MACsec and the MACsec Key Agreement Protocol
MACsec is the IEEE 802.1AE standard for authenticating and encrypting packets between two MACsec-capable devices. The switch supports 802.1AE encryption with MACsec Key Agreement (MKA) on on switch-to-host links for encryption between the switch and host device. The switch also supports MACsec encryption for switch-to-switch (inter-network device) security using MKA-based key exchange protocol. The MKA protocol provides the required session keys and manages the required encryption keys.
 Note |
When switch-to-switch MACsec is enabled, all traffic is encrypted except EAP-over-LAN (EAPOL) packets. |
 Important |
On the ESS-3300, MACsec is supported on 1 gigabit ethernet downlink ports only. |
Link layer security can include both packet authentication between switches and MACsec encryption between switches (encryption is optional).
|
Connections |
MACsec support |
|
Switch-to-host |
MACsec MKA encryption |
|
Switch-to-switch |
MACsec MKA encryption |
Cisco TrustSec is meant only for switch-to-switch links and is not supported on switch ports connected to end hosts, such as PCs or IP phones. MKA is supported on switch-to-host facing links as well as switch-to-switch links. Host-facing links typically use flexible authentication ordering for handling heterogeneous devices with or without IEEE 802.1x, and can optionally use MKA-based MACsec encryption. Network Edge Access Topology (NEAT) is used for compact switches to extend security outside the wiring closet.
MACsec and MACsec Key Agreement (MKA) are implemented after successful authentication using certificate-based MACsec or Pre Shared Key (PSK) framework.
MKA Policies
To enable MKA on an interface, a defined MKA policy should be applied to the interface. You can configure these options:
-
Policy name, not to exceed 16 ASCII characters.
-
Confidentiality (encryption) offset of 0, 30, or 50 bytes for each physical interface
Single-Host Mode
The figure shows how a single EAP authenticated session is secured by MACsec by using MKA.
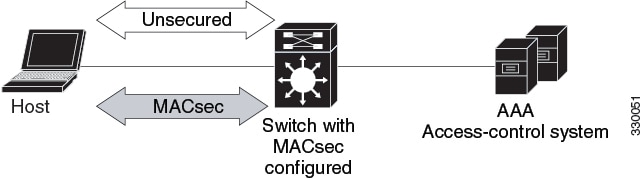
Switch-to-Switch MKA MACsec Must Secure Policy
When MACsec is enabled on an interface, all interface traffic except EAPoL traffic is secured by default ("must-secure" is the default) on both the ingress and the egress. Unencrypted packets are dropped until the MKA session is secured. However, to enable MACsec on selected interfaces, you can choose to allow unencrypted packets to be transmitted or received from the same physical interface by setting macsec access-control to should-secure. This option allows unencrypted traffic to flow until the MKA session is secured. After the MKA session is secured, only encrypted traffic can flow. For configuration details, see Configuring MACsec MKA on an Interface using PSK.
MKA/MACsec for Port Channel
MKA/MACsec can be configured on the port members of a port channel. MKA/MACsec is agnostic to the port channel since the MKA session is established between the port members of a port channel.
 Note |
Etherchannel links that are formed as part of the port channel can either be congruent or disparate i.e. the links can either be MACsec-secured or non-MACsec-secured. MKA session between the port members is established even if a port member on one side of the port channel is not configured with MACsec. |
We recommend that you enable MKA/MACsec on all the member ports for better security of the port channel.
MACsec Cipher Announcement
Cipher Announcement allows the supplicant and the authenticator to announce their respective MACsec Cipher Suite capabilities to each other. Both the supplicant and the authenticator calculate the largest common supported MACsec Cipher Suite and use the same as the keying material for the MKA session.
 Note |
Only the MACsec Cipher Suite capabilities which are configured in the MKA policy are announced from the authenticator to the supplicant. |
There are two types of EAPoL Announcements:
-
Unsecured Announcements (EAPoL PDUs) : Unsecured announcements are EAPoL announcements carrying MACsec Cipher Suite capabilities in an unsecured manner. These announcements are used to decide the width of the key used for MKA session prior to authentication.
