Deployment Workflow for Cisco SD-WAN
Using the workflow in the table below, you can deploy Cisco SD-WAN vEdge Cloud, or vEdge SP Cloud, or the Physical site.
|
Task |
See |
|---|---|
|
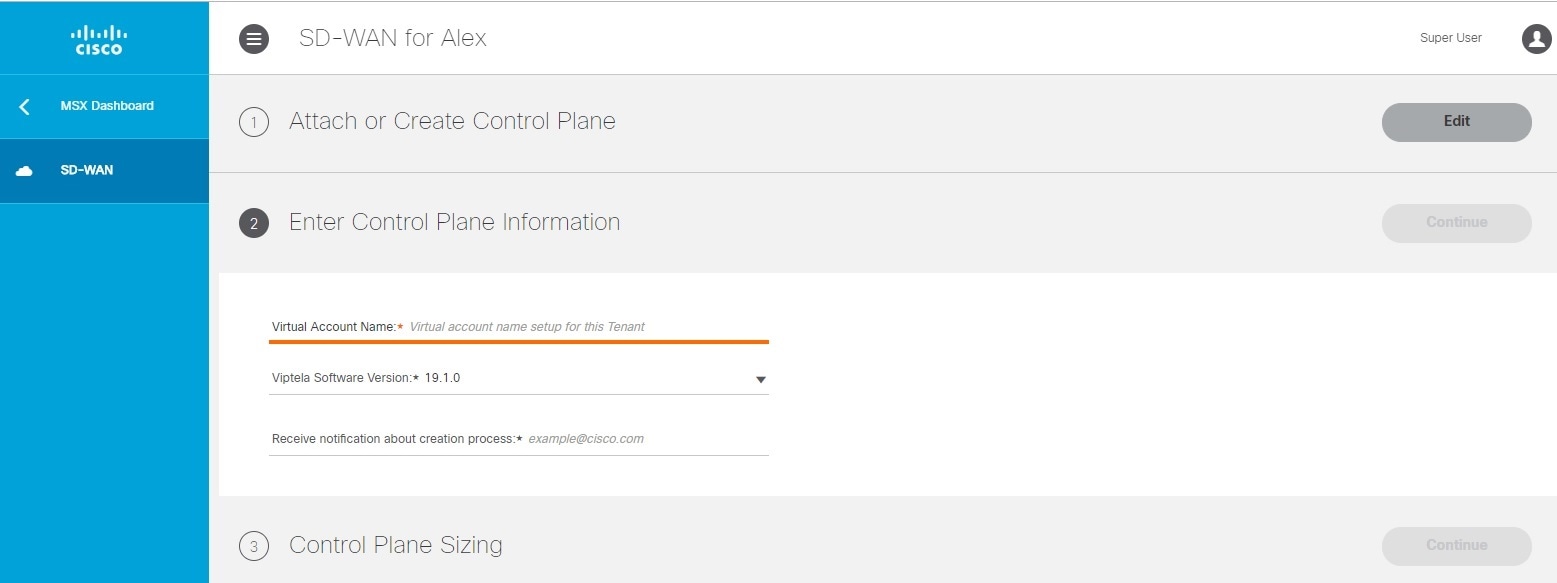
