- Introduction
- Cisco Service Control Solution Overview
- Cisco SCA BB System Overview
- Introduction to Traffic Processing
- Getting Started with Cisco SCA BB Console
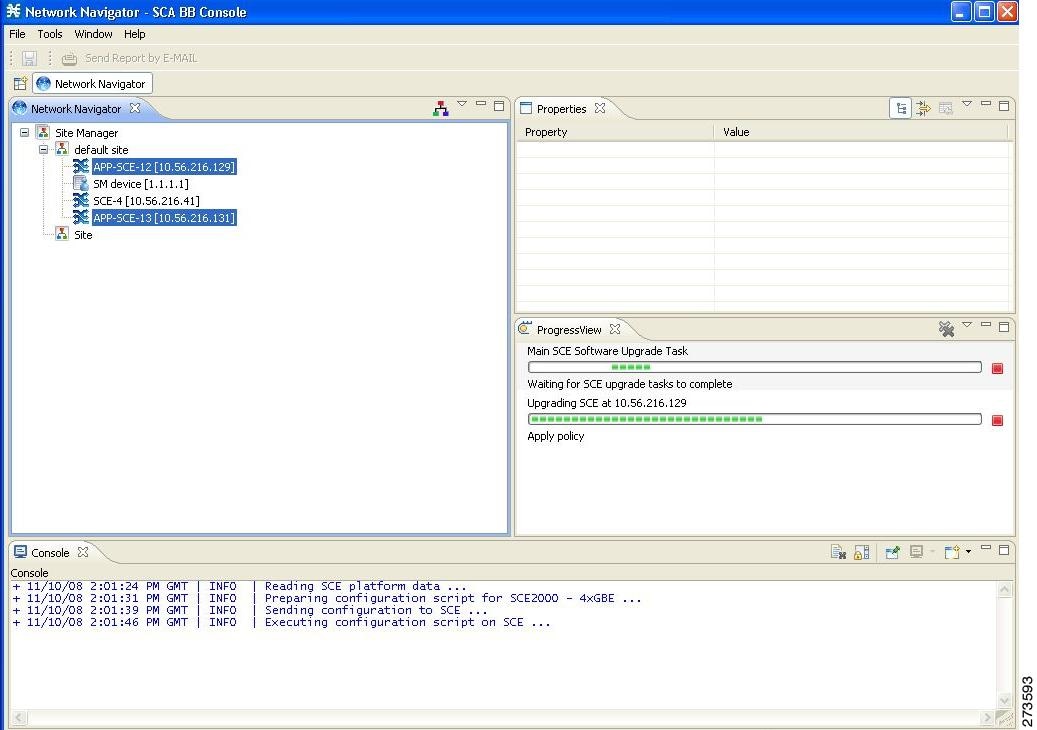
- The Network Navigator
- Using the Service Configuration Editor
- Traffic Classification Using Service Configuration Editor
- Traffic Accounting and Reporting Using the Service Configuration Editor
- Traffic Control Using the Service Configuration Editor
- Service Configuration Editor: Additional Options
- Subscriber Manager GUI Tool
- Anonymous Group Manager GUI Tool
- The Signature Editor Overview
- Additional Management Tools and Interfaces
Cisco Service Control Application for Broadband (Cisco SCA BB) User Guide
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- February 17, 2015
Chapter: Getting Started with Cisco SCA BB Console
- How to Install Cisco SCA BB
Getting Started with Cisco SCA BB Console
The module guides you through the process of installing or upgrading the Cisco SCA BB:
- Describes the concept of the Console as a collection of tools, presents each tool and its role. This module also describes how to launch the tools and navigate between these tools.
- Explains how to install Protocol Packs, which contain new and updated protocol signatures
- Concludes with a QuickStart that describes how to apply your first service configuration and generate your first report
This section consists of the following sections:
- How to Install Cisco SCA BB
- How to Upgrade Cisco SCA BB Components
- Working with Protocol Packs
- Launching the Cisco SCA BB Console
- How to Use the Cisco SCA BB Console
- QuickStart with the Cisco SCA BB Console
How to Install Cisco SCA BB
 Note | On a Windows XP machine, the Cisco SCA BB application can only be installed in the administrator user group. During installation the Cisco SCA BB application changes registry entries, therefore installation in normal user groups is not allowed. The installer must have administrator privileges assigned. |
You install Cisco SCA BB in two stages:
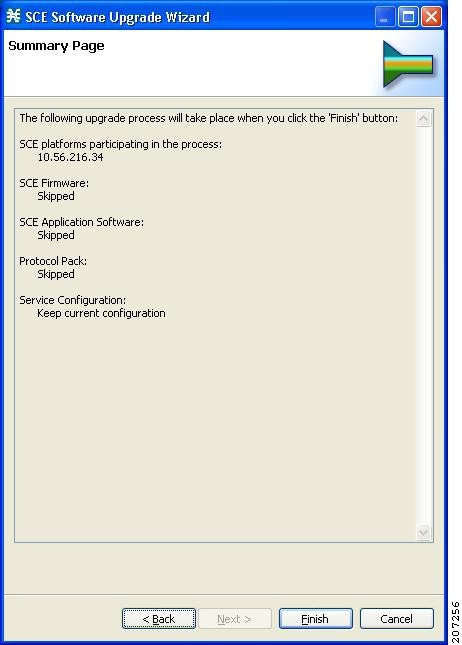
If you are upgrading an existing installation of Cisco SCA BB, see the Upgrading the SCE Using the SCE Software Upgrade Wizard section or the Working with Protocol Packs section.
- The Cisco SCA BB Installation Package
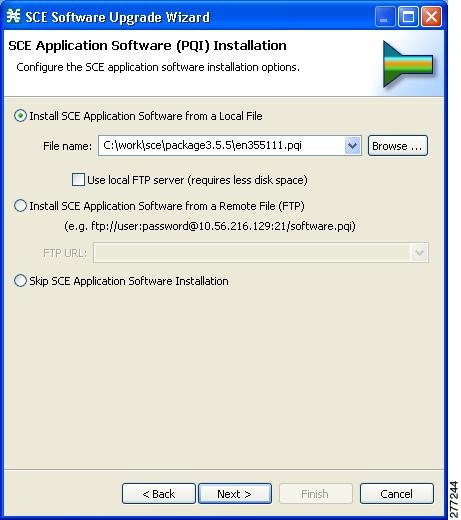
- Installing Cisco SCA BB Application Components
- Prerequisites
- How to Install Cisco SCA BB Front Ends
The Cisco SCA BB Installation Package
The Cisco SCA BB installation package is a ZIP file located in the CCO.
The installation package consists of the following files:
- The installer for the Console: scas-bb-console-<version>-<build>.exe.
- A Cisco installation application package file (PQI file) for each type of Cisco SCE platform. Each PQI file is located in a subfolder whose name is the platform name.
- The file scas_bb_util.tgz, which contains the files for the Cisco SCA BB Service Configuration Utility ( servconf) , the Cisco SCA BB Signature Configuration Utility ( sigconf) , the Cisco SCA BB Real-Time Monitoring Configuration Utility ( rtmcmd) (together with real-time monitoring report templates), and the BGP Autonomous System Dynamic Detection scripts and files ( routerInfo.properties , asFetch.bat , asFetch.sh ).
- The file PCubeEngageMib.mib, which defines the SCAS BB MIB, located in the SNMP subfolder.
- The Cisco SCA BB Service Configuration Java API distribution file: serviceconfig-java-api-dist.tgz.
- The file surfcontrol.xml, which lists the content categories for content filtering using SurfControl Content Port Authority, located in the URL Filtering subfolder.
Installing Cisco SCA BB Application Components
Cisco SCA BB has two software components that reside on the Cisco SCE platform:
- The Cisco SCA BB SLI, which performs traffic processing
- The Cisco SCA BB SCE applicative management plug-in, which performs some service configuration operations
Cisco SCA BB also has one software component that resides on the Subscriber Manager device:
- The Cisco SCA BB Subscriber Manager applicative management plug-in, which performs some application-specific subscriber management operations
To install these components from the Console, see the How to Install PQI Files on Cisco SCE Devices and Managing Collection Manager Devices sections.
