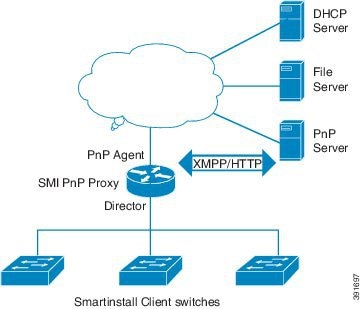
Information about SMI Proxy
Prior to Cisco IOS XE 3.6.0E releases, Smart Install was the routine way to manage zero-touch deployments (ZTD) for Catalyst devices. Cisco's solution toward ZTD, Plug and Play (PnP) provides an agent that runs on each networking device and a server that manages your network devices with respect to configuration, image, and more.
Table 4-1 Feature History Information for SMI Proxy
|
|
|
Cisco IOS XE 3.6.0E and IOS 15.2(2)E |
The PnP Agent is available on Catalyst 4500 series, Catalyst 3850, Catalyst 3650, IE 2000, IE 3000, IE 3010, Catalyst 2K and Catalyst 3K switches. Devices running older releases (prior to Cisco IOS-XE 3.6.0E, and IOS 15.2(2)E) rely on existing ZTD solutions such as SmartInstall to enable IOS version updates. Devices running the older release cannot communicate with the central PNP Server. These devices require a migration path to reach the PNP Server. |
Cisco IOS XE 3.6.3E and Cisco IOS 15.2(2)E3 and Cisco IOS XE 3.7.3E and Cisco IOS 15.2(3)E3 |
Beginning with the specified releases, the Catalyst 4500, Catalyst 3850, Catalyst 3750, Catalyst 3650, and Catalyst 3560 switches support SMI PnP Proxy. This feature leverages SMI functionality in an existing network device and allows for image and configuration upgrade of devices running older versions. SMI Proxy is applicable only to platforms that support SMI Director. The SMI Proxy feature will run on a network device that is running the required Cisco IOS release and is configured for PNP Agent and SMI Proxy. This device will bridge the communication from older devices running SmartInstall to the PNP Server. It will "proxy" as the PNP Agent for devices running older versions, enabling these devices to behave as if the SMI Proxy device is the SMI Director. The SMI Proxy device will contact the central PnP Server on behalf of the device running older versions to retrieve image and configuration information. |
Cisco IOS XE 3.6.3E and Cisco IOS 15.2(3)E3 |
Beginning with this release, the Catalyst 4500, Catalyst 3850, Catalyst 3750, Catalyst 3650, and Catalyst 3560 support PnP discovery process via various discovery mechanisms and security methods. |
This section contains:
How SMI Proxy Interacts with Smart Install Devices and the PnP Agent
After accepting different requests from various smart install clients, SMI Proxy provides all the mandatory information to the PnP Agent for each request. PnP Agent then forwards these requests to the PnP Server on behalf of the smart install client. The PnP Agent forwards the corresponding response from the PnP server to the SMI Proxy for further processing.
SMI Proxy allows a central PnP Server administrator to possess a single view of the network with respect to the image and configuration, even when some of the switches in the network are only SMI-capable.
How SMI Clients and Directors Communicate
Smart Install clients can communicate with a director only within the network. SMI Proxy leverages existing client communication with the director, extracting relevant data from a networking device.
SMI Proxy mediates between Smart Install clients and the PnP Server, maintaining a database similar or equivalent to the data gleaned by the director.
How SMI Proxy and PnP Agent Communicate
SMI Proxy can trigger the PnP server to send service requests in the following ways:
- When a new SMI client device boots, it sends the "device came up notification" request to SMI Proxy, which sends the information request to the PnP Server through the PnP Agent.
- If SMI Proxy receives a backoff request for any SMI client, it starts the backoff timer. After the timer expires, SMI Proxy sends the work information request to PnP Server through PnP Agent.
- When the SMI Proxy receives the work information "bye" request from PnP Server, it immediately sends the work request to the PnP Server.
- When SMI Proxy receives the client request, PnP Agent sends that request to PnP Server and awaits a response. PnP Agent then evaluates whether the response is intended for the local device or the proxied client. If the former, the PnP Agent consumes the message; else, it is communicated to SMI Proxy.
SMI Proxy and Tailored Configuration Files
The director (IBD) controls which image or configuration is forwarded to the client switches (for example, SMI IBC). It is essential to upgrade older switches that do not run an SMI-capable image. To enable IBD to communicate with such switches and suitably upgrade them, a tailored configuration file was introduced.