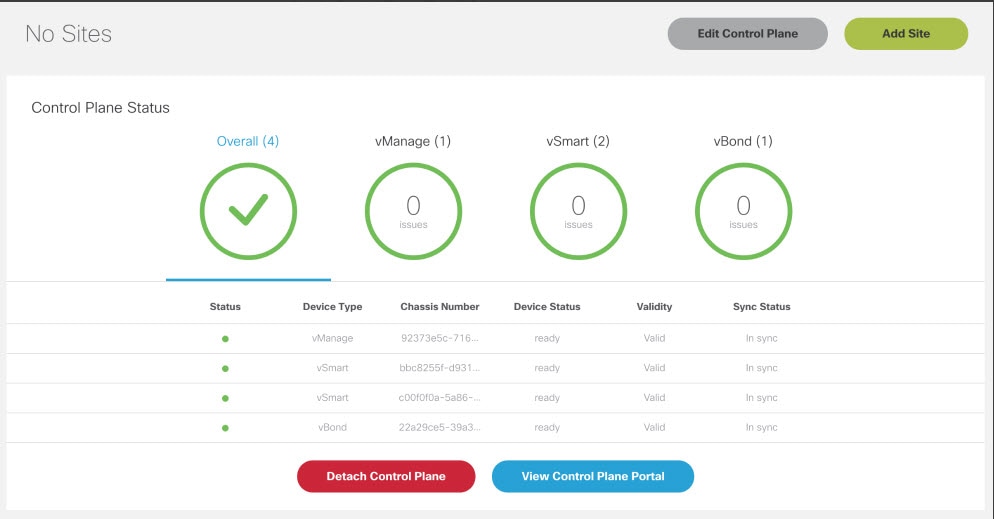
1. Attach an existing control plane or create a new control plane. |
Setting Up Control and Management Plane on AWS and OpenStack for Cisco SD-WAN |
|
