This document provides information about Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0.x, including product overview, solution components, new features and functionality, compatibility information, and known issues and limitations.
Overview
Cisco Crosswork Network Controller empowers customers to simplify and automate intent-based network service provisioning, monitoring and optimization in a multi-vendor network environment with a common GUI and API.
The solution combines intent-based network automation to deliver critical capabilities for service orchestration and fulfillment, network optimization, service path computation, device deployment and management, and anomaly detection. Using telemetry gathering and automated responses, Cisco Crosswork Network Controller delivers network optimization capabilities that would be nearly impossible to replicate even with a highly skilled and dedicated staff operating the network.
The fully integrated solution combines core capabilities from multiple innovative, industry-leading products including Cisco Network Services Orchestrator (NSO), Cisco Segment Routing Path Computation Element (SR-PCE), Cisco WAN Automation Engine (WAE), Cisco Crosswork Data Gateway, and an evolving suite of applications operating on the Cisco Crosswork Infrastructure. Its unified user interface allows real-time visualization of the network topology and services, as well as service and transport provisioning, via a single pane of glass. While its feature-rich API allows operators to seamlessly integrate the solution with other applications they use to operate, monitor, and provision services on the network.
Primary Use Cases:
-
Orchestrated service provisioning: Provisioning of layer 2 VPN (L2VPN) and layer 3 VPN (L3VPN) services with underlay transport policies to define, meet, and maintain service-level agreements (SLA), using the UI or APIs. Using Segment Routing Flexible Algorithm (Flex-Algo) provisioning to customize and compute IGP shortest paths over a network according to specified constraints and visualizing the resulting path.
-
Real-time network and bandwidth optimization: Intent-based closed-loop optimization, congestion mitigation, and dynamic bandwidth management based on Segment Routing and RSVP-TE. Optimization of bandwidth resource utilization by setting utilization thresholds on links and calculating tactical alternate paths when thresholds are exceeded.
-
Circuit Style Segment Routing Traffic Engineering (CS SR-TE) policy provisioning with network topology visualization:
-
Straightforward verification of CS SR-TE policy configurations
-
Visualization of CS SR-TE details, bi-directional active and candidate paths
-
Operational status details
-
Failover behavior monitoring for individual CS SR-TE policies
-
A percentage of bandwidth reservation for each link in the network
-
Manually triggered recalculations of existing CS SR-TE policy paths that may no longer be optimized due to network topology changes
-
-
Local Congestion Management: Local Congestion Mitigation (LCM) provides localized mitigation recommendations within surrounding interfaces, with the use of standard protocols. Data is gathered in real-time and when congestion is detected, solutions are suggested. LCM has a “human-in-the-loop” aspect which ensures that the control of making changes in the network is in the hands of the operator. Likewise, LCM also offers operators the option to automate changes – allowing the system to implement changes to the network on its own.
-
Visualization of network and service topology and inventory: Visibility into device and service inventory and visualization of devices, links, and transport or VPN services and their health status on maps with logical or geographical contexts.
-
Performance-based closed-loop automation: Automated discovery and remediation of problems in the network by allowing Key Performance Indicator (KPI) customization and monitoring of pre-defined remediation tasks when a KPI threshold is breached. For this use case, Health Insights and Change Automation functions must be installed.
-
Planning, scheduling, and automating network maintenance tasks: Scheduling an appropriate maintenance window for a maintenance task after evaluating the potential impact of the task (using WAE Design). Automating the execution of maintenance tasks (such as throughput checks, software upgrades, SMU installs) using playbooks. For this use case, Health Insights and Change Automation functions must be installed.
-
Zero-touch provisioning (ZTP) and onboarding of devices: Onboarding new IOS-XR and IOS-XE devices and automatically provisioning Day0 configuration, resulting in faster deployment of new hardware at lower operating costs. For this use case, the Zero Touch Provisioning function must be installed.
-
Visualization of native Segment Routing (SR) paths: Visualizing the native path using the traceroute SR-MPLS multipath command to get the actual paths between the source and the destination can be achieved using Path Query. A traceroute command runs on the source device for the destination TE-Router ID and assists in retrieving the paths.
-
Provision, Visualize, and Analyze Tree Segment Identifier Policies in Multipath Networks: Creating and visualizing static Tree-SID policies using the UI. Static mVPN Tree-SID policies, associated with existing or newly created L3VPN service models (SR MPLS point-to-multi-point), can be visualized and analyzed to assist in efficient management and troubleshooting of your multicast network.
-
Transport Slice Provisioning: Cisco Crosswork Network Controller offers direct support for network slicing at the OSI transport layer. Using this solution, network engineering experts can design slices around customer intents and then add them to a catalog. Network line operators can then simply pick the slice that best meets the customer's needs, specify the slice endpoints, and (where needed) set any custom constraints or options built into the chosen slice. Once the slice is provisioned, the path chosen can be visualized. Customers wishing an even greater amount of insight can use Service Health to gather additional performance data about the service.
