| ADSL-LINE-MIB.mib |
CISCO-UBE-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-ANALYZER-MIB.mib |
| ADSL-TC-MIB.mib |
CISCO-UNIFIED-COMPUTING -ADAPTOR-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-ATM-COS-MIB.mib |
| AGENTX-MIB.mib |
CISCO-UNIFIED-COMPUTING -COMPUTE-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-ATM-MIB.mib |
| AIRESPACE-REF -MIB.mib |
CISCO-UNIFIED-COMPUTING -ETHER-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-BFD-MIB.mib |
| AIRESPACE-SWITCHING -MIB.mib |
CISCO-UNIFIED-COMPUTING -FC-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-CFGMGMT -MIB.mib |
| AIRESPACE-WIRELESS -MIB.mib |
CISCO-UNIFIED-COMPUTING -MEMORY-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-CHASSIS-DEFINES -MIB.mib |
| ALARM-MIB.mib |
CISCO-UNIFIED-COMPUTING -MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-CHASSIS-FWDD -MIB.mib |
| ALCATEL-IEEE8021 -PAE-MIB.mib |
CISCO-UNIFIED-COMPUTING -NETWORK-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-COLLECTOR-MIB.mib |
| APS-MIB.mib |
CISCO-UNIFIED-COMPUTING -PROCESSOR-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-COS-MIB.mib |
| ARUBA-TC.mib |
CISCO-UNIFIED-COMPUTING -TC-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-DCU-MIB.mib |
| ATM-FORUM-MIB.mib |
CISCO-VLAN-IFTABLE -RELATIONSHIP-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-DFC-MIB.mib |
| ATM-FORUM-TC-MIB.mib |
CISCO-VLAN-MEMBERSHIP -MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-DOM-MIB.mib |
| ATM-MIB.mib |
CISCO-VOICE-COMMON- DIAL-CONTROL-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-EVENT-MIB.mib |
| ATM-TC-MIB.mib |
CISCO-VOICE-DIAL- CONTROL-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-EX-MAC- NOTIFICATION-MIB.mib |
| ATM2-MIB.mib |
CISCO-VOICE-DNIS-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-EX-SMI.mib |
| BFD-STD-MIB.mib |
CISCO-VPDN-MGMT- MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-EXPERIMENT- MIB.mib |
| BGP4-MIB.mib |
CISCO-VTP-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-FIREWALL- MIB.mib |
| BGP4-V2-MIB-JUNIPER.mib |
CISCO-WIRELESS-NOTIFICATION -MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-HOSTRESOURCES -MIB.mib |
| BRIDGE-MIB.mib |
CISCOSB-DEVICEPARAMS -MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-IF-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-AAA-SERVER -MIB.mib |
CISCOSB-HWENVIROMENT.mib |
JUNIPER-IPFORWARD -MIB.mib |
| CISCO-AAA-SESSION -MIB.mib |
CISCOSB-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-IPSEC-FLOW -MON-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-AAL5-MIB.mib |
CISCOSB-Physicaldescription -MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-IPv4-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-ACCESS-ENVMON -MIB.mib |
COGNIO-SMI.mib |
JUNIPER-IPv6-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-ATM-EXT-MIB.mib |
COGNIO-TRAPS-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-JDHCP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-ATM-PVCTRAP -EXTN-MIB.mib |
DIAL-CONTROL-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-JDHCPV6-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-ATM-QOS-MIB.mib |
DIFFSERV-DSCP-TC.mib |
JUNIPER-JS-AUTH-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-AUTH-FRAMEWORK -MIB.mib |
DIFFSERV-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-JS-CERT-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-BGP-POLICY- ACCOUNTING-MIB.mib |
DISMAN-EVENT-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-JS-DNS-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-BGP4-MIB.mib |
DISMAN-EXPRESSION-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-JS-IDP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-BULK-FILE-MIB.mib |
DISMAN-NSLOOKUP-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-JS-IF-EXT-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-CBP-TARGET-MIB.mib |