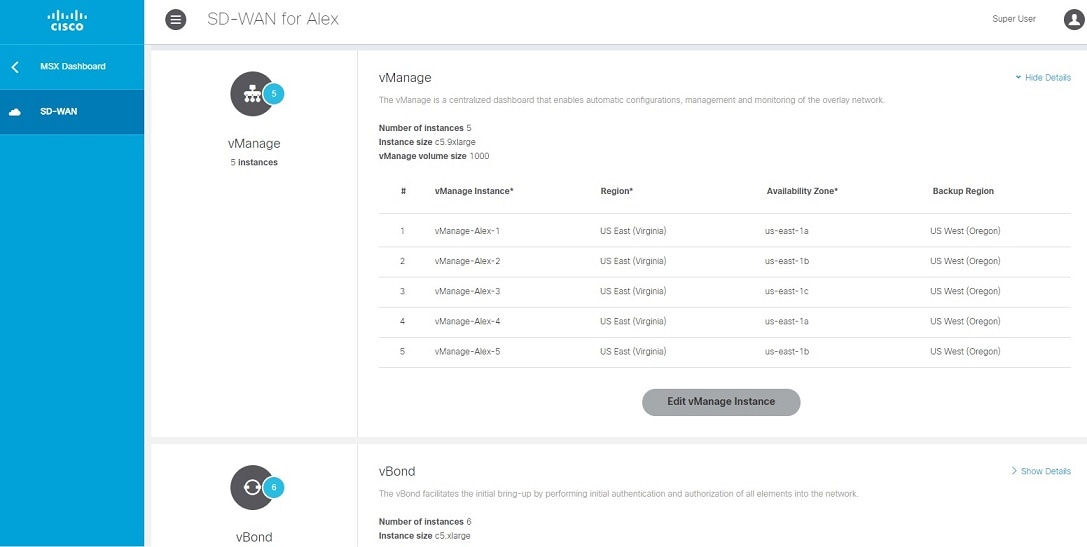
2. Complete Control Plane post deployment tasks. |
For more information, see Postdeployment Tasks for SD-WAN Control Plane. |
|
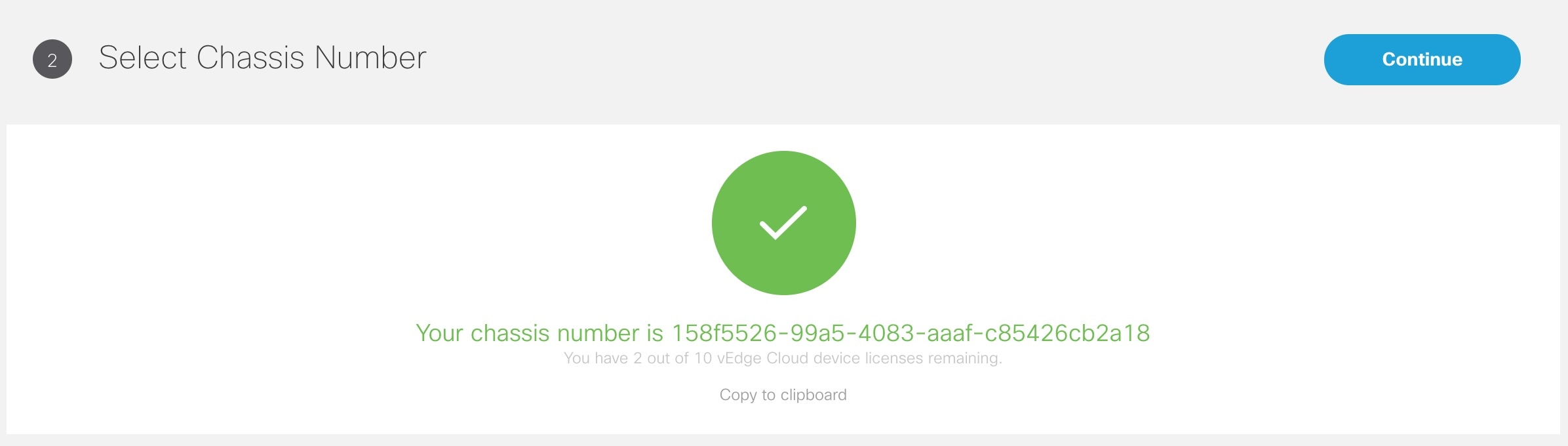