To install these components from a command line, see the Installing PQI Files from the Command Line section.
Prerequisites
Before installing Cisco SCA BB, verify that the SCE platform and, if used, the Cisco Service Control Subscriber Manager are operational and are running appropriate versions of their software.
- Verifying that the SCE Platform is Operational
- Verifying that the SCE Platform is Running an Appropriate Version of the OS
- Verifying that the Subscriber Manager is Correctly Installed
- Verifying that an Appropriate Version of the Subscriber Manager is Running
Verifying that the SCE Platform is Operational
Verifying that the SCE Platform is Running an Appropriate Version of the OS
| Step 1 | At the SCE platform CLI prompt (SCE#), type show version . |
| Step 2 | Press Enter . The response shows the version of the OS running on the SCE platform. |
Verifying that the Subscriber Manager is Correctly Installed
Verifying that an Appropriate Version of the Subscriber Manager is Running
| Step 1 | Open a Telnet session to the Subscriber Manager. |
| Step 2 | Go to the Subscriber Manager bin directory and type p3sm version . |
| Step 3 | Press Enter . Displays the Subscriber Manager version. |
How to Install Cisco SCA BB Front Ends
You should install the following Cisco SCA BB front ends:
- The Console
- The Cisco SCA BB Service
Configuration Utility (
servconf)
, the Cisco SCA BB Signature Configuration Utility (
sigconf)
, and the Cisco SCA BB Real-Time Monitoring Configuration tool
(
rtmcmd)
(together with associated real-time monitoring report
templates).
- servconf requires access to the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) (see “Installing the Java Runtime Environment” section).
- Cisco SCA BB Hardware Requirements
- Cisco SCA BB Operating System Requirements
- Installing the Java Runtime Environment
- Installing the Cisco SCA BB Console
- Installing the Cisco SCA BB Configuration Utilities
Cisco SCA BB Hardware Requirements
- At least 1024-MB RAM is required to run the Console.
- The minimal supported screen resolution for the Console is 1024x768 pixels.
Cisco SCA BB Operating System Requirements
The SCA Reporter GUI front end can be installed on any computer running Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, or Windows 7.
Installing the Java Runtime Environment
The Cisco SCA BB Service Configuration Utility, servconf, requires access to JRE version 1.6 update 43.
Installing the Cisco SCA BB Console
Installing the Cisco SCA BB Configuration Utilities
How to Upgrade Cisco SCA BB Components
Upgrading Cisco SCA BB includes upgrading each of these software components:
 Note | This section describes the upgrade of Cisco SCA BB application components only. For a full description of the entire Cisco solution upgrade procedure, consult the solution upgrade document accompanying the formal release. |
- When you upgrade old PQB files, some protocol IDs are changed automatically. Messages such as the following may be displayed to indicate the change:
- When you upgrade a device with a new SPQI or PQI file, all other devices that are not upgraded may fail.
- New Cisco SCA BB releases do not use the default Dynamic Signature Script (DSS) file (see that it was installed for a previous Cisco SCA BB release).
- If a protocol pack for the new release is available, install it after the product installation is complete. Do not install an old protocol pack on top of a new product installation.
Upgrading the SCE Using the SCE Software Upgrade Wizard
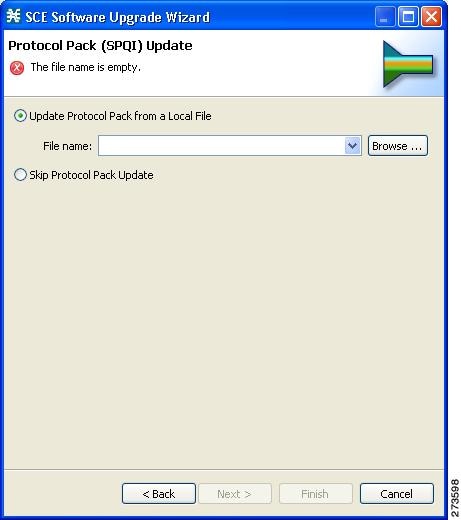
Working with Protocol Packs
Cisco SCA BB uses stateful Layer 7 capabilities for classification of traffic flows.
When the system handles a traffic flow, the flow is assigned a signature ID according to the set of Layer 3 to Layer 7 parameters (the signature) characterizing this flow. Typically, these signatures come embedded in Cisco SCA BB.
To enable rapid response to the ever-changing protocol environment, Cisco SCA BB was enhanced to allow signatures to be updated dynamically. You can load a protocol support plug-in onto an operational system, enhancing the protocol support of the system without compromising the stability of the system (no update of an existing software component is required) and without any service downtime.
- Protocol Packs
- Installing Protocol Packs
- How to Install the Service Hierarchy Tree
- Verifying Version Compatibility for Protocol Packs
- Verifying the Installation of a Protocol Pack
- Causes for Protocol Pack Installation Failure and Remedies
- Hitless Upgrade of the SLI
Protocol Packs
Periodically, Cisco publishes protocol packs containing new and improved protocol signatures for Cisco SCA BB. A typical protocol pack is a file containing signatures for detecting network worms, popular peer-to-peer applications, and other relevant protocols. When loaded into SCE platforms, these signatures improve Cisco SCA BB classification abilities.
 Note | You can install a protocol pack on an SCE platform only if a PQI is already installed on the platform. |
A protocol pack for Cisco SCA BB may be either a DSS file or an SPQI file:
- Loading a DSS file to the SCE platform requires no downtime of Cisco SCA BB or the platform.
- Loading an SPQI file to the
SCE platform entails updating the SCE application:
- If hitless upgrade (see Hitless Upgrade of the SLI section ) is enabled, there is no downtime of the SCE platform when loading the SPQI file.
- If hitless upgrade is not enabled, loading an SPQI file requires a short downtime (up to one minute) of the SCE platform. During that time, network traffic bypasses the platform and is neither controlled nor reported.
 Note | If hitless upgrade is disabled, SPQI installation can cause the loss of the following subscriber data from all subscribers: package ID, real-time monitoring flag, and quota settings. Subscribers are assigned default values for these properties. |
Installing Protocol Packs
- The Cisco SCA BB Service Configuration Utility (see the Cisco SCA BB Service Configuration Utility section)
- The Network Navigator tool (see the How to Install a Protocol Pack section )
 Note | If the protocol pack is an SPQI file you can enable and configure the hitless upgrade option using Hitless Upgrade CLI commands. (See the Hitless Upgrade of the SLI section.) |
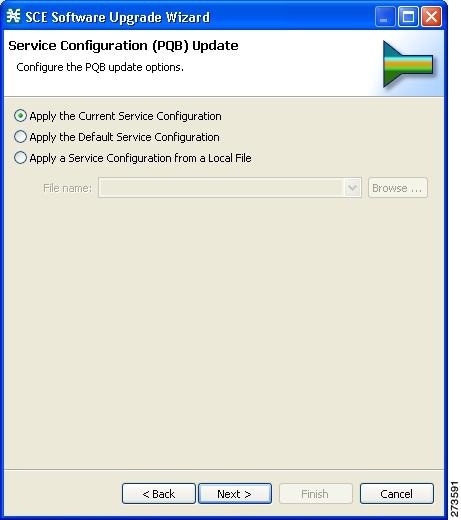
The tool or utility performs the following steps: Retrieves the current service configuration from the SCE platform and (optionally) stores a backup copy in a folder that you specify.
 Note | Cisco SCE does not support direct downgrade of higher PP versions to a lower PP version. While downgrading the protocol pack from a higher version to a lower version, the Cisco SCA BB console displays an error message and prevents you from applying the policy on the Cisco SCE. |
| Step 1 | Retrieves the current service configuration from the SCE platform and (optionally) stores a backup copy in a folder that you specify. |
| Step 2 | Imports the signatures that are in the DSS or SPQI file into the service configuration. This action overwrites any DSS that was previously imported into the service configuration. |
| Step 3 | For each new signature that includes a Buddy Protocol attribute (an attribute that points to an existing protocol) (see The Buddy Protocol section)—Adds the new signature to all services that include the buddy protocol. |
| Step 4 | If the protocol pack is an SPQI file—Replaces the SCE application. This action causes a short (up to one minute) downtime in SCE platform service. |
| Step 5 | Applies the new service configuration to the SCE platform. If the protocol pack is an SPQI file and the hitless upgrade option is enabled, you can monitor the progress of the upgrade using the hitless upgrade CLI commands (see the Hitless Upgrade CLI Commands section.) |
How to Install the Service Hierarchy Tree
Opening a PQB using the Client (GUI) exposes its service hierarchy tree (signatures, flavors, protocols, and so on). The client defines the Service Configuration Hierarchy.
