Prerequisites for Cisco Umbrella Integration
-
Cisco Umbrella subscription license must be available. Go to https://umbrella.cisco.com/products/umbrella-enterprise-security-packages and click Request a quote to get the license.
-
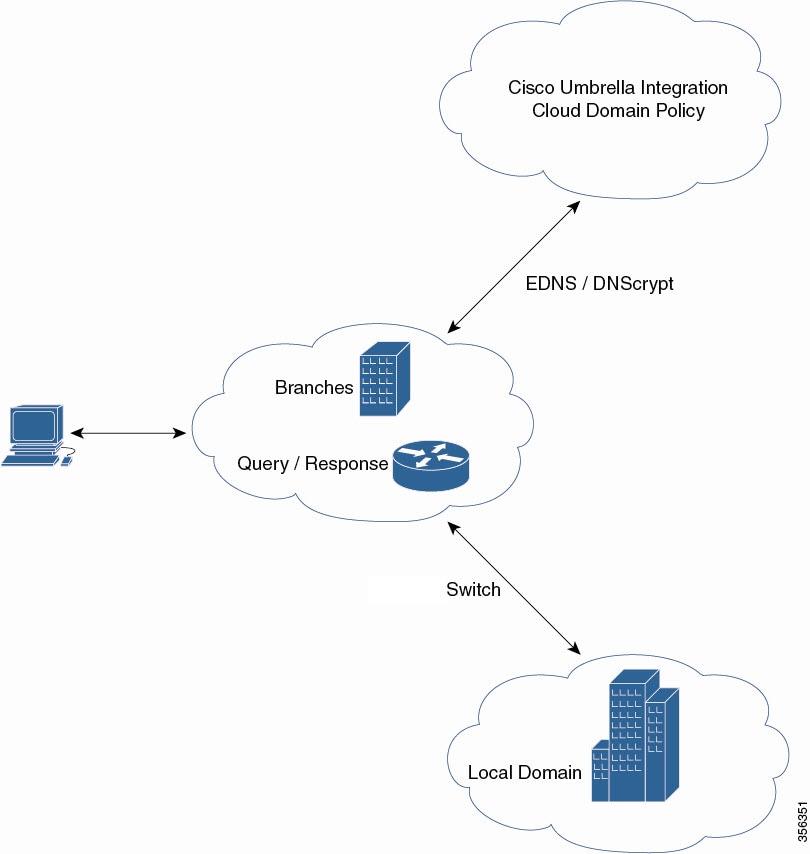
The device must be set as the default Domain Name System (DNS) server gateway and the domain name server traffic should go through the Cisco device.
-
Communication for device registration to the Umbrella server is through HTTPS. This requires a root certificate to be installed on the device. You can download the certificate using this link: https://www.digicert.com/CACerts/DigiCertSHA2SecureServerCA.crt.
-
The Cisco Industrial Ethernet switch runs the Cisco IOS XE release 17.2.1 software image or later.
-
The Cisco Industrial Ethernet switch must have a DNA Advantage or higher license to enable Umbrella.
The following network requirements must be met:
-
The device must be set as the default DNS server gateway and ensure that the Domain Name Server (DNS)traffic goes through the Cisco Industrial Ethernet switch.
-
Communication for device registration to the Cisco Umbrella server is via HTTPS. This requires a root certificate to be installed on the router. To download this certificate directly from a link instead of pasting it in, you can find the certificate here:
https://www.digicert.com/CACerts/DigiCertSHA2SecureServerCA.crt
-
For initial registration, the interface configured as “umbrella out” must be able to access api.opendns.com over port 443 in order to complete initial registration.


 Feedback
Feedback