Solution Components
Cisco Crosswork Network Controller components hosted on the Crosswork cluster:
|
Component |
Version |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Crosswork Infrastructure |
6.0 |
A resilient and scalable platform on which all of the Cisco Crosswork applications can be deployed. The infrastructure is based on a cluster architecture for extensibility, scalability, and high availability. For installation, configuration and administration procedures, refer to the following documents: |
|
Optimization Engine |
6.0 |
Provides closed-loop tracking of the network state and real-time network optimization in response to changes in network state, allowing operators to effectively maximize network capacity utilization, as well as increase service velocity. Provides traffic engineering visualization of SR-MPLS, SRv6, and RSVP-TE policies. |
|
Active Topology |
6.0 |
Enables VPN (L2VPN, L3VPN) service provisioning, service oriented transport (SR-MPLS, SRv6, CS-SR, RSVP-TE) provisioning and topology visualization of the provisioned services with the ability to customize the service provisioning and visualization through service model extensibility. |
|
Service Health |
6.0 |
Overlays a service level view of the environment and allows operators to monitor the health of services (for example, L2/L3 VPN) based on rules established by the operator. |
|
Health Insights |
6.0 |
Performs real-time Key Performance Indicator (KPI) monitoring, alerting, and troubleshooting. It builds dynamic detection and analytics modules that allow operators to monitor and alert on network events based on user-defined logic. |
|
Change Automation |
6.0 |
Automates the process of deploying changes to the network. |
|
Crosswork Data Gateway |
6.0 |
A secure, common collection platform for gathering network data from multi-vendor devices that supports multiple data collection protocols including MDT, SNMP, CLI, standards-based gNMI (dial-in), and syslog. |
|
Zero Touch Provisioning |
6.0 |
Automatic onboarding of new IOS-XR and IOS-XE devices and provisioning of Day0 configuration, resulting in faster deployment of new hardware at a lower operating cost. |
|
Element Management Functions |
6.0 |
A library of functions that provides deep inventory collection, alarm management, and image management using Inventory, Fault, and Software Image Management (SWIM) functions. |
Some of Cisco Crosswork Network Controller's functionality is enabled by the following products:
|
Products |
Version |
Description |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Cisco Network Services Orchestrator |
6.1.4 |
An orchestration platform that makes use of pluggable function packs to translate network-wide service intent into device-specific configuration. Cisco NSO provides flexible service orchestration and lifecycle management across physical network elements and cloud-based virtual network functions (VNFs), fulfilling the role of the Network Orchestrator (NFVO) within the ETSI architecture. It provides complete support for physical and virtual network elements, with a consistent operational model across both. It can orchestrate across multi-vendor environments and support multiple technology stacks, enabling extension of end-to-end automation to virtually any use case or device.
|
||
|
Cisco Segment Routing Path Computation Element (SR-PCE) |
7.11.1 |
An IOS-XR multi-domain stateful PCE supporting both segment routing (SR) and Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP). Cisco SR-PCE builds on the native Path Computation Engine (PCE) abilities within IOS-XR devices, and provides the ability to collect topology and segment routing IDs through BGP-LS, calculate paths that adhere to service SLAs, and program them into the source router as an ordered list of segments. |
Cisco Crosswork Network Controller Packages
Cisco Crosswork Network Controller solution is distributed as two packages (Essentials and Advantage) with additional add-on services.
|
Package |
Contents |
Version |
|---|---|---|
|
Cisco Crosswork Network Controller Essentials |
|
6.0 |
|
Cisco Crosswork Network Controller Advantage |
|
6.0 |
| Contents |
Description |
Version |
|---|---|---|
|
Change Automation |
An application that automates the process of deploying changes to the network. Orchestration is defined via an embedded Ansible Playbook and then configuration changes are pushed to Cisco Network Services Orchestrator (NSO) to be deployed to the network. |
6.0 |
|
Health Insights |
An application that performs real-time Key Performance Indicator (KPI) monitoring, alerting, and troubleshooting. Cisco Crosswork Health Insights enables programmable monitoring and analytics, and builds dynamic detection and analytics modules that allow operators to monitor and alert on network events based on user-defined logic. |
6.0 |
|
Zero Touch Provisioning |
An application that streamlines on-boarding and provisioning of Day 0 configuration resulting in faster deployment IOS-XR and IOS-XE devices at a lower operating cost. |
6.0 |
What's New
The following tables list the primary new features and functionality introduced in Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0:
|
Feature |
What's New? |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Local Congestion Mitigation (LCM) feature pack |
