Set Up the Supercluster
Before you begin
-
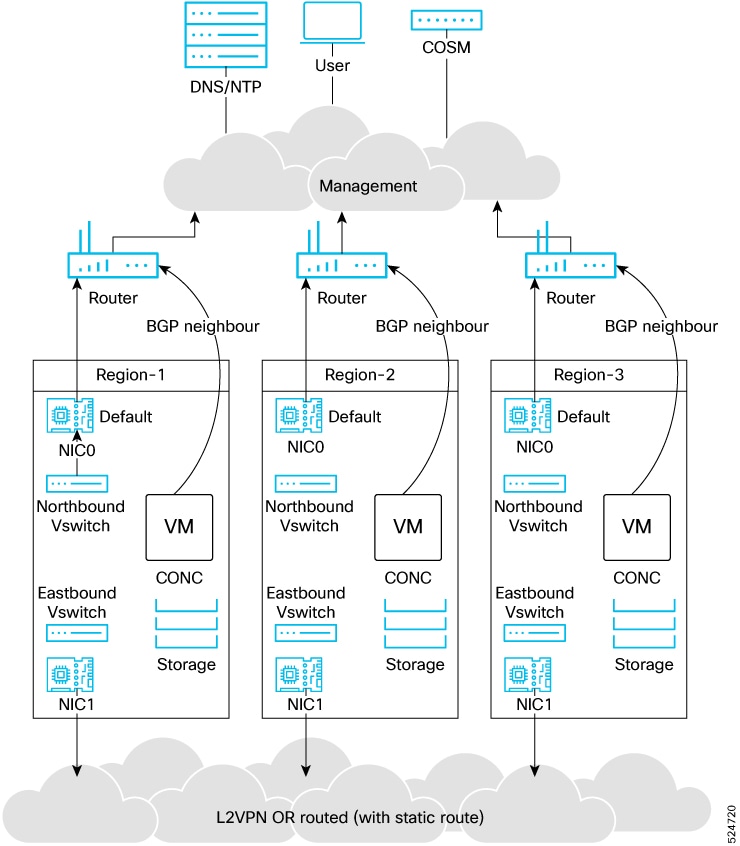
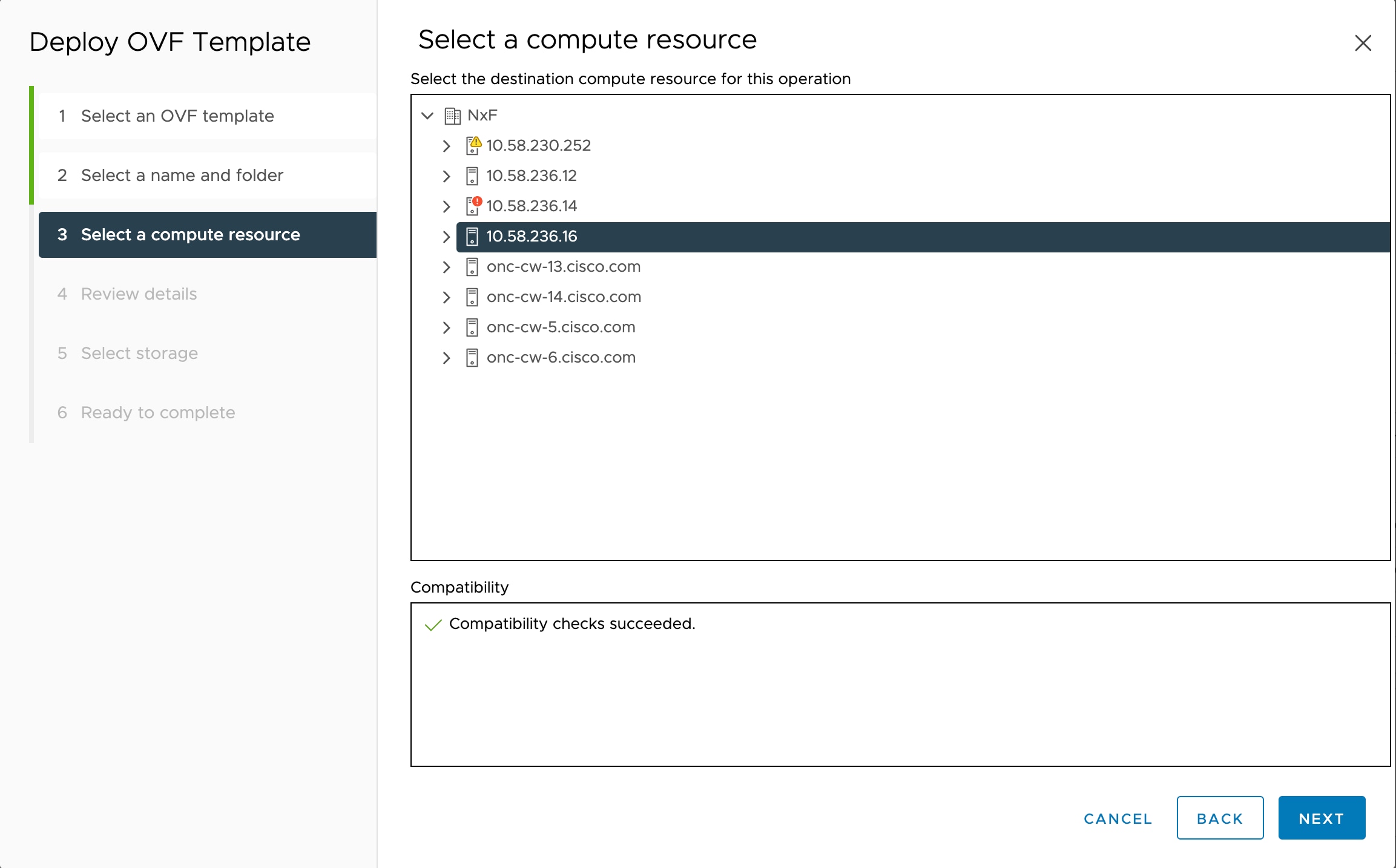
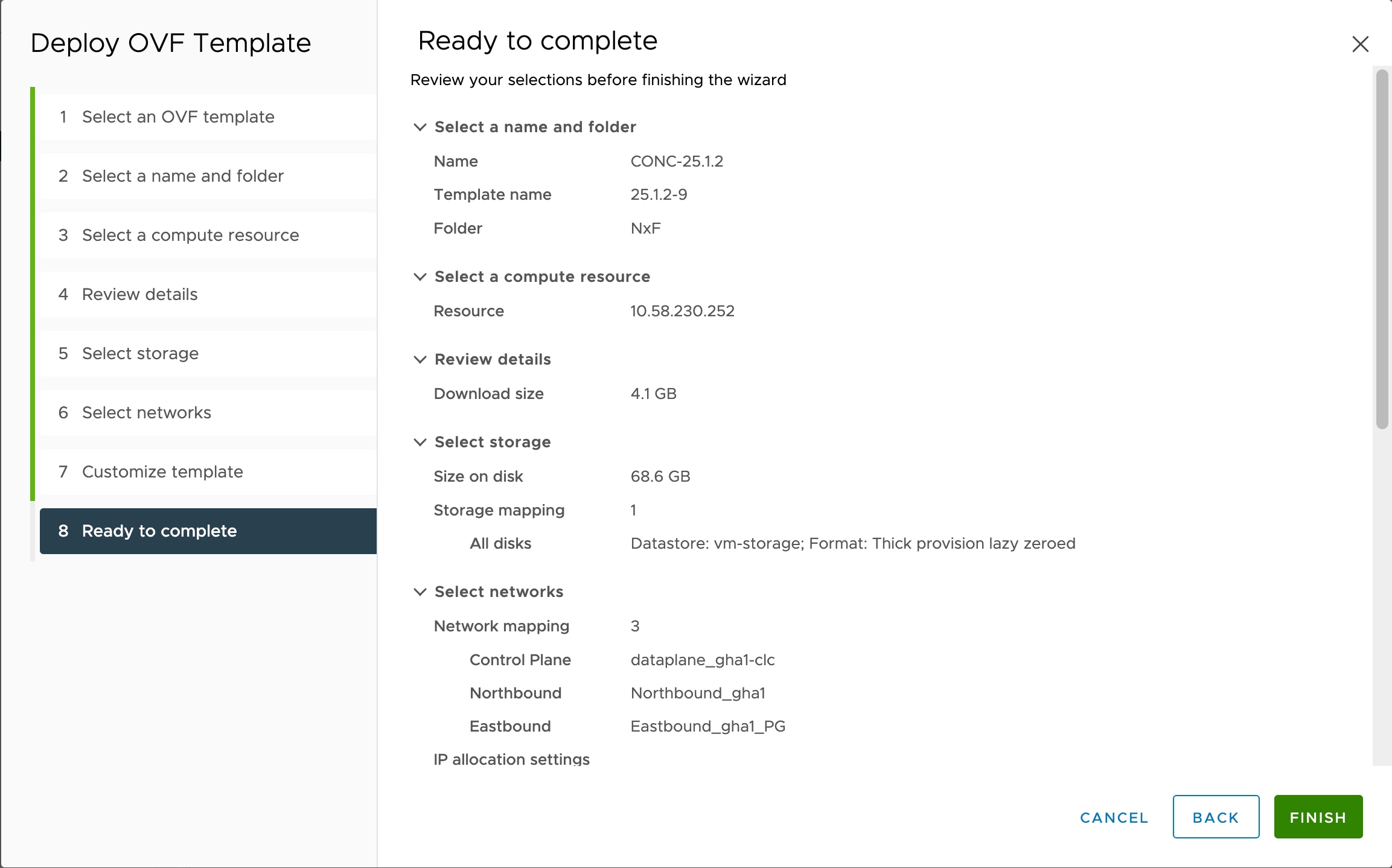
You must have created 3 VMs for geo-redundant deployment of Cisco Optical Network Controller. For more details, see Install and Deploy Geo Redundant Cisco Optical Network Controller.
-