DISMAN-PING-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-JS-IPSEC-VPN -MIB.mib |
| CISCO-CBP-TARGET -TC-MIB.mib |
DISMAN-SCHEDULE-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-JS-NAT-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-CBP-TC-MIB.mib |
DISMAN-SCRIPT-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-JS-POLICY-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-CCME-MIB.mib |
DISMAN-TRACEROUTE-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-JS-SCREENING-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-CDP-MIB.mib |
DOT3-OAM-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-JS-SMI.mib |
| CISCO-CEF-MIB.mib |
DRAFT-MSDP-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-L2ALD-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-CEF-TC.mib |
DS0-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-L2CP-FEATURES -MIB.mib |
| CISCO-CLASS-BASED -QOS-MIB.mib |
DS1-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-LDP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-CONFIG-COPY -MIB.mib |
DS3-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-MAC-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-CONFIG-MAN -MIB.mib |
ENTITY-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-MAG-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-CONTENT-ENGINE -MIB.mib |
ENTITY-SENSOR-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-CONTEXT-MAPPING -MIB.mib |
ENTITY-STATE-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-MIMSTP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-DATA-COLLECTION -MIB.mib |
ENTITY-STATE-TC-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-MPLS-LDP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-DEVICE-EXCEPTION -REPORTING-MIB.mib |
ESO-CONSORTIUM-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-OTN-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-DIAL-CONTROL -MIB.mib |
ETHER-WIS.mib |
JUNIPER-PAE-EXTENSION -MIB.mib |
| CISCO-DOT11-ASSOCIATION -MIB.mib |
EXPRESSION-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-PFE-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-DOT11-HT-PHY -MIB.mib |
EtherLike-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-PING-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-DOT11-IF-MIB.mib |
FDDI-SMT73-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-PMon-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-DOT11-SSID- SECURITY-MIB.mib |
FR-MFR-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-POWER-SUPPLY- UNIT-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-DOT3-OAM-MIB.mib |
FRAME-RELAY-DTE-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-PW-ATM-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-DS3-MIB.mib |
FRNETSERV-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-PW-TDM-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-DYNAMIC-TEMPLATE -MIB.mib |
GMPLS-LSR-STD-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-RMON-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-DYNAMIC-TEMPLATE -TC-MIB.mib |
GMPLS-TC-STD-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-RPF-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-EIGRP-MIB.mib |
GMPLS-TE-STD-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-RPM-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-EMBEDDED-EVENT -MGR-MIB.mib |
HC-PerfHist-TC-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-RPS-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-ENHANCED-IMAGE-MIB.mib |
HC-RMON-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-RSVP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-ENHANCED-MEMPOOL-MIB.mib |
HCNUM-TC.mib |
JUNIPER-SCU-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-ENTITY-ASSET-MIB.mib |
HOST-RESOURCES-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-SECURE-ACCESS-PORT-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-ENTITY-EXT-MIB.mib |
