- Introduction
- Cisco Service Control Solution Overview
- Cisco SCA BB System Overview
- Introduction to Traffic Processing
- Getting Started with Cisco SCA BB Console
- The Network Navigator
- Using the Service Configuration Editor
- Traffic Classification Using Service Configuration Editor
- Traffic Accounting and Reporting Using the Service Configuration Editor
- Traffic Control Using the Service Configuration Editor
- Service Configuration Editor: Additional Options
- Subscriber Manager GUI Tool
- Anonymous Group Manager GUI Tool
- The Signature Editor Overview
- Additional Management Tools and Interfaces
Cisco Service Control Application for Broadband (Cisco SCA BB) User Guide
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- February 17, 2015
Chapter: Cisco Service Control Solution Overview
Cisco Service Control Solution Overview
This chapter provides a general overview of the Cisco Service Control solution. It introduces the Cisco service control concept and capabilities.
It also briefly describes the hardware capabilities of the Cisco Service Control Engine (Cisco SCE) platform and the Cisco-specific applications that together compose the Cisco service control solution.
- Cisco Service Control Solution
- Cisco Service Control Capabilities
- Cisco SCE Platform Description
- Management and Collection
Cisco Service Control Solution
The Cisco service control solution is delivered through a combination of hardware and specific software solutions that address various service control challenges. Service providers can use the Cisco SCE platform to support classification, analysis, and control of Internet and IP traffic.
Service control enables service providers to:
- Capitalize on existing infrastructure.
- Analyze, charge for, and control IP network traffic at multigigabit wire line speeds.
- Identify and target high-margin content-based services and enable their delivery.
As the downturn in the telecommunications industry has shown, the business models of the IP Service Providers require rework to make them profitable. Having spent billions of dollars to build ever larger data links, providers have incurred massive debts and faced rising costs. At the same time, access and bandwidth have become commodities where prices continually fall and profits disappear. Service providers have realized that they must offer value-added services to derive more revenue from the traffic and services running on their networks.
Cisco service control solutions allow IP Service Providers to capture profits from IP Services through detailed monitoring, precise, real-time control, and awareness of services as they are delivered.
Service Control for Broadband Service Providers
Service providers of any access technology (DSL, cable, mobile, and so on) targeting residential and business consumers must find new ways to get maximum leverage from their existing infrastructure, while differentiating their offerings with enhanced IP Services.
The Cisco service control application for broadband adds a layer of service intelligence and control to existing networks that can:
- Report and analyze network traffic at subscriber and aggregate level for capacity planning
- Provide customer-intuitive tiered application services and guarantee application service level agreements (SLAs)
- Implement different service levels for different types of customers, content, or applications
- Identify network abusers who are violating the acceptable use policy (AUP)
- Identify and manage peer-to-peer traffic, NNTP (news) traffic, and spam abusers
- Enforce the AUP
- Integrate Service Control solutions easily with existing network elements and business support systems (BSS) and operational support systems (OSS)
Cisco Service Control Capabilities
The core of the Cisco service control solution is the network hardware device: the Cisco Service Control Engine (Cisco SCE). The core capabilities of the Cisco SCE platform, which support a wide range of applications for delivering service control solutions, include:
- Subscriber and application
awareness—Application-level drilling into IP traffic for real-time
understanding and controlling of usage and content at the granularity of a
specific subscriber.
- Subscriber
awareness—The ability to map between IP flows and a specific subscriber to
maintain the state of each subscriber transmitting traffic through the Cisco
SCE platform and to enforce an appropriate policy on this subscriber’s traffic.
Subscriber awareness is achieved either through dedicated integrations with subscriber management repositories, such as a DHCP or a RADIUS server, or through sniffing of RADIUS or DHCP traffic.
- Application
awareness—The ability to understand and analyze traffic up to the application
protocol layer (Layer 7).
For application protocols implemented using bundled flows (such as FTP, which is implemented using Control and Data flows), the Cisco SCE platform understands the bundling connection between the flows and treats them accordingly.
- Subscriber
awareness—The ability to map between IP flows and a specific subscriber to
maintain the state of each subscriber transmitting traffic through the Cisco
SCE platform and to enforce an appropriate policy on this subscriber’s traffic.
- Application-layer, stateful, real-time traffic control—The ability to perform advanced control functions, including granular bandwidth (BW) metering and shaping, quota management, and redirection, using application-layer, stateful, real-time traffic transaction processing. This feature requires highly adaptive protocol and application-level intelligence.
- Programmability—The ability
to add new protocols quickly and adapt to new services and applications in the
service provider environment. Programmability is achieved using the Cisco
Service Modeling Language (SML).
Programmability allows new services to be deployed quickly and provides an easy upgrade path for network, application, or service growth.
- Robust and flexible back-office integration—The ability to integrate with existing third-party systems at the service provider, including provisioning systems, subscriber repositories, billing systems, and OSS systems. The Cisco SCE provides a set of open and well-documented APIs that allows a quick integration process.
- Scalable high-performance service engines—The ability to perform all of these operations at wire speed.
Cisco SCE Platform Description
The Cisco SCE family of programmable network devices performs application-layer stateful-flow inspection of IP traffic, and controls the traffic based on configurable rules. The Cisco SCE platform devices use ASIC components and reduced instruction set computer (RISC) processors to exceed beyond packet counting and expand into the contents of network traffic.
The Cisco SCE platform devices:
- Are programmable.
