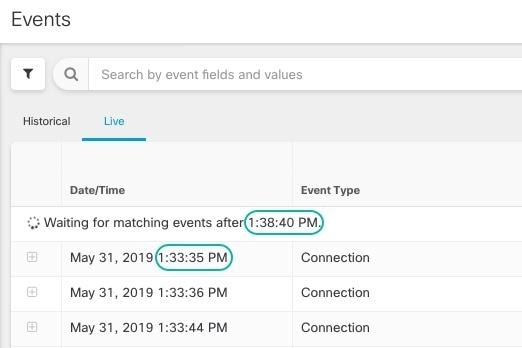
Viewing Live Events
The Live events page shows the most recent 500 events that match the filter and search criteria you entered. If the Live events page displays the maximum of 500 events, and more events stream in, Security Cloud Control displays the newest live events, and transfers the oldest live events to the Historical events page, keeping the total number of live events at 500. That transfer takes roughly a minute to perform. If no filtering criteria is added, you will see all the latest Live 500 events generated by rules configured to log events.
The event timestamps are shown in UTC.
Changing the filtering criteria, whether live events are playing or paused, clears the events screen and restarts the collection process.
To see live events in the Security Cloud Control Events viewer:
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
In the left pane, choose . |
|
Step 2 |
Click the Live tab. |
What to do next
See how to play and pause events by reading .
Play/Pause Live Events
You can "play" ![]() or "pause"
or "pause" ![]() live events as they stream in. If live events are "playing," Security Cloud Control displays events that match the filtering criteria specified in the Events viewer in the order they are received. If events
are paused, Security Cloud Control does not update the Live events page until you restart playing live events. When you restart playing events, Security Cloud Control begins populating events in the Live page from the point at which you restarted playing events. It doesn't back-fill the
ones you missed.
live events as they stream in. If live events are "playing," Security Cloud Control displays events that match the filtering criteria specified in the Events viewer in the order they are received. If events
are paused, Security Cloud Control does not update the Live events page until you restart playing live events. When you restart playing events, Security Cloud Control begins populating events in the Live page from the point at which you restarted playing events. It doesn't back-fill the
ones you missed.
To view all the events that Security Cloud Control received whether you played or paused live event streaming, click the Historical tab.
Auto-pause Live Events
After displaying events for about 5 consecutive minutes, Security Cloud Control warns you that it is about to pause the stream of live events. At that time, you can click the link to continue streaming live events for another 5 minutes or allow the stream to stop. You can restart the live events stream when you are ready.
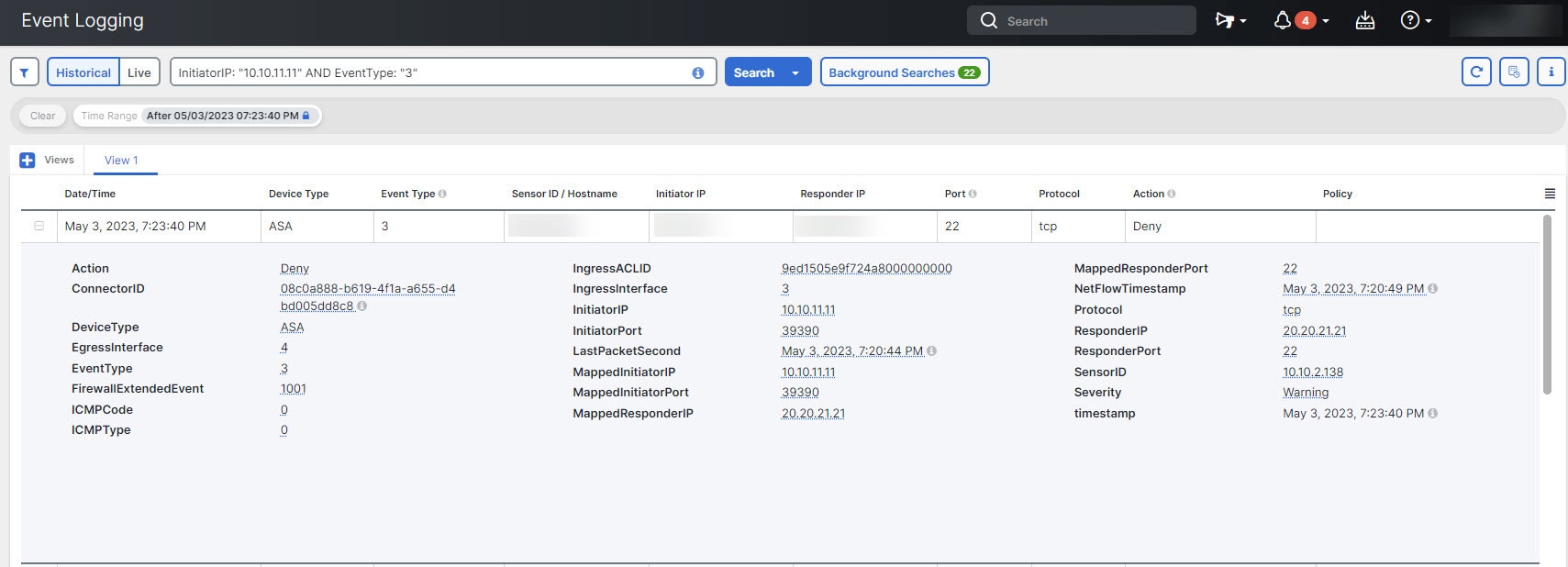
Receiving and Reporting Events
There may be a small lag between the Secure Event Connector or the Security Service Exchange receiving events and Security Cloud Control posting events in the Live events viewer. You can view the gap on the Live page. The time stamp of the event is the time it was received by Secure Event Connector or the Security Service Exchange.

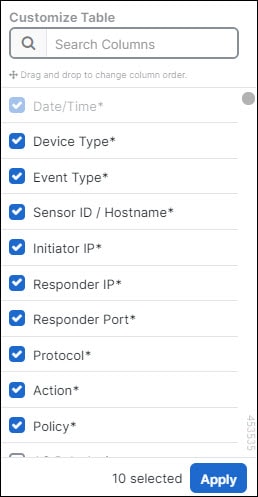
 .
.

 ) to pin the
) to pin the 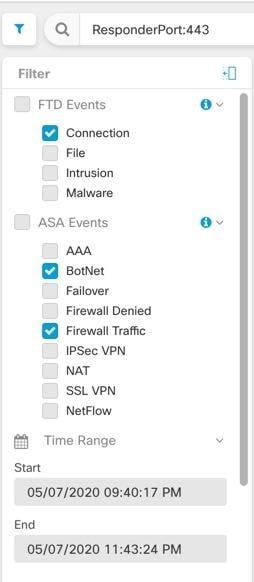
 Feedback
Feedback