HOST-RESOURCES-TYPES.mib |
JUNIPER-SMI.mib |
| CISCO-ENTITY-FRU-CONTROL-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-ALARM-RELIABILITY-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-SONET-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-ENTITY-QFP-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-BASE-TRAP-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-SP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-ENTITY-REDUNDANCY-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-BFD-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-SRX5000-SPU-MONITORING-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-ENTITY-REDUNDANCY-TC-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-BGP-ACCOUNTING-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-SYSLOG-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-ENTITY-SENSOR-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-BGP-GR-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-TRACEROUTE-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-ENTITY-VENDORTYPE-OID-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-BGP-VPN-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-USER-AAA-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-ENVMON-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-BRAS-L2TP-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-UTIL-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-EPM-NOTIFICATION-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-BRAS-MULTICAST-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-VIRTUALCHASSIS-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-ETHER-CFM-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-BRAS-PPPoX-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-VLAN-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-ETHERLIKE-EXT-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-BRAS-SRVCFG-STATICUSER-MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-VPN-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-FABRIC-C12K-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-BRAS-USERVLAN-MIB.mib |
L2TP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-FIREWALL-TC.mib |
HUAWEI-BULKSTAT-MIB.mib |
LANGTAG-TC-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-FLASH-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-CCC-MIB.mib |
LLDP-EXT-DOT1-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-FRAME-RELAY-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-CE-PING-MIB.mib |
LLDP-EXT-DOT3-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-FTP-CLIENT-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-CLOCK-MIB.mib |
LLDP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-HSRP-EXT-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-CONFIG-MAN-MIB.mib |
MAU-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-HSRP-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-CPU-MIB.mib |
MGMD-STD-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IETF-ATM2-PVCTRAP-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-DATASYNC-MIB.mib |
MPLS-FTN-STD-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IETF-BFD-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-DC-TRAP-MIB.mib |
MPLS-L3VPN-STD-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IETF-FRR-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-DEVICE-EXT-MIB.mib |
MPLS-LDP-ATM-STD-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IETF-IPMROUTE-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-DEVICE-MIB.mib |
MPLS-LDP-FRAME-RELAY-STD-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IETF-ISIS-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-DHCPR-MIB.mib |
MPLS-LDP-GENERIC-STD-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IETF-MPLS-ID-STD-03-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-DIALER-MIB.mib |
