This section provides a brief overview of the NX-OS Programmable Interface infrastructure.
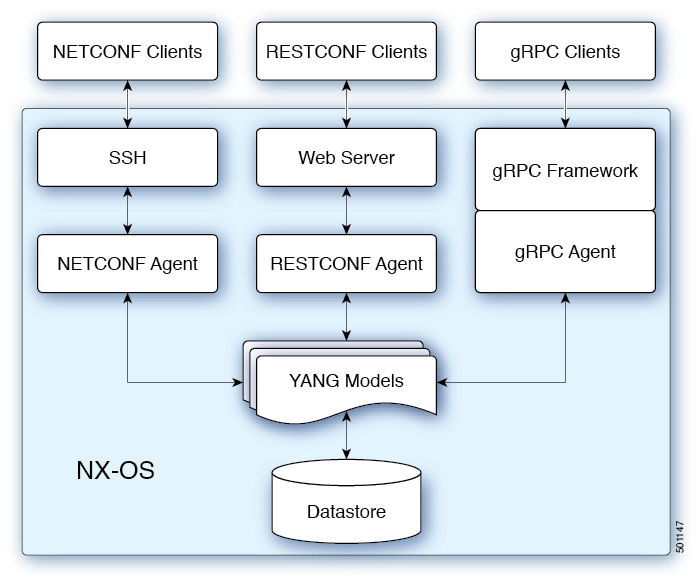
When a request is received whether via NETCONF, RESTConf, or gRPC, the request is converted into an abstract message object
that distributed to the underlying model infrastructure based on the namespace in the request. Using the namespace, the appropriate
model is selected and the request is passed to it for processing. The model infrastructure executes the request (read or write)
on the device data store returning the results to the agent of origin for response transmission back to the requesting client.
NX-OS Programmable Interface Agents
Agents provide an interface between the Device and clients. They specify the transport, the protocol and the encoding of the
communications with the Device. NX-OS Programmable Interfaces supports three agents: NETCONF, RESTConf and gRPC, each providing
different interfaces for configuration management of the Device via YANG models.
Table 1. NX-OS Programmable Interface Agents
|
Agent
|
Transport
|
Protocol
|
Encoding
|
|
NETCONF
|
SSH
|
RFC 6241[1]
|
XML
|
|
RESTConf
|
HTTP
|
draft-ietf-netconf-restconf-10[2]
|
XML or JSON
|
|
gRPC
|
HTTP
|
gRPC Protocol Spec[3]
|
Google Protobuf
|
The protocol specifications are described in the following documents:
Model Infrastructure
The Model Infrastructure takes requests received from the Agent, determines the namespace associated with the YANG model in
the request and selects the model component matching the namespace to process the request. When the selected model component
completes request processing, the processing results are sent to the requesting Agent for transmission back to the client.
The Model Infrastructure is also responsible for handling protocol initiation requests involving authentication, handshaking,
and so forth as specified by the Agent protocol.
Device YANG Model
The Device Configuration is described in a YANG model called a Device Model. The Device Model is manifested in the Model Infrastructure
as another model component with the Device namespace.
Common YANG Models
A Common Model is another kind of model component that contains within its elements, YANG Paths to the equivalent Device Model
elements. These equivalent Device Model elements are used to read and write Device Model data in the Device YANG context.


 Feedback
Feedback