|
||||
| SR Circuit Style Manager (CSM) feature pack |
|
||||
|
Bandwidth on Demand feature pack |
|
||||
|
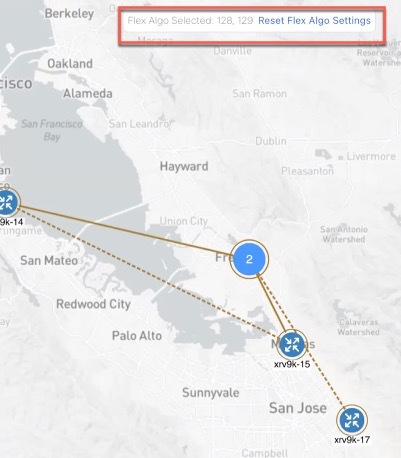
Flexible Algorithm |
|
||||
|
Tree-SID |
PCE warnings and path compute elements are displayed in Tree-SID policy details: 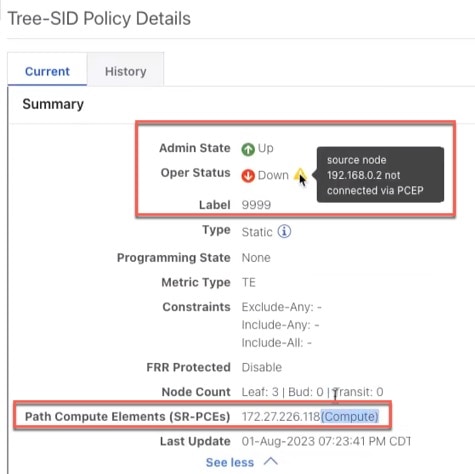 |
||||
|
Performance Metrics of TE policies |
When Service Health is installed and SR-PM collection is enabled, you can view KPI metrics (Delay, Jitter, and Liveness) from the Traffic Engineering table or from the TE tunnel details. To view the KPI metrics for the policy:
SR-MPLS policies KPI metrics contain Delay, Delay Variance (Jitter) or Liveness (Boolean value) along with traffic utilization. For example: 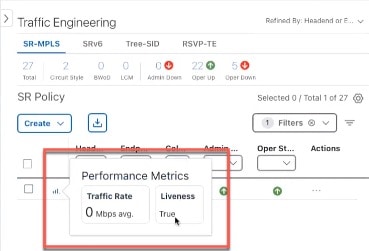 RSVP-TE Tunnel KPI metrics include Delay and Delay Variance (Jitter) along with Utilization. For example: 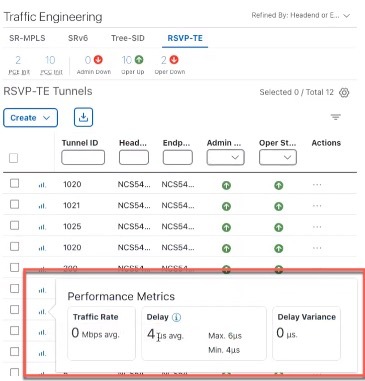 |
||||
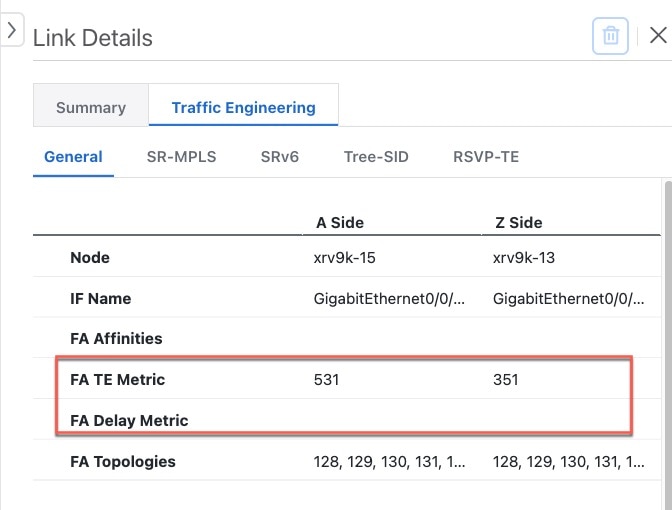
| Asymmetric delay for links |
In previous releases, only one side of the link delay value for an interface was considered during computation. When you configure delays on both remote and local nodes, the calculation of each delay on each interface is now taken into consideration when computing a path.
|
||||
| Unique TE tunnel and device detail URLs |
TE tunnel or device details are now assigned unique URLs that can be shared. The URL sends the user to the Policy or Device Details page after logging in.
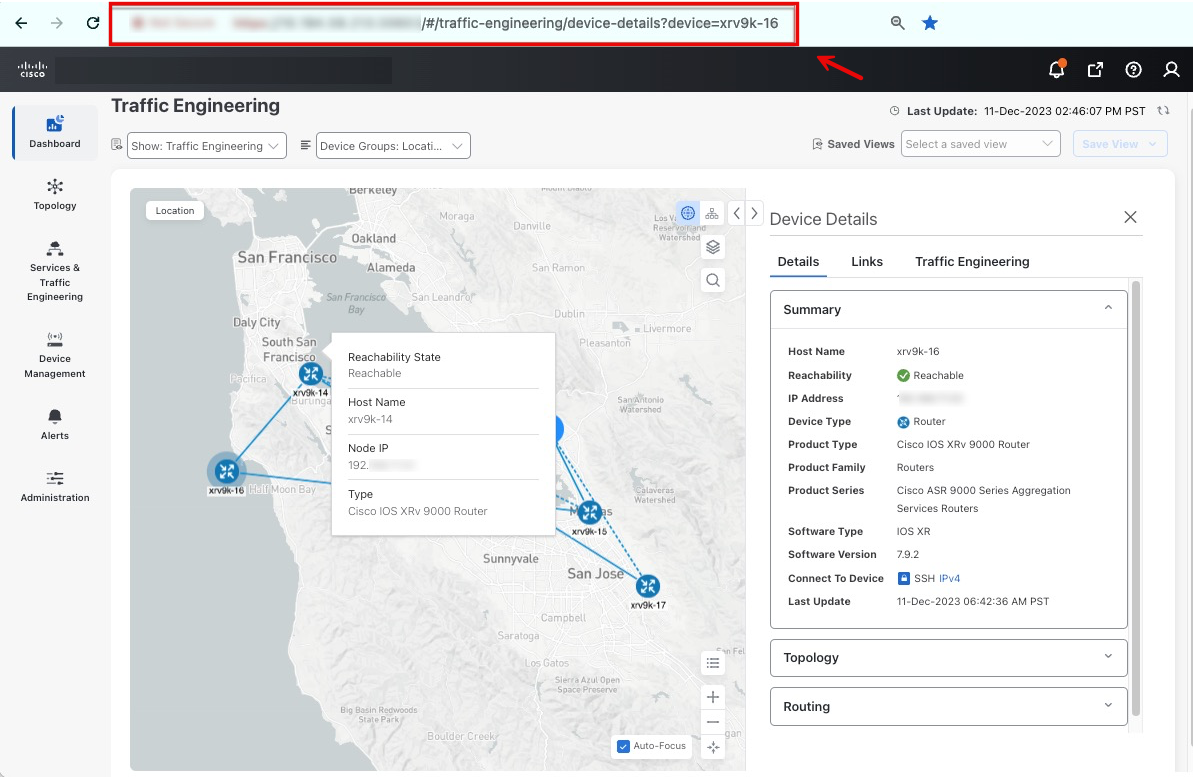 |
||||
| Increased performance and memory footprint |
Improvements made in topology discovery time, network model building, and processing cache, bandwidth, metric, and TE tunnel type information. |
||||
|
Transport Slicing |
Cisco Crosswork Network Controller offers direct support for network slicing at the transport level. This slice “instance” is a unique slice provisioned in the network but with a set of Service Level Requirements chosen from a set of pre-created Network Slice Templates (NST). The Slice Management Function (SMF) in turn communicates with each sub-domain controller, called a Network Slice Subnet Management Function (NSSMF) which in turn provisions the corresponding domain specific slice instance across its own sub-domain boundaries (called a Network Slice Subnet Instance (NSSI)) using a similar set of domain specific Network Slice Subnet Templates (NSST). Cisco Crosswork Network Controller also offers:
|
|
Feature |
What's New? |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Introduced a new monitoring status - Monitoring Error |
Errors due to a component failures, operational errors or device errors are now displayed as Monitoring Errors on the UI. You can filter these errors using the mini-dashboard or the filters. |
||
|
Ability to rate-limit monitoring requests |
To efficiently manage service monitoring requests, Service Health has implemented a rate-limiting process. This means that there may be a delay in publishing service monitoring requests if the number of requests raised per minute exceeds a specific threshold. The thresholds are defined as follows:
The rate-limiting process also extends to the monitoring data, that is metrics and Events of Significance (EOS), sent by Crosswork Data Gateways to the Crosswork Tracker component. For example, during a restore process, when all Crosswork Data Gateways send metrics again to the Crosswork Tracker component, the rate at which the Crosswork Tracker processes this data and forwards it to Assurance Graph Manager is regulated. This may lead to a delayed reporting of Events of Significance (EOS) following the restore. In the event of delays, an event is triggered with a severity level of 'Warning' and a corresponding description to notify you of the delay. The event is cleared once Service Health resumes normal publishing of monitoring requests. |
||
|
Ability to monitor performance metrics of TE policies using SR-PM |
To measure the performance metrics of VPN services using the SR-MPLS or RSVP-TE Traffic Engineering policies, Service Health leverages Segment Routing Performance Measurement (SR-PM). This feature enables measuring metrics on the underlay SR-TE policy to enforce Service Level Agreements in VPN services. |
||
| Monitor service health with external probes from Accedian Skylight |
Crosswork Network Controller can leverage external probing, provided by Accedian Skylight, to measure metrics of the network services. The metrics are compared with the contracted SLA (defined in the Heuristic package), and the results are made available on the Crosswork Network Controller UI. After an L3VPN service is provisioned and service monitoring is enabled, the probe intent and probe topology are learned (from provisioned service) and a probe session to monitor the service starts automatically by invoking relevant RESTConf APIs. Service Health processes the metrics and raises symptoms as needed to be displayed on the UI. You can view historical data for upto 24 hours from the Probe Sessions. The maximum number of probe sessions per service are capped at 200 (for all connection types).
|
|
Feature |
What's New? |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Simplified Topology Rebuild Tool |
