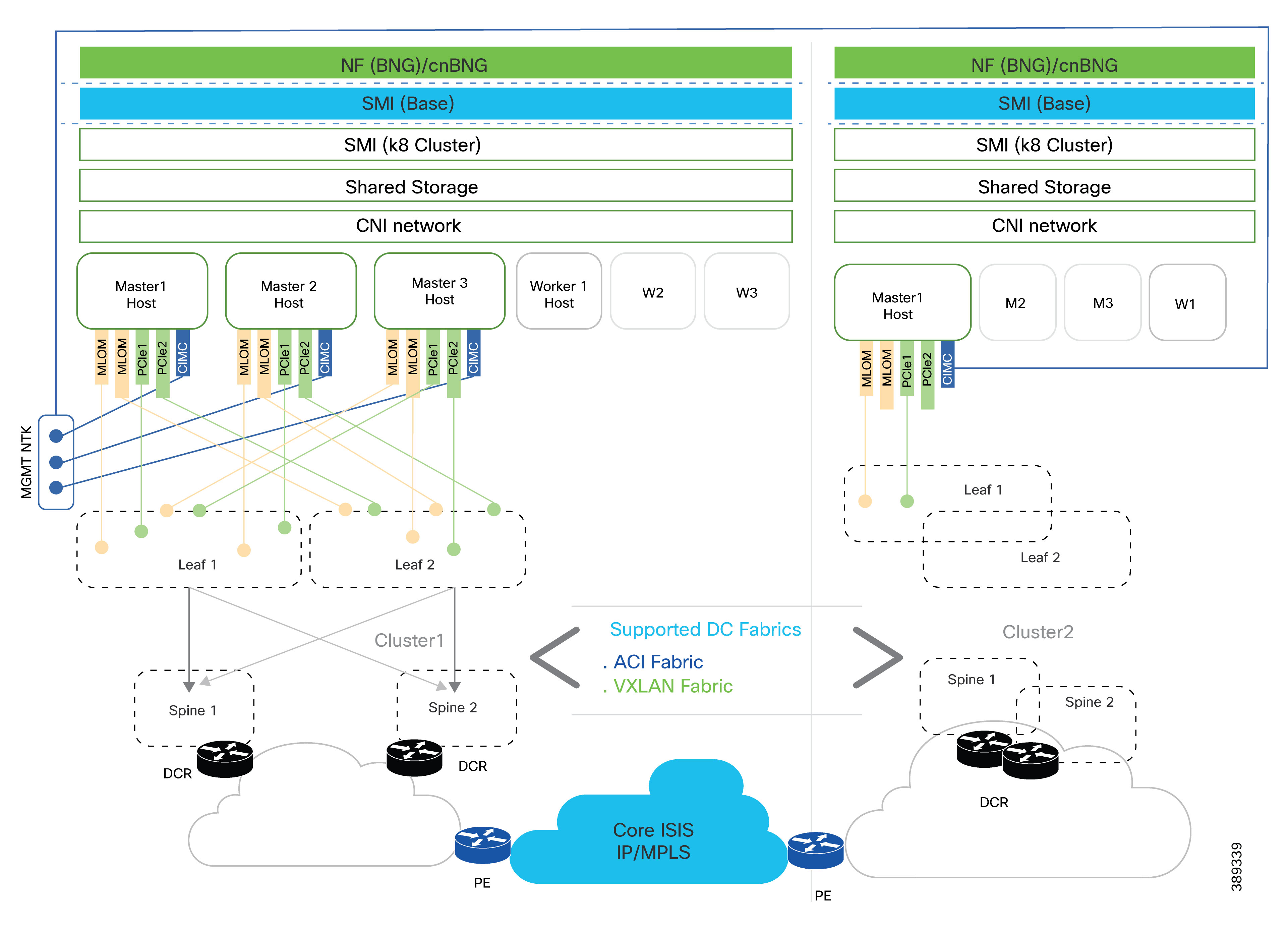
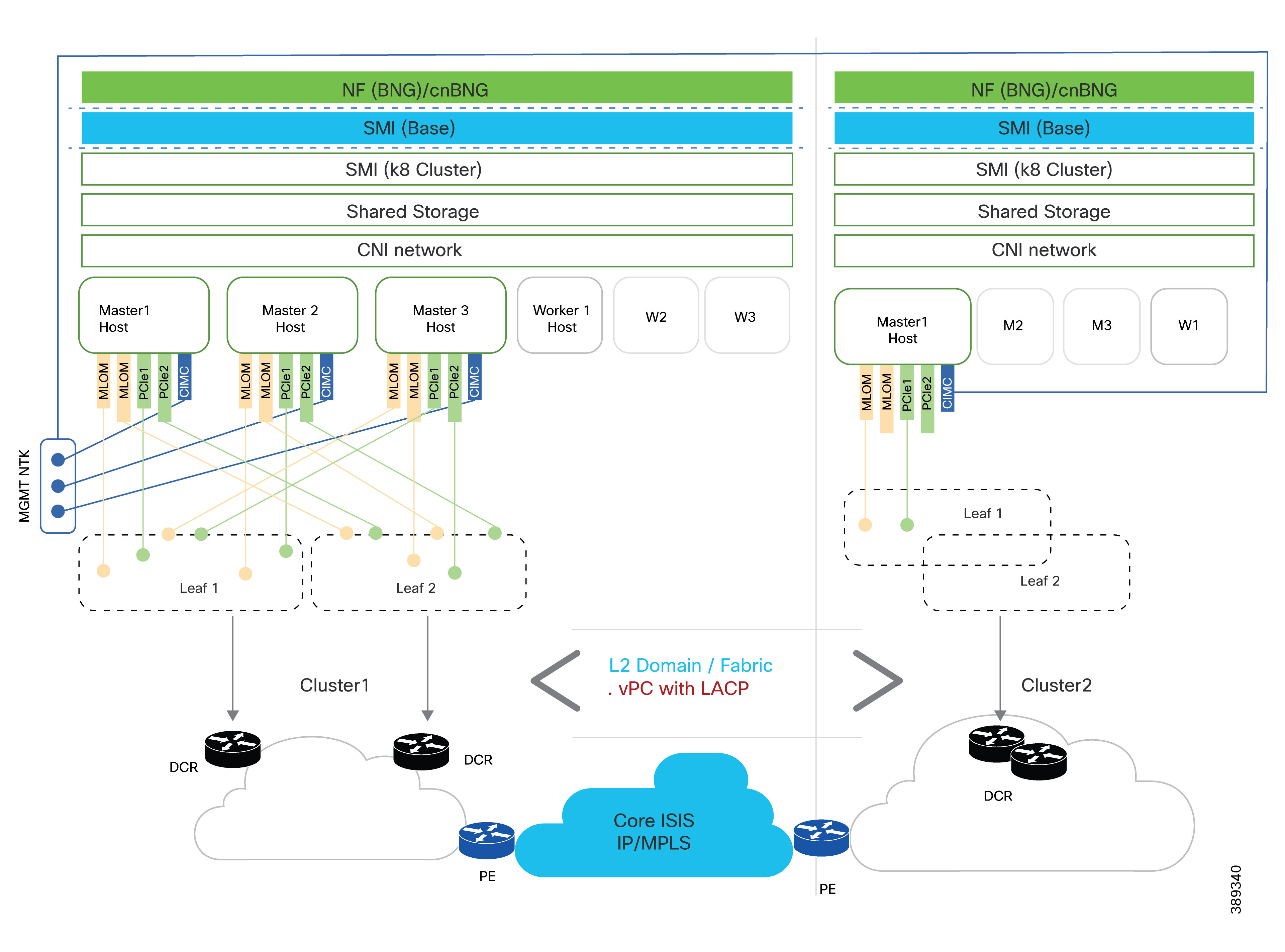
Flexible deployment models
Cisco cnBNG is inherently fabric-agnostic and performance-sensitive, making it suitable for a variety of deployment scenarios:
Supported deployment models:
-
Modern VXLAN-based fabrics
-
Cisco ACI policy-driven fabrics
-
Traditional vPC + LACP designs
cnBNG offers deployment flexibility. It operates on a Kubernetes cluster of servers, which can be as simple as a single node (All-in-One) or scaled across multiple nodes for higher availability. Each node is dual-homed to the data center fabric, ensuring both link and device redundancy for uninterrupted service.
 Feedback
Feedback