Raw socket
|
Feature name |
Release information |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Raw socket |
Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN Release 17.18.1a Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Manager Release 20.18.1 |
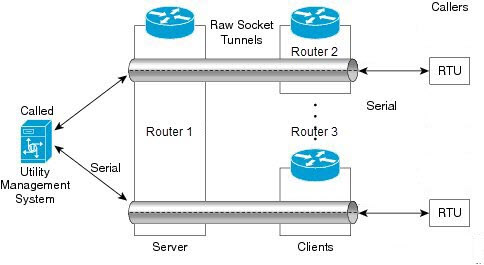
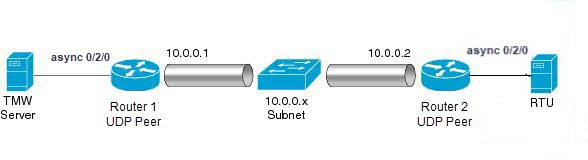
You can transport serial data across your IP networks by configuring TCP or UDP options through configuration groups on supported Cisco rugged routers. |

 Feedback
Feedback