Architecture overview
Cisco Crosswork Workflow Manager 2.0 architecture is a microservice-based solution that operates on top of the Crosswork Infrastructure. This section shows a diagram presenting its core architectural components along with short descriptions of each.
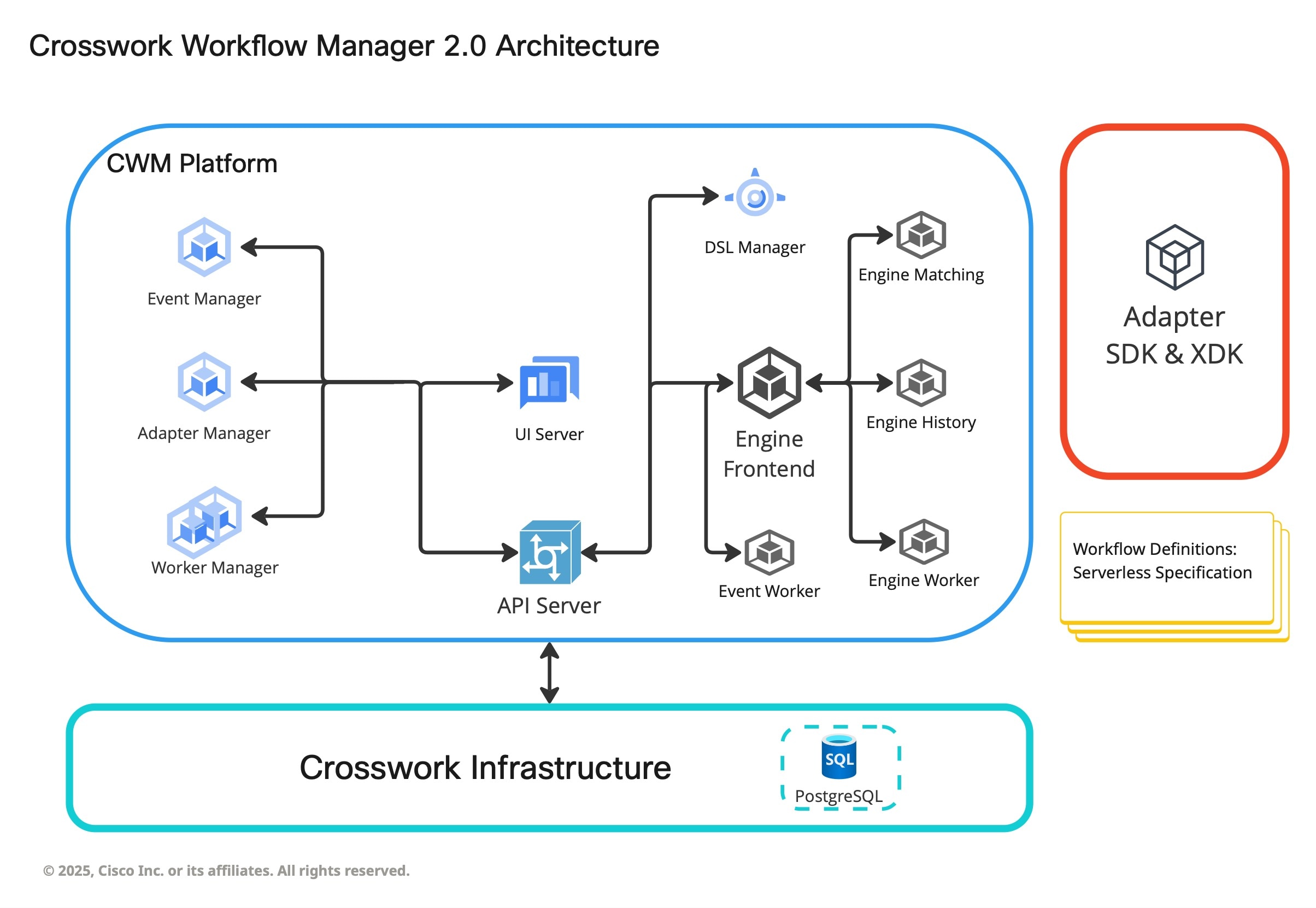
-
UI Server: Allows operators to add and instantiate workflows, enter workflow data, list running workflows, monitor job progress. The Administration section of the CNC UI enables users to add workers, manage worker processes and assign activities from adapters to workers.
-
REST API: Includes all interaction with the CWM application: deploying adapters, publishing and instantiating workflows, managing workers, resources and secrets.
-
API Server: Dispatches API requests to relevant microservices.
-
Engine: The core component that conducts how workflows are handled. It interprets and manages the execution of workflow definitions.
-
Engine Worker (Workflow Worker): Executes the workflow tasks. It receives the workflow tasks from the Engine, executes them in the correct order, and sends the results back to the Engine.
-
Worker Manager: Manages the Workflow Workers. It ensures that the correct number of workers are running and that they are properly configured.
-
Adapter Manager: Manages the adapters used by the system. It installs, configures, and updates adapters ("plugins") and ensures that they are compatible with the system.
-
Event Manager: Manages incoming and outgoing events, dispatching them to correct event queues. Events are signals coming from external sources with which the workflows can interact.
-
Adapter SDK & XDK: Helps developers create new adapters to integrate with external systems. The XDK application extends the capabilities of the Adapter SDK to enable developers to automatically build interfaces and message logic for custom adapters.
-
Workflow Definitions: Workflow code written in the JSON format based on the Serverless Workflow specification.
-
Crosswork Infrastructure: Runtime platform for the CWM application. It is a collection of services that provide the necessary infrastructure to support the deployment and management of the application within a Cluster deployment.
-
PostgreSQL: The database that the system uses to store and manage its data.
-
DSL Engine: Executes the Domain-Specific Language (DSL) used to define the workflows. It parses the DSL, generates the appropriate workflow code, and compiles it for execution.
-
Engine Matching: Matches incoming events with the appropriate workflow. It determines which workflow should execute based on the event data and the defined workflow constraints.
-
Engine History Tracks the history of executed workflows. It stores the metadata and execution details of all completed, running, and failed workflows.

 Feedback
Feedback