Verify that the VM is powered on. Wait for the IP addresses for the VM on vSphere to appear.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
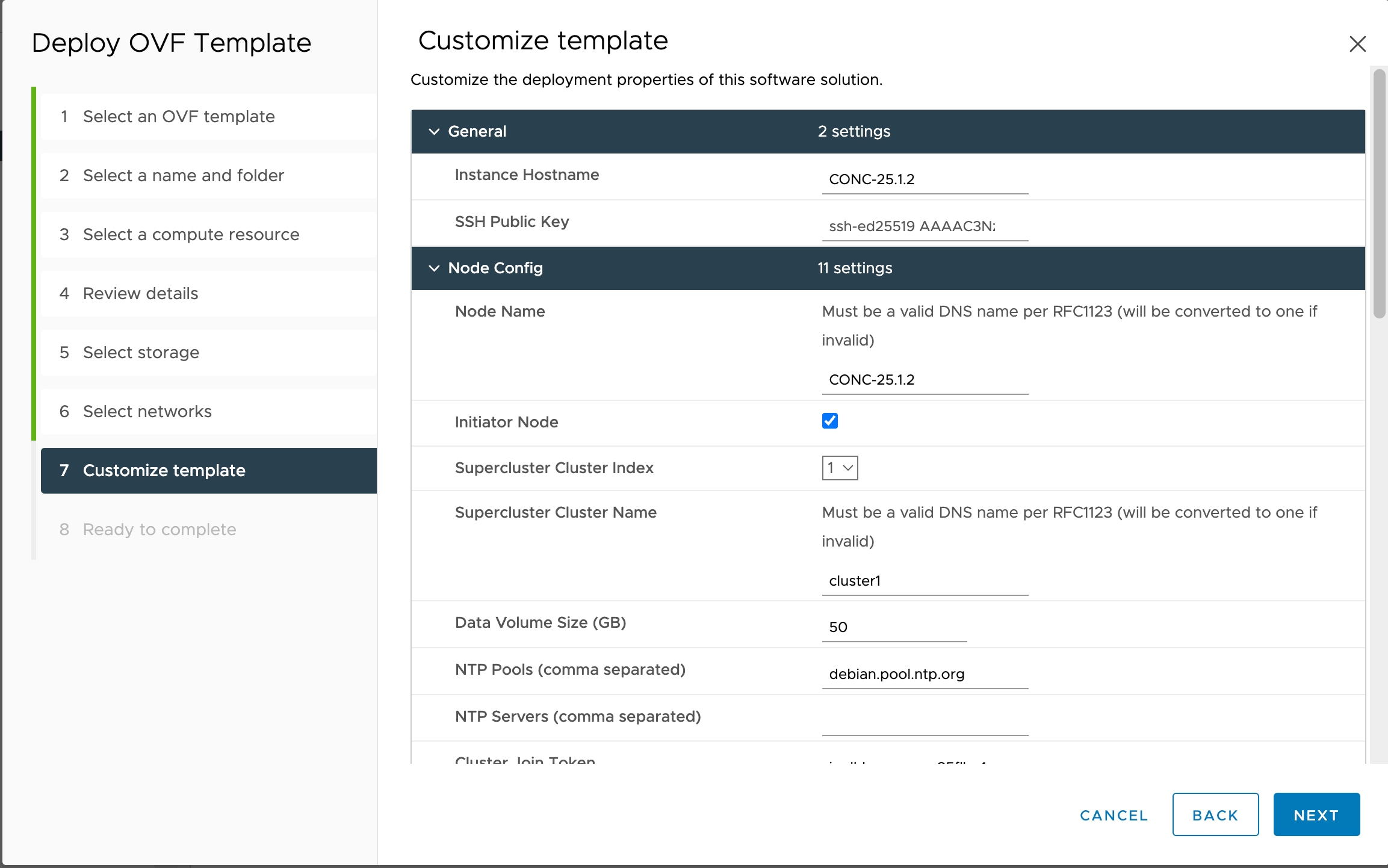
After the VMs are created, try connecting to the VM using the pem key which was generated earlier, see SSH Key Generation. For this, use the private key that is generated along with the public key during customizing the public key options. |
||
|
Step 2 |
