Logging into the System Administration Cockpit
Use the system administrator account to log into the System Administration Cockpit. While it is possible to view system settings in the System Administration Cockpit, making changes is considered a privileged task. To make system changes, be sure to login with elevated write access permissions.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Open a web browser, and visit the System Administration Cockpit page for the system. By default, the System Administration Cockpit page is at port
|
| Step 2 |
Before you log into the System Administration Cockpit, make sure to check the Reuse my password for privileged tasks check box, as shown in this screenshot. Example: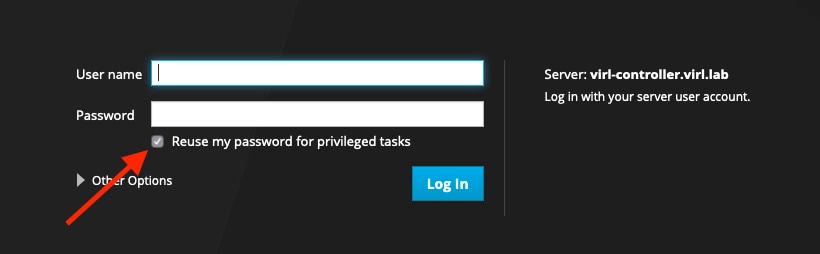 |
| Step 3 |
After you log into the System Administration Cockpit, you can verify that your current session has elevated privileges by looking for the Privileged indicator at the top of the page. Example: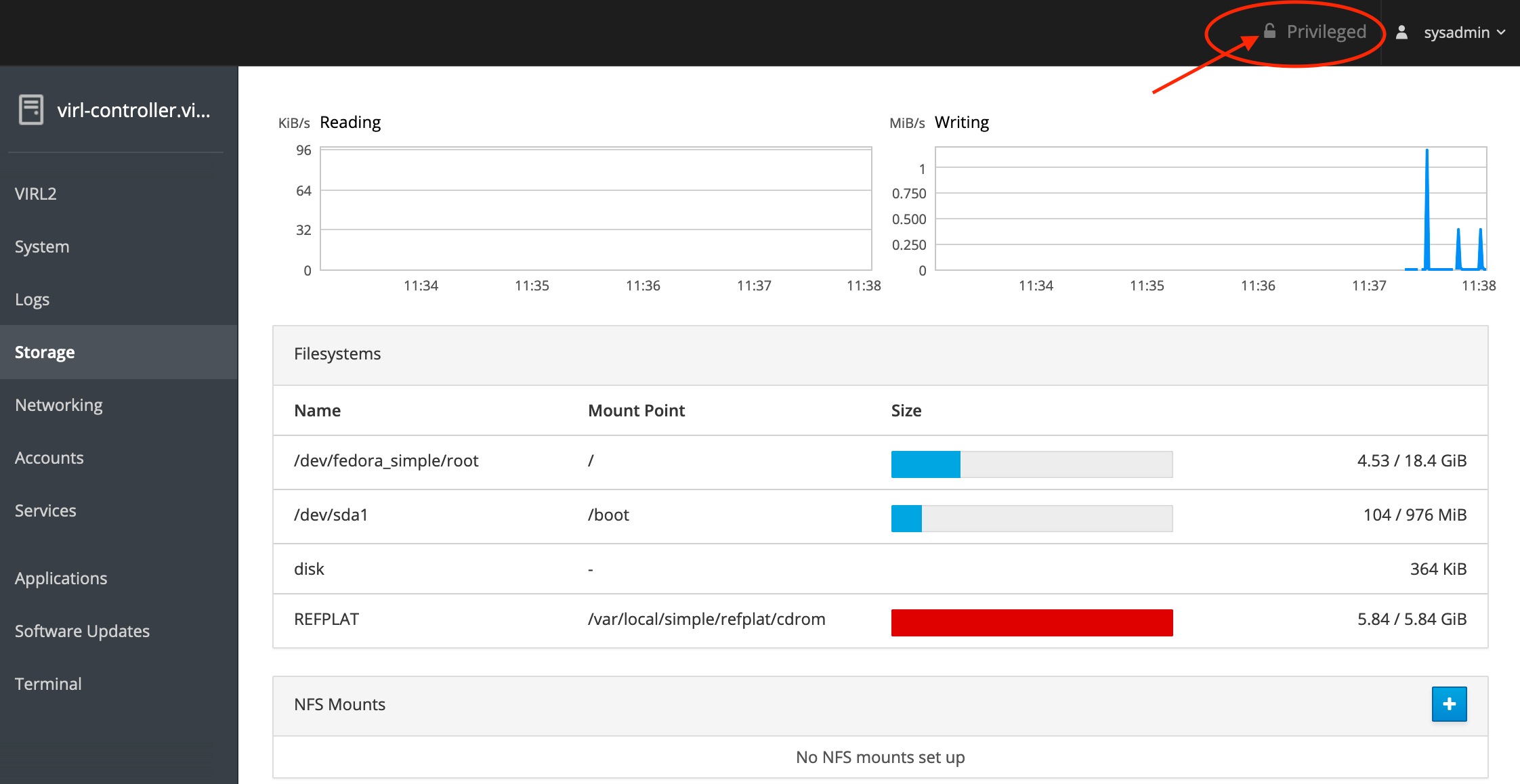 |

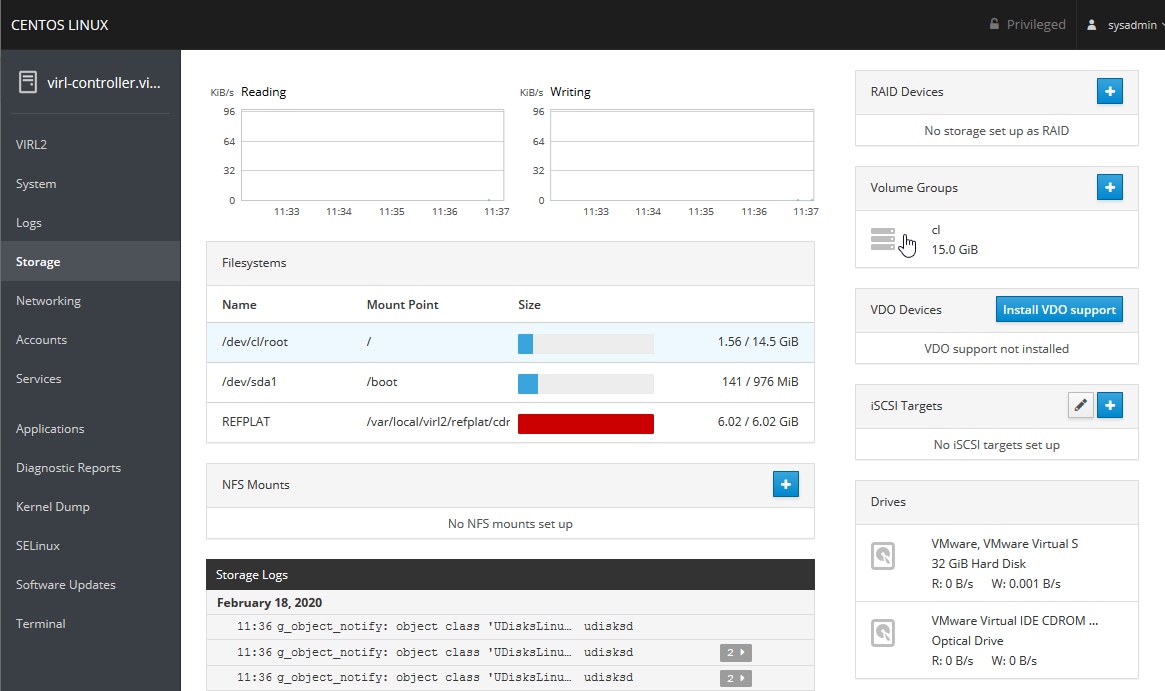
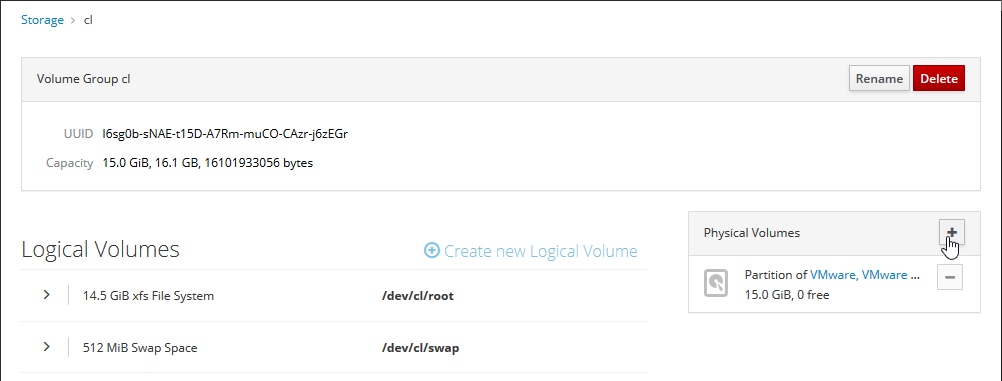

 Feedback
Feedback