFC2544PortType)# exit
| Exits to the config-controller mode. |
Configuration Example
The example shows how to disable loop protection on destination port on NID-2:
Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# deleteTrafficTestLoop deleteLoopConfig loopPotect interface 3 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# deleteTrafficTestLoop review Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# deleteTrafficTestLoop commit Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# exit
Setting RFC 2544 Reporting Parameters on NID-1
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure terminal
Example: Switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | controller nid
1/NID_ID
Example: Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 |
Enters the controller configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | RFC2544PortType
Example: Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType
| Enters the RFC2544PortType mode. |
| Step 4 | setReportParams
rfc2544Reports
reportAction {delete
reportName
|
save
{reportName
|
tftpPath}
|
start {reportName
|
profileName
|
description}
|
stop
reportName
|
rename {oldName
|
newName}}
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setReportParams rfc2544Reports reportAction start profileName profile1 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setReportParams rfc2544Reports reportAction start reportName profile1 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setReportParams rfc2544Reports reportAction start description profile1 |
Sets RFC 2544 reporting parameters. |
| Step 5 | setReportParams review
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setReportParams review
| Displays the setReportParams configuration. |
| Step 6 | setReportParams commit
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setReportParams commit
| Sends the setReportParams configuration to the ME 1200 NID. |
| Step 7 | exit
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# exit
| Exits to the config-controller mode. |
Configuration Example
The example shows how to set the RFC 2544 reporting parameters on NID-1:
Switch(config)# controller nid 1/1 Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setReportParams rfc2544Reports reportAction start profileName profile1 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setReportParams rfc2544Reports reportAction start reportName profile1 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setReportParams rfc2544Reports reportAction start description profile1 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setReportParams review Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setReportParams commit Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# exit
Displaying RFC 2544 Profile and Report on NID-1
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure terminal
Example: Switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | controller nid
1/NID_ID
Example: Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 |
Enters the controller configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | RFC2544PortType
Example: Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType
| Enters the RFC2544PortType mode. |
| Step 4 | showRfc2544
showRequest
show
{profiles
|
report}
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# showRfc2544 showRequest show profiles
| Displays RFC 2544 profile. |
| Step 5 | showRfc2544
review
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# showRfc2544 review
|
Displays the showRfc2544 configuration. |
| Step 6 | showRfc2544
commit
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# showRfc2544 commit
| Sends the setRfc2544Profile configuration to the ME 1200 NID. |
| Step 7 | showRfc2544
showRequest
show
{profiles
|
report}
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# showRfc2544 showRequest show report
| Displays RFC 2544 profile. |
| Step 8 | showRfc2544
review
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# showRfc2544 review
|
Displays the showRfc2544 configuration. |
| Step 9 | showRfc2544
commit
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# showRfc2544 commit
| Sends the setRfc2544Profile configuration to the ME 1200 NID. |
| Step 10 | exit
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# exit
| Exits to the config-controller mode. |
Configuration Example
The example shows how to display RFC 2544 profile and report on NID-1:
Switch(config)# controller nid 1/1 Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# showRfc2544 showRequest show profiles Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# showRfc2544 review Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# showRfc2544 commit
ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.t = 1 ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.profile[0].profileName = 'profile1' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.profile[0].description = 'profile1' ShowRfc2544 Commit Success!!!
Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# showRfc2544 showRequest show report Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# showRfc2544 review Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# showRfc2544 commit
ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.t = 2 ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[0].reportName = 'Report1' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[0].created = '1970-01-04T07:29:25+00:00' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[0].status = 'Succeeded' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[1].reportName = 'Rep15' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[1].created = '1970-01-02T01:57:34+00:00' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[1].status = 'Failed' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[2].reportName = 'Rep16' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[2].created = '1970-01-02T02:08:12+00:00' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[2].status = 'Succeeded' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[3].reportName = 'profile1' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[3].created = '1970-01-02T03:48:16+00:00' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[3].status = 'Failed' ShowRfc2544 Commit Success!!!
Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# exit
Creating VLAN Profile on NID-1
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure terminal
Example: Switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 2 | controller nid
1/NID_ID
Example: Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 |
Enters the controller configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 | RFC2544PortType
Example: Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType
| Enters the RFC2544PortType mode. | ||
| Step 4 | setRfc2544Profile
Rfc2544Profile {profileName
|
description
|
megLevel
|
egressPort
|
seqNoCheck {enable
|
disable}
|
dwellTime
|
mepType {portDownMep
|
vlanDownMep}
|
vlanId
|
pcp
|
dei
|
dMac}
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile profileName vlan-profile Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile egressPort 3 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile mepType vlanDownMep Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile vlanId 999 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile megLevel 4 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile description vlanprofile |
Creates RFC profile.
| ||
| Step 5 | setRfc2544Profile review
Example: Switch(config-controllerRFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile review
| Displays the setRfc2544Profile. | ||
| Step 6 | setRfc2544Profile commit
Example: Switch(config-controllerRFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile commit
| Sends the setRfc2544Profile configuration to the ME 1200 NID. | ||
| Step 7 | exit
Example: Switch(config-controllerRFC2544PortType)# exit
| Exits to the config-controller mode. |
Configuration Example
The example shows how to create VLAN profile on NID-1:
Switch(config)# controller nid 1/1 Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile profileName vlan-profile Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile egressPort 3 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile mepType vlanDownMep Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile vlanId 999 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile megLevel 4 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile Rfc2544Profile description vlanprofile Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544Profile review Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setrfc2544profile commit Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# exit
Getting RFC 2544 Profile for VLAN on NID-1
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure terminal
Example: Switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | controller nid
1/NID_ID
Example: Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 |
Enters the controller configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | RFC2544PortType
Example: Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType
| Enters the RFC2544PortType mode. |
| Step 4 | getRfc2544Profile
rfc2544Request
profileName
profileName
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# getRfc2544Profile rfc2544Request profileName vlan-profile
| Gets the RFC 2544 profile. |
| Step 5 | getRfc2544Profile
review
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# getRfc2544Profile review
|
Displays the getRfc2544Profile configuration. |
| Step 6 | getRfc2544Profile
commit
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# getRfc2544Profile commit
| Sends the getRfc2544Profile configuration to the ME 1200 NID. |
| Step 7 | exit
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# exit
| Exits to the config-controller mode. |
Configuration Example
The example shows how to get RFC 2544 profile for VLAN on NID-1:
Switch(config)# controller nid 1/1 Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# getRfc2544Profile rfc2544Request profileName vlan-profile Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# getRfc2544Profile review Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# getRfc2544Profile commit
GetRfc2544Profile_Output.Rfc2544Profile.profileName = 'vlan-profile'
GetRfc2544Profile_Output.Rfc2544Profile.description = 'vlanprofile'
GetRfc2544Profile_Output.Rfc2544Profile.megLevel = 4
GetRfc2544Profile_Output.Rfc2544Profile.egressPort = 3
GetRfc2544Profile_Output.Rfc2544Profile.seqNoCheck.t = 2
GetRfc2544Profile_Output.Rfc2544Profile.seqNoCheck.u.disable = ''
GetRfc2544Profile_Output.Rfc2544Profile.dwellTime = 2
GetRfc2544Profile_Output.Rfc2544Profile.mepType.t = 2
GetRfc2544Profile_Output.Rfc2544Profile.mepType.u.vlanDownMep = ''
GetRfc2544Profile_Output.Rfc2544Profile.vlanId = 999
GetRfc2544Profile_Output.Rfc2544Profile.pcp = 0
GetRfc2544Profile_Output.Rfc2544Profile.dei = 0
GetRfc2544Profile_Output.Rfc2544Profile.dMac = '00-00-00-00-00-01'
GetRfc2544Profile Commit Success!!!
Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# exit
Setting RFC 2544 Reporting Parameters for VLAN on NID-1
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure terminal
Example: Switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | controller nid
1/NID_ID
Example: Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 |
Enters the controller configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | RFC2544PortType
Example: Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType
| Enters the RFC2544PortType mode. |
| Step 4 | setReportParams
rfc2544Reports
reportAction {delete
reportName
|
save
{reportName
|
tftpPath}
|
start
{reportName
|
profileName
|
description}
|
stop
reportName
|
rename
{oldName
|
newName}}
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setReportParams rfc2544Reports reportAction start profileName vlan-profile Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setReportParams rfc2544Reports reportAction start reportName vlan-profile Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setReportParams rfc2544Reports reportAction start description vlan-profile |
Sets RFC 2544 reporting parameters. |
| Step 5 | setReportParams review
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setReportParams review
| Displays the setReportParams configuration. |
| Step 6 | setReportParams commit
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setReportParams commit
| Sends the setReportParams configuration to the ME 1200 NID. |
| Step 7 | exit
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# exit
| Exits to the config-controller mode. |
Configuration Example
The example shows how to set the RFC 2544 reporting parameters for VLAN on NID-1:
Switch(config)# controller nid 1/1 Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setReportParams rfc2544Reports reportAction start profileName vlan-profile Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setReportParams rfc2544Reports reportAction start reportName vlan-profile Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setReportParams rfc2544Reports reportAction start description vlan-profile Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setReportParams review Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setReportParams commit Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# exit
Displaying RFC 2544 Report for VLAN on NID-1
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure terminal
Example: Switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | controller nid
1/NID_ID
Example: Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 |
Enters the controller configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | RFC2544PortType
Example: Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType
| Enters the RFC2544PortType mode. |
| Step 4 | showRfc2544
showRequest
show
{profiles
|
report}
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# showRfc2544 showRequest show profiles
| Displays RFC 2544 profile. |
| Step 5 | showRfc2544
review
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# showRfc2544 review
|
Displays the showRfc2544 configuration. |
| Step 6 | showRfc2544
commit
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# showRfc2544 commit
| Sends the setRfc2544Profile configuration to the ME 1200 NID. |
| Step 7 | showRfc2544
showRequest
show
{profiles
|
report}
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# showRfc2544 showRequest show report
| Displays RFC 2544 profile. |
| Step 8 | showRfc2544
review
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# showRfc2544 review
|
Displays the showRfc2544 configuration. |
| Step 9 | showRfc2544
commit
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# showRfc2544 commit
| Sends the setRfc2544Profile configuration to the ME 1200 NID. |
| Step 10 | exit
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# exit
| Exits to the config-controller mode. |
Configuration Example
The example shows how to display RFC 2544 report for VLAN on NID-1:
Switch(config)# controller nid 1/1 Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# showRfc2544 showRequest show report Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# showRfc2544 review Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# showRfc2544 commit
ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.t = 2 ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[0].reportName = 'Report1' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[0].created = '1970-01-04T07:29:25+00:00' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[0].status = 'Succeeded' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[1].reportName = 'Rep15' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[1].created = '1970-01-02T01:57:34+00:00' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[1].status = 'Failed' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[2].reportName = 'Rep16' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[2].created = '1970-01-02T02:08:12+00:00' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[2].status = 'Succeeded' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[3].reportName = 'profile1' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[3].created = '1970-01-02T03:48:16+00:00' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[3].status = 'Failed' ShowRfc2544 Commit Success!!!
Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# exit
Deleting RFC 2544 Profile on NID-1
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure
terminal
Example: Switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | controller nid
1/NID_ID
Example: Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 |
Enters the controller configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | RFC2544PortType
Example: Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType
| Enters the RFC2544PortType mode. |
| Step 4 | deleterfc2544
rfc2544DeleteConfig {profileName
profileName
|
delete {btob
|
dMAC
|
description
|
dwellTime
|
frameLoss
|
frameSizes
|
ifc
|
latency
|
megLevel
|
rfc2544
|
throughput
|
vid}}
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# deleteRfc2544 rfc2544DeleteConfig profileName profile1
|
Deletes RFC profile.
