- Managing Cisco NFVI
- Cisco VIM REST API
- Monitoring Cisco NFVI Performance
- Managing Cisco NFVI Security
- Managing Cisco NFVI Storage
- Overview to Cisco VIM Insight
- Managing Cisco VIM through Insight
- Managing Blueprints
- Managing Pod Through Cisco VIM Insight
- Day 2 Operations of Cisco VIM Insight
- Overview to the Cisco Virtual Topology System
- Managing Backup and Restore Operations
- Troubleshooting
Managing Backup and
Restore Operations
The following topics describe Cisco NFVI management node backup and restore operations.
Managing Backup and Restore Operations
The management node hosts critical services such as Cisco VIM REST API, Cobbler for PXE, ELK for Logging/Kibana dashboard, and VMTP for cloud validation in Cisco VIM.
The management node is not redundant during the initial Cisco VIM offering, hence it is recommended to take backup of the management node. Using the saved management node information, you can restore the management node if you are facing any issues with the platform.
- Backing up the Management Node
- Backup with Forwarding ELK logs to External Syslog Server
- Backing up VIM Insight
Backing up the Management Node
An administrator must maintain the number of back up snapshots on the management node. The backup of the management node is possible only after complete deployment of at least one Cisco VIM. Two copies of backup directories are maintained at the management node itself and the older copy will be overwritten when a next backup is performed.
During the backup operation, activities such as pod management, software update or upgrade, and addition or deletion or replacement of nodes cannot be performed.
The REST API and ELK services are stopped during the backup operation, the OpenStack logs are cached on the control, compute, and storage nodes till the restoration of the management node is completed.
As part of the backup operation, two files are created: .backup_files and .backup_hash. .backup_files is a list of files that are backed up, while the second one is the hash. These two files are placed under the backup directory /var/cisco/backup_<tag>_<date-time> at the management node and also at the /var/cisco/ directory of all three controllers. These two files are used during the restore validation. When user attempt to restore from a particular backup, these two files within this backup are compared to those at the controllers. If there is any discrepancy, the restore validation will fail and user will be prompted to either terminate the restore operation or continue despite the validation failure. Only one copy of the .backup_files and .backup_hash are kept at the controllers, that is every time a new backup is created, these two files are overwritten with the most recent ones. Hence the restore validation will only pass when the latest backup is used for restore.
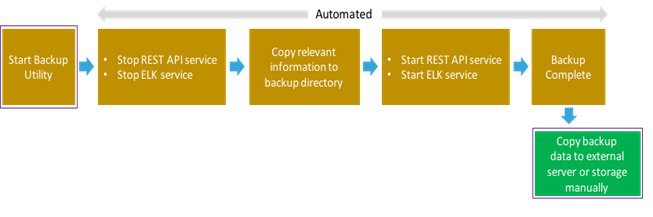
What to Do Next
The backup operation takes approximately 30 minutes and creates the backup_<tag>_<date-time> directory in the /var/cisco/ path.
Copy the directory to a remote server to recover the management node using rsync.
For example, to copy the backup directory to the remote server 20.0.0.5 /var/cisco/directory , execute the following command sequence:
rsync -e ssh -rtvpX --numeric-ids /var/cisco/backup_2017-01-09_14-04-38 root@20.0.0.5:/var/cisco/
 Note | On the remote server, protect the backup directory for any unauthorized access as the backup files may contain sensitive information |
At the remote server, change directory to where the backup directory is copied to; in this example /var/cisco/backup_<tag>_<date-time>/.
To verify if the backup is not corrupted or modified, execute ./check_integrity.
Check_integrity depends on the following packages, they should be installed on the server where check_integrity is executed.
python-prettytable python-jinja2 python-babel python-markupsafe python-setuptools pytz
Backup with Forwarding ELK logs to External Syslog Server
When the feature Forwarding ELK logs to External Syslog Server is enabled, during the backup process, in both the auto-backup and manual backup, the ELK logs are not collected. For manual backups, user can override by appending the -a or --add-elk option to the backup command. The -s or --skip-elk option is to skip the ELK logs collection regardless of the forwarding feature is enabled or not.