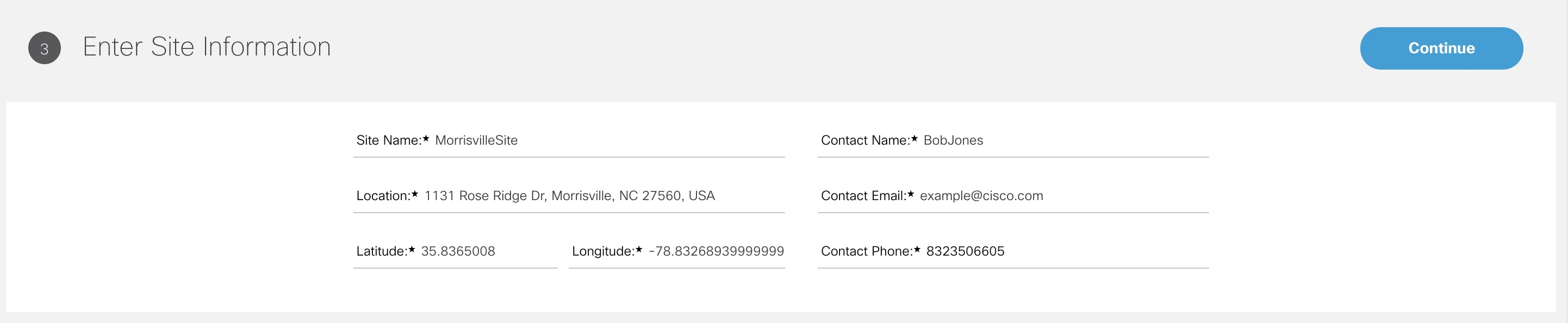
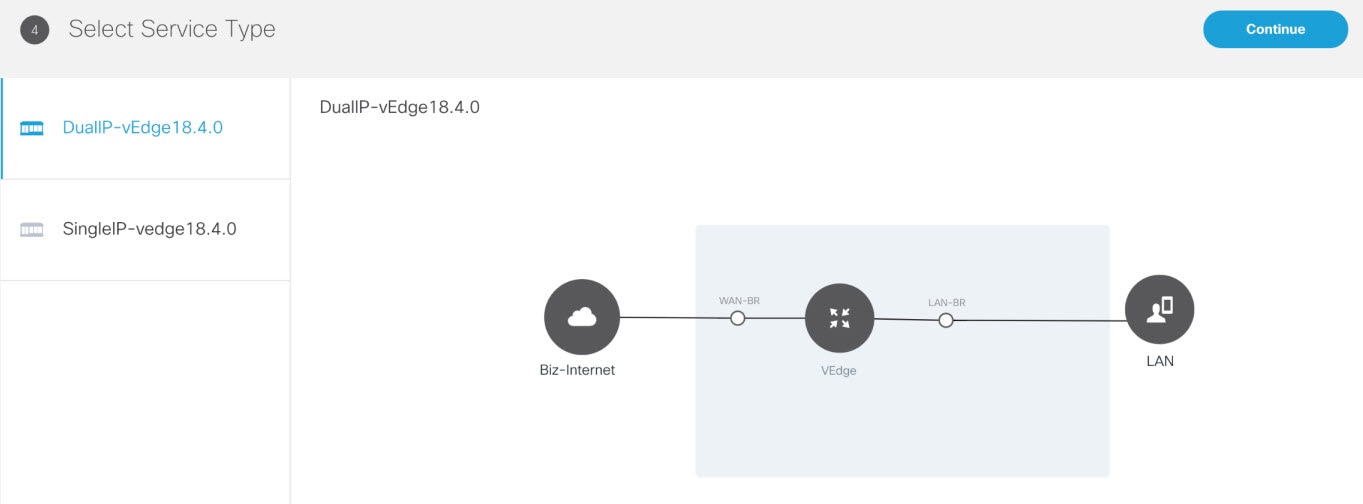
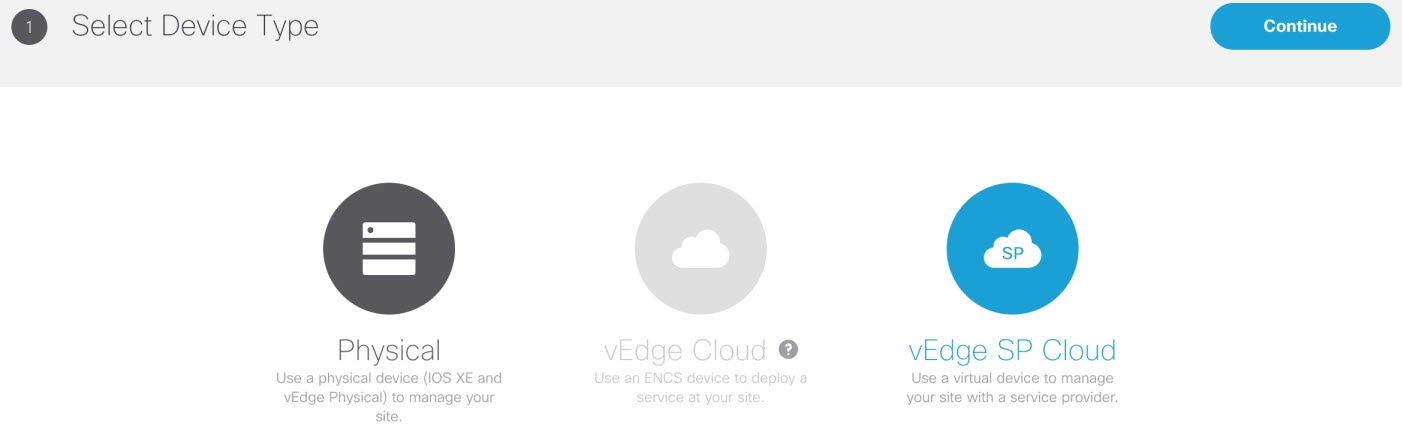
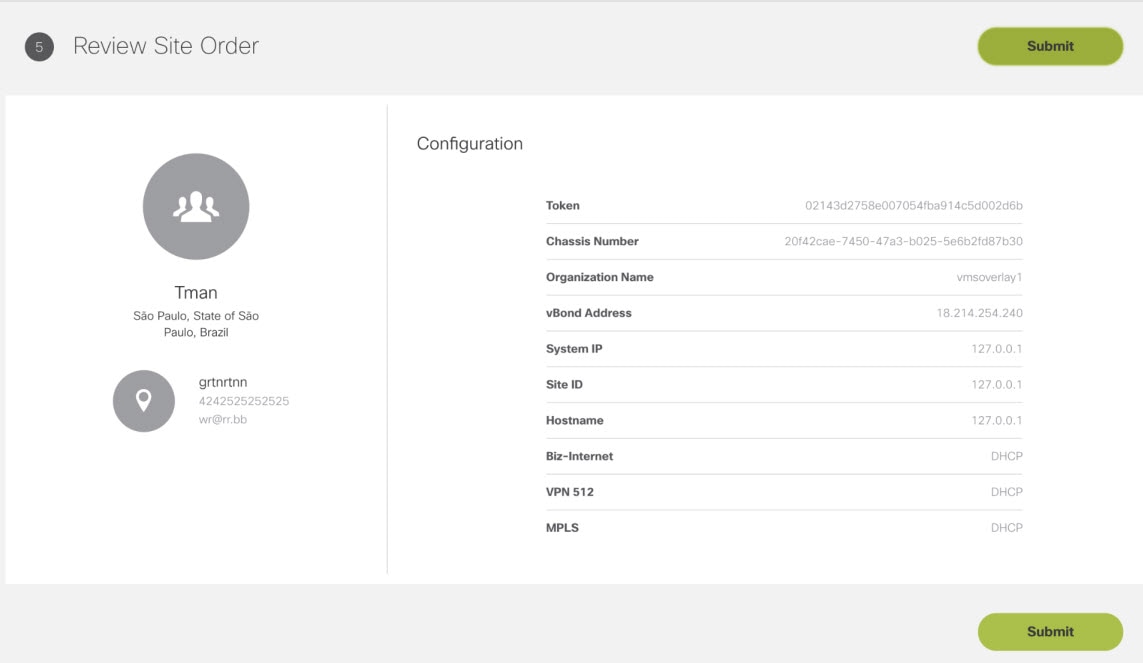
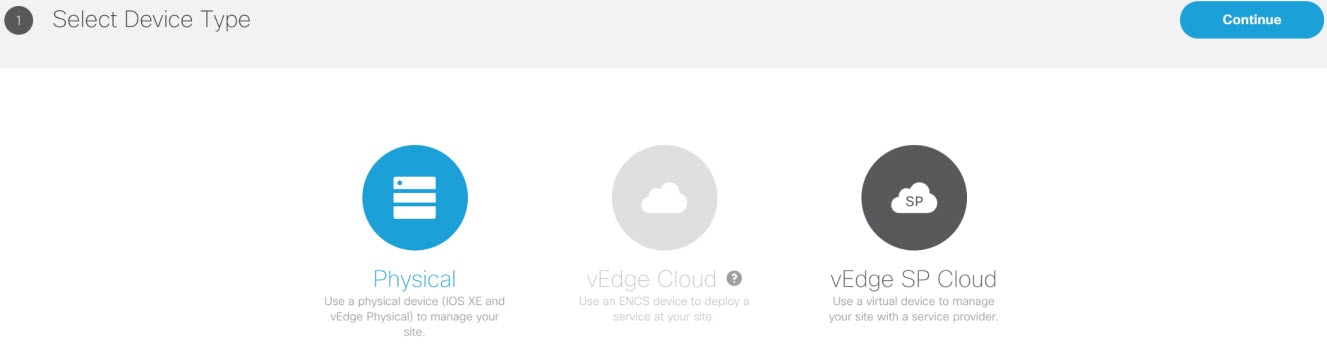