-
Secure Announcements (MKPDUs) : Secure announcements revalidate the MACsec Cipher Suite capabilities which were shared previously through unsecure announcements.
Once the session is authenticated, peer capabilities which were received through EAPoL announcements are revalidated with the secure announcements. If there is a mismatch in the capabilities, the MKA session tears down.
Limitations for MACsec Cipher Announcement
-
MACsec Cipher Announcement is supported only on the switch-to-host links.
-
The MKA session between the supplicant and the authenticator does not tear down even if the MACsec Cipher Suite capabilities configured on both do not result in a common cipher suite.
MKA Statistics
Some MKA counters are aggregated globally, while others are updated both globally and per session. You can also obtain information about the status of MKA sessions.
This is an example of the show mka statistics command output:
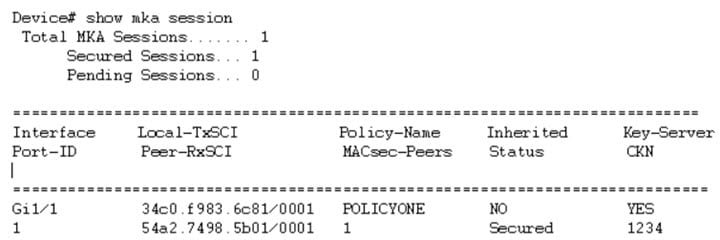
Switch# show mka sessions
Total MKA Sessions....... 1
Secured Sessions... 1
Pending Sessions... 0
====================================================================================================
Interface Local-TxSCI Policy-Name Inherited Key-Server
Port-ID Peer-RxSCI MACsec-Peers Status CKN
====================================================================================================
Gi1/0/1 204c.9e85.ede4/002b p2 NO YES
43 c800.8459.e764/002a 1 Secured 0100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Switch#show mka sessions interface G1/0/1
Summary of All Currently Active MKA Sessions on Interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1...
====================================================================================================
Interface Local-TxSCI Policy-Name Inherited Key-Server
Port-ID Peer-RxSCI MACsec-Peers Status CKN
====================================================================================================
Gi1/0/1 204c.9e85.ede4/002b p2 NO YES
43 c800.8459.e764/002a 1 Secured 0100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Switch#show mka sessions interface G1/0/1 de
MKA Detailed Status for MKA Session
===================================
Status: SECURED - Secured MKA Session with MACsec
Local Tx-SCI............. 204c.9e85.ede4/002b
Interface MAC Address.... 204c.9e85.ede4
MKA Port Identifier...... 43
Interface Name........... GigabitEthernet1/0/1
Audit Session ID.........
CAK Name (CKN)........... 0100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Member Identifier (MI)... D46CBEC05D5D67594543CEAE
Message Number (MN)...... 89567
EAP Role................. NA
Key Server............... YES
MKA Cipher Suite......... AES-128-CMAC
Latest SAK Status........ Rx & Tx
Latest SAK AN............ 0
Latest SAK KI (KN)....... D46CBEC05D5D67594543CEAE00000001 (1)
Old SAK Status........... FIRST-SAK
Old SAK AN............... 0
Old SAK KI (KN).......... FIRST-SAK (0)
SAK Transmit Wait Time... 0s (Not waiting for any peers to respond)
SAK Retire Time.......... 0s (No Old SAK to retire)
MKA Policy Name.......... p2
Key Server Priority...... 2
Delay Protection......... NO
Replay Protection........ YES
Replay Window Size....... 0
Confidentiality Offset... 0
Algorithm Agility........ 80C201
Send Secure Announcement.. DISABLED
SAK Cipher Suite......... 0080C20001000001 (GCM-AES-128)
MACsec Capability........ 3 (MACsec Integrity, Confidentiality, & Offset)
MACsec Desired........... YES
# of MACsec Capable Live Peers............ 1
# of MACsec Capable Live Peers Responded.. 1
Live Peers List:
MI MN Rx-SCI (Peer) KS Priority
----------------------------------------------------------------------
38046BA37D7DA77E06D006A9 89555 c800.8459.e764/002a 10
Potential Peers List:
MI MN Rx-SCI (Peer) KS Priority
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Dormant Peers List:
MI MN Rx-SCI (Peer) KS Priority
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Switch#show mka sessions de
Switch#show mka sessions detail
MKA Detailed Status for MKA Session
===================================
Status: SECURED - Secured MKA Session with MACsec
Local Tx-SCI............. 204c.9e85.ede4/002b
Interface MAC Address.... 204c.9e85.ede4
MKA Port Identifier...... 43
Interface Name........... GigabitEthernet1/0/1
Audit Session ID.........
