- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges
- Information About IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges
IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges
First Published: April 19, 2010
Last Updated: May 26, 2011
Service provider bridges (also called provider bridges) allow devices in a service provider network to transparently carry the Layer 2 control frames of a customer. Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) bridge protocol data units (BPDUs) or Cisco Discovery Protocol frames are carried separately from the service provider traffic and from other customer traffic in the network of a service provider.
User network interface (UNI) ports of a provider bridge interface with customer devices have a specific set of requirements defined by the IEEE 802.1ad standard. These requirements enable provider bridges to have the same functionality as Layer 2 protocol tunneling and Q-in-Q (QnQ) bridges.
This document describes the IEEE 802.1ad implementation on Cisco devices using Layer 2 switch ports.
- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges
- Information About IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges
- How to Configure IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges
- Configuration Examples for IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges
- Additional References for IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges
- Feature Information for IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges
- Glossary
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Restrictions for IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges
Information About IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges
- Service Provider Bridges
- MAC Addresses for Layer 2 Protocols
- Overview of IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges
Service Provider Bridges
Provider bridges pass the network traffic of multiple customers. The traffic flow of each customer must be isolated from one another. For Layer 2 protocols within customer domains to function properly, geographically separated customer sites must appear to be connected via a LAN and the provider network must be transparent.
The IEEE has reserved 33 Layer 2 MAC addresses for customer devices that operate Layer 2 protocols. If a provider bridge uses these standard MAC addresses for its Layer 2 protocols, the Layer 2 traffic of the customer devices and the service provider is mixed together. Provider bridges solve this traffic-mixing issue by providing Layer 2 protocol data unit (PDU) tunneling when a provider bridge (S-bridge) component and a provider edge bridge (C-bridge) component are used. The figure below shows the topology.
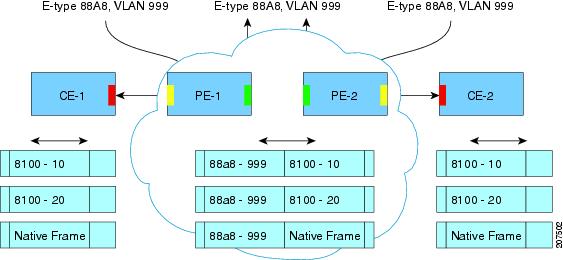
S-Bridge Component
The S-bridge component is capable of inserting or removing a service provider VLAN (S-VLAN) for all traffic on a particular port. IEEE 802.1ad adds a new tag called a Service tag (S-tag) to all ingress frames traveling from the customer to the service provider.
The VLAN in the S-tag is used for forwarding the traffic in the service provider network. Different customers use different S-VLANs, which results in isolation of traffic of each customer. In the S-tag, provider bridges do not understand the standard Ethertype. Hence, they use an Ethertype value that is different from the standard 802.1Q Ethertype value. This difference makes customer traffic that is tagged with the standard Ethertype appear as untagged in the provider network. The customer traffic is tunneled in the port VLAN of the provider port. 802.1ad service provider user network interfaces (S-UNIs) and network-network interfaces (NNIs) implement the S-bridge component.
For example, a VLAN tag has a VLAN ID of 1, the C-tag Ethertype has a value of 8100 0001, the S-tag Ethertype has a value of 88A8 0001, and the class of service (CoS) has a value of zero.
C-tag S-tag
------------------------------------------------------- --------------------------------------------------
0x8100 | Priority bits | CFI | C-VLAN-ID 0x88A8 | Priority bits | 0 | S-VLAN-ID
------------------------------------------------------- --------------------------------------------------
C-Bridge Component
All customer VLANs (C-VLANs) that enter a user network interface (UNI) port in an S-bridge component receive the same service (marked with the same S-VLAN). C-VLAN components are not supported, but a customer may want to tag a particular C-VLAN packet separately to differentiate between services. Provider bridges allow C-VLAN packet tagging with a provider edge bridge, called the C-bridge component of the provider bridge. C-bridge components are C-VLAN aware and can insert or remove a C-VLAN 802.1Q tag. The C-bridge UNI port is capable of identifying the customer 802.1Q tag and inserting or removing an S-tag on the packet on a per-service instance or C-VLAN basis. A C-VLAN tagged service instance allows service instance selection and identification by C-VLAN. The 801.1ad customer user network interfaces (C-UNIs) implement the C-component.
MAC Addresses for Layer 2 Protocols
Layer 2 protocol data units (PDUs) of customers that are received by a provider bridge are not forwarded. Hence, Layer 2 protocols running at customer sites do not know the complete network topology. By using different set of addresses for the Layer 2 protocols running on provider bridges, IEEE 802.1ad causes Layer 2 PDUs of the customers device that enter the provider bridge to appear as unknown multicast traffic and forwards it on customer ports (on the same service provider VLAN (S-VLAN)). Layer 2 protocols of customer device can then run transparently.