In SMI proxy mode, to acquire the PID, VID, and SN of each client, SMI Proxy follows the "reverse telnet" mechanism supported by SMI on older devices.
Starting with Cisco IOS XE 3.6.3E/ Cisco IOS 15.2(2)E3 and Cisco IOS XE 3.7.3E/ Cisco IOS 15.2(3)E3 a director device supports and treats all clients as older devices. The proxy device uses the tailored configuration file to telnet [to] clients and acquire the output data for the show version command. When the proxy device reloads, a new tailored configuration file, client_cfg_pnp.txt, is generated.
This is an example of a newly-created tailored configuration file:
ip http authentication enable <ckadapa>:this config is required
SMI Proxy Database
SMI functionality works off the MAC address whereas the PnP solution, the UDI. SMI Proxy creates the UDI and adds the entry in SMI Proxy database for further communications (e.g., when SMI Proxy wants to send information from the SMI Client to the PnP Server). With the client's MAC address, SMI Proxy searches the database to acquire the SMI Client's UDI. When SMI Proxy wants to send the message received from PnP server to the SMI Client, it uses UDI to acquire the MAC address of the SMI Client. SMI Proxy uses this MAC address to send that message to respective SMI Clients.
This file is created locally under "flash:/vstack" or "bootflash:/vstack" based on the platform with the name smi_pnp_proxy_db.txt. Before creating the entry, SMI Proxy searches for the entry in the database. If the entry is missing, SMI Proxy adds it to the database, which is stored in the file and contains the entries for stale devices that were in the network previously. If the entry exists, SMI Proxy takes no action. Whenever the device on which SMI Proxy is running reboots, while that device is booting, the device retrieves the database from the file. Clearing this database is disallowed. The show command alone can display the entries.
Enabling Proxy on the Device
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps to enable SMI Proxy:
|
|
|
Step 1 |
config terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
Step 2 |
[no] vstack proxy {ip-address smi-ip | interface interface name} [startup-vlan vlan_value] [pnp-profile profile-name] |
Enables SMI SMI Proxy mode. The [no] form of the vstack proxy command turns off support for SMI clients.
- Enter ip-address and the IP address. Launches SMI and enables director functionality on a device. This is a two-step "internal" process:
a. SMI Proxy calls functions related to the vstack director director_IP command. where director_IP must match with at least one of the switch IP. In a scenario where an external DHCP server provides the addresses and the director IP to switches, the switch with matching director and switch IP addresses is eligible for only vstack basic configurations. SMI Proxy calls functions related to the vstack director director_IP command. where director_IP must match with at least one of the switch IP. In a scenario where an external DHCP server provides the addresses and the director IP to switches, the switch with matching director and switch IP addresses is eligible for only vstack basic configurations. b. Executes the vstack, vstack director, vstack basic, and vstack startup-vlan commands to enable ‘Director’ functionality on the switch. Executes the vstack, vstack director, vstack basic, and vstack startup-vlan commands to enable ‘Director’ functionality on the switch.
- Enter interface and the interface name.
Given the interface name, the SMI Proxy uses the associated IP address to enable director functionality.
- Enter startup-vlan and the VLAN value.
Defined to support a non-Vlan1 scenario. Specifies the default VLAN that the director should use for Smart Install operations. Depending on the VLAN that is specified in the command, DHCP snooping is enabled on that VLAN so that the director can identify new switches that are connected to the network. If this command is not entered, however, VLAN 1 is used as default.
- (Optional) Enter pnp-profile and profile name.
