Information About Redirect DNS in a Service-Side VPN
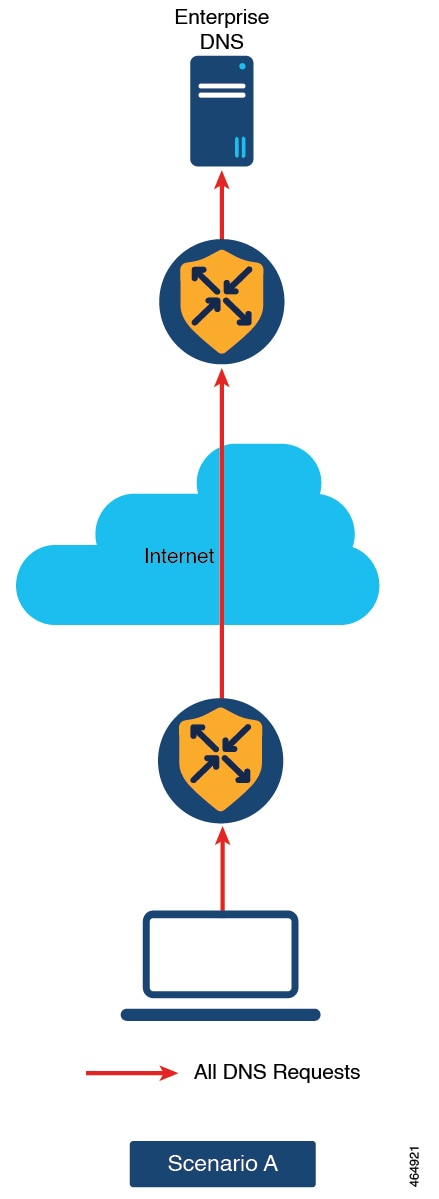
The Redirect DNS feature enables Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN devices to respond to DNS queries using a specific configuration and associated host table cache that are selected based on certain characteristics of the queries. In a redirect DNS environment, multiple DNS databases can be configured on the device. The Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN software can be configured to choose one of the DNS name server configurations whenever the device responds to a DNS query, by forwarding or resolving the query. Prior to Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN Release 17.8.1a, redirect DNS is supported only through NAT Direct Internet Access (DIA) path.
When an application-aware routing policy allows a Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN device to send application traffic to a service VPN and receive application traffic from a service VPN, the device performs a DNS lookup to determine the path to reach the application server. If the router does not have a connection to the internet, it sends DNS queries to an edge device that has such a connection, and that device determines how to reach a server for that application.
 Note |
In a network in which the device that is connected to the internet is in a geographically distant data center, the resolved DNS address points to a server that is also geographically distant from the site where the service VPN is located. |
Because you can configure a Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN device to be an internet exit point, it is possible for any router to reach the internet directly to perform DNS lookups.
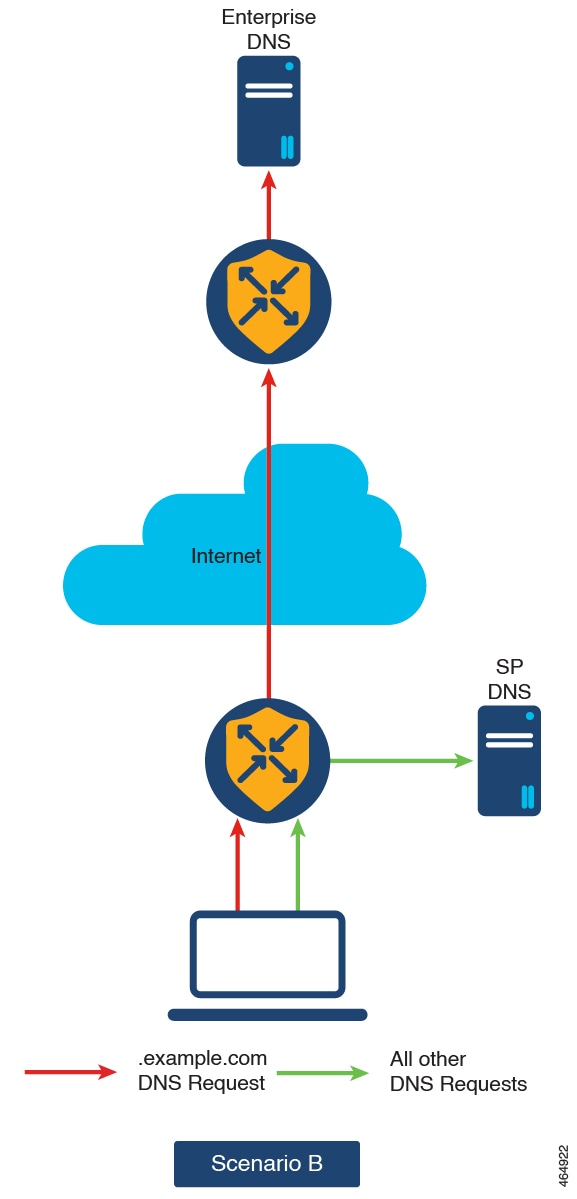
You can configure redirect DNS with either a centralized data policy or, if you want to apply SLA criteria to the data traffic, you can use application-aware routing policy.
Key differences between dns-app-list and app-list
-
dns-app-list: This construct is specifically designed to capture DNS traffic related to applications. It allows processing DNS requests and responses on an application-by-application basis, which is useful for scenarios like split DNS configurations. This approach is beneficial when DNS traffic must be handled differently for each application.
-
app-list: This is used to match actual application traffic. It is suitable for identifying and processing traffic that is directly related to applications, rather than DNS queries associated with those applications.
Considerations for using dns-app-list and app-list
-
Use dns-app-list to differentiate DNS traffic for specific applications, especially in environments where DNS traffic needs to be managed separately from the application traffic itself.
-
Use app-list for general application traffic classification where there is no need to separately identify or process DNS traffic.
 Feedback
Feedback