When loading a PQB file from the SCE, the PQB Hierarchy Tree must be of the same version as the one in the client. In other words, the PQB must be the same version as the Client, otherwise the PQB doe not open.
Because the client can be connected with different SCE with different versions, and each PQB can have different Service Hierarchy Tree definition, you must install the relevant Service Hierarchy Tree in the Client (GUI) before opening a PQB.
The client can install the service hierarchy tree according to the SCE version. The GUI installation comes with a fixed set of service hierarchy elements which are placed in a specific version-related jar file. You can select between different jar files related to different versions.
The SCE service hierarchy tree is different than the client version. When installing a service hierarchy tree for a SCE:
- Always back up user PQB before upgrade to PPXY and keep a copy since the PQB is changed.
- Remove/Reinstall Service Tree Protocol.
 Note | Common SCABB console is going to be used for SCE 8000, SCE10000 and vSCE platform releases.
|
To view, install, and remove the service hierarchy tree use the following procedures:
Viewing and Installing the Service Hierarchy Tree
| Step 1 | To view the service hierarchy tree, open the Protocol Pack tab. |
| Step 2 | From the
toolbar, select Service Configuration Editor.
 |
| Step 3 | Select Windows > Preferences and then select Service Configuration. |
| Step 4 | Select Protocol
Pack from the Service Configuration tree. The upper window provides information
related to service hierarchy tree related to the GUI.
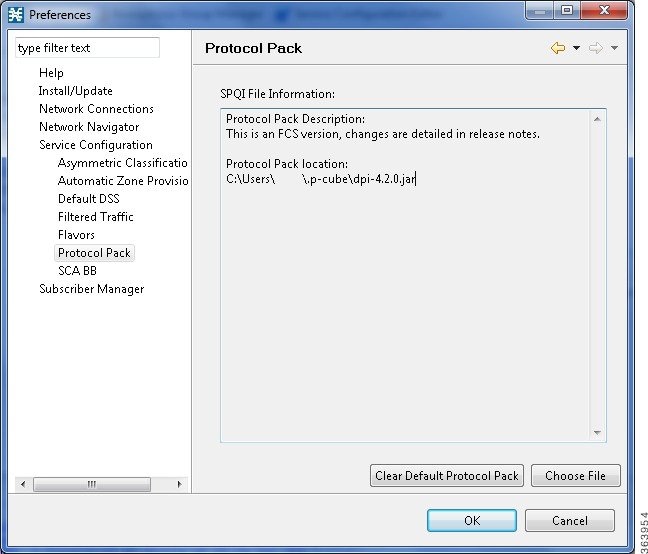 |
| Step 5 | To install a
new service hierarchy tree, click the Choose File button and select either a
jar file or an SPQI file.
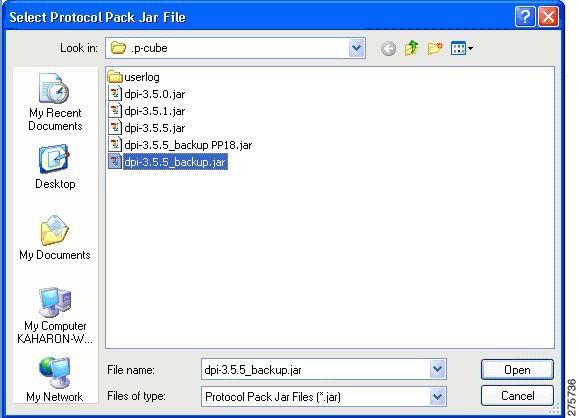 |
| Step 6 | Click
Open, and approve the warning message by clicking
OK .
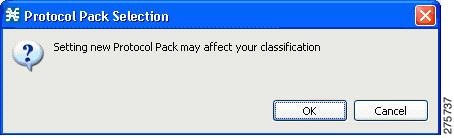 |
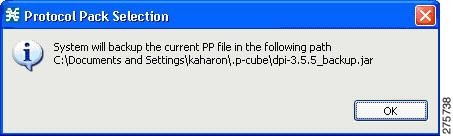
| Step 7 | To back up the
current protocol pack and install the new service hierarchy tree, approve the
backup message by clicking
OK.
 |
Removing the Service Hierarchy Tree
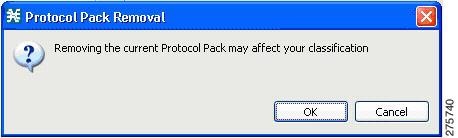
| Step 1 | To remove the
service hierarchy tree and to return to the default configuration, click the
Clear Default Protocol Pack button in the Preferences window.
 |
| Step 2 | Accept the
operation by clicking OK on the Protocol Pack Removal message screen.
 |
Verifying Version Compatibility for Protocol Packs
A protocol pack is compatible only with specific versions of the SCE application. When working with protocol packs, verify that the protocol pack version matches the SCE application version. For example, only use a protocol pack for 4.0.0 on SCE application version 4.0.0.
The version compatibility information for each protocol pack is included in the release notes of the protocol pack.
| Step 1 | Verify that the correct version of
servconf
is installed and running correctly.
The version of the utility should match that of the protocol pack. |
| Step 2 | Verify that the correct version of the SCE application is
installed.
The application version should match that of the protocol pack. |
| Step 3 | Verify that a service configuration (PQB) is applied to the SCE platform. |
Verifying the Installation of a Protocol Pack
| Step 1 | At the SCE platform CLI prompt (SCE#), type show version . |
| Step 2 | Press Enter . The response shows the version of the OS running on the SCE platform. This response includes information about the installed protocol pack version. |
| Step 3 | Retrieve the PQB from the SCE platform and view it using the Console. |
| Step 4 | Verify that the new protocols from the protocol pack were added to the service configuration. |
Causes for Protocol Pack Installation Failure and Remedies
The problems that may cause the installation of a protocol pack to fail and their remedies include:
- Missing or incorrect version of the JRE—Install the correct version of the JRE (see “Installing the Java Runtime Environment” section ).
- Incorrect or missing SCE application version on the SCE platform—Verify that the correct version of the SCE application is installed (see “How to Verify Version Compatibility for Protocol Packs” section ).
- No service configuration (PQB) is applied to the SCE platform—Create a new PQB and apply it using the Console.
- servconf failed to import the new signatures into the PQB—Use the --force-signature update signature option when running servconf (see “servconf Syntax” section).
When reporting problems to Cisco, include the servconf log file, located at <user.home>\.p-cube\servconf.log. With Windows, this usually maps to C:\Documents and Settings\<username>\.p-cube\servconf.log or C:\Users\<username>\.p-cube\servconf.log.
Hitless Upgrade of the SLI
Hitless upgrade is the Cisco SCA BB method of upgrading the software components that reside on the SCE platform without incurring any service downtime.
- Hitless upgrade of Protocol Packs is available on SCE 8000.
- Hitless upgrade of Protocol Packs is available on SCE 10000.
If hitless upgrade is enabled, classification, reporting, and control continue uninterrupted when you install an SPQI file (see Working with Protocol Packs section ). You can install SPQI files using either the Console or servconf, the Cisco SCA BB Service Configuration Utility. An SPQI file is a package that includes the required (SLI) files.
 Note | When you apply a new policy or during Protocol Pack upgrade, there is a delay of 30 seconds before the rules are applied to the new flows. |
After the new application is loaded on the SCE platform:
- The new application services all new flows and bundles.
- The old application continues to service existing flows (and new flows that belong to bundles of existing flows).
- Both applications share available memory.
Until all old flows die or are killed, the hitless upgrade is considered to be in progress. To make the hitless upgrade process bounded, you can set criteria that triggers the explicit killing of all flows still executing on the old application. Two such criteria exist:
- When a specified amount of time has passed since the process started.
- When the number of old flows goes below a specified threshold.
