Troubleshoot Security Cloud Control
Troubleshooting Login Failures
Login Fails Because You are Inadvertently Logging in to the Wrong Security Cloud Control Region
Make sure you are logging into the appropriate Security Cloud Control region. After you log into https://sign-on.security.cisco.com, you will be given a choice of what region to access.
See Signing in to Security Cloud Control in Different Regions for information about which region you shoud sign into.
Troubleshooting Login Failures after Migration
Solution If you try to log in to Security Cloud Control and you know you are using the correct username and password and your login is failing, or you try "forgot password" cannot recover a viable password, you may have tried to login without creating a new Cisco Security Cloud Sign On account, you need to sign up for a new Cisco Security Cloud Sign On Account.
Solution See: Create a New Cisco Security Cloud Sign On Account and Configure Duo Multi-factor Authentication.
Solution You may have created a Cisco Security Cloud Sign On account with a different username than your Security Cloud Control tenant. Contact the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) to standardize your user information between Security Cloud Control and Cisco Secure Sign-On.
Solution You may be attempting to log in using an old bookmark you saved in your browser. The bookmark could be pointing to https://cdo.onelogin.com.
Solution Log in to https://sign-on.security.cisco.com.
-
Solution If you have not yet created a Cisco Secure Sign-On account, create an account.
-
Solution If you have created your new secure sign-on account, click the Security Cloud Control tile on the dashboard that corresponds to the region in which your tenant was created:
-
Solution Cisco Security Cloud Control APJ
-
Solution Cisco Security Cloud Control Australia
-
Solution Cisco Security Cloud Control EU
-
Solution Cisco Security Cloud Control India
-
Solution Cisco Security Cloud Control US
-
-
Solution Update your bookmark to point to https://sign-on.security.cisco.com.
Troubleshooting Access and Certificates
Resolve New Fingerprint Detected State
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
In the left pane, click . |
|
Step 2 |
Click the Devices tab. |
|
Step 3 |
Click the appropriate device type tab. |
|
Step 4 |
Select the device in the New Fingerprint Detected state. |
|
Step 5 |
Click Review Fingerprint in the New Fingerprint Detected pane. |
|
Step 6 |
When prompted to review and accept the fingerprint:
|
|
Step 7 |
After you resolve the new fingerprint issue, the connectivity state of the device may show Online and the Configuration Status may show "Not Synced" or "Conflict Detected." Review Resolve Configuration Conflicts to review and resolve configuration differences between Security Cloud Control and the device. |
Troubleshooting Network Problems Using Security and Analytics Logging Events
Here is a basic framework you can use to troubleshoot network problems using the Events Viewer.
This scenario assumes that your network operations team has had a report that a user can't access a resource on the network. Based on the user reporting the issue and their location, the network operations team has a reasonable idea of which firewall controls their access to resources.
 Note |
This scenario also assumes that an FDM-managed device is the firewall managing the network traffic. Security Analytics and Logging does not collect logging information from other device types. |
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
In the left pane, click . |
|
Step 2 |
Click the Historical tab. |
|
Step 3 |
Start filtering events by Time Range. By default, the Historical tab shows the last hour of events. If that is the correct time range, enter the current date and time as the End time. If that is not the correct time range, enter a start and end time encompassing the time of the reported issue. |
|
Step 4 |
Enter the IP address of the firewall that you suspect is controlling the user's
access in the Sensor ID field. If it could be more than
one firewall, filter events using attribute:value pairs in the search
bar. Make two entries and combine them with an OR statement. For example:
|
|
Step 5 |
Enter the user's IP address in the Source IP field in the Events filter bar. |
|
Step 6 |
If the user can't access a resource, try entering that resource's IP address in the Destination IP field. |
|
Step 7 |
Expand the events in the results and look at their details. Here are some details to look at:
|
|
Step 8 |
If the rule action is preventing access, look at the FirewallRule and FirewallPolicy fields to identify the rule in the policy that is blocking access. |
Troubleshooting SSL Decryption Issues
Handling Web Sites Where Decrypt Re-sign Works for a Browser but not an App (SSL or Certificate Authority Pinning)
Some apps for smart phones and other devices use a technique called SSL (or Certificate Authority) pinning. The SSL pinning technique embeds the hash of the original server certificate inside the app itself. As a result, when the app receives the resigned certificate from the Firepower Threat Defense device, the hash validation fails and the connection is aborted.
The primary symptom is that users cannot connect to the web site using the site's app, but they can connect using the web browser, even when using the browser on the same device where the app fails. For example, users cannot use the Facebook iOS or Android app, but they can point Safari or Chrome at [/bookmap/topic/concept/reference/concept/conbody/section/p/xref {"link-https"}) https://www.facebook.com (xref] and make a successful connection.
Because SSL pinning is specifically used to avoid man-in-the-middle attacks, there is no workaround. You must choose between the following options:
More Details
If a site works in a browser but not in an app on the same device, you are almost certainly looking at an instance of SSL pinning. However, if you want to delve deeper, you can use connection events to identify SSL pinning in addition to the browser test.