If the topology is not displaying status as expected, you can now place the system into maintenance mode and then choose to rebuild the topology. This will force the system to create a new topology model and avoid the complicated steps from previous versions.
|
|
Feature |
What's New? |
|---|---|
|
Ability to reattempt the import of Controller Certificate file |
When Crosswork Infrastructure and Crosswork Data Gateway are deployed simultaneously, on the first reboot Data Gateway attempts to the download the Controller Certificate file from Crosswork Infrastructure. If the Infrastructure deployment is in-progress, Crosswork Data Gateway may not find the certificate. In the past, you had to wait for the Data Gateway VM to restart before downloading the certificate through the Interactive Console menu. With Crosswork Data Gateway's latest release, you can let Data Gateway retry the certificate download multiple times. If the file download fails, the Crosswork Data Gateway will now retry automatically. For information on importing the certificate, see the Import Controller Signing Certificate File section in Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0 Installation Guide. |
|
Parameter to configure the CLI session timeouts for devices |
The SSH Session Timeout parameter is implemented to indicate the duration of the CLI connection on a device. For information on how to configure the SSH Session Timeout parameter, see the Configure Crosswork Data Gateway Global Parameters section in Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0 Administration Guide. |
|
Changes to the Crosswork Data Gateway APIs |
The Crosswork Data Gateway APIs have been altered in the following ways:
For information on change logs, see Cisco Devnet. |
|
NETCONF Collector support is decommissioned |
The NETCONF collector enabled data collection over the NETCONF protocol. Support for the NETCONF collector has been discontinued in configurations, such as the base VM, application layer, Docker, and dg-manager. |
|
Feature |
What's New? |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Device Level RBAC |
This release introduces role-based access control (RBAC) at a device granularity for provisioning and device configuration workflows. Each user must be assigned a role that determines what functions they can access along with a Device Group that determines on which devices they can manage or deploy services. For more information, see the Manage Device Access Groups section in the Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0 Administration Guide. |
||
|
Geo Redundancy |
This release introduces the first phase of the geo redundancy solution for Crosswork Network Controller and its components in case of a region or data center failure. For more information, see the Enable Geo Redundancy section in the Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0 Installation Guide.
|
|
Feature |
What's New? |
|---|---|
|
Documentation |
|
Compatibility Information
The following tables list the hardware and software versions that have been tested and are known to be compatible with Cisco Crosswork.
Many features on Crosswork Network Controller depend on the underlying router XR/XE versions and the SR-PCE software. In the below tables, you can review those that are supported and working in combination with software versions on router platforms and SR-PCE.
Cisco Crosswork Infrastructure Support
| Software | Supported Version | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Cisco Operating System
|
|
||
|
Hypervisor and vCenter |
|
||
|
Browsers |
|
||
|
Crosswork Data Gateway |
|
||
|
Cisco Network Services Orchestrator (Cisco NSO) |
|
||
|
Cisco Network Element Driver (NED)
|
|||
|
Cisco Segment Routing Path Computation Element (SR-PCE) |
|
Cisco IOS Software Version Support
| Operating System | Version | PCE-Init | PCC-Init | NSO + CFP CLI | NSO + CFP NETCONF | Crosswork Infrastructure | Optimization Engine | ZTP (Secure)2 | Service Health |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
IOS-XR |
6.7.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.0.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.1.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.2.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.3.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.3.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.4.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.4.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.5.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.6.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.7.13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.8.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
7.8.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
7.9.16
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
7.9.28
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
7.10.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.11.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| IOS-XE |
17.6.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17.7.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17.8.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17.9.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17.12.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Only Secure ZTP config download is supported.