The default value for the first criterion is 60 (minutes); the default value for the second is zero (flows). This means that the replace operation is guaranteed to complete after no more than one hour (sooner, if all old flows die naturally). But the application does not kill any old flow before one hour completes.
These criteria are configurable by CLI commands.
You can initiate the explicit killing of all old flows using a manual command.
- Hitless Upgrade CLI Commands
- Description of Hitless Upgrade CLI Commands
- Entering Line Interface Configuration Mode
Hitless Upgrade CLI Commands
You can configure, monitor, and control hitless upgrade using the SCE platform Command-Line Interface (CLI). For more information about the SCE platform CLI, see the Cisco SCE 8000 CLI Command Reference. Cisco SCE 10000 CLI Command Reference.
Use the following CLI commands to configure the criteria for completing a hitless upgrade:
replace completion time <minutes>
no replace completion time
default replace completion time
replace completion num-flows <num>
no replace completion num-flows
default replace completion num-flows
These commands are line interface configuration commands. To run these commands you must enter line interface configuration mode and see the SCE(config if)# prompt displayed. For details on interface configuration mode, see How to Enter Line Interface Configuration Mode section.
The following two CLI commands are EXEC mode commands.
Use the following CLI command to monitor the progress of a hitless upgrade:
show applications slot <num> replace
Use the following CLI command to force immediate completion of a hitless upgrade:
application slot <num> replace force completion
Description of Hitless Upgrade CLI Commands
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
|
replace completion time <minutes> |
Sets the time criterion for killing all old flows and completing the hitless upgrade. Specifying a value of zero disables this criterion—the hitless upgrade is completed only when the number-of-flows criterion is met. |
|
no replace completion time |
Sets the time criterion for completing the hitless upgrade to zero. |
|
default replace completion time |
Resets the time criterion for completing the replace operation to the default value of 60. |
|
replace completion num-flows <num> |
Sets the number-of-flows criterion for completing the hitless upgrade operation. When the number of old flows drops below the number specified by this criterion, the remaining flows are killed and the hitless upgrade is complete. |
|
no replace completion num-flows |
Sets the number-of-flows criterion for completing the hitless upgrade to zero. |
|
default replace completion num-flows |
Resets the number-of-flows criterion for completing the hitless upgrade to the default value of zero. |
|
show applications slot <num> replace |
Shows the current hitless upgrade state: |
|
application slot <num> replace force completion |
Forces the current hitless upgrade process to complete (killing all old flows). |
Entering Line Interface Configuration Mode
Launching the Cisco SCA BB Console
| Step 1 | Choose Start
> All Programs > Cisco SCA > SCA BB Console
5.1.x > SCA BB Console
5.1.x.
The
Cisco SCA BB Console splash screen appears. After the Console has loaded, the
main window of the Console appears. The first time that you launch the Console,
the Welcome view is open in the main window.
 | ||
| Step 2 | Close the
Welcome view and click Go to the console .
The
Welcome view closes. The Network Navigator tool is open in the Console.
|
How to Use the Cisco SCA BB Console
The Console is the front end of Cisco SCA BB. You use it to configure the services that the SP offers to you.
The Console consists of the following tools:
- Network Navigator tool
- Service Configuration Editor tool
- Signature Editor tool
- Subscriber Manager GUI tool
- Anonymous Groups Manager GUI tool
The Console GUI has a menu bar and a standard toolbar. Underneath the toolbar is another bar that displays the button of any open Console tool. When you launch a tool, a button is added to this bar. To switch between open tools, click the appropriate button on the bar.

 Note | The title of the Console window shows the active tool and the active service configuration. |
The Welcome View of the Console links to a number of Configuration Wizards that can configure the initial, basic configuration of your system:
- Cisco SCA BB Configuration Wizards
- The Network Navigator Tool
- The Service Configuration Editor Tool
- The Signature Editor Tool
- The Subscriber Manager GUI Tool
- The Anonymous Group Manager Tool
- Online Help
Cisco SCA BB Configuration Wizards
The configuration wizards available from the Welcome view are (three of these wizards can also be executed from the Network Navigator tool):
- Usage Analysis wizard—Creates a simple model of devices and connects to them.
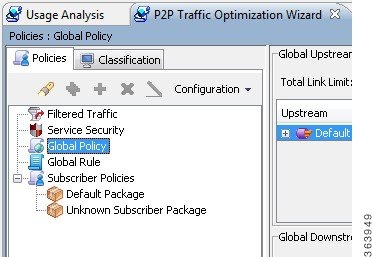
- The P2P Traffic
Optimization wizards:
- P2P Traffic Optimization wizard—Creates a simple model of devices, connects to them, and limits P2P traffic to a specified percentage of total available bandwidth.
- P2P Traffic Optimization at a Peering Point wizard—Creates a simple model of devices, connects to them, limits P2P traffic to a specified percentage of total available bandwidth, and allows you to enable asymmetric routing classification mode.
- Reporter database Configuration wizard—Connects the Cisco SCA BB Reporter tool to a database.
Asymmetric Routing
Traffic processing depends on the routing environment. The Cisco Service Control solution can operate in two typical routing schemes: symmetric and asymmetric. In asymmetric routing, for a significant number of flows, only one direction (inbound or outbound) is routed through the SCE platform.
Anonymous Subscriber Mode
Anonymous subscriber mode is a mode in which entities defined as IP addresses are treated as subscribers.
Using the Usage Analysis Wizard
The Usage Analysis wizard allows you to create a simple model of devices and connect to them.
 Note | If they do not exist, devices defined in the wizard are added to the default site in the Site Manager tree. |
| Step 1 | From the
Console main menu, choose
Help
> Welcome .
The
Welcome view opens.
 | ||||
| Step 2 | Click
Usage
Analysis Wizard.
| ||||
| Step 3 | Click
Next.
The SCE
IP Addresses page of the Usage Analysis wizard opens.
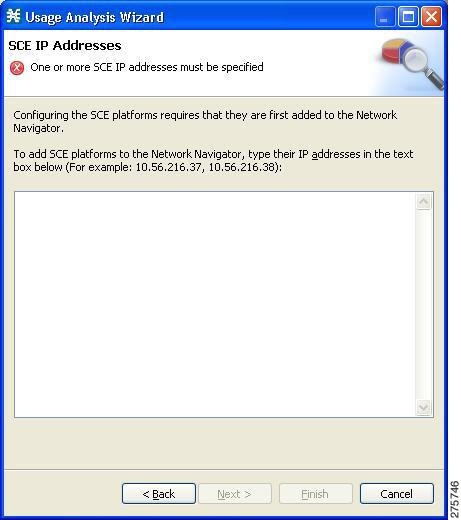 | ||||
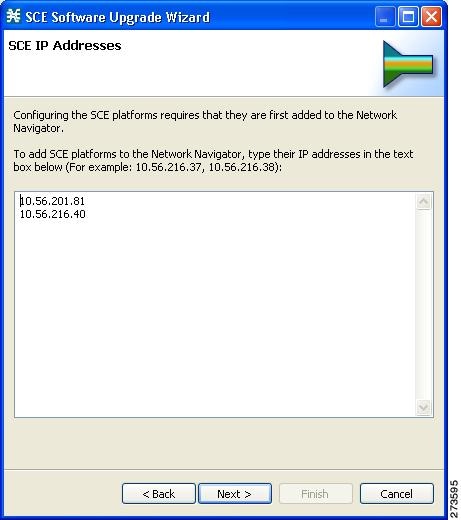
| Step 4 | In the edit
box, enter the IP addresses of the SCE devices that should be added to the
model.
If you started from the Network Navigator, the IP addresses of the SCE devices that you selected are displayed in the edit box. You can add additional addresses.
| ||||
| Step 5 | Click
Next.
The SCE
Usernames and Passwords page of the Usage Analysis wizard opens.