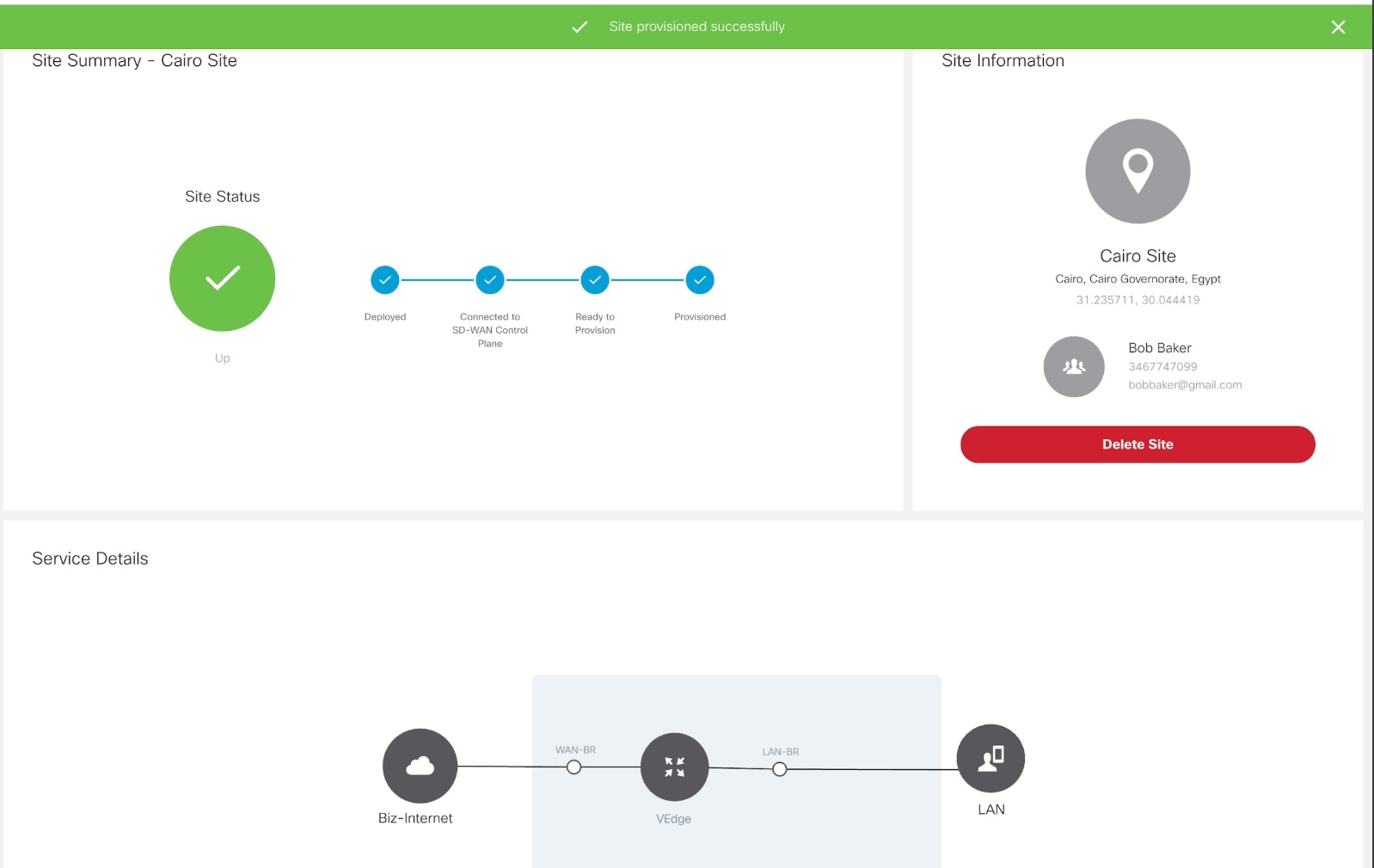
3. Add a vEdge Cloud or vEdge SP Cloud or a Physical Site/Device. |
|
|
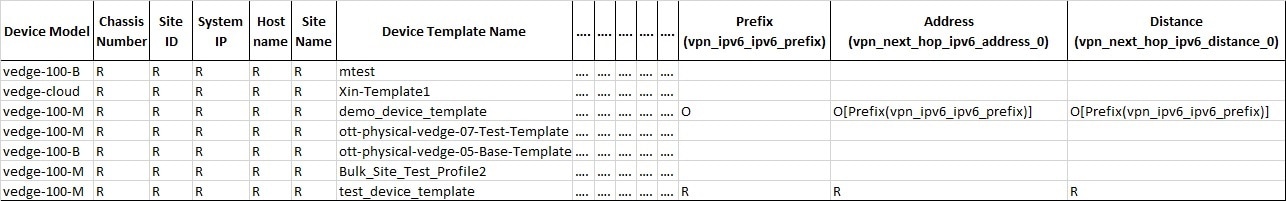
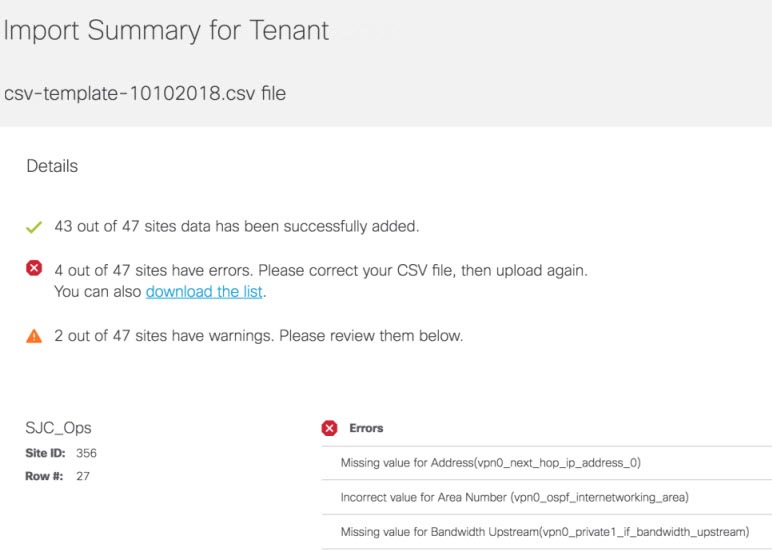
4. (Optional) If you have details of