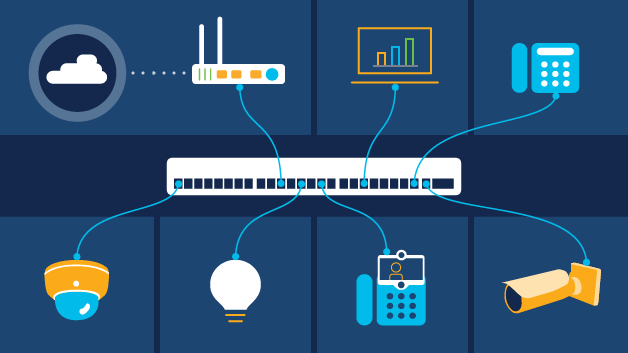
What is Power over Ethernet (PoE)?
PoE refers to the ability to provide low-voltage (less than 100W), direct current (DC) electrical power to network devices via the same twisted-pair copper Ethernet cables that are used to transmit data. This eliminates the need for a separate AC power source and allows for more flexible placement options, without concern for proximity to a power outlet.
PoE is a low-cost, reliable, and flexible approach to powering smart devices in a network. It is crucial to enabling smart buildings and their ecosystems of network-connected devices such as lighting, window shades, sensors, HVAC controllers, cameras, and security systems.
What are the benefits of PoE lighting?
Using PoE to power low-voltage DC-powered LED lighting has many benefits over both traditional lighting options (incandescent, fluorescent and CFL, and halogen) and newer AC-powered LED options.
Using low-voltage LED lighting alone can offer a dramatic reduction in energy required per lumen compared to incandescent and halogen equivalents. But using PoE to power and connect lighting has several significant advantages. It can:
- Reduce up-front construction costs and time to completion when used for cabling, installation, and configuration. There is also a dramatic reduction in carbon footprint, since no conduit or high-voltage copper wiring need to be installed.
- Lower capital expenditures, labor, and materials costs related to construction and maintenance.
- Allow for greater flexibility in design and placement.
- Enable the optimization and quantification of energy consumption by using the building's network as a sensor and interconnecting shades. This saves money and reduces carbon footprint.
- Require less energy, run cooler, and be a smaller form factor since no AC/DC transforming or transformer is required.
- Use pervasive 90W Cisco Universal Power Over Ethernet (UPOE+) to power, monitor, and control LED lighting, IoT devices, and centralized and automated environmental controls.
- Improve lighting through automation. Personalized environments can attract tenants and increase revenue per square foot.
What is LED lighting?
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current is passed through it in a process called electroluminescence.
The wavelength of the light produced—and hence the color—depends on the type of semiconductors used. White light has been traditionally the only option, but the use of gallium nitride (GaN)-based LEDs has significantly expanded the palette of colors available. It has also enhanced the ability to adjust brightness and change colors in real time, opening many new possibilities and applications.
Different semiconductor materials with different bandgaps produce different colors of light. The precise wavelength/color can be tuned by altering the composition of the light-emitting (active) region.
The main semiconductor materials used to manufacture LEDs are:
- Indium gallium nitride (InGaN): Used in blue, green, and ultraviolet high-brightness LEDs.
- Aluminum gallium indium phosphide (AlGaInP): Used in yellow, orange, and red high-brightness LEDs.
- Aluminum gallium arsenide (AlGaAs): Used in red and infrared LEDs.
- Gallium phosphide (GaP): Used in yellow and green LEDs.
What are the advantages of LED lighting?
Low-voltage LED lighting can offer a dramatic reduction in energy required per lumen when compared to incandescent, halogen metal halide, and fluorescent equivalents. In fact, LED lighting is 30 percent more efficient than even the most efficient alternative, T8 fluorescent.