Cisco Optical Network Controller Overview
Cisco Optical Network Controller (Cisco ONC) is an SDN Domain Controller for Cisco optical networks. Cisco Optical Network Controller behaves as a Provisioning Network Controller (PNC) and performs these functions.
-
Collects information about the inventory and topology of the managed network.
-
Monitors the physical or virtual topology of the network.
-
Notifies of changes in topology and service changes.
-
Supports the creation and deletion of optical paths.
SDN domain controller
SDN domain controller is a specialized SDN controller that
-
manages and controls devices within a specific technology domain, in this case, optical domain, and
-
communicates with the higher-level SDN controller via east-west interfaces
Cisco Optical Network Controller functions
Cisco Optical Network Controller collects data necessary for optical applications. This data is used to provide abstract network information to higher layer controllers. This abstraction enables centralized control of optical network.
Cisco Optical Network Controller supports several functions.
-
Optical Domain Controller
Cisco Optical Network Controller behaves as a domain controller for Cisco optical products. The domain controller feeds data into hierarchical controllers. Cisco Optical Network Controller has a North Bound Interface (NBI) based on the TAPI standard which enables it to connect to any hierarchical controller which has a TAPI compliant South Bound Interface (SBI) and provides its functions to the controller.
-
Path Compute Engine (PCE)
PCE service provides optical path computation to ensure optically valid paths are provisioned within the supplied constraints. PCE uses the latest network status.
-
Model Based Network Abstraction
Cisco Optical Network Controller supports a standardized TAPI model which enables it to abstract the device level details from the hierarchical controller.
 Note |
|
Software Requirements
Cisco Optical Network Controller, Release 25.1.x supports these software versions.
| Hardware and Software | Version |
|---|---|
| NCS 1001 | Cisco IOS XR Release 7.10.1 |
| NCS 1004 | Cisco IOS XR Release 24.3.1 |
| NCS 1014 | Cisco IOS XR Releases 25.1.1 and 24.3.1 |
| NCS 1010 | Cisco IOS XR Releases 25.1.1 and 24.3.1 |
| Cisco Optical Site Manager | |
|
NCS 1000 |
Cisco IOS XR Releases 25.1.1 and 24.3.1 |
|
NCS 2000 |
Release 25.1.1 |
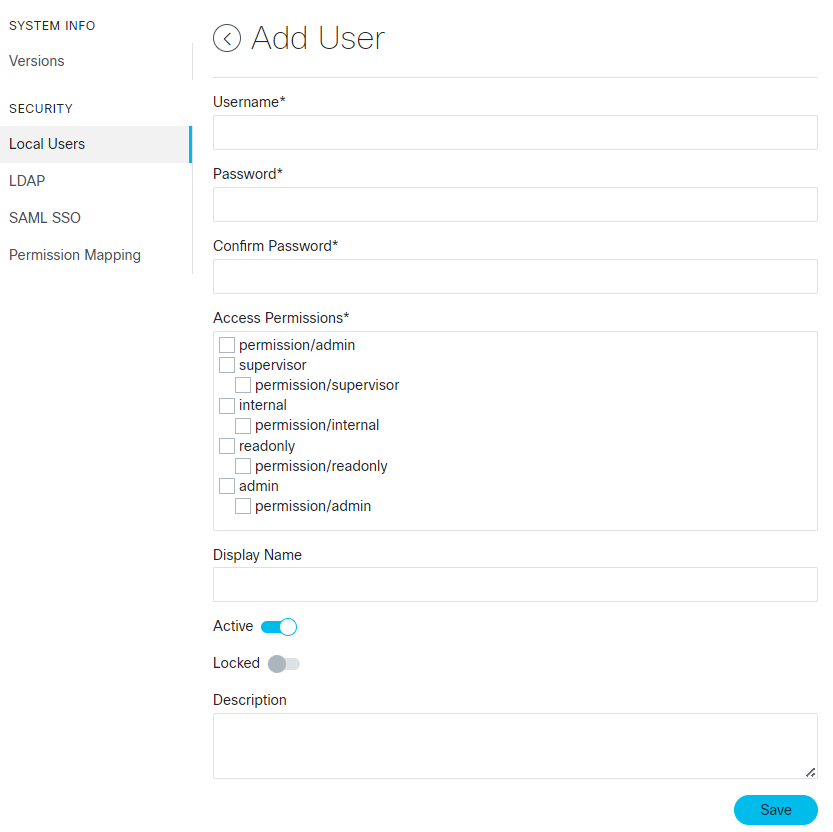
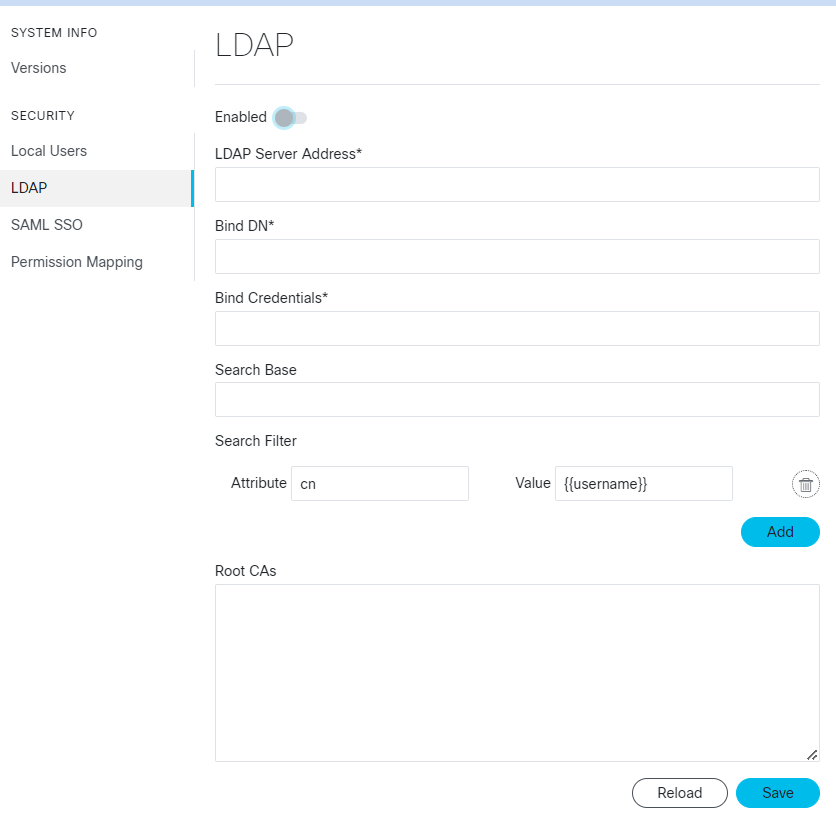
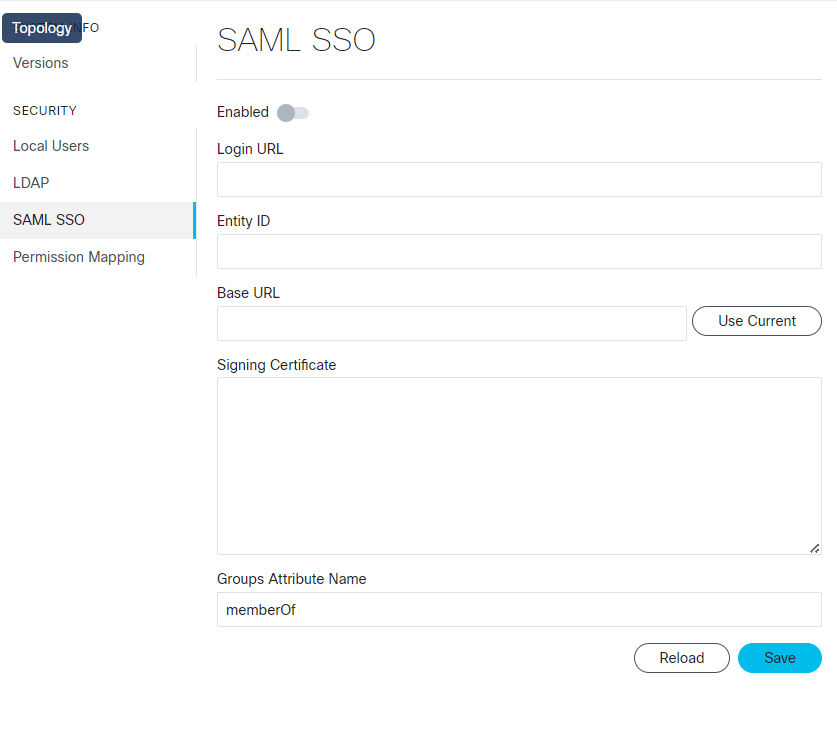
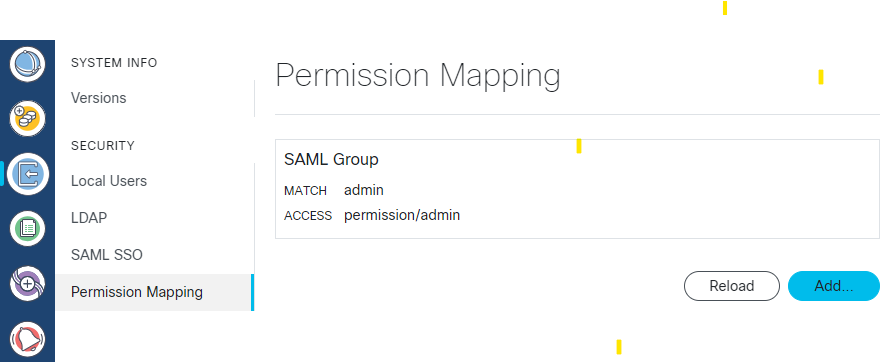
 Feedback
Feedback