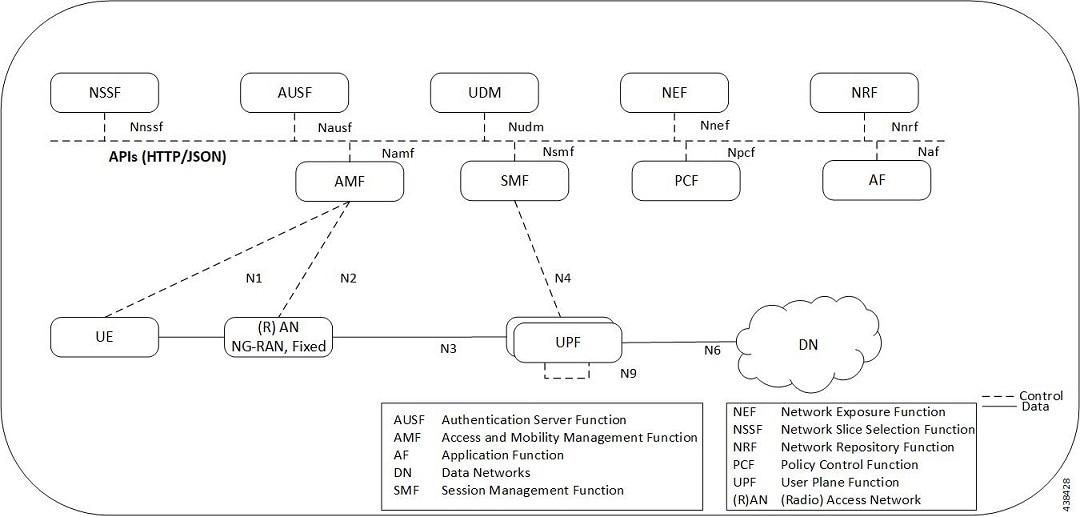
The following diagram illustrates, at a high-level, the deployment architecture of UPF along with other NFs.
Virtualized Packet Core—Single Instance (VPC-SI)
VPC-SI consolidates the operations of physical Cisco ASR 5500 chassis running StarOS
into a single Virtual Machine (VM) able to run on commercial off-the-shelf (COTS)
servers. VPC-SI can be used as a stand-alone single VM within an enterprise, remote
site, or customer data center. Alternatively, VPC-SI can be integrated as a part of
a larger service provider orchestration solution.
VPC-SI only interacts with supported hypervisors KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine)
and VMware ESXi. It has little or no knowledge of physical devices.
The UPF functions as user plane node in 5G-based VNF deployments. UPF is deployed as
a VNFC running a single, stand-alone instance of the StarOS. Multiple UPF VNFCs can
be deployed for scalability based on your deployment requirements.
Hypervisor Requirements
VPC-SI has been qualified to run under the following hypervisors:
-
Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) - QEMU emulator 2.0. The VPC-SI StarOS
installation build includes a libvirt XML template and ssi_install.sh for VM
creation under Ubuntu Server14.04.
-
KVM - Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.2: The VPC-SI StarOS installation build
includes an install script called qvpc-si_install.sh.
-
VMware ESXi 6.7: The VPC-SI StarOS installation build includes OVF (Open
Virtualization Format) and OVA (Open Virtual Application) templates for VM
creation via the ESXi GUI.
vNIC Options
The supported vNIC options include:
-
VMXNET3—Paravirtual NIC for VMware
-
VIRTIO—Paravirtual NIC for KMV
-
ixgbe—Intel 10 Gigabit NIC virtual function
-
enic—Cisco UCS NIC
-
SR-IOV—Single-root input/output virtualization
The SR-IOV specification provides a mechanism by which a single root function (for
example, a single Ethernet port) can appear to be multiple separate physical
devices. Intel 82599 10G is an SR-IOV capable device and can be configured (usually
by the Hypervisor) to appear in the PCI configuration space as multiple functions
(PFs and VFs). The virtual functions (VFs) can be assigned to Nova VMs, causing
traffic from the VMs to bypass the Hypervisor and go directly to the fabric
interconnect. This feature increases traffic throughput to the VM and reduces CPU
load on the UCS Servers.
Capacity, CEPS and Throughput
Sizing a VPC-SI instance requires modeling of the expected call model.
Many service types require more resources than others. Packet size, throughput per
session, CEPS (Call Events per Second) rate, IPSec usage (site-to-site, subscriber,
LI), contention with other VMs, and the underlying hardware type (CPU speed, number
of vCPUs) will further limit the effective number of maximum subscribers.
Qualification of a call model on equivalent hardware and hypervisor configuration is
required.
Sample VPP Configuration
For 5G-UPF, the FORWARDER_TYPE is "vpp".
The following is a sample output of VPP configuration.
show cloud configuration
Thursday January 30 12:18:10 UTC 2020
Card 1:
Config Disk Params:
-------------------------
FORWARDER_TYPE=vpp
VNFM_INTERFACE=MAC:fa:11:3e:22:d8:33
MGMT_INTERFACE=MAC:fa:11:3e:44:af:9e
VNFM_IPV4_ENABLE=true
VNFM_IPV4_DHCP_ENABLE=true
SERVICE1_INTERFACE=MAC:fa:11:3e:11:9d:23
SERVICE2_INTERFACE=MAC:fa:11:3e:99:ec:7b
VPP_CPU_WORKER_CNT=8
VPP_DPDK_TX_QUEUES=9
VPP_DPDK_RX_QUEUES=8
CHASSIS_ID=xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Local Params:
-------------------------
No local param file available

Note |
For additional information about VPC-SI build components, boot parameters,
configuring VPC-SI boot parameters, VM configuration, vCPU and vRAM options, VPP
configuration parameters, and so on, refer the VPC-SI System
Administration Guide.
|
UPF Deployment with VPC-SI
For additional information on VPC-SI, supported operating system and hypervisor
packages, platform configurations, software download and installation, as well as
UPF deployment, contact your Cisco Account representative.
For information on Release Package, refer the corresponding Release Notes included
with the build.
UPF Deployment with SMI Cluster Manager
The Ultra Cloud Core Subscriber Microservices Infrastructure (SMI) provides a run
time environment for deploying and managing Cisco's cloud native network functions
(cNFs), also referred to as applications.
It is built around open source projects like Kubernetes (K8s), Docker, Helm, etcd,
confd, and gRPC, and provides a common set of services used by deployed cNFs.
The SMI is a layered stack of cloud technologies that enable the rapid deployment of,
and seamless life cycle operations for microservices-based applications.
The SMI stack consists of SMI Cluster Manager that creates the Kubernetes (K8s)
cluster and the software repository. The SMI Cluster Manager also provides ongoing
Life Cycle Management (LCM) for the cluster including deployment, upgrades, and
expansion.
The SMI Cluster Manager leverages the Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM)—a
virtualization technology—to deploy the User Plane Function (UPF) VMs.
For more information, refer the UCC SMI Operations Guide.


 Feedback
Feedback