MPLS-LDP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IETF-MPLS-TE-EXT-STD-03-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-DLDP-MIB.mib |
MPLS-LDP-STD-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IETF-MPLS-TE-P2MP-STD-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-E-TRUNK-MIB.mib |
MPLS-LSR-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IETF-MSDP-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-ENTITY-TRAP-MIB.mib |
MPLS-LSR-STD-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IETF-PIM-EXT-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-EPON-MIB.mib |
MPLS-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IETF-PIM-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-FIREWALL-MIB.mib |
MPLS-TC-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IETF-PW-ATM-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-FR-QOS-MIB.mib |
MPLS-TC-STD-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IETF-PW-ENET-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-FTP-MIB.mib |
MPLS-TE-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IETF-PW-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-GTL-MIB.mib |
MPLS-TE-STD-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IETF-PW-MPLS-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-GTSM-MIB.mib |
MPLS-VPN-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IETF-PW-TC-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-HGMP-MIB.mib |
MSDP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IETF-PW-TDM-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-HTTP-MIB.mib |
NET-SNMP-AGENT-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IETF-VPLS-BGP-EXT -MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-HWTACACS-MIB.mib |
NET-SNMP-EXAMPLES -MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IETF-VPLS-GENERIC -MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-IF-QOS-MIB.mib |
NET-SNMP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IETF-VPLS-LDP-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-IMA-MIB.mib |
NET-SNMP-TC.mib |
| CISCO-IF-EXTENSION-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-IPV6-MIB.mib |
NHRP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IGMP-FILTER-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-KOMPELLA-MIB.mib |
NOTIFICATION-LOG-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IMAGE-LICENSE-MGMT -MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-L2IF-MIB.mib |
OLD-CISCO-CHASSIS-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IMAGE-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-L2MULTICAST-MIB.mib |
OLD-CISCO-INTERFACES- MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IMAGE-TC.mib |
HUAWEI-L2TP-EXT-MIB.mib |
OLD-CISCO-SYS-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IP-LOCAL-POOL -MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-L2VPN-MIB.mib |
OLD-CISCO-SYSTEM-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IP-TAP-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-L3VLAN-MIB.mib |
OPT-IF-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IP-URPF-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-LDT-MIB.mib |
ORiNOCO-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IPMROUTE-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-LINE-MIB.mib |
OSPF-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IPSEC-FLOW-MONITOR -MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-LLDP-MIB.mib |
OSPF-TRAP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IPSEC-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-LOOPDETECT -MIB.mib |
OSPFV3-MIB-JUNIPER.mib |
| CISCO-IPSEC-POLICY-MAP -MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-MEMORY-MIB.mib |
