Access the
Networking Stack
The Cisco IOS XR Software serves as a networking stack for communication. This section explains how applications on IOS XR can communicate with internal processes, and with servers or outside devices.
Communication Outside Cisco IOS XR
To communicate outside Cisco IOS XR, applications use the fwdintf interface address that maps to the loopback0 interface or a configured Gigabit Ethernet interface address. For information on the various interfaces on IOS XR, see Application Hosting on the Cisco IOS XR Linux Shell.
To have an iPerf or Chef client on IOS XR communicate with its respective server outside IOS XR, you must configure an interface address as the source address on XR. The remote servers must configure this route address to reach the respective clients on IOS XR.
This section provides an example of configuring a Gigabit Ethernet interface address as the source address for external communication.
Using a Gigabit Ethernet Interface for External Communication
To configure a GigE interface on IOS XR for external communication, use these steps:
-
Configure a GigE interface.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/0/1 RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios(config-if)# ipv4 address 192.57.43.10 255.255.255.0 RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios(config-if)# no shut RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios(config-if)# commit Fri Oct 30 07:51:14.785 UTC RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios(config-if)# exit RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios(config)# exit
-
Verify whether the configured interface is up and operational on IOS XR.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios# show ipv4 interface brief Fri Oct 30 07:51:48.996 UTC Interface IP-Address Status Protocol Loopback0 1.1.1.1 Up Up Loopback1 8.8.8.8 Up Up GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 192.164.168.10 Up Up GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1 192.57.43.10 Up Up GigabitEthernet0/0/0/2 unassigned Shutdown Down MgmtEth0/RP0/CPU0/0 192.168.122.197 Up Up RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios#
-
Enter the Linux bash shell and verify if the configured interface is up and running.
/* If you are using Cisco IOS XR Version 6.0.0, run the following command */ RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios# run ip netns exec tpnns bash /* If you are using Cisco IOS XR Version 6.0.2, run the following command */ RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios# bash [xr-vm_node0_RP0_CPU0:~]$ ifconfig Gi0_0_0_0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 52:46:04:87:19:3c inet addr:192.164.168.10 Mask:255.255.255.0 inet6 addr: fe80::5046:4ff:fe87:193c/64 Scope:Link UP RUNNING NOARP MULTICAST MTU:1514 Metric:1 RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:3 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:210 (210.0 B) Gi0_0_0_1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 52:46:2e:49:f6:ff inet addr:192.57.43.10 Mask:255.255.255.0 inet6 addr: fe80::5046:2eff:fe49:f6ff/64 Scope:Link UP RUNNING NOARP MULTICAST MTU:1514 Metric:1 RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:3 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:210 (210.0 B) Mg0_RP0_CPU0_0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 52:46:12:7a:88:41 inet addr:192.168.122.197 Mask:255.255.255.0 inet6 addr: fe80::5046:12ff:fe7a:8841/64 Scope:Link UP RUNNING NOARP MULTICAST MTU:1514 Metric:1 RX packets:3 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:6 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:294 (294.0 B) TX bytes:504 (504.0 B) fwd_ew Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:00:00:00:00:0b inet6 addr: fe80::200:ff:fe00:b/64 Scope:Link UP RUNNING NOARP MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:4 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:6 errors:0 dropped:1 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:392 (392.0 B) TX bytes:532 (532.0 B) fwdintf Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:00:00:00:00:0a inet6 addr: fe80::200:ff:fe00:a/64 Scope:Link UP RUNNING NOARP MULTICAST MTU:1482 Metric:1 RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:2 errors:0 dropped:1 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:140 (140.0 B) lo Link encap:Local Loopback inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0 inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:8 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:8 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:0 RX bytes:672 (672.0 B) TX bytes:672 (672.0 B) lo:0 Link encap:Local Loopback inet addr:1.1.1.1 Mask:255.255.255.255 UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:1500 Metric:1 -
Exit the Linux bash shell and configure the GigE interface as the source address for external communication.