Only Secure ZTP config download is supported.
As SMUs become available, this document will be updated.
Only Secure ZTP config download is supported.
As SMUs become available, this document will be updated.
Only Secure ZTP config download is supported.
 Note |
Software Maintenance Updates (SMUs) are required for both PCC/Headend and SR-PCE versions indicated in the table. To download the Cisco IOS XR versions and updates, see the IOS XR Software Maintenance Updates (SMUs) document. |
Generic Device Support
Although not officially supported, Cisco Crosswork allows the management of generic Cisco and non-Cisco devices, with limited inventory and fault functions.
|
Generic Device Type |
Cisco and non-Cisco device |
|
Supported Features |
Device Details Module Details Interfaces |
|
Supported MIBs |
SNMPv2 ENTITY-MIB IF-MIB |
|
Supported APIs |
|
|
Supported Faults |
Linkup/ Linkdown (IF-MIB) Warm start (SNMPv2-MIB) Cold start (SNMPv2-MIB) Authentication Failure (SNMPv2-MIB) |
|
Supported Software Type |
Juniper - JUNOS Huawei - VRP Nokia - TIMOS |
Traffic Engineering Compatibility Information
The following table details Traffic Engineering and Network Bandwidth Management support for IOS Versions, SR-PCE, and Cisco devices.
Cisco IOS Support
We recommend that the SR-PCE version you use be equal to or higher than the PCC software version. PCC 7.11.1 is recommended and has been validated to work with Traffic Engineering 6.0 features. Other listed PCC versions are supported, but may not support all Traffic Engineering features because of PCC version limitations.
 Note |
Software Maintenance Updates (SMUs) are required for both PCC/Headend and SR-PCE versions indicated in the table. To download the Cisco IOS XR versions and updates, see the IOS XR Software Maintenance Updates (SMUs) document. The correct SMUs to download will have "Optima" or the bug ID appended to the filename. For example: asr9k-x64-7.3.2.Optima.tar or xrv9k-7.3.2.CSCvy63506.tar. |
|
Cisco IOS XR |
Cisco ASR 9901 (64-bit) |
Cisco XRv 900010 | Cisco 8000 series | Cisco NCS 5500 series |
Cisco NCS 540 series11 |
Cisco NCS 560 series |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
7.3.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.3.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.4.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.4.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.5.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.6.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.7.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.7.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.8.1 + SMU (CSCwc93705) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.8.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.9.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.9.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.10.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.11.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS XE Version |
Cisco ASR 920 |
Cisco ASR 903 RSP 3 |
|---|---|---|
|
17.4.112 |
|
|
|
17.5.1 |
|
|
|
17.6.3 |
|
|
|
17.7.1 |
|
|
|
17.8.1 |
|
|
|
17.9.1 |
|
|
|
17.12.1 |
|
|
 Note |
|
Scale Support
To support large scale deployment, the applications that make up Cisco Crosswork Network Controller (Optimization Engine, Active Topology, and other applications) are built with workload and endpoint load balancing using the Crosswork infrastructure's cluster architecture.
|
Feature |
Scale Support |
|---|---|
|
Devices |
15,000 |
|
Total Interfaces13 |
500,00014 |
|
Provision of SR-TE policies and RSVP-TE tunnel (PCE-initiated) |
75,000 |
|
IGP links |
200,000 |
|
VPN Services (L2VPN, L3VPN) |
150,000 |
 Note |
Scale numbers will reduce if Layer 2 collection is enabled (for example, when LLDP, CDP, or LAG collection is enabled). |
 Note |
The Crosswork Network Controller Essentials package requires a minimum of 3 Virtual Machines (VMs) and the Crosswork Network Controller Advantage package requires a minimum of 5 VMs. For more information, see the Crosswork Network Controller Installation Guide. |
Networking Technology Support for Traffic Engineering
The following is the networking support information for SR-PCE 7.11.1.
| Category |
Description |
Notes / Details |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR |
SR-MPLS PCE initiated policies |
Policies that are provisioned or discovered by Crosswork Network Controller. |
||
|
SR |
PCC initiated policies and ODN policies |
Policies that are discovered by Crosswork Network Controller. |
||
|
SR |
Explicit path SR-TE policies |
Policies that are PCC initiated (SID list with labeled SID list with addresses), PCE reported, PCE initiated. Includes SRv6 TE discovery of PCC initiated policies. |
||
|
SR |
Dynamic path SR-TE policies |
PCC computed, PCE reported, PCE delegated |
||
|
SR |
Single consistent Segment Routing Global Block (SRGB) configured on routers throughout domain covered by Crosswork Network Controller |
— |
||
|
SR |
Egress Peer Engineering (EPE) PeerAdjacency SIDs, PeerNode SIDs |
|
||
|
SR |
Prefix SID |
Regular/Strict Node SIDs + FA. Includes SRv6 Locators. |
||
|
SR |
Adjacency SID |
B-flag (protected/unprotected), P-flag (Persistent). Includes SRv6 Locators. |
||
|
SR |
SR policy optimization objective min-metric (IGP, TE, and Latency) |
PCE initiated provisioning and PCC initiated discovery |
||
|
SR |
SR policy path constraints (affinity and disjointness, protected segments) |
|
||
|
SR |
Binding SID for explicit or dynamic policies |
Discovered for PCC initiated and PCE initiated policies. It is configurable for PCE initiated policies. |
||
|
SR |
Profile ID (Discovered and configurable for PCE-init) |
Parameter used for applying features on PCC to PCE initiated policies. |
||
|
SR |
Flexible Algorithm (Flex Algo) for SR-MPLS and SRv6 policies |
|
||
|
SR |
Discovery and visualization of multiple candidate paths |
— |
||
|
SR |
Binding SIDs as Segment List Hops for SR policies |
Discovery and visualization of PCC initiated policies. |
||
|
SR |
Tree-SID |
Visualization and provisioning of PCE initiated policies. |
||
|
SR |
SR policies with Loopback IPs (Prefixes) other than TE router ID for headend/endpoint and prefix SIDs in segment list |
Prefix (node) SIDs associated with specific IGP domain / area. |
||
|
SR |
Maximum SID Depth (MSD) |
|
||
|
SR |
Global Max Latency |