multiple sites available, you can import these details into MSX. |
|
|
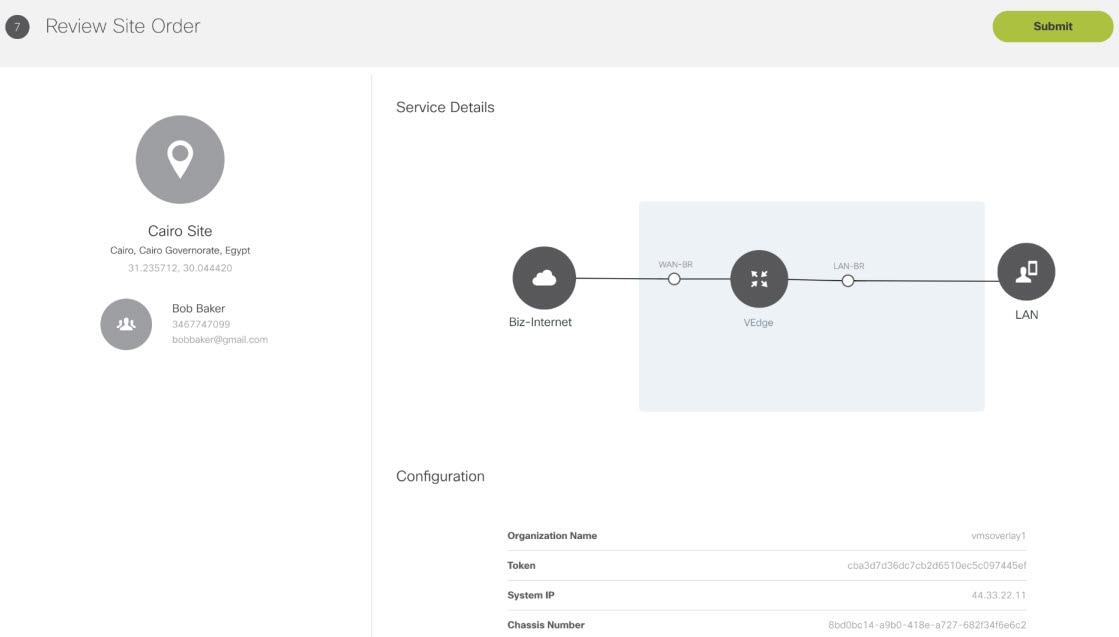
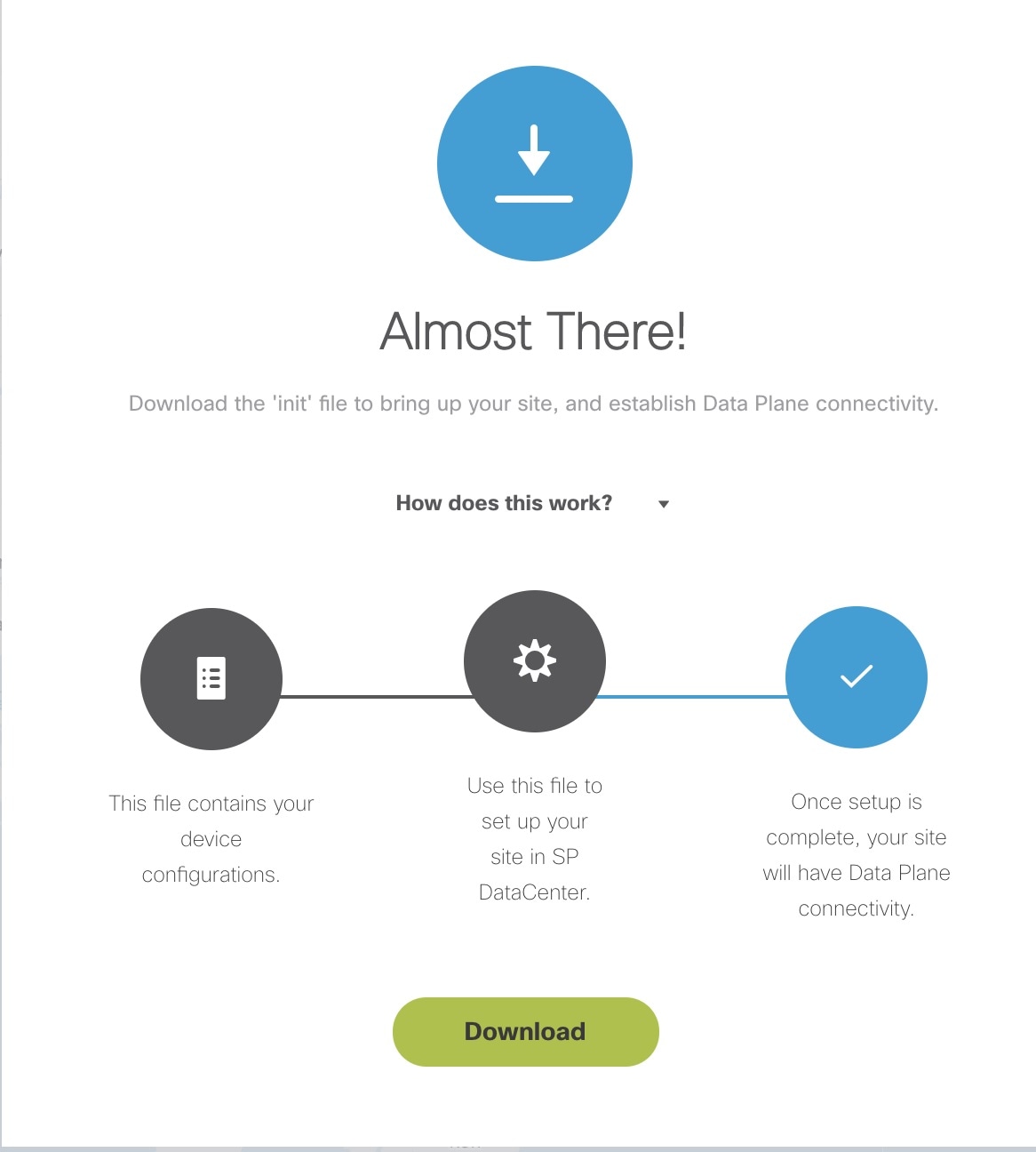
5. Push the site details to the Control Plane such that the