Log in to each VM using the private key.
|
||
|
Step 3 |
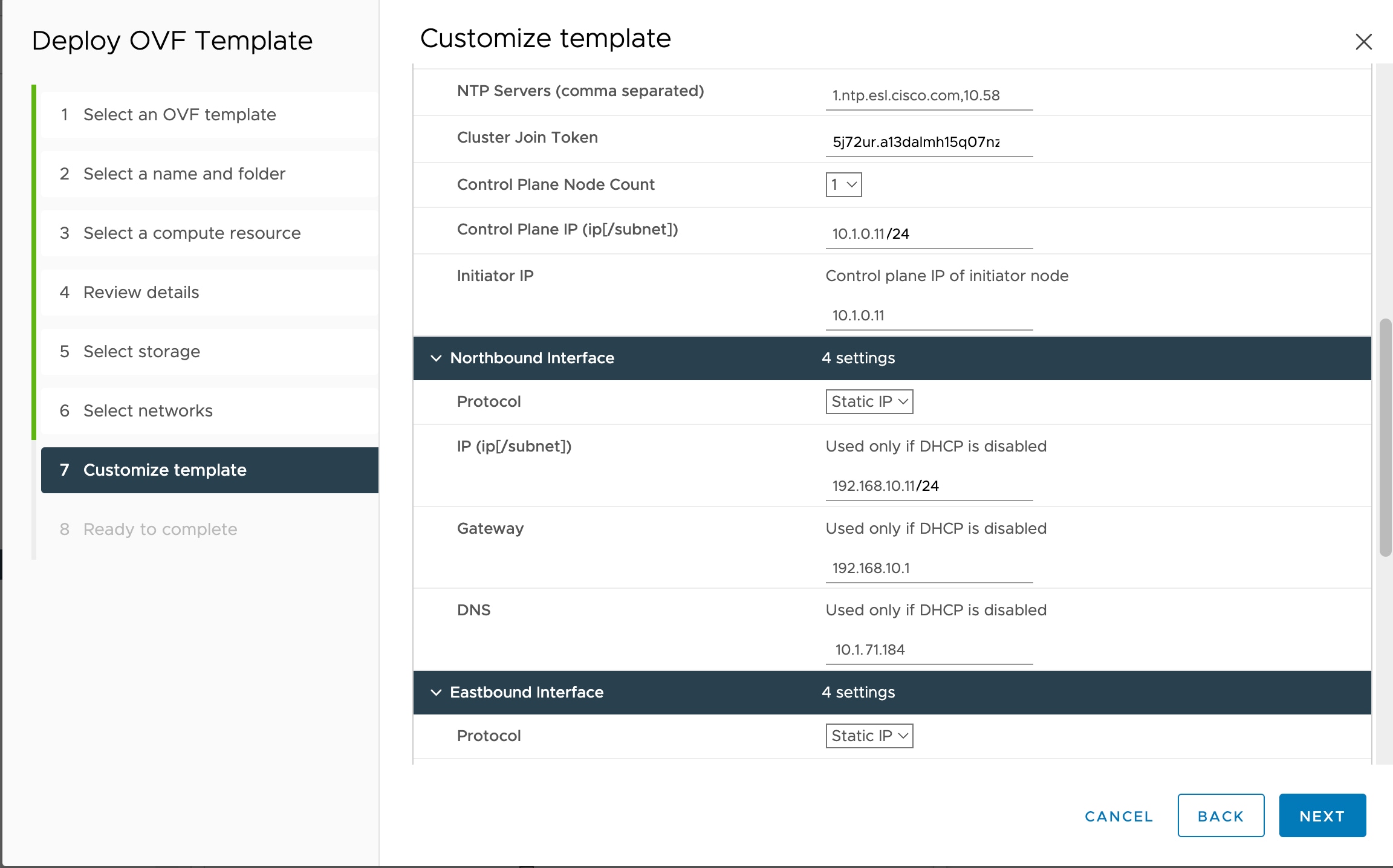
If peer nodes Eastbound IPs are in different subnets, you must create static routes between the nodes for the eastbound traffic flow among the nodes. From each node, create routes to each of the two other nodes. |
||
|
Step 4 |
Use the ping command to verify connectivity between the nodes. |
||
|
Step 5 |