SMI Proxy is associated with the profile name. If the profile name is not specified, SMI Proxy is associated with default profile name pnp-zero-touch. |
Step 3 |
end |
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Step 4 |
copy running-config startup config |
(Optional) Saves your entries in the configuration file. |
Step 5 |
show vstack config |
Verifies the configuration. |
Step 6 |
show vstack proxy-db |
Displays the SMI clients that are present in the SMI proxy database. |
Once SMI Proxy is enabled, the following commands are not accessible:
- vstack director ip
- vstack basic
- vstack join-window
- vstack backup
When SMI Proxy is enabled the output of the configuration vstack command is as follows:
dhcp-localserver Configure vstack dhcp parameters
proxy Configure smi pnp proxy feature
startup-vlan Configure vstack startup management vlan
vlan Configure vstack management vlan
This example shows how to configure SMI Proxy on interface vlan 1:
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# vstack proxy interface vlan 1 startup-vlan 1
This example shows how to configure SMI Proxy at ip-address 4.1.1.1:
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# vstack proxy ip-address 4.1.1.1 startup-vlan 1
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)#vstack proxy ip-address 4.1.1.1 startup-vlan 1 pnp-profile pnp-zero-touch
Unsupported Services
More than 20 services are supported by the PnP Solution, out of which only seven are supported by SMI Proxy:
If the PnP Server requests a service not in this list, SMI Proxy sends an error message:
Enum: PNP_ERROR_UNSUPPORTED_REQUEST
Error string: "SMI PROXY:Not supported service request"
When a configuration upgrade request is sent from a PnP service, by default, the PnP server sends a request to the SMI Proxy, to copy the configuration upgrade to the running configuration. As SMI supports only copying the configuration upgrade to the startup configuration on proxied SMI clients, the SMI Proxy sends an error message. Once the PnP server receives this error message, it sends a request to copy the configuration upgrade to the startup configuration to SMI Proxy, which is then forwarded to the SMI client.
The following enum and error strings are sent:
Enum: XSVC_ERROR_CONFIG_UPGRADE_UNSUPPORTED
Error string: "SMI PROXY: Config upgrade apply to Running Config is not supported"
SMI proxy does not support device hardware information requests and device file information requests and the PnP service sends the following enum and error strings:
For device hardware information requests:
Enum: XSVC_ERROR_DEVICE_INFO_UNSUPPORTED
Error string: "SMI PROXY:Client device hardware info not supported"
For device file information requests:
Enum: XSVC_ERROR_DEVICE_INFO_UNSUPPORTED
Error string: "SMI PROXY:Client device filesystem info not supported"
Guidelines and Restrictions
- The SMI Proxy requires SMI Director and PnP Agent on a device.
- When SMI Proxy is enabled, features like join-window and scenarios such as switch replacement are not supported. The latter is handled as a new client addition.
- Central PnP Server supports only homogeneous stack upgrades.
- After SMI Proxy is enabled, SMI Director is disabled.
- SMI Director and SMI Proxy are mutually exclusive.
- In SMI Proxy mode, once a device has completed a configuration or image upgrade successfully, you should not clear the entry of that device in the vstack download-status list. If an SMI client requires a write erase and reload, ensure that the entry is not present in the vstack download-status list.
vstack proxy
To enable the PnP proxy, use the vstack proxy privileged EXEC command. To disable the PnP proxy, use the no form of the command.
[no] vstack proxy {ip_address smi-ip | interface interface_name} [startup-vlan vlan_value] pnp-profile profile-name ]
Syntax Description
ip_address smi-ip |
Launches the SmartInstall feature and enables director functionality on the device with the specified IP address. |
interface interface_name |
Launches the SmartInstall feature and enables director functionality on the device with the IP address of the interface. Internally, the stack proxy command executes vstack, vstack director, vstack basic, and vstack startup-vlan commands to enable Director functionality on the switch. |
startup-vlan vlan_value |
Specifies the default VLAN that the director should use for Smart Install operations. |
pnp-profile profile-name |
(Optional) Specifies the profile name to associate with SMI Proxy. |
Command Modes
Configuration mode
Command History
|
|
|
3.6.3E |
This command was introduced. |
15.2(2)E3 |
This command was introduced. |
3.7.3E |
This command was introduced. |
15.2(3)E3 |
This command was introduced. |
Usage Guidelines
You can specify either the IP address or the interface name. If you specify the interface name, SMI Proxy uses the IP address of the interface.Depending on the specified VLAN, DHCP snooping is enabled on that VLAN so that the director can identify new switches that are connected to the network.
Note SMI Director and Proxy are mutually exclusive with respect to configuration commands. SMI Director configuration commands are not visible after a device is configured in proxy mode. However, Proxy reuses SMI Director functionality internally
SMI Director and Proxy are mutually exclusive with respect to configuration commands. SMI Director configuration commands are not visible after a device is configured in proxy mode. However, Proxy reuses SMI Director functionality internally
Depending on the specified VLAN, DHCP snooping is enabled on that VLAN so that the director can identify new switches that are connected to the network. If this command is not entered, VLAN 1 is used as default.
After Proxy is enabled, the vstack director and vstack basic commands are inaccessible.
Optionally, SMI Proxy will be associated with the profile name entered. If no profile name is specified then SMI Proxy will be associated with default profile name pnp-zero-touch.