- Provide stateful inspection of bidirectional traffic flows, and mapping these flows with user ownership.
- Provide real-time classification of network use. The classification provides the basis of the Cisco SCE platform advanced traffic-control and bandwidth-shaping functionality.
Where most bandwidth shaper functionality ends, the Cisco SCE platform provides further control and shaping options, including:
- Layer 7 stateful wire-speed packet inspection and classification
- Robust support for more than
600 protocols and applications, including:
- General—HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, Telnet, Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP), Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), Post Office Protocol 3 (POP3), Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP), Wireless Application Protocol (WAP), and others
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) file sharing—FastTrack-KazaA, Gnutella, BitTorrent, Winny, Hotline, eDonkey, DirectConnect, Piolet, and others
- P2P VoIP—Skype, Skinny, DingoTel, and others
- Streaming and Multimedia—Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP), Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), HTTP streaming, Real Time Protocol (RTP) and Real Time Control Protocol (RTCP), and others
- Programmable system core for flexible reporting and bandwidth control
- Transparent network and BSS and OSS integration into existing networks
- Subscriber awareness that relates traffic and usage to specific customers
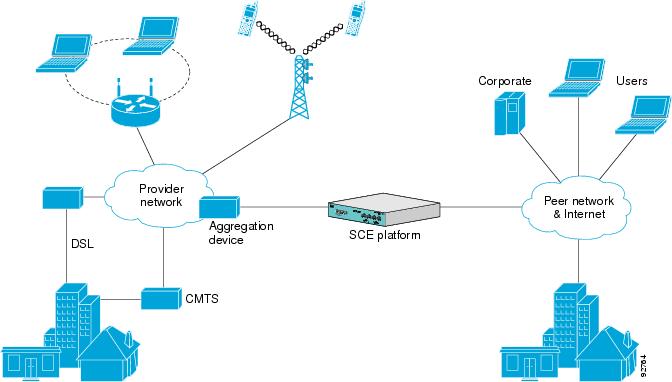
Management and Collection
The Cisco service control solution includes a complete management infrastructure that provides the following management components to manage all aspects of the solution:
These management interfaces are designed to comply with common management standards and to integrate easily with existing OSS infrastructure.
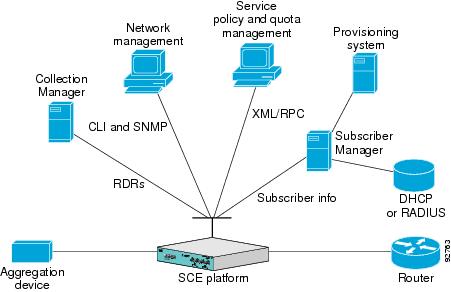
Network Management
The Cisco service control solution provides complete network Fault, Configuration, Accounting, Performance, Security (FCAPS) Management.
Two interfaces provide network management:
- Command-line interface (CLI)—Accessible through the Console port or through a Telnet connection, the CLI is used for configuration and security functions.
- SNMP—Provides fault management (through SNMP traps) and performance-monitoring functionality.
Subscriber Management
Where the Cisco service control application for broadband (Cisco SCA BB) enforces policies on different subscribers and tracks usage on an individual subscriber basis, the Cisco Service Control Subscriber Manager may be used as middleware software for bridging between OSS and Cisco SCE platforms. Subscriber information is stored in the Subscriber Manager database and can be distributed between multiple platforms according to actual subscriber placement.
The Subscriber Manager provides subscriber awareness by mapping network IDs to subscriber IDs. It can obtain subscriber information using dedicated integration modules that integrate with AAA devices, such as RADIUS or DHCP servers.
Subscriber information may be obtained in one of two ways:
- Push Mode—The Subscriber Manager pushes subscriber information to the Cisco SCE platform automatically upon logon of a subscriber.
- Pull Mode—The Subscriber Manager sends subscriber information to the Cisco SCE platform in response to a query from the Cisco SCE platform.
Service Configuration Management
Service configuration management is the ability to configure the general service definitions of a service control application. A service configuration file containing settings for traffic classification, accounting and reporting, and control is created and applied to a Cisco SCE platform. The Cisco SCA BB application provides tools to automate the distribution of these configuration files to Cisco SCE platforms. This standards-based approach makes it easy to manage multiple devices in a large network.
Service Control provides a GUI to edit and create these files and a complete set of APIs to automate their creation.
Data Collection
Data collection occurs as follows:
- Cisco SCE Platform analyzes and process the data passing through it and generates Raw Data Records (RDRs).
- Cisco SCE Platform then
forwards these RDRs to Cisco service control management suite collection
manager using a simple TCP-based protocol (RDR-Protocol).
The collection manager software is an implementation of a collection system that receives RDRs from one or more Cisco SCE platforms.
- The collection manager
collects these records and processes them in one of its adapters. Each adapter
performs a specific action on the RDR.
RDRs contain various information and statistics, depending on the configuration of the system. The main categories of RDRs include:
- Transaction RDRs—Records generated for each transaction , where a transaction is a single event detected in network traffic. The identification of a transaction depends on the particular application and protocol.
- Subscriber Usage RDRs—Records generated per subscriber, describing the traffic generated by that subscriber for a defined interval.
- Link RDRs—Records generated per link, describing the traffic carried on the link for a defined interval.
- Zone RDRs—Records generated per zone, describing the traffic carried on the zone for a defined interval.
 Feedback
Feedback