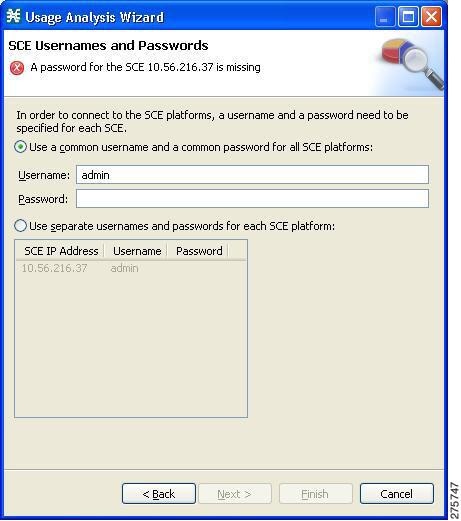 | ||||
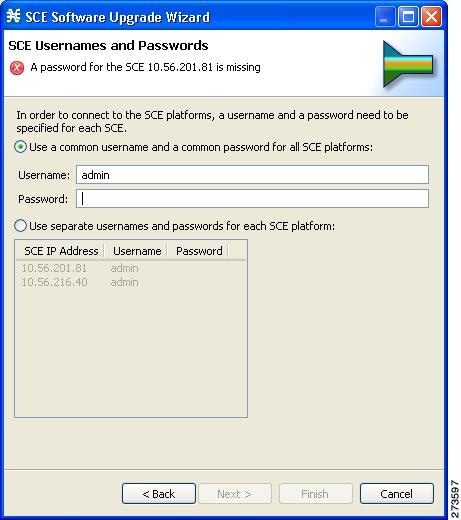
| Step 6 | Enter the
usernames and passwords for the SCE devices.
Do one of the following:
| ||||
| Step 7 | Click
Next.
The CM Setup page of the Usage Analysis wizard opens. 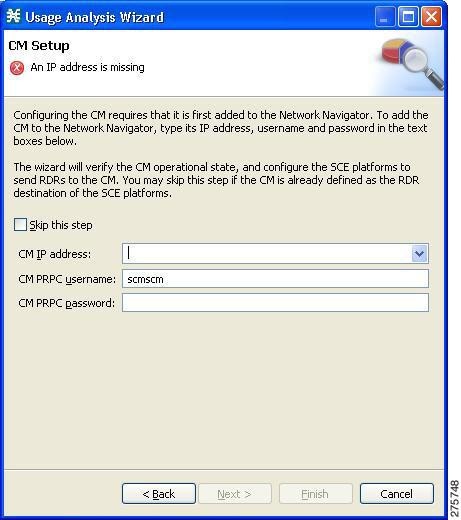 | ||||
| Step 8 | Define the SCSM
Collection Manager (CM) to use with this configuration.
Do one of the following:
If you started from the Network Navigator, this information is retrieved and displayed. You can modify these parameters.
| ||||
| Step 9 | Click
Next.
The Reporter Setup page of the Usage Analysis wizard opens. 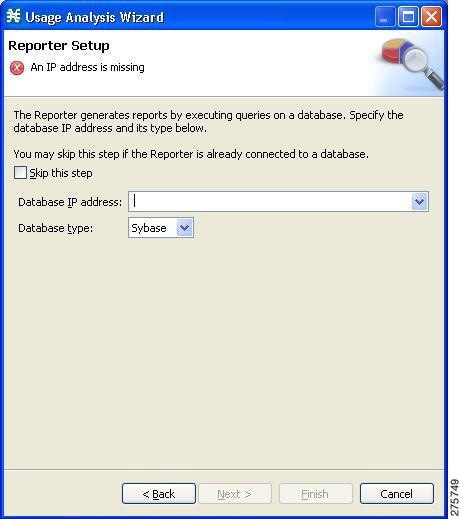 | ||||
| Step 10 | Define the
database to which the Reporter tool should connect.
Do one of the following:
If you started from the Network Navigator, this information is retrieved and displayed. You can modify these parameters.
| ||||
| Step 11 | Click
Next.
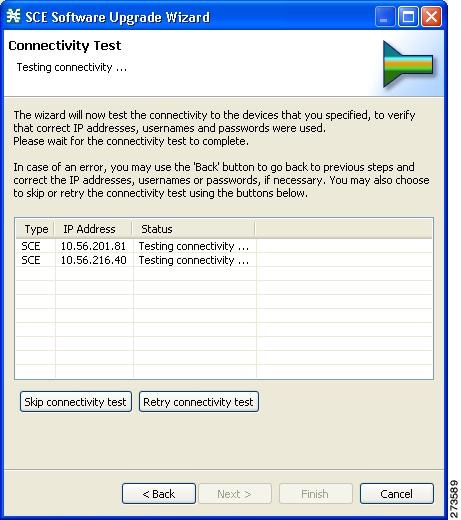
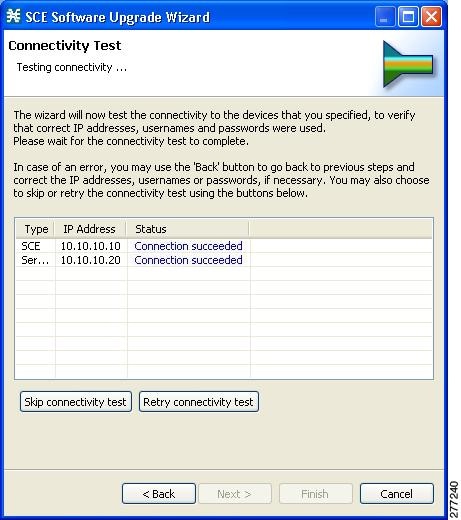
The Connectivity Test page of the Usage Analysis wizard opens. 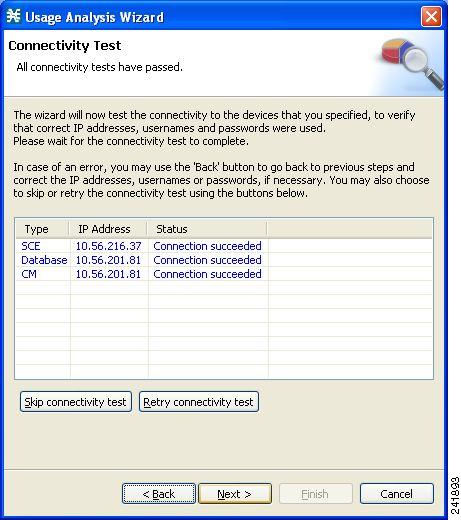 The wizard tests to see that the connections to the defined devices can be made.
| ||||
| Step 12 | Click
Next.
The Anonymous Subscribers page of the Usage Analysis wizard opens. 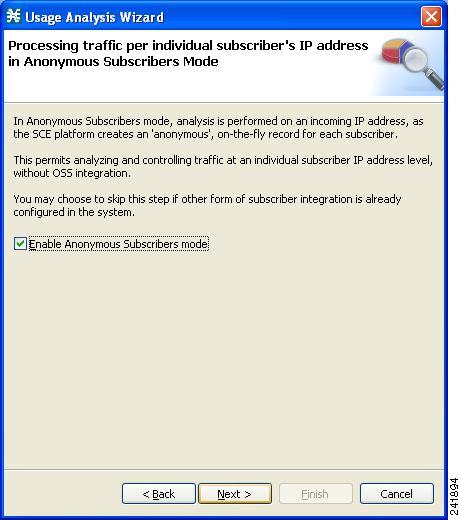 | ||||
| Step 13 | To disable anonymous subscriber mode, uncheck the Enable Anonymous Subscribers mode check box. | ||||
| Step 14 | Click
Next.
The Confirmation page of the Usage Analysis wizard opens . 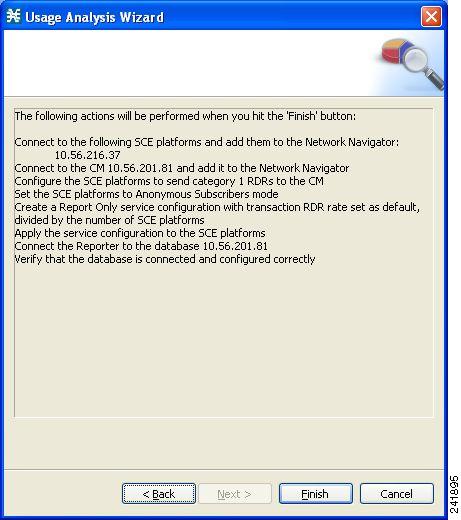 The actions that the wizard is about to take are listed on the page. | ||||
| Step 15 | Click
Finish.