After SMI Proxy is enabled, the following configuration commands are not accessible:
- vstack director ip
- vstack basic
- vstack join-window
- vstack backup
Examples
This example shows how to configure SMI Proxy at ip-address 4.1.1.1:
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# vstack proxy ip-address 4.1.1.1 startup-vlan 1
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)#vstack proxy ip-address 4.1.1.1 startup-vlan 1 pnp-profile pnp-zero-touch
Related Commands
|
|
|
show vstack proxy-db [detail] |
Displays the status of the SMI Proxy database. |
debug vstack
To enable debugging of the Smart Install feature, use the debug vstack privileged EXEC command. To disable debugging, use the no form of this command.
debug vstack { all | backup | cli | director-db | download | emulation | fsm | group | join-window | protocol | smi-proxy }
no debug vstack { all | backup | cli | director-db | download | emulation | fsm | group | join-window | protocol | smi-proxy }
Syntax Description
all |
Displays all Smart Install debug messages. |
backup |
Displays all Smart Install backup management debug messages. |
cli |
Displays Smart Install command-line interface (CLI) debug messages. |
director-db |
Displays Smart Install director database messages. |
download |
Displays Smart Install download debug messages. |
emulation |
Displays Smart Install emulation debug messages. |
fsm |
Displays Smart Install session-management debug messages. |
group |
Displays Smart Install group debug messages. |
join-window |
Displays all Smart Install join window debug messages. |
protocol |
Displays Smart Install protocol debug messages. |
smi-proxy |
Displays Smart Install SMI PnP proxy operations. |
Command Default
Smart Install debugging is disabled.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
|
|
|
12.2(52)SE |
This command was introduced. |
15.1(1)SY |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(1)SY. |
3.4SG |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.4SG. |
15.1(2)SG |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG. |
15.0(2)EX |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2)EX. |
15.0(2)EX1 |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release15.0(2)EX1. |
3.2(0)SE |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 3.2(0)SE. |
Usage Guidelines
The undebug vstack command is the same as the no debug vstack command.
Examples
This is example output from the debug vstack all command on a client:
Vstack debug all debugging is on
*May 15 22:37:56.739: VSTACK_DIR_DB: smi_parse_cdp_cache_entry: Got Neighbor on the port Gi2/5/13
*May 15 22:37:56.739: VSTACK_DIR_DB: smi_parse_cdp_cache_entry: Mac addr after masking Neig mac 6073.5cb6.6000, Local Mac 0026.99c9.b000
*May 15 22:37:56.739: VSTACK: smi_parse_cdp_cache_entry:processing the cdp pkt for mgmt vlan
*May 15 22:37:56.739: VSTACK:
received vlan_plus_seqno=20370001, seq no for vlan = 8247,prev_seq_no=8247
*May 15 22:37:56.739: VSTACK_DIR_DB: smi_parse_cdp_cache_entry:string in parse WS-C3750G-24TS-1U
*May 15 22:37:56.739: VSTACK:
smi_send_mgmt_vlan_to_cdp: Seq no + Mgmt Vlan = 20370001. After conversion Mgmt vlan withseq no = 540475393,len=9
The following example shows output of the debug vst smi-proxy command
SMI PNP PROXY:EXEC cli vstack execution successful
Following are more example of error logs:
Mar 30 02:27:51.149: VSTACK_SMI_PROXY:
smi_proxy_recv_msg_from_pnp_proxy: Received the PnP service request service type:21
Mar 30 02:27:51.149: VSTACK_SMI_PROXY: smi_proxy_backoff_request_handler:Received the backoff request from pnp agent
Mar 30 02:27:51.149: VSTACK_SMI_PROXY:
smi_proxy_backoff_request_handler: Enqueuing backoff response for the device id:PID:WS-C3750X-24,VID:V02,SN:FDO1613R2TA
Mar 30 02:27:51.183: VSTACK_SMI_PROXY:
smi_pnp_proxy_send_work_req: Sending work request for the device id:PID:WS-C3750X-24,VID:V02,SN:FDO1613R2TA
Mar 30 02:27:51.183: VSTACK_SMI_PROXY:
smi_pnp_proxy_malloc_proxy_data: Malloc Success
Mar 30 02:27:51.183: VSTACK_SMI_PROXY:
smi_pnp_proxy_malloc_svc_data: Malloc done
Mar 30 02:27:51.183: VSTACK_SMI_PROXY:
smi_pnp_proxy_send_work_req: Enqueuing the work request for UDI:PID:WS-C3750X-24,VID:V02,SN:FDO1613R2TA
Related Commands*
|
|
|
show debugging |
Displays information about the types of debugging that are enabled. |
show vstack
To display Smart Install information, use the show vstack privileged EXEC command on the Smart Install director or a client.