Configured on PCE and applied to all PCE delegated SRTE policies with a latency metric. |
||
|
SR |
Inter-domain SRTE policies (inter-IGP domain, inter-AS) |
PCE delegated and Bandwidth on Demand policies. |
||
|
SR |
Node SID reuse across different IGP domains |
Recommended to not reuse node SIDs in adjacent IP domains. Inter domain explicit path policies with a label-only hop that is a node SID used in adjacent domains may be unresolvable if hop after ABR hop. |
||
|
SR-IGP |
Application-Specific Link Attribute (ASLA) Delay / TE metric |
Crosswork collects and uses ASLA delay and TE metric in Flex Algo topology computations and SRTE policy IGP paths. |
||
|
SR-IGP |
Visualizing native SR-IGP path |
Path Query OAM feature to use traceroute on device to report actual SR-IGP multi-paths to destination node (SR-MPLS only) |
||
|
SR |
Dynamic Circuit Style |
Path computation and bandwidth reservation through the Circuit Style feature pack. |
||
|
RSVP |
PCE initiated tunnels (provisioned by or discovered by Crosswork Network Controller), PCC initiated tunnels discovered by Crosswork Network Controller |
— |
||
|
RSVP |
ERO strict hops, ERO loose hops (PCC initiated only) |
— |
||
|
RSVP |
FRR protection on Crosswork Network Controller provisioned tunnels |
— |
||
|
RSVP |
Path optimization objective min-metric (IGP|TE|Latency) |
— |
||
|
RSVP |
Path constraints (affinity, disjointness) |
Only 2 RSVP tunnels per disjoint group or sub-id | ||
|
RSVP |
Binding Label (explicit | dynamic) |
— |
||
|
RSVP |
Signaled Bandwidth |
— |
||
|
RSVP |
Setup and Hold Priority |
— |
||
|
RSVP |
Path Protection (partial support) |
Paths discovered as independent tunnels if multiple paths are up. Cisco XR only reports active path. Other vendors may report all active paths. |
||
|
PCEP |
PCEP Session discovery |
Each PCEP session a PCC has with a PCE along with its details is displayed as part of node details |
||
|
IPv4/IPv6 |
Dual Stack IPv4 or IPv6 |
Nodes can be IPv4, IPv6 or IPv4/IPv6 capable |
||
|
IPv4 |
Unnumbered Interfaces (partial) |
Topology discovery, SR policies with unnumbered IF hops discovery/provisioning, LCM policy support |
||
|
IPv6 |
IPv6 Link Local Interfaces |
Discovery of IPv6 link local interfaces as part of topology and as a hop in an SRv6 TE policy |
||
|
IPv6 |
IPv6 Router ID |
Nodes with IPv6 and IPv6 Router ID only with support for SRv6 only |
|
Category |
Description |
Notes / Details |
|---|---|---|
|
SR |
Provisioning multiple candidate paths via Crosswork Network Controller |
— |
|
SR |
Per-Flow Policies (PFP) |
PFP (ODN or manually configured) not supported in PCEP. This PFP is the mapping of forward class to PDP with matching color and EP. Underlying PDP is reported as normal. |
|
SR |
Multiple segment lists per candidate path |
This configuration is not supported in Crosswork. These segment lists will not be discovered if configured on a PCC. High level requirements:
|
|
SR |
Anycast SIDs |
— |
|
SR |
SR policy provisioned (SR-PCE initiated) with IPv6 endpoints or hops |
— |
|
SR |
SR-MPLS policy optimization objective min-metric with margin |
Not supported for policies provisioned by Crosswork Network Controller. Margin is not discovered for PCC initiated policies. |
|
SR |
SR-MPLS policy constraints (resource exclusion or metric bound) |
Not supported for policies provisioned by Crosswork Network Controller. Constraints are not discovered for PCC initiated policies. |
|
SR |
Heterogeneous SRGBs |
Different SRGBs configured on nodes are not supported. SRGB must be configured to ensure proper discovery and visualization of SR policy paths. |
|
SR |
Egress Peer Engineering (EPE) Peer Set SIDs |
No discovery |
|
SR |
Routers that are not SR-capable |
All nodes assumed SR capable when computing SR policy IGP paths. LCM and BWoD SR policy path computation will not exclude non-SR capable nodes in IGP path. |
|
SRv6 |
PCE initiated provisioning of SRv6 policies is not supported. |
— |
|
SRv6 |
Traffic collection on SRv6 policies is not currently supported. |
Requires telemetry (gNMI) for policy counters (no SNMP support) |
|
IGP |
ISIS Overload bit |
Affects IGP paths for all policies and PCE path computation (BWoD, LCM). PCE reports but does not process. |
|
IGP |
OSPF MADJ Interfaces |
No support for discovering OSPF Multi-area adjacencies |
|
IGP |
Multiple IGP instances on same interface |
Single interface that participates in multiple IGP instances are not supported. |
|
IGP |
Crosswork Network Controller supports L1 or L2 adjacencies on links but not both on the same link. |
— |
|
RSVP |
Configuring loose hop Explicit Route Object (ERO) in Crosswork |
Only strict hops can be configured. If strict hops are not configured for every hop along the path and those hops are not remote interface IPs or loopbacks, unexpected behavior may occur |
|
RSVP |
Named tunnels configured on PCCs |
Required for Juniper RSVP HEs |
|
RSVP |
Tunnels with Loopback IPs other than TE router ID for headend/endpoint and path hops |
— |
|
RSVP |
Display of active FRR protected path in UI |
Crosswork Network Controller will discover FRR tunnels which are displayed in UI but will not associate an actively protected tunnel with the FRR tunnel. Path in UI will not include FRR protected path when protection is active. |
|
RSVP |
P2MP tunnels |
— |
|
RSVP |
Path protected RSVP LSPs |
No association between paths discovered. |
|
LDP |
Local Congestion Mitigation (LCM) in Mixed SR/LDP networks |
LCM will not work in a mixed SR/LDP network with PEs that are LDP only. LDP traffic destined to the LDP-only egress PE attempted to be steered into Autoroute LCM tactical polices will be blackholed |
|
IPv4 |
IPv4 Unnumbered Interfaces |
BWoD, Circuit Style Support, and RSVP |
|
IPv4/IPv6 |
Secondary IP addresses for interfaces |
Not supported. Unpredictable behavior if discovered. |
|
IPv4/IPv6 |
Overlapping IP addresses in different IGP domains |
IP addresses for IGP interfaces and nodes (router-ids) are assumed to be unique across all domains |
|
IPv6 |
IPv6 Router ID |
SR and RSVP not supported (SRv6 only) |
Important Notes
Take into consideration the following important information before starting to use Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0.x:
-
Topology visualization:
-
Bandwidth utilization information is only available for physical interfaces and is not available for logical interfaces.