|
| Step 5 | deleteRfc2544 review
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# deleteRfc2544 review
| Displays the deleteRfc2544 configuration. |
| Step 6 | deleteRfc2544 commit
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# deleteRfc2544 commit
| Sends the deleteRfc2544 configuration to the ME 1200 NID. |
| Step 7 | exit
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# exit
| Exits to the config-controller mode. |
Configuration Example
The example shows how to delete RFC 2544 profile on NID-1:
Switch(config)# controller nid 1/1 Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# deleteRfc2544 rfc2544DeleteConfig profileName profile1 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# deleteRfc2544 review Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# deleteRfc2544 commit Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# exit
Modifying RFC 2544 with Frameloss and Backtoback
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure terminal
Example: Switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | controller nid
1/NID_ID
Example: Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 |
Enters the controller configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | RFC2544PortType
Example: Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType
| Enters the RFC2544PortType mode. |
| Step 4 | SetRfc2544TestToRun
testParameters {profileName
profileName
|
frameSizes
|
testToRun {throughput
|
latency
|
frameLoss
|
backToBack}
|
thoughputTParams {trialDuration
|
minRate
|
maxRate
|
accuracy
|
allowedFrameLoss}
|
latencyTParams {trialDuration
|
delayMessInterval
|
allowedFrameLoss}
|
frameLossTParams {trialDuration
|
minRate
|
maxRate
|
rateStep}
|
backToBackTParams {trialDuration
|
trialCount}}
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun testParameters profileName vlan-profile Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun testParameters backToBackTParams trialCount 2 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun testParameters frameLossTParams minRate 100 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun testParameters frameLossTParams maxRate 200 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun testParameters frameLossTParams rateStep 10 |
Modifies RFC 2544 with Frameloss and Backtoback.
|
| Step 5 | SetRfc2544TestToRun review
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# SetRfc2544TestToRun review
| Displays the SetRfc2544TestToRun configuration. |
| Step 6 | SetRfc2544TestToRun commit
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# SetRfc2544TestToRun commit
| Sends the SetRfc2544TestToRun configuration to the ME 1200 NID. |
| Step 7 | SetRfc2544TestToRun
testParameters {profileName
profileName
|
frameSizes
|
testToRun {throughput
|
latency
|
frameLoss
|
backToBack}
|
thoughputTParams {trialDuration
|
minRate
|
maxRate
|
accuracy
|
allowedFrameLoss}
|
latencyTParams {trialDuration
|
delayMessInterval
|
allowedFrameLoss}
|
frameLossTParams {trialDuration
|
minRate
|
maxRate
|
rateStep}
|
backToBackTParams {trialDuration
|
trialCount}}
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun testParameters testToRun backToBack enable Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun testParameters testToRun frameLoss enable Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun testParameters testToRun latency disable Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun testParameters testToRun throughput disable Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun testParameters profileName vlan-profile |
Modifies RFC 2544 with Frameloss and Backtoback.
|
| Step 8 | SetRfc2544TestToRun review
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# SetRfc2544TestToRun review
| Displays the SetRfc2544TestToRun configuration. |
| Step 9 | SetRfc2544TestToRun commit
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# SetRfc2544TestToRun commit
| Sends the SetRfc2544TestToRun configuration to the ME 1200 NID. |
| Step 10 | exit
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# exit
| Exits to the config-controller mode. |
Configuration Example
The example shows how to modify and enable RFC 2544 with Frameloss and Backtoback:
Switch(config)# controller nid 1/1 Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun testParameters profileName vlan-profile Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun testParameters backToBackTParams trialCount 2 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun testParameters frameLossTParams minRate 100 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun testParameters frameLossTParams maxRate 200 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun testParameters frameLossTParams rateStep 10 Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun review Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun commit Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun testParameters testToRun backToBack enable Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun testParameters testToRun frameLoss enable Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun testParameters testToRun latency disable Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun testParameters testToRun throughput disable Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun testParameters profileName vlan-profile Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun review Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# setRfc2544TestToRun commit Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# exit
Getting RFC 2544 Profile after Modifying Frameloss and Backtoback
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure terminal
Example: Switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | controller nid
1/NID_ID
Example: Switch(config)# controller nid 1/2 |
Enters the controller configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | RFC2544PortType
Example: Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType
| Enters the RFC2544PortType mode. |
| Step 4 | getRfc2544TestToRun
rfc2544Request
profileName
profileName
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# getRfc2544TestToRun rfc2544Request profileName vlan-profile
| Gets the RFC 2544 profile. |
| Step 5 | getRfc2544TestToRun
review
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# getRfc2544TestToRun review
|
Displays the getRfc2544Profile configuration. |
| Step 6 | getRfc2544TestToRun
commit
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# getRfc2544TestToRun commit
| Sends the getRfc2544Profile configuration to the ME 1200 NID. |
| Step 7 | exit
Example: Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# exit
| Exits to the config-controller mode. |
Configuration Example
The example shows how to get RFC 2544 Profile after modifying frameloss and backtoback:
Switch(config)# controller nid 1/1 Switch(config-controller)# RFC2544PortType Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# getRfc2544TestToRun rfc2544Request profileName vlan-profile Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# getRfc2544TestToRun review Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# getRfc2544TestToRun commit
GetRfc2544TestToRun_Output.testParameters.profileName = 'vlan-profile' GetRfc2544TestToRun_Output.testParameters.frameSizes = '64-128-256-512-1024-1280-1518-2000' GetRfc2544TestToRun_Output.testParameters.testToRun.throughput = false GetRfc2544TestToRun_Output.testParameters.testToRun.latency = false GetRfc2544TestToRun_Output.testParameters.testToRun.frameLoss = true GetRfc2544TestToRun_Output.testParameters.testToRun.backToBack = true GetRfc2544TestToRun_Output.testParameters.thoughputTParams.trialDuration = 60 GetRfc2544TestToRun_Output.testParameters.thoughputTParams.minRate = 800 GetRfc2544TestToRun_Output.testParameters.thoughputTParams.maxRate = 1000 GetRfc2544TestToRun_Output.testParameters.thoughputTParams.accuracy = 2 GetRfc2544TestToRun_Output.testParameters.thoughputTParams.allowedFrameLoss = 0 GetRfc2544TestToRun_Output.testParameters.latencyTParams.trialDuration = 120 GetRfc2544TestToRun_Output.testParameters.latencyTParams.delayMessInterval = 10 GetRfc2544TestToRun_Output.testParameters.latencyTParams.allowedFrameLoss = 0 GetRfc2544TestToRun_Output.testParameters.frameLossTParams.trialDuration = 60 GetRfc2544TestToRun_Output.testParameters.frameLossTParams.minRate = 800 GetRfc2544TestToRun_Output.testParameters.frameLossTParams.maxRate = 1000 GetRfc2544TestToRun_Output.testParameters.frameLossTParams.rateStep = 5 GetRfc2544TestToRun_Output.testParameters.backToBackTParams.trialDuration = 2000 GetRfc2544TestToRun_Output.testParameters.backToBackTParams.trialCount = 50 GetRfc2544TestToRun Commit Success!!!
Switch(config-controller-RFC2544PortType)# exit
Verifying RFC 2544
Use the following commands to verify the RFC 2544 status on the controller.
-
showRfc2544 com
This command displays the RFC 2544 report. The following is a sample output from the command:
Switch(config-controller-SPAN)# showRfc2544 comSwitch(config-controller-SPAN)# showRfc2544 com reviewCommands in queue: showRfc2544 com
Switch(config-controller-SPAN)# showSpanConfig commitShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.t = 2 ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[0].reportName = 'Jul3' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[0].created = '1970-01-04T01:02:24+00:00' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[0].status = 'Failed' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[1].reportName = 'July3' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[1].created = '1970-01-04T01:15:37+00:00' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[1].status = 'Failed' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[2].reportName = 'repjuly3' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[2].created = '1970-01-04T01:52:07+00:00' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[2].status = 'Succeeded' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[3].reportName = 'Report1' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[3].created = '1970-01-04T07:29:25+00:00' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[3].status = 'Succeeded' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[4].reportName = 'rep-vlan' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[4].created = '1970-01-04T21:01:59+00:00' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[4].status = 'Failed' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[5].reportName = 'Report20' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[5].created = '1970-01-01T08:15:17+00:00' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[5].status = 'Failed' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[6].reportName = 'Rep22' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[6].created = '1970-01-01T09:36:14+00:00' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[6].status = 'Failed' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[7].reportName = 'profile2' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[7].created = '1970-01-02T00:55:43+00:00' ShowRfc2544_Output.showResponse.u.report[7].status = 'Failed' ShowRfc2544 Commit Success!!!
Additional References
Related Documents
| Related Topic | Document Title |
|---|---|
Cisco ME 3800x and ME 3600x Switches Software Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15.4(1)S |
MIBs
| MIB | MIBs Link |
|---|---|
MIBs Supporting Cisco IOS |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
Technical Assistance
| Description | Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online resources, including documentation and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. To receive security and technical information about your products, you can subscribe to various services, such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter, and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
 Feedback
Feedback