show vstack { download-status [ detail ]
show vstack proxy-db[detail]
Syntax Description
config |
Displays Smart Install configuration parameters. |
host |
Displays information about a client within the Smart Install topology. This command is available only on the director. |
ip_address |
The IP address of the director or a client. |
join-window configuration |
Displays the join-window configurations. |
status |
Displays the status of the CDP database. This command is available only on the director. |
detail (Optional) |
Displays detailed information for the previous keyword. For example, show vstack download-status detail can display a detailed reason for a zero-touch update failure. |
download-status |
Displays a tabulated output of the Smart Install image and configuration download successes and failures. Note Use this command to determine the status of updates. Note Beginning with IOS XE 3.6.0E (or 15.2.(2)E), the show download-status command displays the download upgrade of the image upgrade for a Catalyst 4500 platform. Additional fields are introduced in the output of the show download-status details command. |
client |
Displays client information through the remote command |
1 |
Displays information about client 1 in the Smart Install network. Numbers are shown for as many clients as are in the network. |
client_ ip_address |
Information about the client with the specified IP address. |
all |
Displays information about all clients. |
group |
Displays Smart Install group information. |
built-in |
Displays information about preconfigured (built-in) groups. |
product_family |
The identified (built-in) product family ID. To see the available product families, enter a ? after built-in. If product_family is set to 4500 for Catalyst 4500 series switches. |
port_config |
The switch port configuration. The available choices depend on the product family. To see the available port configurations, enter a ? after the product family. If product_family is set to 4500, port_config means supervisor configuration. |
chassis_config |
The chassis type to configure. If product_family is set to 4500, the chassis type selected here is supported by the supervisor engine assigned to port_config. |
configured |
This keyword displays only the groups that are configured rather than showing all the groups. |
custom |
Information about user-defined groups. |
group_name |
Th custom group name. |
client_password |
The password that is required to access the client switch to get information on running-config | tech-support | version of the client switch. |
running-config |
Displays the current operating configuration for the selected client. |
tech-support |
Displays system information for technical support assistance. |
version |
Displays system hardware and software status. |
neighbors |
Displays information about the specified neighbors:
- 1 —Neighbors of client 1
- client_ip_address —Neighbors of the specified client
- all —All neighbors in the Smart Install network
- group —Neighbors of the specified group or groups
|
proxy-db |
Displays the status of the Proxy database. Note This command is available only on the SMI Director. Displays all the SMI client entries that are present in the Proxy database. |
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Note The command with some, but not all, of the keywords are available at the user EXEC level.
The command with some, but not all, of the keywords are available at the user EXEC level.
Command History
|
|
|
12.2(52)SE |
This command was introduced. |
12.2(55)SE |
The client, join-window configuration, neighbors, 1, running-config, tech-support, and version keywords were added. |
15.1(1)SY |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(1)SY. |
3.4SG |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.4SG. |
15.1(2)SG |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SG. |
15.0(2)EX |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2)EX. |
15.0(2)EX1 |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release15.0(2)EX1. |
3.2(0)SE |
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 3.2(0)SE. |
15.2(2)E |
The option for post install (script) was introduced for show vstack config, show vstack download-status, show vstack download-status detail, show vstack status, and show vstack status detail commands |
3.6.0E |
The option chassis type for the built-in keyword was introduced. The option proxy-db was introduced. |
Usage Guidelines
The outputs of the show commands are different when entered on the director or on the client. Not all keywords are available on the client.
In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(58)SE and later or Release 15.1(1)SY, the output of the show vstack status command shows whether or not Smart Install is enabled on the director. If enabled, it also includes this additional information about clients:
- Device status (Smart Install capable or not)
- Health status (active or inactive)
- Join-window status (allowed, hold, or denied), and
- Upgrade status for image or configuration (in progress, complete, or failed).
Beginning with Cisco IOS Release 3.6.0E (IOS 15.2(2)E), the output of the show vstack status command remains unchanged, but the meaning of the following fields have changed:
Note These changes are for Catalyst 4500 Series Switch only.
These changes are for Catalyst 4500 Series Switch only.