-
-
Crosswork Infrastructure:
-
It is recommended to deploy Crosswork on a highly available cluster with shared storage.
-
Managed devices, VM host, VMs, and all integrated components should use the same NTP source to avoid time synchronization issues.
-
Confirm that the DNS and NTP servers are properly configured and reachable on the network the Crosswork cluster will be using.
-
Cisco recommends using Terminal Access-Control System Plus (TACACS+), Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) or Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to track access and prevent unauthorized usage of Crosswork capabilities.
-
During configuration, note the Cisco Crosswork UI and CLI user names and passwords. Due to added security, the only way to recover the administrator password is to re-install the software.
-
In situations where it is expected to work with SR-PCE (for L3 topology discovery), we recommend the use of dual SR-PCEs in an HA configuration.
-
Use CSV files to quickly import and on-board device, credential, and provider information.
-
-
Obtaining Geomaps for topology map renditions:
Cisco Crosswork Network Controller allows users to obtain downloadable geographical maps (geomaps) based on their specific topology mapping needs. If your environment allows contact with the map provider website we specify in Crosswork, you do not need to download the map files. If your environment does not allow outside access, you will need to download the map files for the areas where your network requires coverage.
-
VPN Service Provisioning:
The Cisco NSO sample function packs are provided as a starting point for VPN service and RSVP-TE provisioning functionality in Cisco Crosswork Network Controller. While the samples can be used “as is” in some limited network configurations, they are intended to demonstrate the extensible design of Cisco Crosswork Network Controller. Answers to common questions can be found here and Cisco Customer Experience representatives can provide answers to general questions about the samples. Support for customization of the samples for your specific use cases can be arranged through your Cisco account team.
 Note |
For licensing and ordering information, work with your Cisco Partner or Cisco Sales representative to review the options described in the Cisco Crosswork Network Controller Ordering Guide. |
Known Issues and Limitations
The table below shows known issues and limitations that should be taken into account before starting to work with Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0.x.
|
Feature |
Limitation |
|---|---|
|
Fault and Alarm Synchronization |
While geo redundancy enables a switch-over to an active cluster, it's important to take into account the timing of backups. Given the interval between the last backup and the restoration process, there is a loss of some alarm data from the devices. This is due to the time lag since the last backup was completed and restored. |
|
Geo redundancy (with astack functionality) |
If switchover is performed on Crosswork cluster containing Service Health, the EOS data may contain partial metrics data (with intermittent gaps in the data metric sequence) for up to 24 hours. |
|
Feature |
Limitation |
|---|---|
|
TE Dashboard |
Traffic Utilization is not supported on Tree-SID and SRv6 policies. |
|
You cannot view the IGP path on the historical data when an event is selected. |
|
|
The metric type for BWoD policies are not visible on the TE Dashboard. |
|
|
Hop count metric and BWoD type are not shown in the TE Dashboard under metric/policy type. |
|
|
State and Path change events are not visible in the Historic tab of a policy until you zoom in by 5 to 6 clicks. |
|
|
IPv4 Unnumbered Interfaces |
Bandwidth on Demand and SR Circuit-Style Manager feature packs will not factor in IPv4 unnumbered interfaces. |
|
Tree-SID policies are not supported. |
|
|
RSVP-TE PCE-initiated tunnels are not supported. |
|
|
Tree-SID |
Only static Tree-SID policies can be created via the UI. Also, you can only update and delete static Tree-SID policies that have been created via the UI. |
|
Tree-SID policies are only supported on devices running Cisco IOS XR software. |
|
|
PCE HA is not supported if the static Tree-SID policy was configured manually on the device (not via the UI). |
|
|
Tree-SID policies are not deleted from the UI when the SR-PCE in HA mode is down. |
|
|
IPv4 Unnumbered interfaces are not supported. |
|
|
Tree-SID policies are not supported in Label Switch Multicast (LSM) routing. In cases where LSM is enabled, IGP updates and traffic utilization data are not supported. |
|
|
LCM will not operate in portions of the network carrying Tree-SID LSPs. |
|
|
On Cisco 8000 Series Routers, only static Tree-SID policies with leaf role are supported. |
|
|
The RestConf API is not supported. |
|
|
Tree-SID policy details do not show IPv6 router ID or SRv6 core information. |
|
|
SR-MPLS |
In the SR-MPLS provisioning screen and while previewing an SR-MPLS policy with an IPv6 address, a parsing error is displayed instead of correct error message: "Request Failed. Endpoint address is IPv6, IPv6 provisioning is not supported yet." |
|
Updating the SID constraint on an existing policy is not allowed by the SR-PCE. The modification screen gives a successful update message, instead of a warning message that it is not allowed. |
|
|
APIs |
The Topology API cannot discover and report IPv6 Link-Local style links. |
|
The Dashboard Export API cannot export CSV files to an external location. It can only export to /mnt/cw_glusterfs/bricks/rscoean/export. |
|
|
BWoD |
BWoD gets disabled when SR Policy Traffic field has 'Measured' selected and Policy Violation field has 'Strict' selected. |
|
VPN Service Provisioning |
Service configuration data copied from Crosswork Network Controller VPN Services UI page cannot be used as a template for service provisioning from the Provisioning UI page. The Provisioning UI page has sample JSON/XML payload for each service type and should be used for service lifecycle management. |
|
Feature |
Limitation |
|---|---|
|
Upgrade |
The following limitations have been identified with Service Health on upgrading from Crosswork Network Controller 5.0 to Crosswork Network Controller 6.0:
|
|
Feature |
Limitation |
|---|---|
|
Upgrade |
When Crosswork Network Controller 5.0 is upgraded to 6.0, critical alarms remain uncleared, despite the data gateway VMs being UP and operational. |
Product Documentation
An Information Portal is now available for Crosswork Network Controller 6.0. Information is categorized per functional area, making it easy to find and easy to access.