# cd installer/tools/mgmt
# ./mgmt_node_backup.py --help
Usage: ./mgmt_node_backup.py [options]
Options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-s, --skip-elk do not collect ELK logs during backup
-a, --add-elk force to also collect ELK logs on backup
Backing up VIM Insight
Administrator maintains the backup for Insight on the management node. The backup of the Insight is done only after the complete deployment of the Insight bootstrap. Only two copies of backup directory are maintained at the management node. The older copy will be overwritten when a next Insight backup/autobackup takes place.
Insight backup is stored at default backup location /var/cisco/insight_backup/insight_backup_<release_tag>_<date>_<time>. If a user wants to take a backup of Insight at a different location use -backupdir/-b option from bootstrap_insight; details of which are provided later in this section.
Insight UI will also trigger an autobackup whenever it detects an operation relating to MySQL database entry to preserve the latest state of Insight.
 Note | Insight backup is not allowed after an update. Update is an intermediate stage between rollback and commit. Any change made relating to MySQL database entry after an update from Insight UI will not be backed up. |
- Autobackup Insight
- Backup Insight at default backup location
- Backup Insight at user defined backup location
Autobackup Insight
If there is a change, Insight Installation will automatically run a daemon process to take the autobackup.
Live status of the process is determined by checking the log located at "/var/log/insight/insight_autobackup/insight_autobackup.logs" or systemctl status insight-autobackup.
 Note | Max of 10 log files of size 1024*1024 are maintained in the directory. |
Following are the scenarios where autobackup is initiated:
|
Insight Operation |
Auto-backup Performed |
|---|---|
|
Adding/Deleting POD |
Yes |
|
Changing POD REST Password and Certificate |
Yes |
|
Add/Edit/Delete all types of users |
Yes |
|
Add/Edit/Delete Roles |
Yes |
|
Modify User and Role association |
Yes |
|
Revoking/Adding user permission |
Yes |
|
Login/Logout |
No |
|
Context Switching |
No |
|
Change User Password |
Yes |
Backup Insight at default backup location
Backup Insight at user defined backup location
What to Do Next
Copy the backup directory to a remote server using rsync to recover the Insight later. We recommend you to copy backup dir using rsync as it preserves the permissions of the files.
For example, to copy the backup directory to the remote server 20.0.0.5 /var/cisco/insight_backup/directory , execute the following command sequence: .
rsync -e ssh -rtvpX --numeric-ids /var/cisco/insight_backup/insight_backup_2.1.5_2017-01-09_14-04-38 root@20.0.0.5:/var/cisco/insight_backup/
On the remote server, protect the backup directory for any unauthorized access, as the backup files may contain sensitive information
Restoring the Management Node
As an administrator, you have to re-image the management node with the same ISO version when the backup is performed, before initiating the restore operation. Restore will fail when there is a version mismatch.
 Note | Version checking is available only for offline installation. |
As part of the restore operation, system checks for management node's IP address information to match the prior configuration. Logs are cached on the control, compute and storage nodes from the moment of the management node fails until its restoration.
If you are using Cisco VIM Insight (in Tech Preview), in the same management node, you will have to re-bootstrap it for installation. During installation, RBAC and Pod registration information will be lost, hence it is advised to make a note of the RBAC and Pod information.

Ensure that you have the br_mgmt and br_api IP addresses of the failed management node.
Management Node Auto-backup
After the successful completion of certain Pod management operations, a backup of the management node is performed automatically. Only one copy of the auto-backup directory is kept at /var/cisco/ at any given time. The directory format is autobackup_<tag>_<timestamp>
Below is a list of operations:
-
Fresh install of Cisco VIM
-
Commit an update
-
Replace controller
-
Add or Remove compute nodes
-
Add or Remove storage node
-
Reconfigure
-
NFVIMON
Enabling or disabling the variable auto-backup, is defined in the setup_data.yaml file. It is enabled by default.
Add the following setup-data.yaml file snippet:
##################################################### # AutoBackup configuration ##################################################### #Default is True #autobackup: True or False
| POD operation | Auto-backup performed |
| Update | No |
| Rollback | No |
| Commit | Yes |
| Update fail with auto rollback | No |
After successful auto-backup directory creation, user can copy it to an external server for later restoration as mentioned in Managing Backup and restore Operations.
During the auto backup, if Forwarding ELK logs to External Syslog server option is enabled, the ElasticSearch database will not be maintained and the ELK logs will not be recovered after restoring the management node.
 Feedback
Feedback