OSPFV3-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IPSLA-AUTOMEASURE -MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-MFLP-MIB.mib |
P-BRIDGE-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IPSLA-ECHO-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-MIB.mib |
PIM-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IPSLA-JITTER-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-MINM-MIB.mib |
PIM-STD-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-IPSLA-TC-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-MIRROR-MIB.mib |
POWER-ETHERNET-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-ISDN-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-MPLSLSR-EXT-MIB.mib |
PPP-IP-NCP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LICENSE-MGMT -MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-MPLSOAM-MIB.mib |
PPP-LCP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LOCAL-AUTH-USER -MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-MPLSOAM-PS -MIB.mib |
PPVPN-TC-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-AAA-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-MSTP-MIB.mib |
PTOPO-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-AP-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-NAT-EXT-MIB.mib |
PerfHist-TC-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-CCX-RM- MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-OSPFV2-MIB.mib |
Q-BRIDGE-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-CDP-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-OSPFV3-MIB.mib |
RADIUS-ACC-CLIENT-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-CLIENT- ROAMING-CAPABILITY.mib |
HUAWEI-PERFORMANCE-MIB.mib |
RADIUS-AUTH-CLIENT-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-CLIENT- ROAMING-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-PIM-BSR-MIB.mib |
RFC-1212.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-DHCP-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-PIM-STD-MIB.mib |
RFC-1215.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-DOT11 -CLIENT-CALIB-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-PORTAL-MIB.mib |
RFC1155-SMI.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-DOT11 -CLIENT-CCX-TC-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-PORTBLOCK-MIB.mib |
RFC1213-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-DOT11 -LDAP-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-PPP-MIB.mib |
RFC1315-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-DOT11 -MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-RANAPS-MIB.mib |
RFC1398-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-DOWNLOAD -MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-RIPV2-EXT-MIB.mib |
RIPv2-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-IDS-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-RM-EXT-MIB.mib |
RMON-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-INTERFACE -MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-RRPP-MIB.mib |
RMON2-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-IPS-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-SECURITY-MIB.mib |
RSTP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-LINKTEST-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-SLB-MIB.mib |
RSVP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-LOCAL -AUTH-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-SNMP-EXT-MIB.mib |
SMON-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-MDNS-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-SSH-MIB.mib |
SNA-SDLC-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-MESH-BATTERY -MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-STACK-MIB.mib |
SNMP-COMMUNITY-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-MESH-LINKTEST -MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-SYS-MAN-MIB.mib |