Restart the systemd-networkd service to apply the changes. Example: |
||
|
Step 6 |
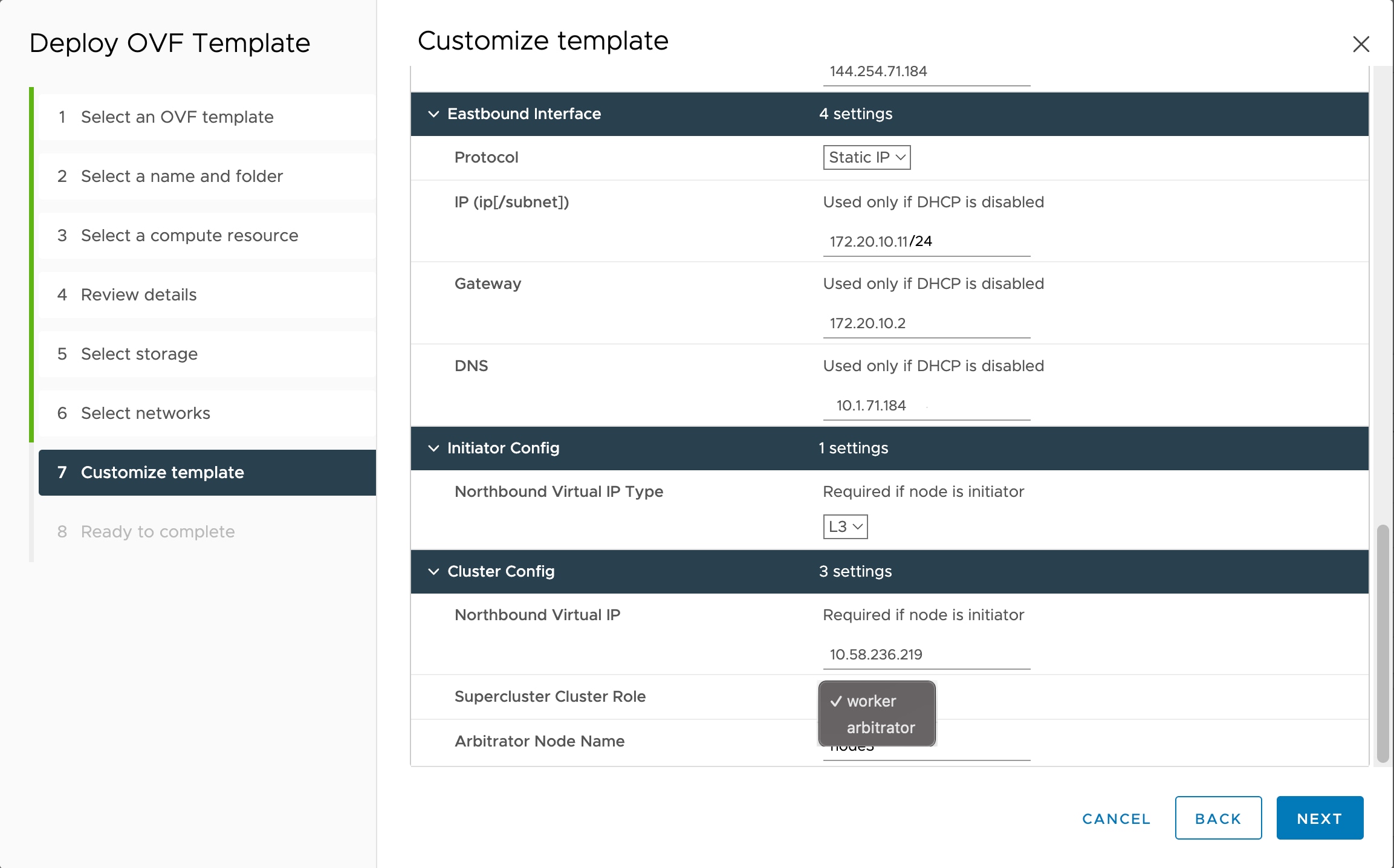
Configure BGP for virtual IP route advertisement. |
||
|
Step 7 |
Retrieve Cluster ID: On each node, run the following command to retrieve the Cluster ID.: Example:
|
||
|
Step 8 |
Connect cluster1 to cluster2. |
||
|
Step 9 |
Connect cluster1 to cluster3. |
||
|
Step 10 |
Connect cluster2 to cluster3. |
||
|
Step 11 |
Check Cluster Connectivity: After all clusters are joined, verify connectivity using the following command:
Example: |
||
|
Step 12 |
Start the Super-Cluster: Once connectivity is verified, start the supercluster using the following command:
Example: |
||
|
Step 13 |
Verify Super-Cluster Status: Check the status of the supercluster to ensure that all nodes are active and properly connected using the following command: Example:This sample output shows the output of the command on the standby node. The output shows the current active and standby clusters.
When DB replication is |
||
|
Step 14 |
Use the sedo system status command to check the status of all the pods.
|
||
|
Step 15 |
You can check the current version using the sedo version command. |

 Feedback
Feedback