- Product-ID—chassis-id is used as the client’s product ID and is collected from CDP. For an asymmetric chassis, the product ID may be updated dynamically.
- MAC Address —For a Catalyst 4500 standalone IBC, you use the chassis’ MAC address whereas for VSS IBC, you use the virtual MAC selected while configuring VSS.
Note The meaning of the fields Hostname, IP and status are unchanged; they are platform-independent.
The meaning of the fields Hostname, IP and status are unchanged; they are platform-independent.
If you disable Smart Install on the director by entering the no vstack global configuration command, the output of the show vstack status [ detail ] and show vstack download-status [ detail ] commands shows only Smart Install: DISABLED. The output of the show vstack config command shows the Smart Install configuration even though it is not in effect.
If the director is a Catalyst 4500 series switch, whether it is a single chassis or a VSS setup, only a single entry of the director appears in the output of the show vstack status detail command. The product ID shown is the chassis sku-id.
Beginning with IOS XE 3.6.0E (or 15.2.(2)E), the following apply:
- All the director entries (multiple, if the director is a stack) will be assigned the value '0,' and all the IBC stack members will have different entries (situation prior to IOS XE 3.6.0E (or 15.2.(2)E)) but they will all have the same device number.
- When you clear a DB entry and that IBC is a stack, the clear vstack dir command will remove all the stack entries from the database.
show vstack proxy-db indicates whether proxy mode is enabled. Proxy database contains the SMI client information about MAC address, UDI, and entry state. This command displays all SMI client entries that are present in proxy database.
After proxy mode is enabled, only four commands are available to the user:
config View configuration parameters under Vstack mode
download-status show the status of config or image download
proxy-db show the proxy database
status show the status of CDP database
Proxy database will contain information about the SMI client's MAC address, IP address. switch health status, UDI, and entry state.
Examples
This is example output from the show vstack config command on a client:
Director# show vstack config
Vstack Director IP address: 1.1.1.163
This is example output from the show vstack config command on a director:
Director# show vstack config
Vstack Director IP address: 1.1.1.163
Vstack default management vlan: 1
Vstack start-up management vlan:1000
Vstack management Vlans: none
Vstack Config file: tftp://1.1.1.100/default-config.txt
Vstack Image file: tftp://1.1.1.100/c3750e-universalk9-tar.122-
Vstack Script file: tftp://1.1.1.100/post-install.txt
Operation Mode: auto (default)
Repository: flash:/vstack (default)
This is example output from the show vstack config command in SMI Proxy mode:
Switch#show vst config
Role: Smi PnP Proxy
Vstack Smi PnP Proxy IP address: 4.1.1.1
Vstack default management vlan: 1
Vstack start-up management vlan: 1
Vstack management Vlans: 1
Switch#
This is example output from the show vstack download-status command on a director:
Director# show vstack download-status
No client-IP client-MAC Method Image-status Config-status Script-status
=== =============== ============== ============== ============ ============ =============
1 172.20.249.3 001e.be67.3000 image-upgrade UPGRADED ** **
2 172.20.249.1 0022.5699.c800 zero-touch UPGRADING UPGRADED UPGRADED
3 172.20.249.2 0022.0d26.6300 image-upgrade NOT STARTED ** **
This is example output from the show vstack status command:
Director# show vstack status
Status: Device_type Health_status Join-window_status Upgrade_status
Device_type: S - Smart install N - Non smart install P - Pending
Health_status: A - Active I - Inactive
Join-window_Status: a - Allowed h - On-hold d - Denied
Image Upgrade: i - in progress I - done X - failed
Config Upgrade: c - in progress C - done x - failed
DevNo MAC Address Product-ID IP_addr Hostname Status
===== ============== ================= =============== ========== =========