The Configuration Output page of the Usage Analysis wizard opens. 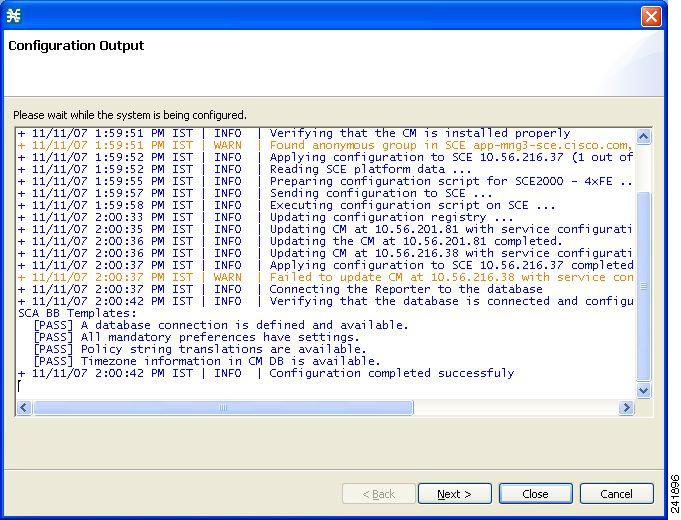 New devices are added to the default site of the Site Manager tree in the Network Navigator. 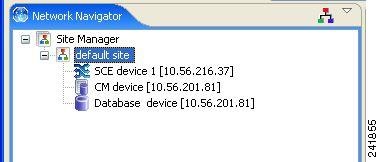 The wizard attempts to connect to all devices that you defined. The operation fails if:
If you defined a CM in Step 8, the SCE devices are configured so that the only category 1 RDR destination is the CM.
A new service configuration named Usage Analysis is created, and opens in the Service Configuration Editor. 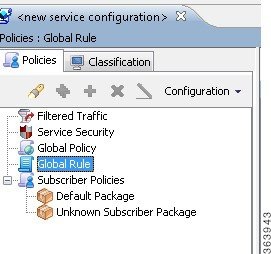 The service configuration has the following characteristics:
The service configuration is applied to the SCE devices. If you defined a database in Step 10:
| ||||
| Step 16 | If you did
not define a database in Step 10, click
Close.
The Usage Analysis wizard closes. Report instances of each of the four report types open in the Report View of the Reporter tool. |
Using the P2P Traffic Optimization Wizards
There are two wizards for optimizing P2P traffic:
- The P2P Traffic Optimization wizard allows you to create a simple model of devices, connect to them, and limit P2P traffic to a specified percentage of total available bandwidth.
- The P2P Traffic Optimization at a Peering Point wizard allows you to create a simple model of devices, connect to them, limit P2P traffic to a specified percentage of total available bandwidth, and enable asymmetric routing classification mode.
 Note | If they do not exist, devices defined in the wizard are added to the default site in the Site Manager tree. |
| Step 1 | From the
Console main menu, choose Help > Welcome .
The
Welcome view opens.
 | ||||
| Step 2 | Click P2P
Traffic Optimization Wizard or P2P Traffic Optimization for Asymmetrical
Routing Wizard .
The
Welcome page of the selected wizard appears.
| ||||
| Step 3 | Click Next .
The SCE
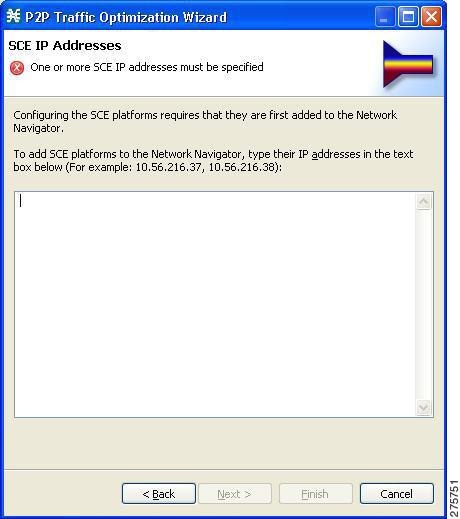
IP Addresses page of the P2P Traffic Optimization wizard opens
| ||||
| Step 4 | In the edit
box, enter the IP addresses of the SCE devices that should be added to the
model.
If you started from the Network Navigator, the IP addresses of the SCE devices that you selected are displayed in the edit box. You can add additional addresses.
| ||||
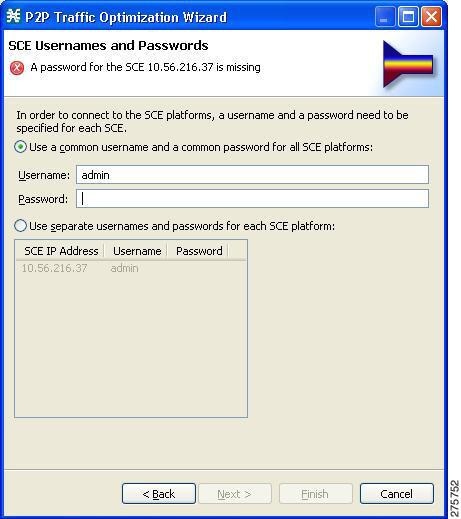
| Step 5 | Click Next .
The SCE
Usernames and Passwords page of the P2P Traffic Optimization wizard opens.
| ||||
| Step 6 | Enter the
usernames and passwords for the SCE devices.
| ||||
| Step 7 | Click Next .
The CM
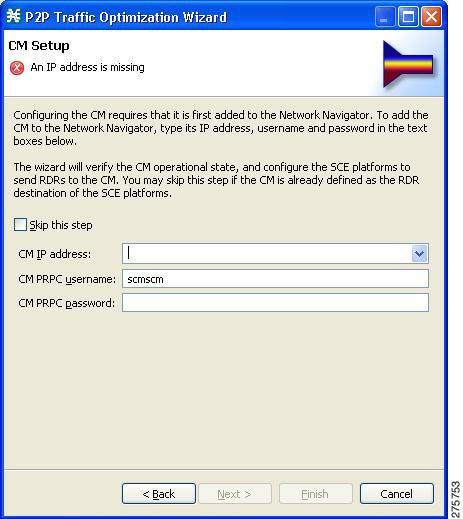
Setup page of the P2P Traffic Optimization wizard opens.
| ||||
| Step 8 | Define the
Cisco Service Control Collection Manager (CM) to use with this configuration.
| ||||
| Step 9 | Click
Next.
The
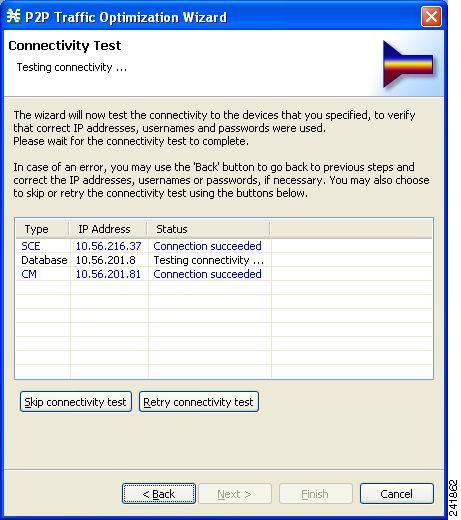
Connectivity Test page of the P2P Traffic Optimization wizard opens. The wizard
tests to see that the connections to the defined devices can be made.
| ||||
| Step 10 | Click Next .
The
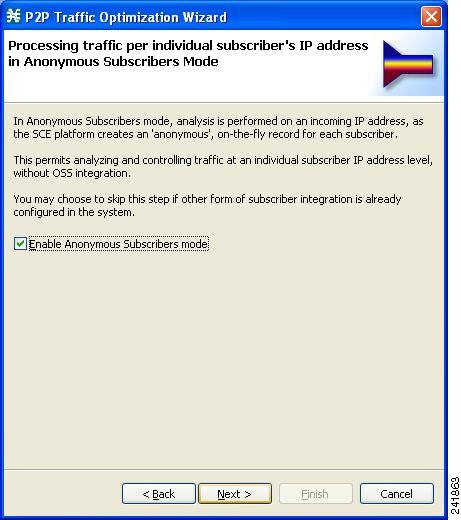
Anonymous Subscribers page of the P2P Traffic Optimization wizard opens.
| ||||
| Step 11 | To disable anonymous subscriber mode, uncheck the Enable Anonymous Subscribers mode check box. | ||||
| Step 12 | Click Next .