CAK Name (CKN)........... 0100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Member Identifier (MI)... D46CBEC05D5D67594543CEAE
Message Number (MN)...... 89572
EAP Role................. NA
Key Server............... YES
MKA Cipher Suite......... AES-128-CMAC
Latest SAK Status........ Rx & Tx
Latest SAK AN............ 0
Latest SAK KI (KN)....... D46CBEC05D5D67594543CEAE00000001 (1)
Old SAK Status........... FIRST-SAK
Old SAK AN............... 0
Old SAK KI (KN).......... FIRST-SAK (0)
SAK Transmit Wait Time... 0s (Not waiting for any peers to respond)
SAK Retire Time.......... 0s (No Old SAK to retire)
MKA Policy Name.......... p2
Key Server Priority...... 2
Delay Protection......... NO
Replay Protection........ YES
Replay Window Size....... 0
Confidentiality Offset... 0
Algorithm Agility........ 80C201
SAK Cipher Suite......... 0080C20001000001 (GCM-AES-128)
MACsec Capability........ 3 (MACsec Integrity, Confidentiality, & Offset)
MACsec Desired........... YES
# of MACsec Capable Live Peers............ 1
# of MACsec Capable Live Peers Responded.. 1
Live Peers List:
MI MN Rx-SCI (Peer) KS Priority
----------------------------------------------------------------------
38046BA37D7DA77E06D006A9 89560 c800.8459.e764/002a 10
Potential Peers List:
MI MN Rx-SCI (Peer) KS Priority
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Dormant Peers List:
MI MN Rx-SCI (Peer) KS Priority
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Switch#sh mka pol
MKA Policy Summary...
Policy KS Delay Replay Window Conf Cipher Interfaces
Name Priority Protect Protect Size Offset Suite(s) Applied
======================================================================================================
*DEFAULT POLICY* 0 FALSE TRUE 0 0 GCM-AES-128
p1 1 FALSE TRUE 0 0 GCM-AES-128
p2 2 FALSE TRUE 0 0 GCM-AES-128 Gi1/0/1
Switch#sh mka poli
Switch#sh mka policy p2
Switch#sh mka policy p2 ?
detail Detailed configuration/information for MKA Policy
sessions Summary of all active MKA Sessions with policy applied
| Output modifiers
<cr>
Switch#sh mka policy p2 de
MKA Policy Configuration ("p2")
========================
MKA Policy Name........ p2
Key Server Priority.... 2
Confidentiality Offset. 0
Send Secure Announcement..DISABLED
Cipher Suite(s)........ GCM-AES-128
Applied Interfaces...
GigabitEthernet1/0/1
Switch#sh mka policy p2
MKA Policy Summary...