SNMP-FRAMEWORK-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-MOBILITY -EXT-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-TAD-MIB.mib |
SNMP-MPD-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-MOBILITY -MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-TASK-MIB.mib |
SNMP-NOTIFICATION-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-NETFLOW -MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-TC-MIB.mib |
SNMP-PROXY-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-REAP-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-TCP-MIB.mib |
SNMP-REPEATER-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-RF-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-TRANSPARENTBRIDGE -MIB.mib |
SNMP-TARGET-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-SI-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-TRNG-MIB.mib |
SNMP-USER-BASED-SM-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-TC-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-TUNNEL-MIB.mib |
SNMP-USM-AES-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-TRUSTSEC -MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-USERLOG-MIB.mib |
SNMP-USM-DH-OBJECTS -MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-TSM-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-VE-MIB.mib |
SNMP-VIEW-BASED-ACM -MIB.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-WLAN-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-VGMP-MIB.mib |
SNMPv2-CONF.mib |
| CISCO-LWAPP-WLAN-SECURITY -MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-VLL-STATISTIC-MIB.mib |
SNMPv2-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-MEDIA-GATEWAY-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-VPLS-EXT-MIB.mib |
SNMPv2-SMI.mib |
| CISCO-MOTION-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-VPLS-TNL-MIB.mib |
SNMPv2-TC-v1.mib |
| CISCO-MPLS-LSR-EXT-STD -MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-WAN-MIB.mib |
SNMPv2-TC.mib |
| CISCO-MPLS-TC-EXT-STD -MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-WLAN-DEVICE-MIB.mib |
SNMPv2-TM.mib |
| CISCO-MPLS-TE-STD-EXT -MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-WLAN-MIB.mib |
SONET-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-NAC-TC-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-WLAN-QOS-MIB.mib |
SYSAPPL-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-NBAR-PROTOCOL- DISCOVERY-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-WLAN-RADIO-MIB.mib |
TCP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-NETSYNC-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-WLAN-SERVICE-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-ALARM-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-NTP-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-WLAN-SYS-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-APS-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-OSPF-MIB.mib |
HUAWEI-WLAN-UPDATE-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-ATM-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-OSPF-TRAP-MIB.mib |
IANA-ADDRESS-FAMILY -NUMBERS-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-BGP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-OTN-IF-MIB.mib |
IANA-GMPLS-TC-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-CFLOWD-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-PAE-MIB.mib |
IANA-ITU-ALARM-TC-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-CHASSIS-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-PAGP-MIB.mib |
IANA-LANGUAGE-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-CLEAR-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-PIM-MIB.mib |
IANA-RTPROTO-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-CONN-PROF-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-PING-MIB.mib |
IANAifType-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-DIAMETER-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-POLICY-GROUP-MIB.mib |
