Information about TCP Optimization
Overview of TCP Optimization
TCP optimization fine tunes the processing of TCP data traffic to decrease round-trip latency and improve throughput.
This article describes optimizing TCP traffic in service-side VPNs on Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN devices.
Optimizing TCP traffic is especially useful for improving TCP traffic performance on long-latency links, such as transcontinental links and the high-latency transport links used by VSAT satellite communications systems. TCP optimization can also improve the performance of SaaS applications.
With TCP optimization, a router acts as a TCP proxy between a client that is initiating a TCP flow and a server that is listening for a TCP flow, as illustrated in the following figure:
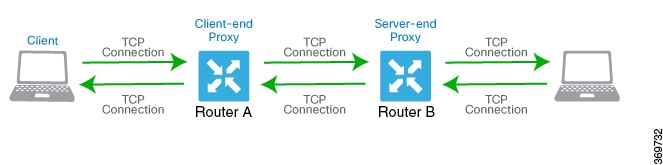
The figure shows two routers acting as proxies. Router A is the proxy for the client, and is called the client proxy. Router B is the proxy for the server, called the server proxy. Without TCP optimization, the client establishes a TCP connection directly to the server. When you enable TCP optimization on the two routers, Router A terminates the TCP connection from the client and establishes a TCP connection with Router B. Router B then establishes a TCP connection to the server. The two routers cache the TCP traffic in their buffers to ensure that the traffic from the client reaches the server without allowing the TCP connection to time out.
It is recommended that you configure TCP optimization on both the routers, the router closer to the client and the router closer to the server. This configuration is sometimes called a dual-ended proxy. It is possible to configure TCP optimization only on the router closer to the client, a scenario called single-ended proxy, but this configuration is not recommended because the TCP optimization process is compromised. TCP is a bidirectional protocol and operates only when connection-initiation messages (SYNs) are acknowledged by ACK messages in a timely fashion.
If both the client and the server are connected to the same router, no TCP optimization is performed.
To use TCP optimization, first enable the feature on the router. Then define which TCP traffic to optimize. Before you configure TCP optimization, to start with the configuration transaction, you can use the following command such as,
ntp server 198.51.241.229 source GigabitEthernet1 version 4Topology and Roles
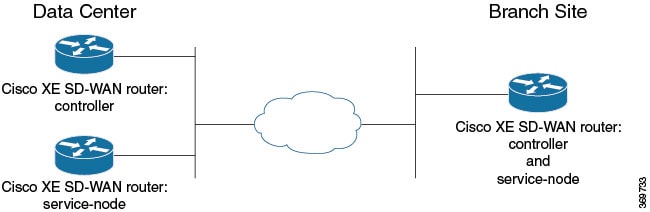
For a branch, the Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN device acts as both controller and service-node.
Data Center
For a data center, the controller and service-node roles are performed by separate Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN devices. This optimizes performance and enables handling more traffic.
The service-node is an external node that has control connections to vManage to receive configurations.
 Note |
The service-node Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN device must have an underlay connection to the controller on the global VRF to establish an appnav tunnel. |
Supported Platforms
Starting from Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN Release 17.2.1r, TCP Optimization is supported on the following platforms.
-
Cisco 4331 Integrated Services Router (ISR 4331)
-
Cisco 4431 Integrated Services Router (ISR 4431)
-
Cisco 4321 Integrated Services Router (ISR 4321)
-
Cisco 4351 Integrated Services Router (ISR 4351)
-
Cisco 4451 Integrated Services Router (ISR 4451)
-
Cisco 4461 Integrated Services Router (ISR 4461)
-
Cisco CSR 1000v Cloud Services Router (CSRv)
Minimum Resource Requirements
-
The platforms must have a minimum of 8 GB of DRAM.
-
The platforms must have four or more data cores, with the exception of Cisco 4321 Integrated Services Router (ISR 4321), which is supported in spite of having fewer than four data cores.
 Feedback
Feedback