There are two ways an app might deal with hash validation failures:
-
Group 1 apps, such as Facebook, send an SSL ALERT Message as soon as it receives the SH, CERT, SHD message from the server. The Alert is usually an "Unknown CA (48)" alert indicating SSL Pinning. A TCP Reset is sent following the Alert message. You should see the following symptoms in the event details:
-
SSL Flow Flags include ALERT_SEEN. -
SSL Flow Flags do not include APP_DATA_C2S or APP_DATA_S2C. -
SSL Flow Messages typically are: CLIENT_HELLO, SERVER_HELLO, SERVER_CERTIFICATE, SERVER_KEY_EXCHANGE, SERVER_HELLO_DONE.
-
-
Group 2 apps, such as Dropbox, do not send any alerts. Instead they wait until the handshake is done and then send a TCP Reset. You should see the following symptoms in the event:
-
SSL Flow Flags do not include ALERT_SEEN, APP_DATA_C2S, or APP_DATA_S2C. -
SSL Flow Messages typically are: CLIENT_HELLO, SERVER_HELLO, SERVER_CERTIFICATE, SERVER_KEY_EXCHANGE, SERVER_HELLO_DONE, CLIENT_KEY_EXCHANGE, CLIENT_CHANGE_CIPHER_SPEC, CLIENT_FINISHED, SERVER_CHANGE_CIPHER_SPEC, SERVER_FINISHED.
-
Troubleshooting Login Failures after Migration
Solution If you try to log in to Security Cloud Control and you know you are using the correct username and password and your login is failing, or you try "forgot password" cannot recover a viable password, you may have tried to login without creating a new Cisco Security Cloud Sign On account, you need to sign up for a new Cisco Security Cloud Sign On Account.
Solution See: Create a New Cisco Security Cloud Sign On Account and Configure Duo Multi-factor Authentication.
Solution You may have created a Cisco Security Cloud Sign On account with a different username than your Security Cloud Control tenant. Contact the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) to standardize your user information between Security Cloud Control and Cisco Secure Sign-On.
Solution You may be attempting to log in using an old bookmark you saved in your browser. The bookmark could be pointing to https://cdo.onelogin.com.
Solution Log in to https://sign-on.security.cisco.com.
-
Solution If you have not yet created a Cisco Secure Sign-On account, create an account.
-
Solution If you have created your new secure sign-on account, click the Security Cloud Control tile on the dashboard that corresponds to the region in which your tenant was created:
-
Solution Cisco Security Cloud Control APJ
-
Solution Cisco Security Cloud Control Australia
-
Solution Cisco Security Cloud Control EU
-
Solution Cisco Security Cloud Control India
-
Solution Cisco Security Cloud Control US
-
-
Solution Update your bookmark to point to https://sign-on.security.cisco.com.
Troubleshooting Objects
Resolve Duplicate Object Issues
Duplicate objects  are two or more objects on the same device with different names but the same values. These objects are usually created accidentally,
serve similar purposes, and are used by different policies. After resolving duplicate object issues, Security Cloud Control updates all affected object references with the retained object name.
are two or more objects on the same device with different names but the same values. These objects are usually created accidentally,
serve similar purposes, and are used by different policies. After resolving duplicate object issues, Security Cloud Control updates all affected object references with the retained object name.
To resolve duplicate object issues:
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
In the left pane, click Objects and choose an option. |
|
Step 2 |
Then filter the objects to find duplicate object issues. |
|
Step 3 |
Select one of the results. In the objects details panel, you will see the DUPLICATE field with the number of duplicates affected:  |
|
Step 4 |
Click Resolve. Security Cloud Control displays the duplicate objects for you to compare. |
|
Step 5 |
Select two of the objects to compare. |
|
Step 6 |
You now have these options:
|
|
Step 7 |
Once the duplicate object issue has been resolved review and deploy the changes you made now, or wait and deploy multiple changes at once. |
Resolve Unused Object Issues
Unused objects  are objects that exist in a device configuration but are not referenced by
another object, an access-list, or a NAT rule.
are objects that exist in a device configuration but are not referenced by
another object, an access-list, or a NAT rule.
Resolve an Unused Object Issue
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
In the left pane, click Objects and choose an option. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Then filter the objects to find unused object issues. |
||
|
Step 3 |
Select one or more unused objects. |
||
|
Step 4 |
You now have these options:
|
||
|
Step 5 |
If you removed the unused object, Preview and Deploy Configuration Changes for All Devices the changes you made now, or wait and deploy multiple changes at once.
|
Remove Unused Objects in Bulk
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
In the left pane, click Objects and choose an option. |
|
Step 2 |
Then filter the objects to find unused object issues. |
|
Step 3 |
Select the unused objects you want to delete:
|
|
Step 4 |
In the Actions pane on the right, click Remove
|
|
Step 5 |
Click OK to confirm you want to delete the unused objects. |
|
Step 6 |
You have two choices to deploy these changes:
|
Resolve Inconsistent Object Issues
Inconsistent objects  are objects with the same name, but different values, on two or more devices. Sometimes users create objects in different
configurations with the same name and content, but over time the values of these objects diverge, which creates the inconsistency.
are objects with the same name, but different values, on two or more devices. Sometimes users create objects in different
configurations with the same name and content, but over time the values of these objects diverge, which creates the inconsistency.