The table below shows Layer 2 MAC addresses that are reserved for the C-VLAN component.
|
Assignment |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Bridge Group Address |
01-80-C2-00-00-00 |
|
IEEE 802.3 Full Duplex PAUSE Operation |
01-80-C2-00-00-01 |
|
IEEE 802.3 Slow_Protocols_Multicast_Address |
01-80-C2-00-00-02 |
|
IEEE 802.1X PAE Address |
01-80-C2-00-00-03 |
|
Provider Bridge Group Address |
01-80-C2-00-00-08 |
|
Provider Bridge GVRP Address |
01-80-C2-00-00-0D |
|
IEEE 802.1AB Link Layer Discovery Protocol Multicast Address |
01-80-C2-00-00-0E |
|
Reserved for future standardization |
01-80-C2-00-00-04 01-80-C2-00-00-05 01-80-C2-00-00-06 01-80-C2-00-00-07 01-80-C2-00-00-09 01-80-C2-00-00-0A 01-80-C2-00-00-0B 01-80-C2-00-00-0C 01-80-C2-00-00-0F |
The table below shows Layer 2 MAC addresses that are reserved for the S-VLAN component. These addresses are a subset of the C-VLAN component addresses, and the C-bridge does not forward the bridge protocol data units (BPDUs) of a provider to a customer network.
|
Assignment |
Value |
|---|---|
|
IEEE 802.3 Full Duplex PAUSE Operation |
01-80-C2-00-00-01 |
|
IEEE 802.3 Slow_Protocols_Multicast_Address |
01-80-C2-00-00-02 |
|
IEEE 802.1X PAE Address |
01-80-C2-00-00-03 |
|
Provider Bridge Group Address |
01-80-C2-00-00-08 |
|
Reserved for future standardization |
01-80-C2-00-00-04 01-80-C2-00-00-05 01-80-C2-00-00-06 01-80-C2-00-00-07 01-80-C2-00-00-09 01-80-C2-00-00-0A |
Overview of IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges
The IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges feature is implemented on switch ports and supports the following IEEE 802.1ad specified functions:
- Layer 2 PDU Destination MAC Addresses for Customer-Facing C-Bridge UNI Ports
- Layer 2 PDU Destination MAC Addresses for Customer-Facing S-Bridge UNI Ports
Layer 2 PDU Destination MAC Addresses for Customer-Facing C-Bridge UNI Ports
The table below shows the Layer 2 protocol data unit (PDU) destination MAC addresses for customer-facing C-bridge user network interface (UNI) ports and how the frames are processed.
|
MAC Address |
Protocol |
Significance on the C-Bridge UNI Port |
Default Action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
01-80-C2-00-00-00 |
Bridge Group Address (end-to-end BPDUs) |
Data, BPDU (based on the CLI configuration of the l2protocol command) |
BPDU |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-01 |
802.3X Pause Protocol |
BPDU |
MAC address processes |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-02 |
Slow protocol address: 802.3ad LACP, 802.3ah OAM, Cisco Discovery Protocol, DTP, PagP, UDLD, VTP |
BPDU |
BPDU |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-03 |
802.1x |
BPDU |
BPDU |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-04 |
Reserved for future media access method |
Drop |
Drop |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-05 |
Reserved for future media access method |
Drop |
Drop |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-06 |
Reserved for future bridge use |
Drop |
Drop |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-07 |
Ethernet Local Management Interface |
BPDU |
BPDU |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-08 |
Provider STP (BPDU) |
Drop |
Drop |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-09 |
Reserved for future bridge use |
Drop |
Drop |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-0A |
Reserved for future bridge use |
Drop |
Drop |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-0B |
Reserved for future S-bridge purposes |
Drop |
Drop |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-0C |
Reserved for future S-bridge purposes |
Drop |
Drop |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-0D |
Provider bridge GVRP address |
Drop |
Drop |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-0E |
802.1ab LLDP |
Data, BPDU (based on the CLI configuration of the l2protocol command) |
BPDU |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-0F |
Reserved for future C- bridge or Q-bridge use |
Drop |
Drop |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-10 |
All bridges address |
BPDU |
Peer |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-20 |
GMRP |
Data |
Data |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-21 |
GVRP |
Data |
Data |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-22-2F |
Other GARP addresses |
Data |
Data |
|
01-00-0C-CC-CC-CC |
Cisco Discovery Protocol, DTP, PagP, UDLD, VTP (end-to-end) |
Data, BPDU (based on the CLI configuration of the l2protocol command) |
BPDU |
|
01-00-0C-CC-CC-CD |
PVST (end-to-end) |
Data, BPDU (based on the CLI configuration of the l2protocol command) |
BPDU |
Layer 2 PDU Destination MAC Addresses for Customer-Facing S-Bridge UNI Ports
If a port is operating as a customer-facing S-bridge user network interface (UNI), the destination MAC addresses shown in the below table are used for defining the Layer 2 protocol protocol data unit (PDU) processing at the S-bridge UNI.
