Architectural Overview
The Ultra Cloud Core is Cisco's solution supporting 3GPP's standards for 5G new radio (NR) standalone (SA) mode. These standards define various network functions (NFs) based on the separation of control plane (CP) and user plane (UP), such as CUPS. This separation enhances network performance and capabilities.
Control Plane Network Functions
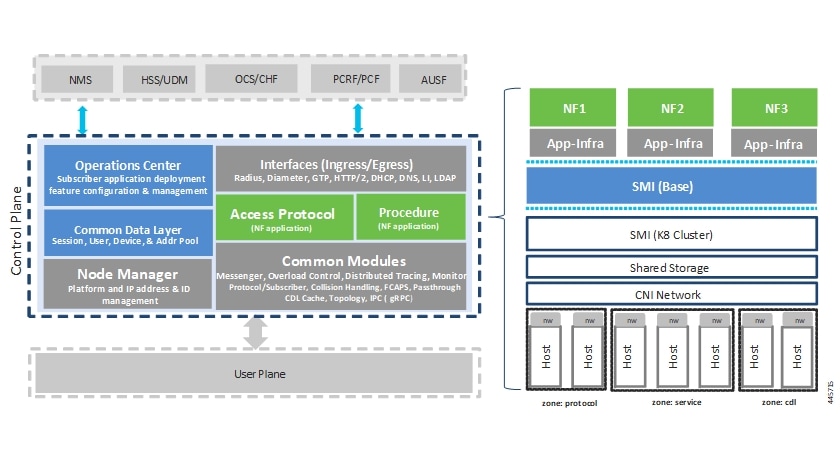
The Ultra Cloud Core's CP-related NFs use a common architecture with the following tenets:
-
Cloud-scale—Fully virtualized for simplicity, speed, and flexibility.
-
Automation and orchestration—Optimized operations, service creation, and infrastructure.
-
Security—Multiple layers of security across the deployment stack from the infrastructure through the NF applications.
-
API exposure—Open and extensive for greater visibility, control, and service enablement.
-
Access agnostic—Support for heterogeneous network types (for example 5G, 4G, 3G, Wi-Fi, and so on).
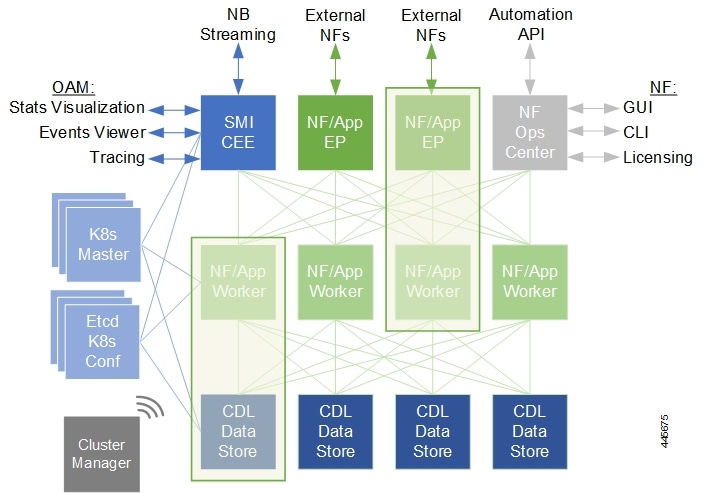
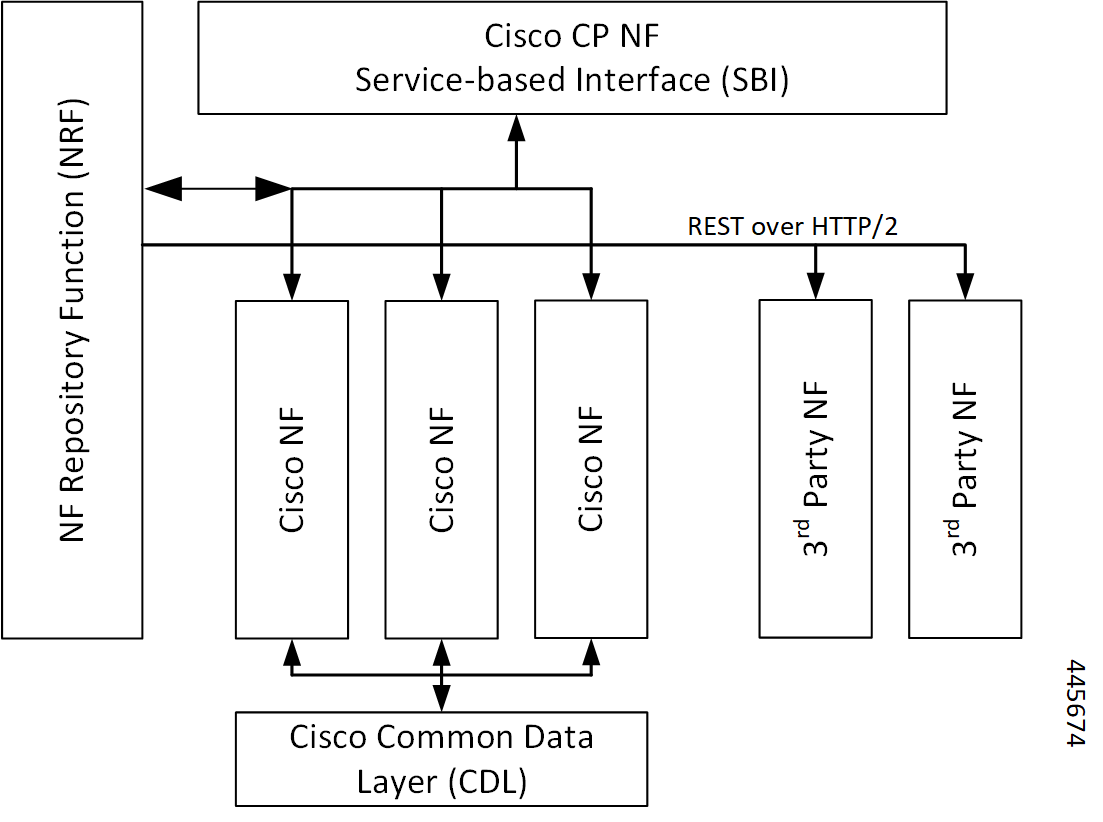
Control plane NFs are designed as containerized applications, such as microservices. They deploy through the Subscriber Microservices Infrastructure (SMI).
The SMI defines the common application layers for functional aspects of the NF such as life-cycle management (LCM), operations and management (OAM), and packaging.
User Plane Network Function
The 5G UP NF within the Ultra Cloud Core is the User Plane Function (UPF). Unlike the CP-related NFs, The 5G UPF uses the same Vector Packet Processing (VPP) technology as the Cisco 4G CUPS architecture. This commonality delivers a consistent set of capabilities between 4G and 5G, such as:
-
Ultrafast packet forwarding.
-
Extensive integrated IP Services such as Subscriber Firewall, Tethering, Deep-Packet Inspection (DPI), Internet Content Adaption Protocol (ICAP), Application Detection and Control (ADC), and header enrichment (HE).
-
Integrated third-party applications for traffic and TCP optimization.

 Feedback
Feedback