IEEE8021-CFM-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-DOT3-OAM-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-POWER-ETHERNET -EXT-MIB.mib |
IEEE8021-PAE-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-FILTER-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-PRIVATE-VLAN-MIB.mib |
IEEE8021-TC-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-GLOBAL-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-PROCESS-MIB.mib |
IEEE802171-CFM-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-IPSEC-STATIC -SA-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-PRODUCTS-MIB.mib |
IEEE8023-LAG-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-LLDP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-PTP-MIB.mib |
IEEE802dot11-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-LOG-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-RADIUS-EXT-MIB.mib |
IF-INVERTED-STACK-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-MSDP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-RF-MIB.mib |
IF-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-OTU-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-RF-SUPPLEMENTAL -MIB.mib |
IGMP-STD-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-ROUTE-POLICY -MIB.mib |
| CISCO-RTTMON-TC-MIB.mib |
INET-ADDRESS-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-SYSTEM-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-SELECTIVE-VRF- DOWNLOAD-MIB.mib |
INT-SERV-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-TC-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-SESS-BORDER-CTRLR -CALL-STATS-MIB.mib |
INTEGRATED-SERVICES-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-TWAMP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-SESS-BORDER-CTRLR -EVENT-MIB.mib |
IP-FORWARD-MIB.mib |
TIMETRA-VRRP-V3-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-SESS-BORDER-CTRLR -STATS-MIB.mib |
IP-MIB.mib |
TOKEN-RING-RMON-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-SMI.mib |
IPMCAST-MIB.mib |
TOKENRING-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-SONET-MIB.mib |
IPMROUTE-MIB.mib |
TRANSPORT-ADDRESS -MIB.mib |
| CISCO-ST-TC.mib |
IPMROUTE-STD-MIB.mib |
TUNNEL-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-STACKWISE-MIB.mib |
IPV6-FLOW-LABEL-MIB.mib |
UCD-DEMO-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-STP-EXTENSIONS -MIB.mib |
IPV6-ICMP-MIB.mib |
UCD-DISKIO-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-SUBSCRIBER-IDENTITY -TC-MIB.mib |
IPV6-MIB.mib |
UCD-DLMOD-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-SUBSCRIBER-SESSION -MIB.mib |
IPV6-MLD-MIB.mib |
UCD-IPFWACC-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-SUBSCRIBER-SESSION -TC-MIB.mib |
IPV6-TC.mib |
UCD-SNMP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-SYSLOG-MIB.mib |
IPV6-TCP-MIB.mib |
UDP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-SYSTEM-EXT-MIB.mib |
IPV6-UDP-MIB.mib |
VPLS-BGP-DRAFT-01 -MIB.mib |
| CISCO-SYSTEM-MIB.mib |
ISDN-MIB.mib |
VPLS-GENERIC-DRAFT -01-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-TAP2-MIB.mib |
ISIS-MIB.mib |
VPLS-LDP-DRAFT-01 -MIB.mib |
| CISCO-TC.mib |
ITU-ALARM-MIB.mib |
VPN-TC-STD-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-TCP-MIB.mib |
ITU-ALARM-TC-MIB.mib |
VRRP-MIB.mib |
| CISCO-TEMP-LWAPP- DHCP-MIB.mib |
JNX-IPSEC-MONITOR-MIB.mib |
ietf-inet-types.mib |
| CISCO-TRUSTSEC-SXP -MIB.mib |
JNX-L2TP-MIB.mib |
ietf-yang-smiv2.mib |
| CISCO-TRUSTSEC-TC -MIB.mib |
JUNIPER-ALARM-MIB.mib |
ietf-yang-types.mib |

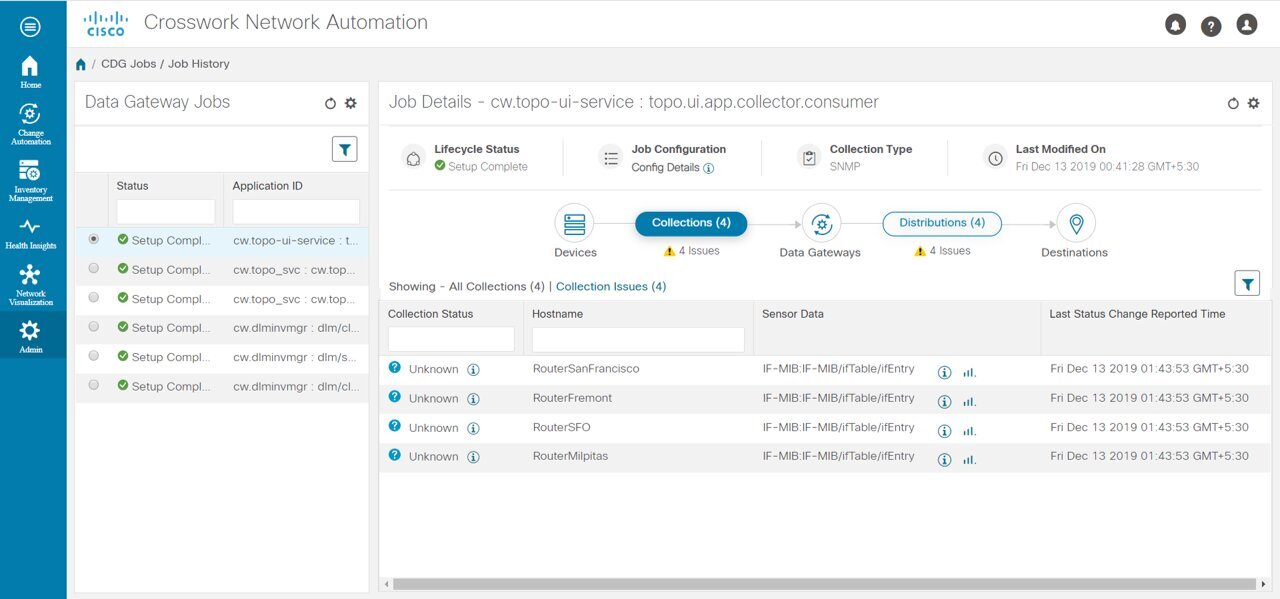
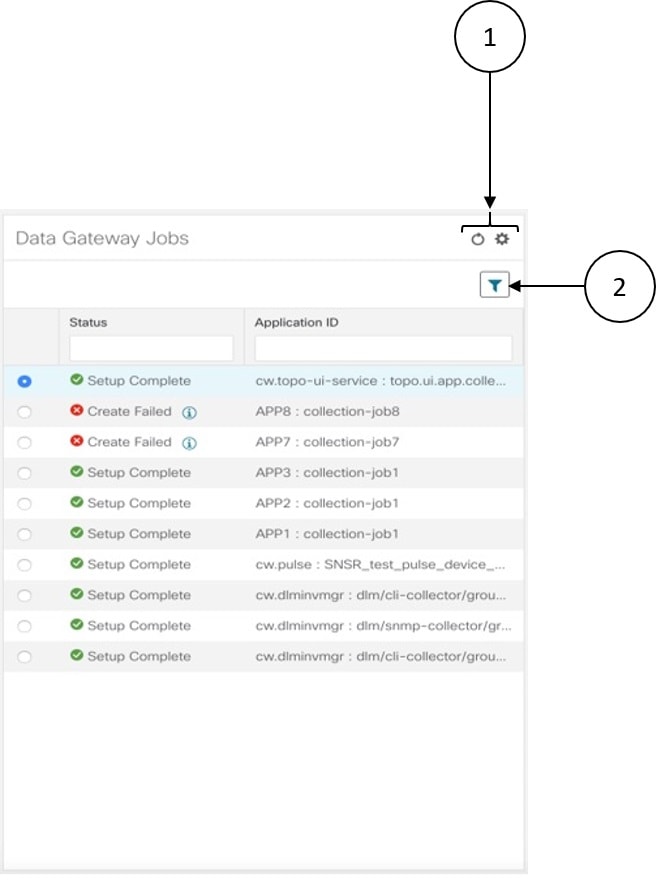
 to refresh the
to refresh the  to choose the columns to make visible in the
to choose the columns to make visible in the 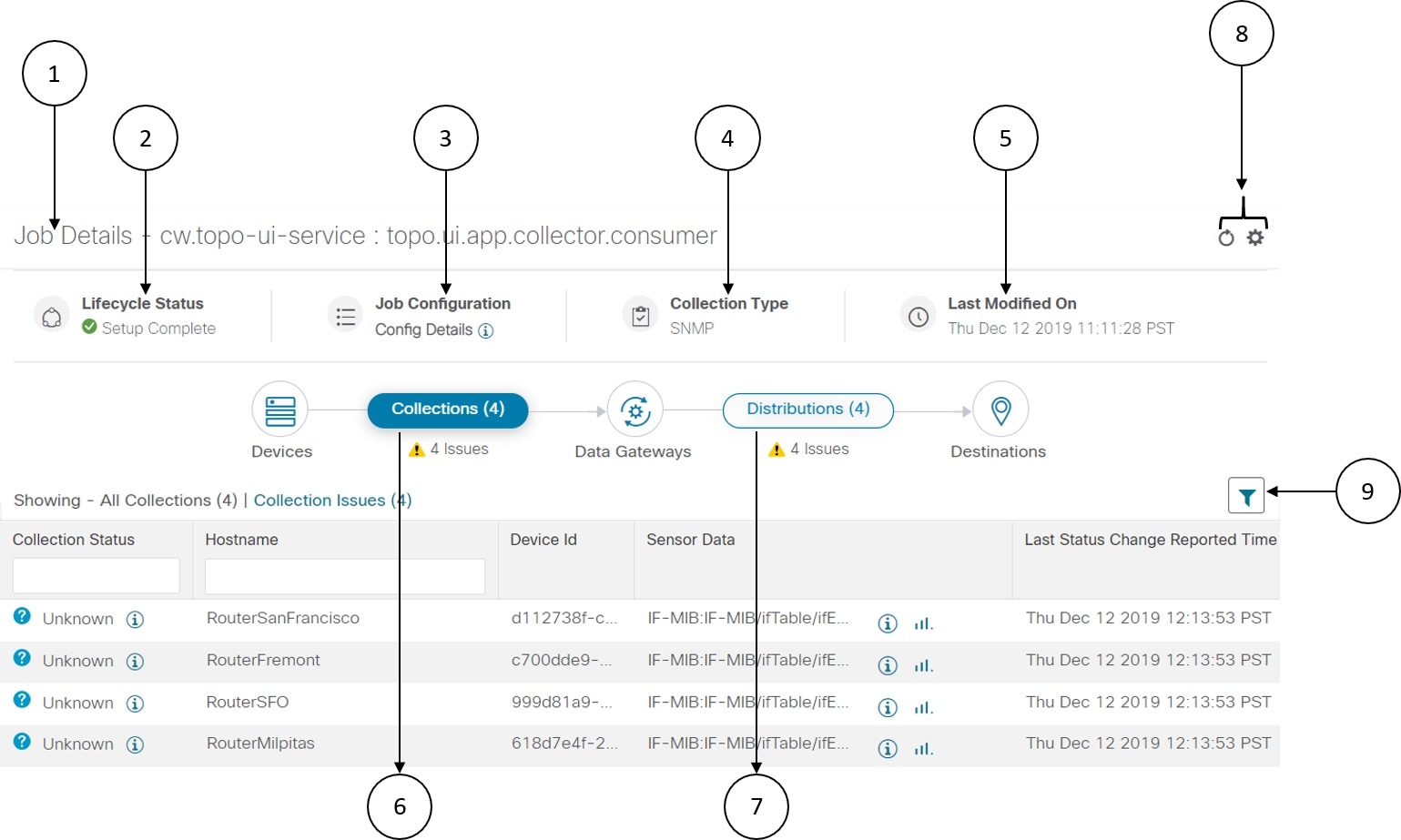
 Feedback
Feedback