0 0018.7363.4200 WS-C3750-24TS 172.20.249.54 IBD-MXD-ST Director
1 0016.4779.b780 WS-C3750G-24TS 172.20.249.54 IBD-MXD-ST Director
2 d0d0.fd37.5a80 WS-C3750X-48P 172.20.249.54 IBD-MXD-ST Director
3 0026.5285.7380 WS-C3750E-24TD 172.20.249.54 IBD-MXD-ST Director
4 0024.13c6.b580 WS-C3750E-24TD 172.20.249.115 DEV-c6.b5c S A a
5 0021.a1ab.9b80 WS-C2960-48TC-S 172.20.249.249 DEV-ab.9bc S A a I C
6 0024.5111.0900 WS-C3750E-24TD 172.20.249.222 DEV-11.094 S A a I C
7 001d.45f3.f600 WS-C3750G-24TS 172.20.249.87 DEV-90.f64 S A a
8 0016.c890.f600 WS-C3750G-24TS 172.20.249.87 DEV-90.f64 S A a
9 001f.2604.8980 WS-C2960-48TC-S 172.20.249.89 DEV-04.89c S A a I C
10 001b.d576.2500 WS-C3750E-24PD 172.20.249.91 DEV-a6.1cc S A a I C
12 0cd9.9649.cb80 WS-C2960S-48TD-L 172.20.249.98 Switch S A a
This is an example output from the show vstack status command if you have disabled Smart Install on the director by entering the no vstack global configuration command:
Switch# show vstack status
Status: Device_type Health_status Join-window_status Upgrade_status
Device_type: S - Smart install N - Non smart install P - Pending
Health_status: A - Active I - Inactive
Join-window_Status: a - Allowed h - On-hold d - Denied
Image Upgrade: i - in progress I - done X - failed
Config Upgrade: c - in progress C - done x - failed
DevNo MAC Address Product-ID IP_addr Hostname Status
===== ============== ================= =============== ========== =========
0 0023.04c2.95c0 WS-C4506-E 1.1.1.1 Switch Director
4 68ef.bd08.6000 WS-C4507R-E 1.1.1.2 IBC_WOW-08 S I a C
This is an example output from the show vstack status detail command:
Director# show vstack status detail
-----------------------------------------------
Device ID : 3750e-163-smi
MAC Address : 0023.5e32.3780
Product-ID : WS-C3750E-24PD
Version : 12.2(0.0.242)DEV
Image : C3750E-UNIVERSALK9-M
(N-1)HOP Entry : Already Root
Latest backup client name: none
-----------------------------------------------
Device ID : 3560g-10net-11
MAC Address : 0013.c4b4.bc00
Product-ID : WS-C3560G-24PS
Image : C3560-IPSERVICESK9-M
(N-1)HOP Entry : 0023.5e32.3780
Latest backup client name: none
-----------------------------------------------
MAC Address : 001d.71ba.f780
Product-ID : WS-C2960PD-8TT-L
Version : 12.2(0.0.242)DEV
Image : C2960-LANBASEK9-M
(N-1)HOP Entry : 0023.5e32.3780
Latest backup file: flash:/vstack/2960pd-47-001d.71ba.f780.REV2
Latest backup client name: 2960pd-47
File checksum : 426154BFAFE1425F527621DC8B647C38
Director# show vstack download-status detail
client-mac: 001e.be67.3000
image downloaded at: 02:47:39 UTC Mar 30 2011
client-mac: 0022.5699.c8000
config downloaded at: 03:02:23 UTC Mar 30 2011
script downloaded at: 02:47:39 UTC Mar 30 2011
client-mac: 0022.0d26.6300
This is example output from the show vstack status command:
Director# show vstack status
Status: Device_type Health_status Join-window_status Upgrade_status
Device_type: S - Smart install N - Non smart install P - Pending
Health_status: A - Active I - Inactive
Join-window_Status: a - Allowed h - On-hold d - Denied
Image Upgrade: i - in progress I - done X - failed
Config Upgrade: c - in progress C - done x - failed
Script Upgrade: p - in progress P - done F - failed
DevNo MAC Address Product-ID IP_addr Hostname Status
===== ============== ================= =============== ========== =========
0 0018.7363.4200 WS-C3750-24TS 172.20.249.54 IBD-MXD-ST Director
1 0016.4779.b780 WS-C3750G-24TS 172.20.249.54 IBD-MXD-ST Director
2 d0d0.fd37.5a80 WS-C3750X-48P 172.20.249.54 IBD-MXD-ST Director
3 0026.5285.7380 WS-C3750E-24TD 172.20.249.54 IBD-MXD-ST Director
4 0024.13c6.b580 WS-C3750E-24TD 172.20.249.115 DEV-c6.b5c S A a
5 0021.a1ab.9b80 WS-C2960-48TC-S 172.20.249.249 DEV-ab.9bc S A a I C
6 0024.5111.0900 WS-C3750E-24TD 172.20.249.222 DEV-11.094 S A a I C P
7 001d.45f3.f600 WS-C3750G-24TS 172.20.249.87 DEV-90.f64 S A a
8 0016.c890.f600 WS-C3750G-24TS 172.20.249.87 DEV-90.f64 S A a
9 001f.2604.8980 WS-C2960-48TC-S 172.20.249.89 DEV-04.89c S A a I C P
10 001b.d576.2500 WS-C3750E-24PD 172.20.249.91 DEV-a6.1cc S A a I C
12 0cd9.9649.cb80 WS-C2960S-48TD-L 172.20.249.98 Switch S A a