The
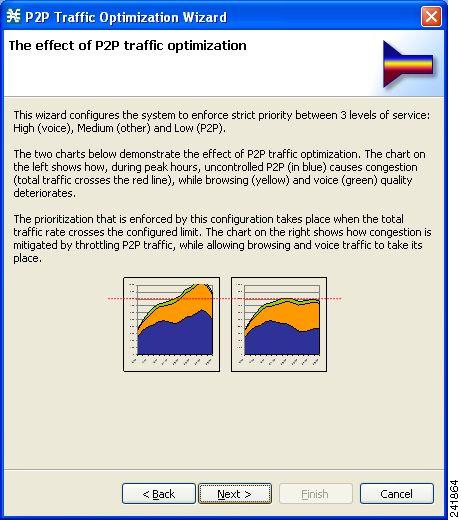
effect of P2P traffic optimization page of the P2P Traffic Optimization wizard
opens. This page explains why you should optimize (limit) P2P traffic.
| ||||
| Step 13 | Click Next .
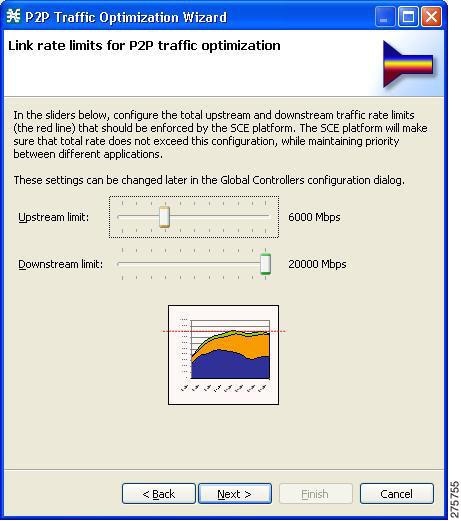
The Link
Rate Limits for P2P Traffic Optimization page of the P2P Traffic Optimization
wizard opens.
| ||||
| Step 14 | Use the sliders to configure the upstream and downstream link rate limits. The scale of each slider is the percentage of the aggregated bandwidth of both links. | ||||
| Step 15 | If you are running the P2P Traffic Optimization wizard, go to Step 20. If you are running the P2P Traffic Optimization for Asymmetrical Routing wizard, continue at the next step. | ||||
| Step 16 | Click Next .
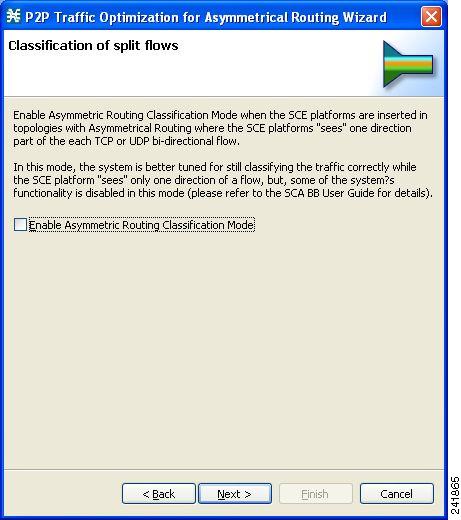
The
Classification of split flows page of the P2P Traffic Optimization wizard
opens.
| ||||
| Step 17 | To enable asymmetric routing classification mode, check the Enable Asymmetric Routing Classification Mode check box. | ||||
| Step 18 | Click Next .
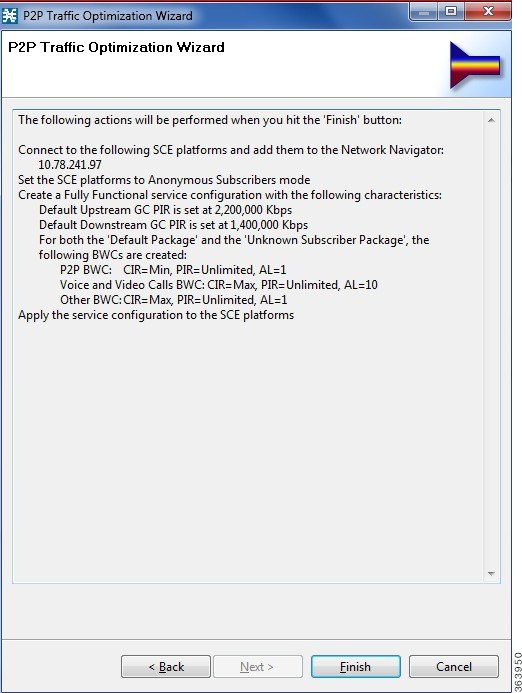
The
Confirmation page of the P2P Traffic Optimization wizard opens. The actions
that the wizard is about to take are listed on the page.
The actions that the wizard is about to take are listed on the page. For an explanation of the bandwidth controller parameters, see Subscriber BWC Parameters section . | ||||
| Step 19 | Click Finish
.
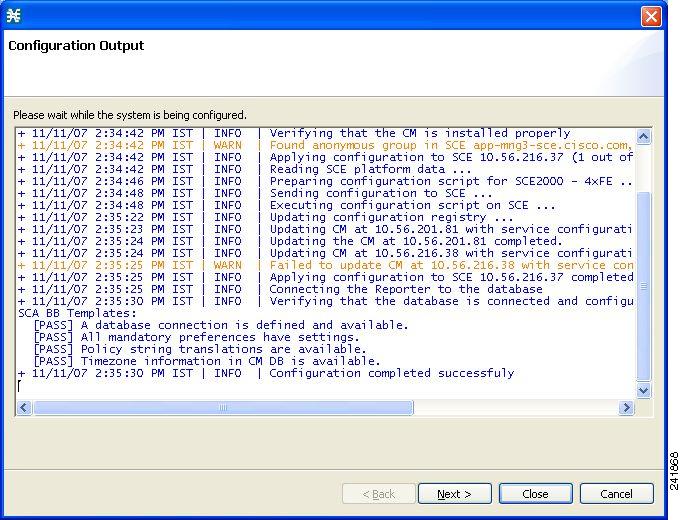
The
Configuration Output page of the P2P Traffic Optimization wizard opens. New
devices are added to the default site of the Site Manager tree in the Network
Navigator.
The wizard attempts to connect to all devices that you defined. The operation fails if:
If you defined a CM in Step 8, the SCE devices are configured so that the only category 1 RDR destination is the CM.
A new service configuration named P2P Traffic Optimization (or P2P Traffic Optimization for Asymmetrical Routing) is created, and opens in the Service Configuration Editor.
The service configuration has the following characteristics:
The service configuration is applied to the SCE devices. If you defined a database in Step 10: | ||||
| Step 20 | If you did
not define a database in Step 10, click
Finish.
The P2P Traffic Optimization wizard closes. Report instances of each of the four report types open in the Report View of the Reporter tool. |
The Network Navigator Tool
The Network Navigator is a tool that allows you to create and manage a simple model of all local and remote devices that are part of the Cisco Service Control solution.
For more information about the Network Navigator, see Using the Network Navigator section.