|
MAC Address |
Protocol |
Significance on the S-Bridge UNI Port |
Default Action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
01-80-C2-00-00-00 |
Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) |
Data, BPDU (based on the CLI configuration of the l2protocol command) |
Data |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-01 |
802.3X Pause Protocol |
BPDU |
MAC address processes |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-02 |
Slow protocol address: 802.3ad LACP, 802.3ah OAM |
BPDU |
BPDU |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-03 |
802.1x |
BPDU |
BPDU |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-04 |
Reserved for future media access method |
Drop |
Drop |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-05 |
Reserved for future media access method |
Drop |
Drop |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-06 |
Reserved for future bridge use |
Drop |
Drop |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-07 |
Ethernet Local Management Interface |
BPDU |
BPDU (drop on NNI) |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-08 |
Provider STP (BPDU) |
BPDU |
BPDU |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-09 |
Reserved for future bridge use |
Drop |
Drop |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-0A |
Reserved for future bridge use |
Drop |
Drop |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-0B |
Reserved for future S-bridge use |
Data |
Data |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-0C |
Reserved for future S-bridge use |
Data |
Data |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-0D |
Provider bridge Generic VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) address |
Data |
Data |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-0E |
802.1ab Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) |
Data, BPDU (based on the CLI configuration of the l2protocol command) |
Data |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-0F |
Reserved for future C- bridge or Q-bridge use |
Data |
Data |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-10 |
All bridges address |
Data |
Data |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-20 |
GARP Multicast Registration Protocol (GMRP) |
Data |
Data |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-21 |
Generic VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) |
Data |
Data |
|
01-80-C2-00-00-22-2F |
Other Generic Attribute Registration Protocol (GARP) addresses |
Data |
Data |
|
01-00-0C-CC-CC-CC |
Cisco Discovery Protocol, Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP), Port Aggregation Protocol (PagP), UniDirectional Link Detection (UDLD), and VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) |
Data, BPDU (based on the CLI configuration of the l2protocol command) |
Data |
|
01-00-0C-CC-CC-CD |
Per-VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST) |
Data, BPDU (based on the CLI configuration of the l2protocol command) |
Data |
How to Configure IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges
Configuring a Switch Port to Process 802.1ad BPDUs
In an 802.1ad network, the default behavior for Layer 2 protocol data units (PDUs) on an interface depends on the 802.1ad interface type. If the interface type is an S-bridge user network interface (UNI), all Layer 2 PDUs are tunneled. If the interface type is a C-bridge UNI, all Layer 2 PDUs are processed (peered).
PDU processing on the S-bridge UNI is the same as on an 802.1ad network-network interface (NNI). Both types of interfaces have the same scope of MAC addresses. Perform the tasks in this section to configure switch port-to-peer (process) BPDUs:
Configuring a Switch Port to Process BPDUs
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
interface
type
number
4. switchport mode {access | trunk}
5. ethernet dot1ad {nni | uni {c-port | s-port}}
6. l2protocol peer [protocol]
7.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges
Example: Configuring an 802.1ad S-Bridge UNI
The following example shows how to configure GigabitEthernet interface 0/2 of a provider edge (PE) as an 802.1ad S-bridge user network interface (UNI). In this example, only Cisco Discovery Protocol protocol data units (PDUs) will be forwarded (tunneled). Cisco Discovery Protocol PDUs are forwarded between the PE and a customer device.
Device# configure terminal Device(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 0/2 Device(config-if)# switchport access vlan 500 Device(config-if)# ethernet dot1ad uni s-port Device(config-if)# l2protocol forward cdp Device(config-if)# end
Example: Configuring an 802.1ad C-Bridge UNI
The following example shows how to configure interface GigabitEthernet 0/3 of a PE as an 802.1ad C-bridge user network interface (UNI). In this example, only Cisco Discovery Protocol protocol data units (PDUs) are processed.
Device# configure terminal Device(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 0/3 Device(config-if)# switchport mode trunk Device(config-if)# ethernet dot1ad uni c-port Device(config-if)# l2protocol peer cdp Device(config-if)# end
Additional References for IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges
Related Documents
|
Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS commands |
|
|
Cisco IOS Carrier Ethernet commands |
Standards and RFCs
|
Standard |
Title |
|---|---|
|
IEEE 802.1ad |
Provider Bridges |
Technical Assistance
|
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to . An account on Cisco.com is not required.|
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges |
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6E |
The IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges feature is the IEEE 802.1ad implementation on Cisco devices using Layer 2 switch ports. In Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6E, this feature is supported on Cisco Catalyst 3850 Series Switches. The following commands were introduced or modified: ethernet dot1ad, l2protocol, and show ethernet dot1ad. |
Glossary
DTP—Dynamic Trunking Protocol.
GARP—Generic Attribute Registration Protocol.
GMRP—GARP Multicast Registration Protocol.
GVRP—Generic VLAN Registration Protocol.
LLDP—Link Layer Discovery Protocol.
OAM—Operations, Administration, and Maintenance.
PagP—Port Aggregation Protocol.
PVST—Per-VLAN Spanning Tree.
UDLD—UniDirectional Link Detection.
VTP—VLAN Trunk Protocol.
 Feedback
Feedback