Cisco Cyber Vision Center beta version
Cisco Cyber Vision Center's beta UI experience includes dashboards displaying data on assets, vulnerabilities, alerts, and organization hierarchies. You can quickly apply data filters to view necessary information.
Access beta UI
The UI experience is a beta feature. Contact cv-beta@cisco.com to access the beta UI and its features. Enable Cisco Cyber Vision Beta UI alongside the classic UI by following the instructions in the reply. To access the beta user interface, click Go to Cyber Vision betafrom the interface menu.
 Note |
If a session is inactive for an hour, you must log in to the Cisco Cyber Vision center again. |
User profile
In the beta UI, you can find your user profile displayed in the top banner. It shows your email address, username, or both, depending on the storage location of your user information (database or LDAP).
Use search bar
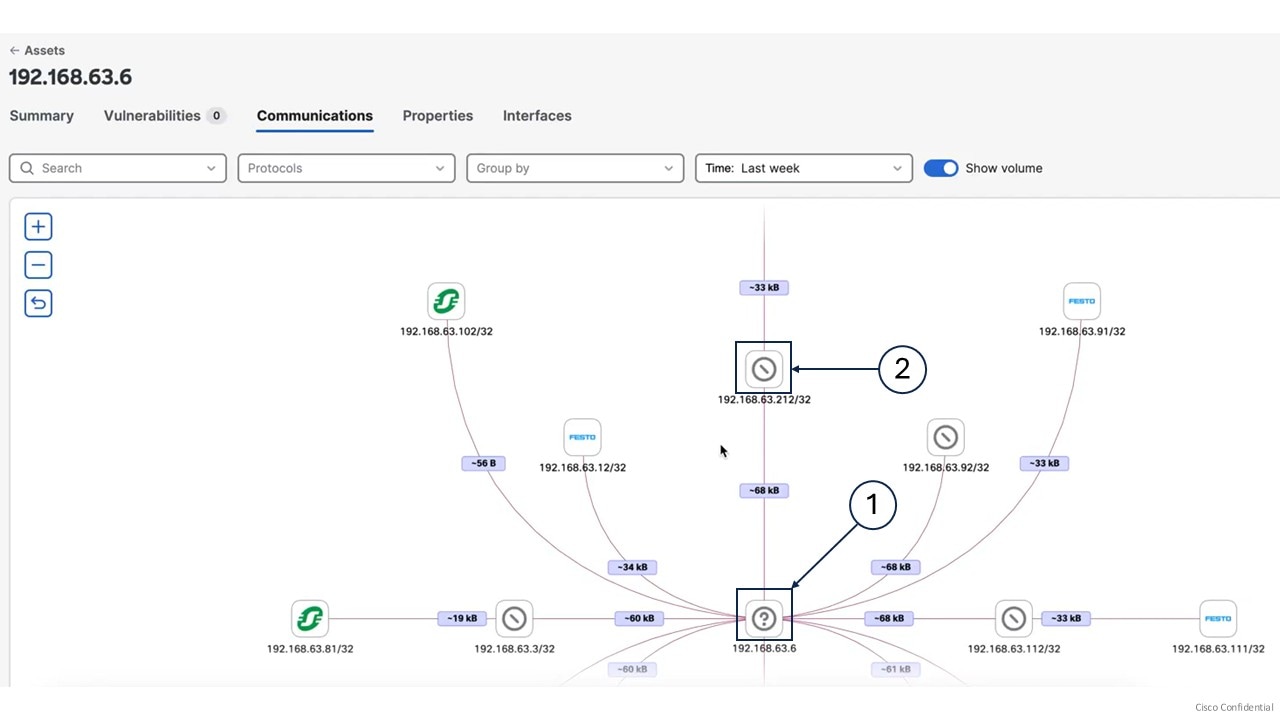
Use the search bar to quickly access an asset.
Procedure
|
To search for an asset, enter the Name, IP Address, or MAC Address in the search bar.
|
Exact matches appear first in the search results.
You can search for both primary and additional interfaces.
Select a search result to view the summary page of the asset.
 Feedback
Feedback