This section contains information about the following procedures:
Opening the Network Navigator Tool
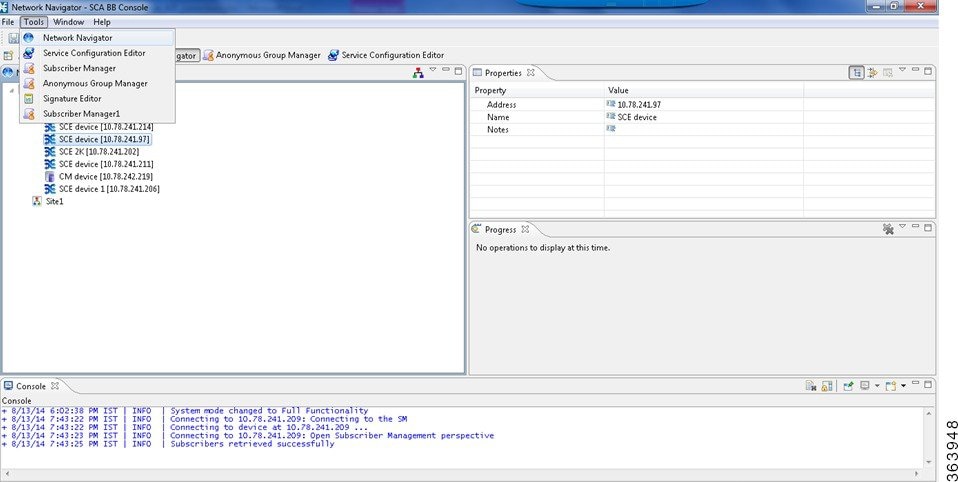 |
Closing the Network Navigator Tool
The Service Configuration Editor Tool
The Service Configuration Editor is a tool that allows you to create service configurations. A service configuration is a data structure that defines how the SCE platform analyses network traffic, what rules apply to the traffic, and what actions the SCE platform takes to enforce these rules.
Most of this document discusses using the Service Configuration Editor. See Using the Service Configuration Editor section .
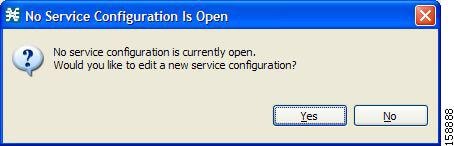
Opening the Service Configuration Editor Tool
| Step 1 | From the
Console main menu, choose
Tools
> Service Configuration Editor.
A No
Service Configuration Is Open dialog box appears.
| ||
| Step 2 | Click
Yes.
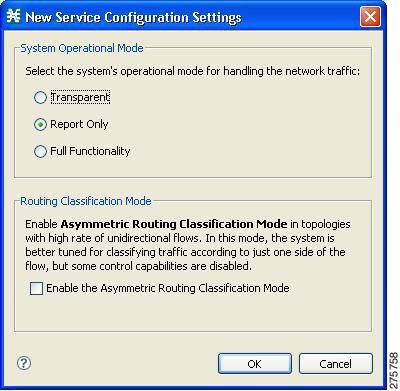
A New
Service Configuration Settings dialog box appears
| ||
| Step 3 | Select one of
the System Operational Mode radio buttons.
| ||
| Step 4 | (Optional, but
highly recommended if your system has a high proportion of unidirectional
flows) To switch to asymmetric routing classification mode, check the Enable
the Asymmetric Routing Classification Mode check box.
| ||
| Step 5 | Click
OK.
A
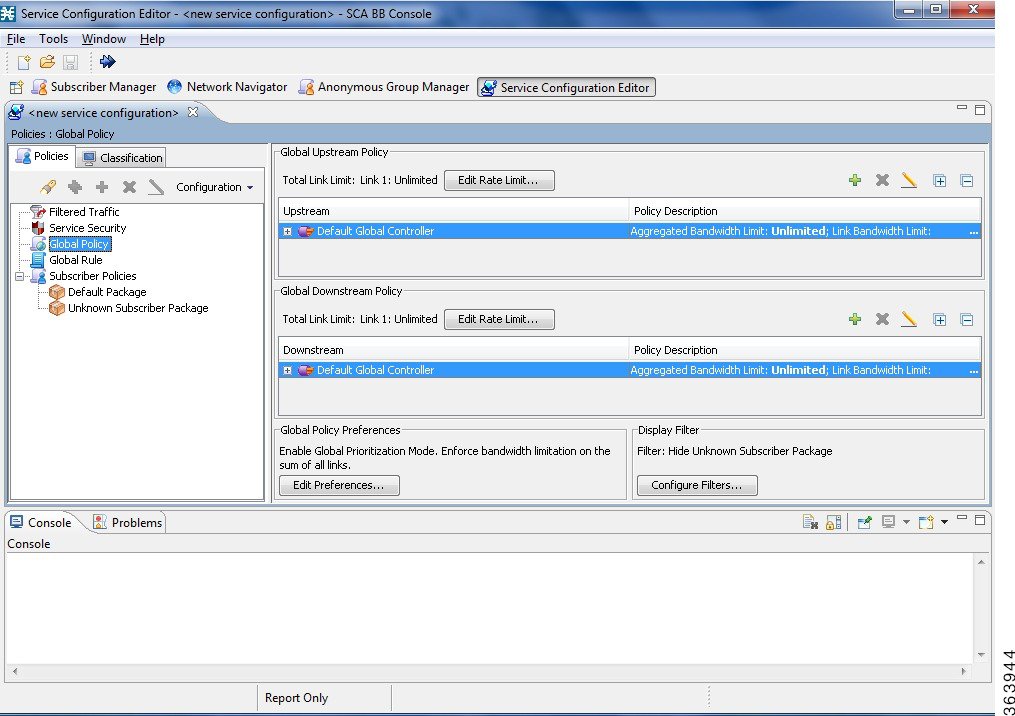
default service configuration opens in the Service Configuration Editor tool.
|
Closing the Service Configuration Editor Tool
The Signature Editor Tool
The Signature Editor is a tool that allows you to create and modify files that can add and modify protocols and protocol signatures in Cisco SCA BB.
For more information about the Signature Editor, see Using the Signature Editor section.
This section contains information about the following procedures:
Opening the Signature Editor Tool
|
Closing the Signature Editor Tool
The Subscriber Manager GUI Tool
The Subscriber Manager GUI is a tool that allows you to connect to a Cisco Service Control Subscriber Manager and then manage subscribers, assign packages to subscribers, edit subscriber parameters, and manually add subscribers.
For more information about connecting to a Cisco Service Control Subscriber Manager and using the Subscriber Manager GUI, see Using the Subscriber Manager GUI Tool section .
For more information about the Cisco Service Control Subscriber Manager, see the Cisco Service Control Management Suite Subscriber Manager User Guide.
This section contains information about the following procedures:
Opening the Subscriber Manager GUI Tool
|
Closing the Subscriber Manager GUI Tool
| Step 1 | Right-click the Subscriber Manager button. |
| Step 2 | From the popup menu that appears, select Close . |
The Anonymous Group Manager Tool
The Anonymous Group Manager GUI allows you to manage anonymous groups within a SCE. You can create, edit, delete anonymous groups, and list all configured groups for a selected SCE. For a selected group, the GUI lists all anonymous subscribers that are part of the group.
For more information, see Using the Anonymous Group Manager Tool section.
Opening the Anonymous Group Manager Tool
Closing the Anonymous Group Manager Tool
Online Help
You can access relevant parts of this user guide from the Console. The following sections provide you with the necessary details:
Accessing the Online Help
 |
Searching Online Help
| Step 1 | From the
Console main menu, choose Help > Search .
The Help
view opens next to the current tool.
| ||
| Step 2 | Enter a word,
phrase, or more complex search expression in the Search expression field.
The Go
button is enabled.
| ||
| Step 3 | Click Go . Help topics containing your search expression are listed under Local Help. | ||
| Step 4 | Click a help
topic to view its contents.
| ||
| Step 5 | By clicking the appropriate link at the bottom of the Help view, you can switch to: |
QuickStart with the Cisco SCA BB Console
This QuickStart section helps you get started with the Console. The section includes an example of using the Network Navigator tool and the Service Configuration Editor to apply the default service configuration to an SCE platform.
Configuring the Console and Applying the Default Service Configuration
| Step 1 | Launch the Console. Choose Start > All Programs > Cisco SCA > SCA BB Console 5.1.x > SCA BB Console 5.1.x. Here x stands for the version within 5. For example, 5.1.0 | ||
| Step 2 | If necessary, close the Welcome view. | ||
| Step 3 | Open the Network Navigator. | ||
| Step 4 | From the Console
main menu, choose
Tools
> Network Navigator.
This step
sets up the Console for network device operations. You should now be able to
see the default site displayed in the Network Navigator view.
| ||
| Step 5 | Add a Cisco SCE
device to the default site.
| ||
| Step 6 | Check the SCE
platform version and operational state.
| ||
| Step 7 | Open the Service
Configuration Editor.
| ||
| Step 8 | Create a new
service configuration.
| ||
| Step 9 | Apply the
service configuration to the SCE platform.
|




 Feedback
Feedback