This is an example output from the show vstack status command if you have disabled Smart Install on the director by entering the no vstack global configuration command:
Director # show vstack status
This is example output from the show vstack status command:
Switch# show vstack status
Status: Device_type Health_status Join-window_status Upgrade_status
Device_type: S - Smart install N - Non smart install P - Pending
Health_status: A - Active I - Inactive
Join-window_Status: a - Allowed h - On-hold d - Denied
Image Upgrade: i - in progress I - done X - failed
Config Upgrade: c - in progress C - done x - failed
Script Upgrade: p - in progress P - done F - failed
DevNo MAC Address Product-ID IP_addr Hostname Status
===== ============== ================= =============== ========== =========
0 0023.04c2.95c0 WS-C4506-E 1.1.1.1 Switch Director
4 68ef.bd08.6000 WS-C4507R-E 1.1.1.2 IBC_WOW-08 S I a C P
This is an example output from the show vstack status detail command:
Director# show vstack status detail
-----------------------------------------------
Device ID : 3750e-163-smi
MAC Address : 0023.5e32.3780
Product-ID : WS-C3750E-24PD
Version : 12.2(0.0.242)DEV
Image : C3750E-UNIVERSALK9-M
(N-1)HOP Entry : Already Root
Latest backup client name: none
-----------------------------------------------
Device ID : 3560g-10net-11
MAC Address : 0013.c4b4.bc00
Product-ID : WS-C3560G-24PS
Image : C3560-IPSERVICESK9-M
(N-1)HOP Entry : 0023.5e32.3780
Latest backup client name: none
-----------------------------------------------
MAC Address : 001d.71ba.f780
Product-ID : WS-C2960PD-8TT-L
Version : 12.2(0.0.242)DEV
Image : C2960-LANBASEK9-M
(N-1)HOP Entry : 0023.5e32.3780
Latest backup file: flash:/vstack/2960pd-47-001d.71ba.f780.REV2
Latest backup client name: 2960pd-47
File checksum : 426154BFAFE1425F527621DC8B647C38
This example shows the output of the show vstack proxy-db command:
IBD# show vstack proxy-db
========= ======================================== ======
001e.f76d.af80 PID:WS-C3750E-48TD,VID:V01,SN:FDO1152V10R NO STATE
After proxy mode is enabled, only three commands are available to the user:
Health_status: A - Active I - Inactive
MAC ADDR IP_addr Hostname Status
========= ============ ============ ======
001e.f76d.af80 5.1.1.4 Switch A
IBD# show vstack proxy-db detail
-------------------------------------------------
MAC Address : 001e.f76d.af80
UDI : PID:WS-C3750E-48TD,VID:V01,SN:FDO1152V10R
After proxy mode is enabled, only the following commands are accessible:
config View configuration parameters under Vstack mode
download-status show the status of config or image download
proxy-db show the proxy database
status show the status of CDP database
After proxy mode is enabled, only three commands are accessible:
config View configuration parameters under Vstack mode
proxy-db show the proxy database
status show the status of CDP database
Related Commands
|
|
|
vstack basic |
Enables the switch or router to be the Smart Install director. This command is accepted only if the director IP address is on the switch or router. |
vstack director |
Configures a Smart Install director IP address. |

![]() SMI Director and Proxy are mutually exclusive with respect to configuration commands. SMI Director configuration commands are not visible after a device is configured in proxy mode. However, Proxy reuses SMI Director functionality internally
SMI Director and Proxy are mutually exclusive with respect to configuration commands. SMI Director configuration commands are not visible after a device is configured in proxy mode. However, Proxy reuses SMI Director functionality internally
![]() The command with some, but not all, of the keywords are available at the user EXEC level.
The command with some, but not all, of the keywords are available at the user EXEC level.
![]() These changes are for Catalyst 4500 Series Switch only.
These changes are for Catalyst 4500 Series Switch only.
![]() The meaning of the fields Hostname, IP and status are unchanged; they are platform-independent.
The meaning of the fields Hostname, IP and status are unchanged; they are platform-independent. Feedback
Feedback