You can also access documentation for all Cisco Crosswork products at https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/cloud-systems-management/crosswork-network-automation/tsd-products-support-series-home.html
The following documents are provided for Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0.x.
|
Document |
What is Included |
|---|---|
| Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0.x Release Notes |
This document |
| Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0 Installation Guide |
Shared installation guide for all the Cisco Crosswork applications and their common infrastructure. Covers:
|
| Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0 Administration Guide |
Shared administration guide for all the Cisco Crosswork applications and their common infrastructure. Covers:
|
| Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0 Solution Workflow Guide |
|
| Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0 Closed-Loop Network Automation |
Provides information on real-time Key Performance Indicator (KPI) monitoring, alerting, and troubleshooting. It also provides information on the automated process of deploying changes to the network. |
| Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0 Service Health Monitoring |
Provides information on monitoring the health of L2VPN and L3VPN services. It provides insights into analyzing and troubleshooting degraded services, as well as visualizing service health status and logical dependency trees. |
|
Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0 Traffic Engineering and Optimization Guide |
Provides information on how to visualize and configure traffic engineering in Crosswork Network Controller. |
|
Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0 Network Bandwidth Management Guide |
Provides information on how to use Crosswork Network Controller feature packs. Feature packs are tools that tackle congestion mitigation and the management of SR-TE policies to find and maintain intent based bandwidth requirements. |
| Open Source Used in Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0 |
Lists of licenses and notices for open source software used in Cisco Crosswork Network Controller 6.0.x. |
|
API Documentation |
Advanced users can extend the Cisco Crosswork functionality using the APIs. API documentation is available on Cisco Devnet. |
Feature Pack Documentation
-
Cisco Crosswork Change Automation NSO Function Pack 6.0.0 Installation Guide
-
Cisco Crosswork NSO Telemetry Traffic Collector Function Pack 6.0.0-62 Installation Guide
-
Cisco Network Services Orchestrator DLM Service Pack 6.0.0 Installation Guide
-
Cisco NSO Transport SDN Function Pack Bundle 6.0.0 Installation Guide
-
Cisco NSO Transport SDN Function Pack Bundle 6.0.0 User Guide
Bugs
If you encounter problems while working with Cisco Crosswork, check this list of open bugs. Each bug ID in the list links to a more detailed description and workaround. You can use the Cisco Bug Search Tool to search for bugs.
-
Go to the Cisco Bug Search Tool.
-
Enter your registered Cisco.com username and password, and click Log In.
The Bug Search page opens.

Note
-
To search for all Cisco Crosswork bugs, from the Product list select Cloud and Systems Management > Routing and Switching Management > Cisco Crosswork Network Automation and enter additional criteria (such as bug ID, problem description, a feature, or a product name) in the Search For field. Examples: "Optimization Engine" or "CSCwc62479"
-
When the search results are displayed, use the filter tools to narrow the results. You can filter the bugs by status, severity, and so on.
 Note |
To export the results to a spreadsheet, click Export Results to Excel. |
Security
Cisco takes great strides to ensure that all our products conform to the latest industry recommendations. We firmly believe that security is an end-to-end commitment and are here to help secure your entire environment. Please work with your Cisco account team to review the security profile of your network.
For details on how we validate our products, see Cisco Secure Products and Solutions and Cisco Security Advisories.
If you have questions or concerns regarding the security of any Cisco products, please open a case with the Cisco Customer Experience team and include details about the tool being used and any vulnerabilities it reports.
Accessibility Features
For a list of accessibility features in Cisco Crosswork Network Controller, visit https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/about/accessibility/voluntary-product-accessibility-templates.html (VPAT) website, or contact accessibility@cisco.com.
All product documents except for some images, graphics, and charts are accessible. If you would like to receive the product documentation in audio format, braille, or large print, contact accessibility@cisco.com.
Support & Downloads
The Cisco Support and Downloads website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies.
Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Downloads website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password.
For more information:
Obtain Additional Information
Information about Cisco products, services, technologies, and networking solutions is available from various online sources.
-
Sign up for Cisco email newsletters and other communications at:
-
Visit the Cisco Customer Experience website for the latest technical, advanced, and remote services to increase the operational reliability of your network. Go to:
-
Obtain general networking, training, and certification titles from Cisco Press publishers at:
 Feedback
Feedback