device is set up for day one configurations. |
|
|
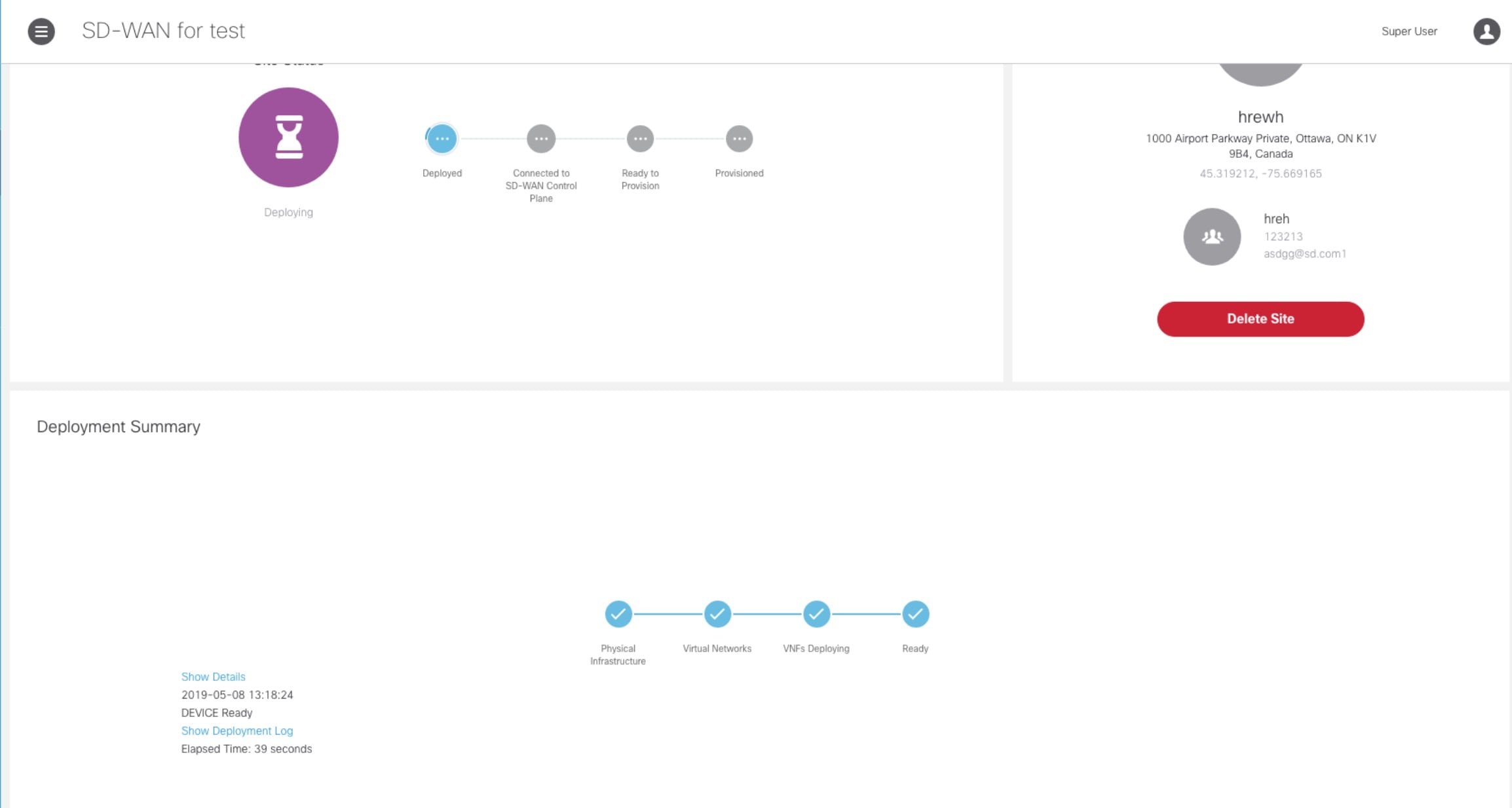
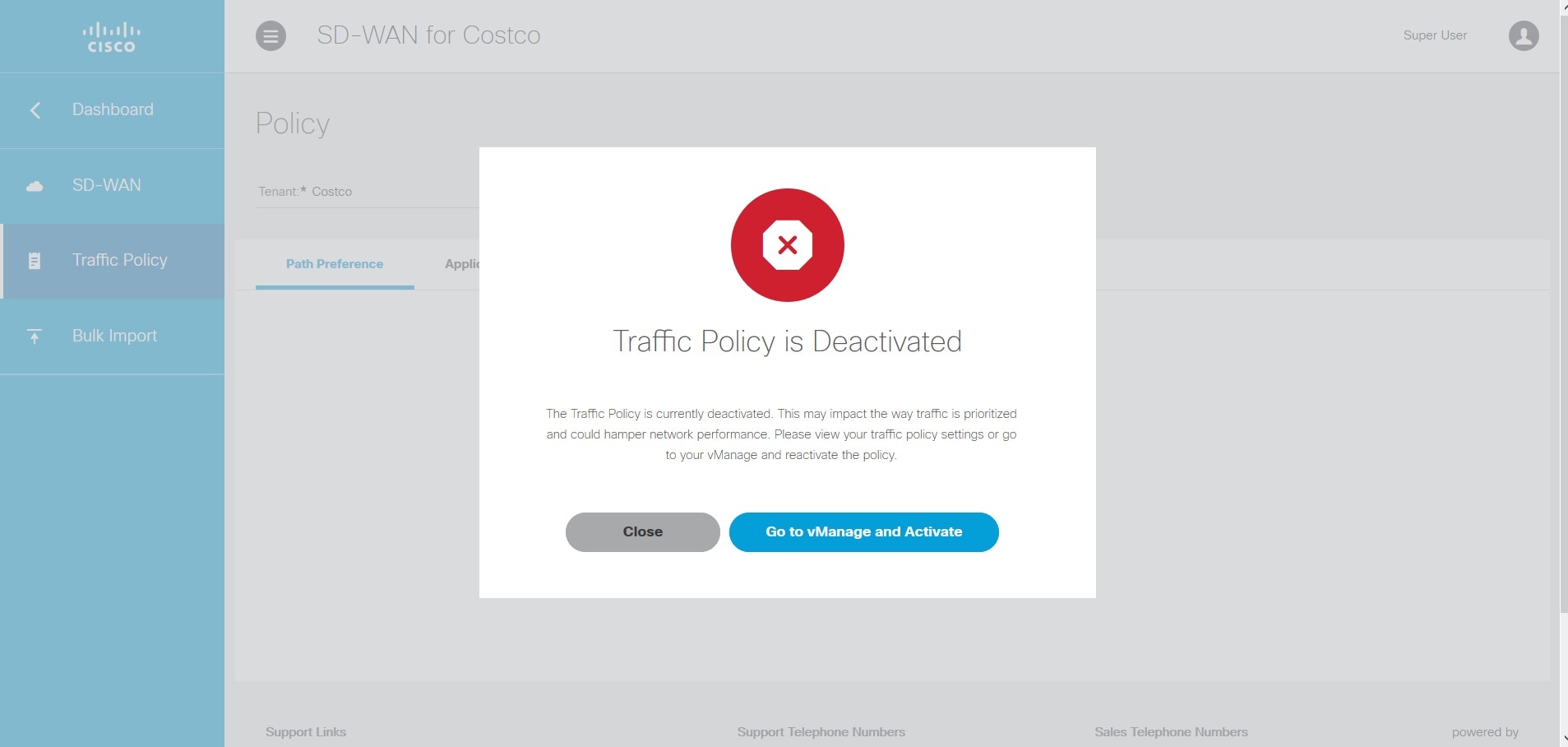
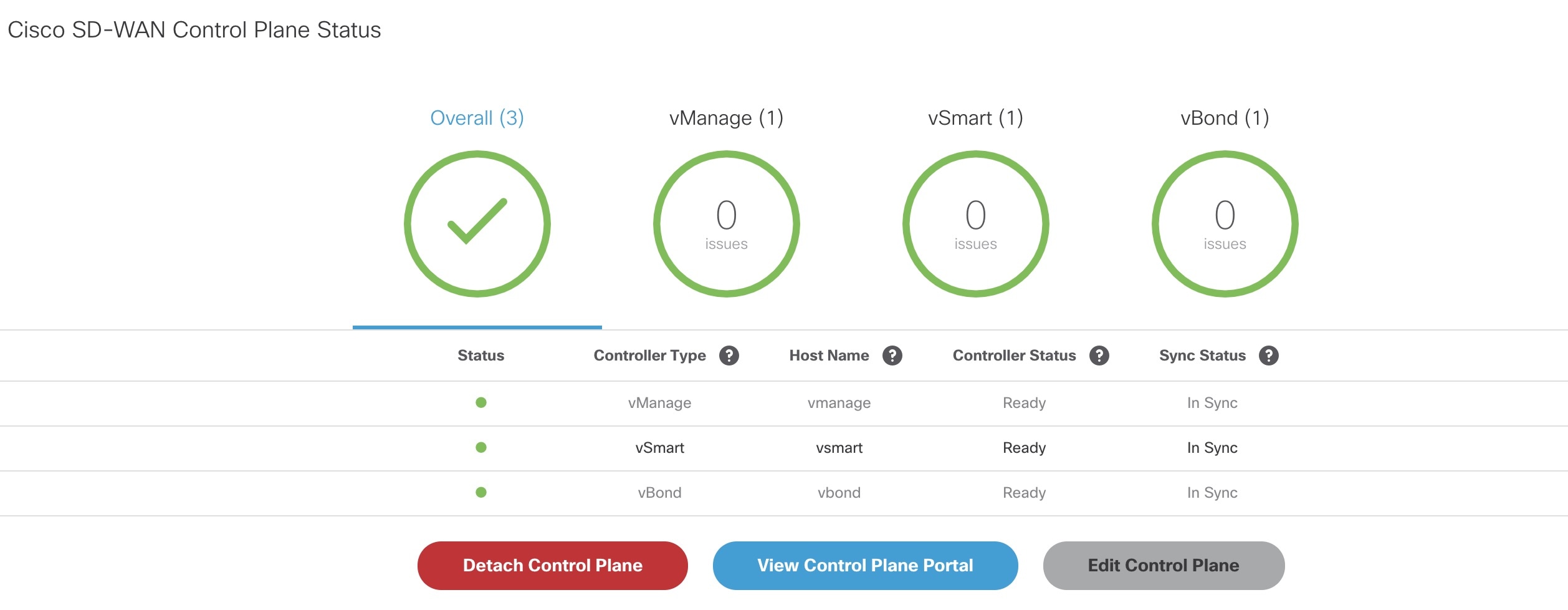
6. Verify all the components of SD-WAN service are deployed. |