Policy KS Delay Replay Window Conf Cipher Interfaces
Name Priority Protect Protect Size Offset Suite(s) Applied
======================================================================================================
p2 2 FALSE TRUE 0 0 GCM-AES-128 Gi1/0/1
Switch#sh mka se?
sessions
Switch#sh mka ?
default-policy MKA Default Policy details
keychains MKA Pre-Shared-Key Key-Chains
policy MKA Policy configuration information
presharedkeys MKA Preshared Keys
sessions MKA Sessions summary
statistics Global MKA statistics
summary MKA Sessions summary & global statistics
Switch#sh mka statis
Switch#sh mka statistics ?
interface Statistics for a MKA Session on an interface
local-sci Statistics for a MKA Session identified by its Local Tx-SCI
| Output modifiers
<cr>
Switch#sh mka statistics inter
Switch#show mka statistics interface G1/0/1
MKA Statistics for Session
==========================
Reauthentication Attempts.. 0
CA Statistics
Pairwise CAKs Derived... 0
Pairwise CAK Rekeys..... 0
Group CAKs Generated.... 0
Group CAKs Received..... 0
SA Statistics
SAKs Generated.......... 1
SAKs Rekeyed............ 0
SAKs Received........... 0
SAK Responses Received.. 1
MKPDU Statistics
MKPDUs Validated & Rx... 89585
"Distributed SAK".. 0
"Distributed CAK".. 0
MKPDUs Transmitted...... 89596
"Distributed SAK".. 1
"Distributed CAK".. 0
Switch#show mka ?
default-policy MKA Default Policy details
keychains MKA Pre-Shared-Key Key-Chains
policy MKA Policy configuration information
presharedkeys MKA Preshared Keys
sessions MKA Sessions summary
statistics Global MKA statistics
summary MKA Sessions summary & global statistics
Switch#show mka summ
Switch#show mka summary
Total MKA Sessions....... 1
Secured Sessions... 1
Pending Sessions... 0
====================================================================================================
Interface Local-TxSCI Policy-Name Inherited Key-Server
Port-ID Peer-RxSCI MACsec-Peers Status CKN
====================================================================================================
Gi1/0/1 204c.9e85.ede4/002b p2 NO YES
43 c800.8459.e764/002a 1 Secured 0100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
MKA Global Statistics
=====================
MKA Session Totals
Secured.................... 1
Reauthentication Attempts.. 0
Deleted (Secured).......... 0
Keepalive Timeouts......... 0
CA Statistics
Pairwise CAKs Derived...... 0
Pairwise CAK Rekeys........ 0
Group CAKs Generated....... 0
Group CAKs Received........ 0
SA Statistics
SAKs Generated............. 1
SAKs Rekeyed............... 0
SAKs Received.............. 0
SAK Responses Received..... 1
MKPDU Statistics
MKPDUs Validated & Rx...... 89589
"Distributed SAK"..... 0
"Distributed CAK"..... 0
MKPDUs Transmitted......... 89600
"Distributed SAK"..... 1
"Distributed CAK"..... 0
MKA Error Counter Totals
========================
Session Failures
Bring-up Failures................ 0
Reauthentication Failures........ 0
Duplicate Auth-Mgr Handle........ 0
SAK Failures
SAK Generation................... 0
Hash Key Generation.............. 0
SAK Encryption/Wrap.............. 0
SAK Decryption/Unwrap............ 0
SAK Cipher Mismatch.............. 0
CA Failures
Group CAK Generation............. 0
Group CAK Encryption/Wrap........ 0
Group CAK Decryption/Unwrap...... 0
Pairwise CAK Derivation.......... 0
CKN Derivation................... 0
ICK Derivation................... 0
KEK Derivation................... 0
Invalid Peer MACsec Capability... 0
MACsec Failures
Rx SC Creation................... 0
Tx SC Creation................... 0
Rx SA Installation............... 0
Tx SA Installation............... 0
MKPDU Failures
MKPDU Tx......................... 0
MKPDU Rx Validation.............. 0
MKPDU Rx Bad Peer MN............. 0
MKPDU Rx Non-recent Peerlist MN.. 0
Switch#

 Feedback
Feedback