[xr-vm_node0_RP0_CPU0:~]$ exit RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios# config Fri Oct 30 08:55:17.992 UTC RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios(config)# tpa address-family ipv4 update-source gigabitEthernet 0/0/0/1 RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios(config)# commit Fri Oct 30 08:55:38.795 UTC

Note
By default, the fwdintf interface maps to the loopback0 interface for external communication. This is similar to binding a routing process or router ID to the loopback0 interface. When you use the tpa address-family ipv4 update-source command to bind the fwdintf interface to a Gigabit Ethernet interface, network connectivity can be affected if the interface goes down.
-
Enter the Linux bash shell and verify whether the GigE interface address is used by the fwdintf interface for external communication.
/* If you are using Cisco IOS XR Version 6.0.0, run the following command */ RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios# run ip netns exec tpnns bash /* If you are using Cisco IOS XR Version 6.0.2, run the following command */ RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios# bash [xr-vm_node0_RP0_CPU0:~]$ ip route default dev fwdintf scope link src 192.57.43.10 8.8.8.8 dev fwd_ew scope link 192.168.122.0/24 dev Mg0_RP0_CPU0_0 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.122.197 [xr-vm_node0_RP0_CPU0:~]$
External communication is successfully enabled on IOS XR.
East-West Communication for Third-Party Applications
East-West communication on IOS XR is a mechanism by which applications hosted in containers interact with native XR applications (hosted in the XR control plane).
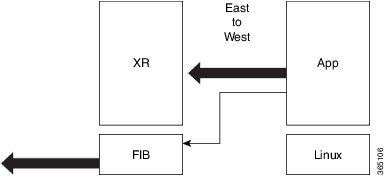
The following figure illustrates how a third-party application hosted on IOS XR interacts with the XR Control Plane.
The application sends data to the Forwarding Information Base (FIB) of IOS XR. The application is hosted in the east portion of IOS XR, while the XR control plane is located in the west region. Therefore, this form of communication between a third-party application and the XR control plane is termed as East-West (E-W) communication.
Third-party applications such as Chef Client and Puppet Agent use this mode of communication to configure and manage containers, packages, and applications on IOS XR. In the future, this support could be extended to IOS XR, configured and managed by such third-party applications.
For a third-party application to communicate with IOS XR, the Loopback1 interface must be configured. This is explained in the following procedure.
-
Configure the Loopback1 interface on IOS XR.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios(config)# interface Loopback1 RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios(config-if)# ipv4 address 8.8.8.8/32 RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios(config-if)# no shut RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios(config-if)# commit RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios(config-if)# exit RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios(config)#
-
Verify the creation of the Loopback1 interface.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios# show ipv4 interface brief Thu Nov 12 10:01:00.874 UTC Interface IP-Address Status Protocol Loopback0 1.1.1.1 Up Up Loopback1 8.8.8.8 Up Up GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 192.164.168.10 Up Up GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1 192.57.43.10 Up Up GigabitEthernet0/0/0/2 unassigned Shutdown Down MgmtEth0/RP0/CPU0/0 192.168.122.197 Up Up RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios#
-
Enter the third-party network namespace or global VRF depending on the version of IOS XR version you are using for your network.
/* If you are using Cisco IOS XR Version 6.0.0, run the following command */ RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios# run ip netns exec tpnns bash /* If you are using Cisco IOS XR Version 6.0.2, run the following command */ RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios# bash
-
Verify whether the Loopback1 interface address has been mapped to the E-W interface.
[xr-vm_node0_RP0_CPU0:~]$ ip route default dev fwdintf scope link src 192.57.43.10 8.8.8.8 dev fwd_ew scope link 192.168.122.0/24 dev Mg0_RP0_CPU0_0 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.122.197 [xr-vm_node0_RP0_CPU0:~]$
 Feedback
Feedback