|
|
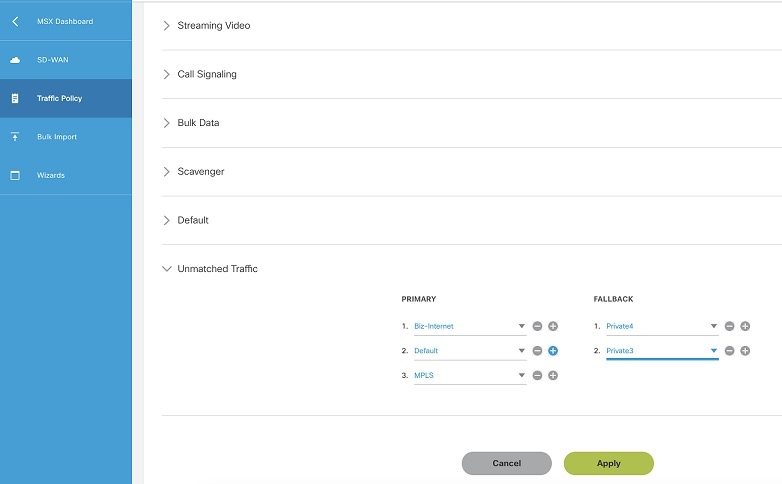
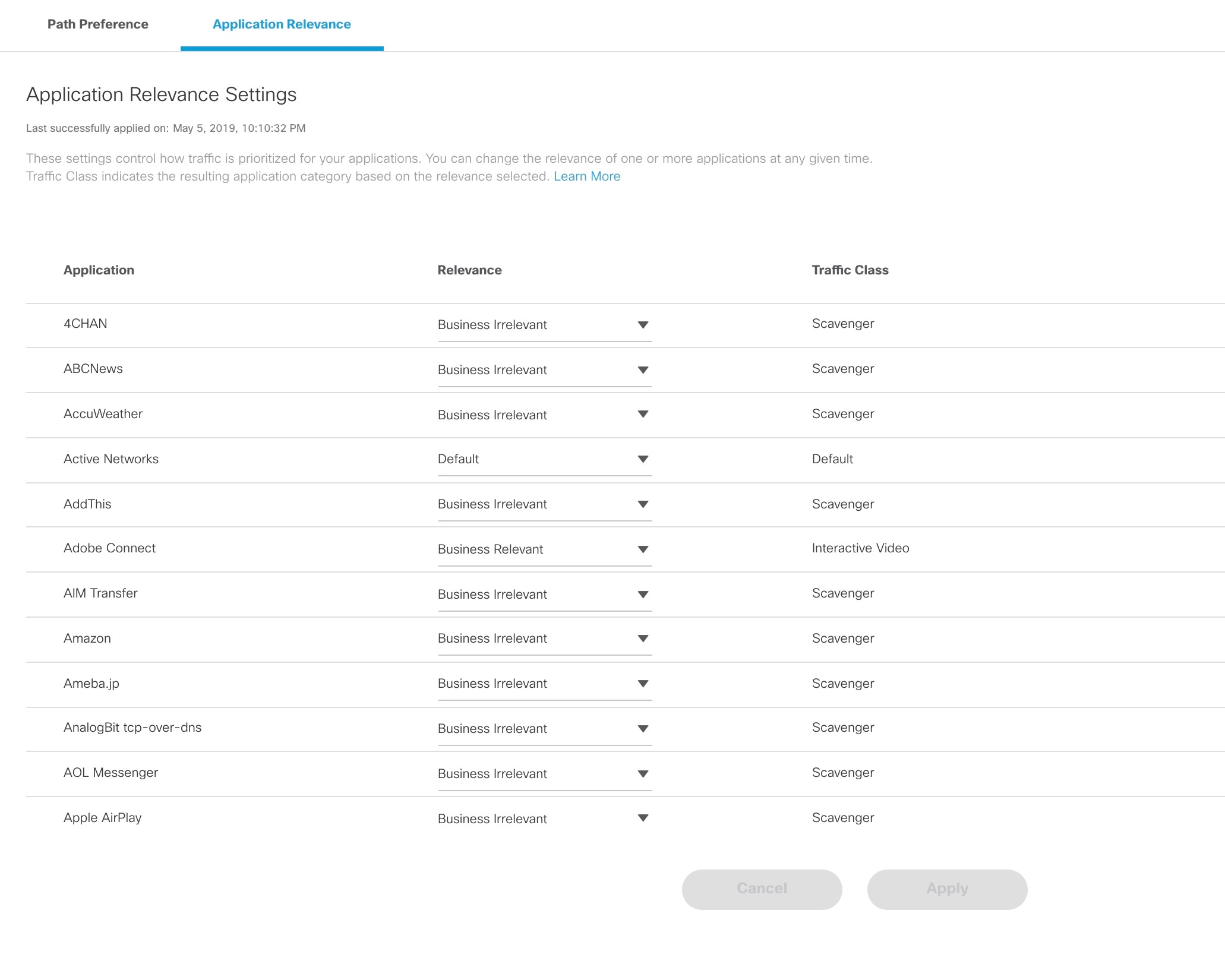
7. Configure Traffic Policies |
Configuring SD-WAN Traffic Policies |


 icon
icon

 Feedback
Feedback