Note: To resolve inconsistent object issues in bulk, see Resolve Object Issues in Bulk.
You can perform the following on inconsistent objects:
-
Ignore: Security Cloud Control ignores the inconsistency between objects and retains their values. The objects will no longer be listed under the inconsistency category.
-
Merge: Security Cloud Control combines all selected objects and their values into a single object group.
-
Rename: Security Cloud Control allows you to rename one of the inconsistent objects and give it a new name.
-
Convert Shared Network Objects to Overrides: Security Cloud Control allows you to combine inconsistent shared objects (with or without overrides) into a single shared object with overrides. The most common default value from the inconsistent objects is set as a default in the newly formed object.

Note
If there are multiple common default values, one of them is selected as the default. The remaining default values and override values are set as overrides of that object.
-
Convert Shared Network Group to Additional Values: - Security Cloud Control allows you to combine inconsistent shared network groups into a single shared network group with additional values. The criteria for this functionality is that the inconsistent network groups to be converted must have a minimum of one common object with the same value. All default values that match this criterion becomes the default values, and the remaining objects are assigned as additional values of the newly formed network group.
For example, consider two inconsistent shared network groups. The first network group 'shared_network_group' is formed with 'object_1' (192.0.2.x) and 'object_2' (192.0.2.y). It also contains additional value 'object_3' (192.0.2.a). The second network group 'shared_network_group' is formed with 'object_1' (192.0.2.x) and additional value 'object_4' (192.0.2.b). On converting the shared network group to additional values, the newly formed group 'shared_network_group' contain 'object_1' (192.0.2.x) and 'object_2' (192.0.2.y)' as default values and 'object_3' (192.0.2.a) and 'object_4' (192.0.2.b) as additional values.

Note
When you create a new network object, Security Cloud Control auto assigns its value as an override to an existing shared network object with the same name. This is also applicable when a new device is onboarded to Security Cloud Control.
The auto-assignment happens only when the following criteria are met:
-
The new network object must be assigned to a device.
-
Only one shared object with the same name and type must be existing in the tenant.
-
The shared object must already contain overrides.
To resolve inconsistent object issues:
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
In the Security Cloud Control navigation bar on the left, click Objects and choose an option. |
|
Step 2 |
Then filter the objects to find inconsistent object issues. |
|
Step 3 |
Select an inconsistent object. In the objects details panel, you will see the INCONSISTENT field with the number of objects affected: 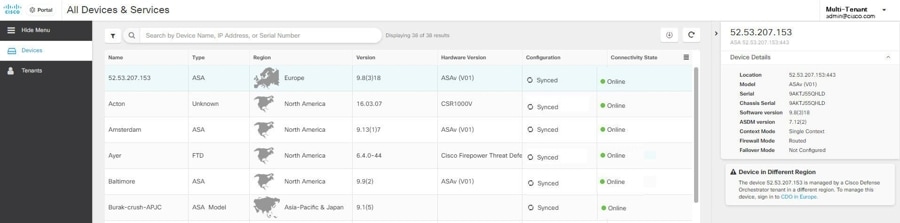
|
|
Step 4 |
Click Resolve. Security Cloud Control displays inconsistent objects for you to compare. |
|
Step 5 |
You now have these options:
|
|
Step 6 |
After resolving the inconsistencies, review and deploy now the changes you made, or wait and deploy multiple changes at once. |
Resolve Object Issues in Bulk
One way to resolve objects with unused, duplicate, or Resolve Inconsistent Object Issues issues is to ignore them. You can select and ignore multiple objects, even if objects exhibit more than one issue. For example, if an object is both inconsistent and unused, you can only ignore one issue type at a time.
 Important |
If the object becomes associated with another issue type at a later time, the ignore action you committed only affects the issues you selected at that time. For example, if you ignored an object because it was a duplicate and the object is later marked inconsistent, ignoring it as a duplicate object does not mean it will be ignored as an inconsistent object. |
To ignore issues in bulk, follow this procedure:
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
In the left pane, click Objects and choose an option. |
|
Step 2 |
To narrow your search, you can filter object issues. |
|
Step 3 |
In the Object table, select all the applicable objects you want to ignore. The Issues pane groups objects by issue type. 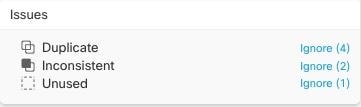
|
|
Step 4 |
Click Ignore to ignore issues by type. You must Ignore each issue type separately. |
|
Step 5 |
Click OK to confirm you want to ignore those objects. |
 to remove the unused object from
to remove the unused object from 
 Feedback
Feedback