Overview of IoT Service (Wired)
Cisco Spaces enables end-to-end wired and wireless IoT device management, monitoring, and business outcome delivery at an enterprise scale using the following:
-
Cisco Spaces: IoT Service
-
Cisco Spaces: IoT Device Marketplace
-
Cisco Spaces App Center
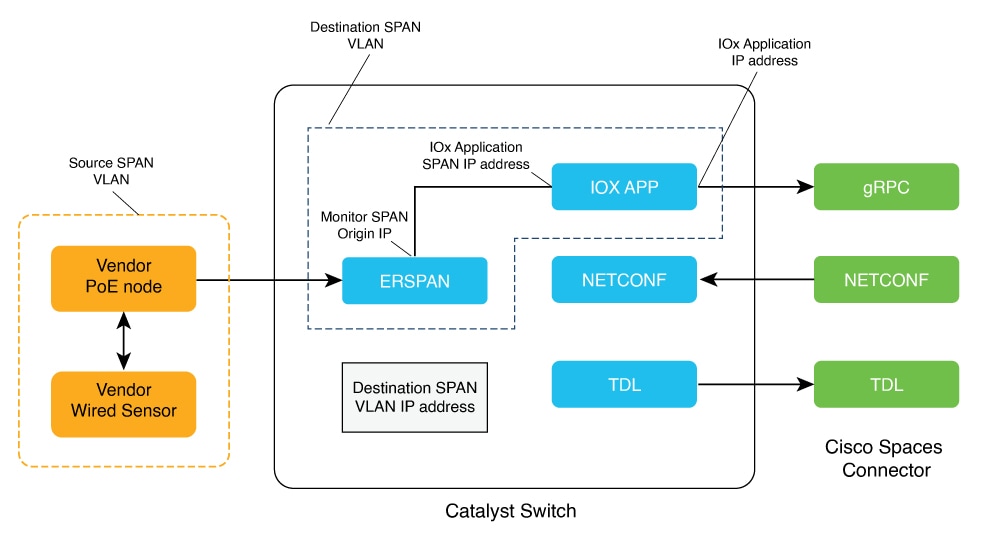
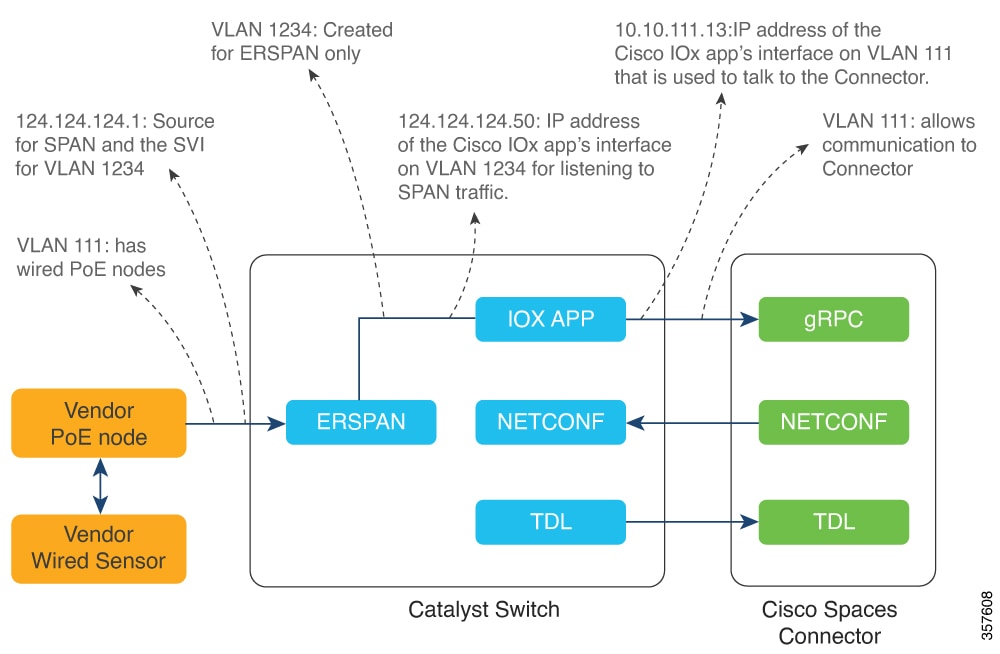
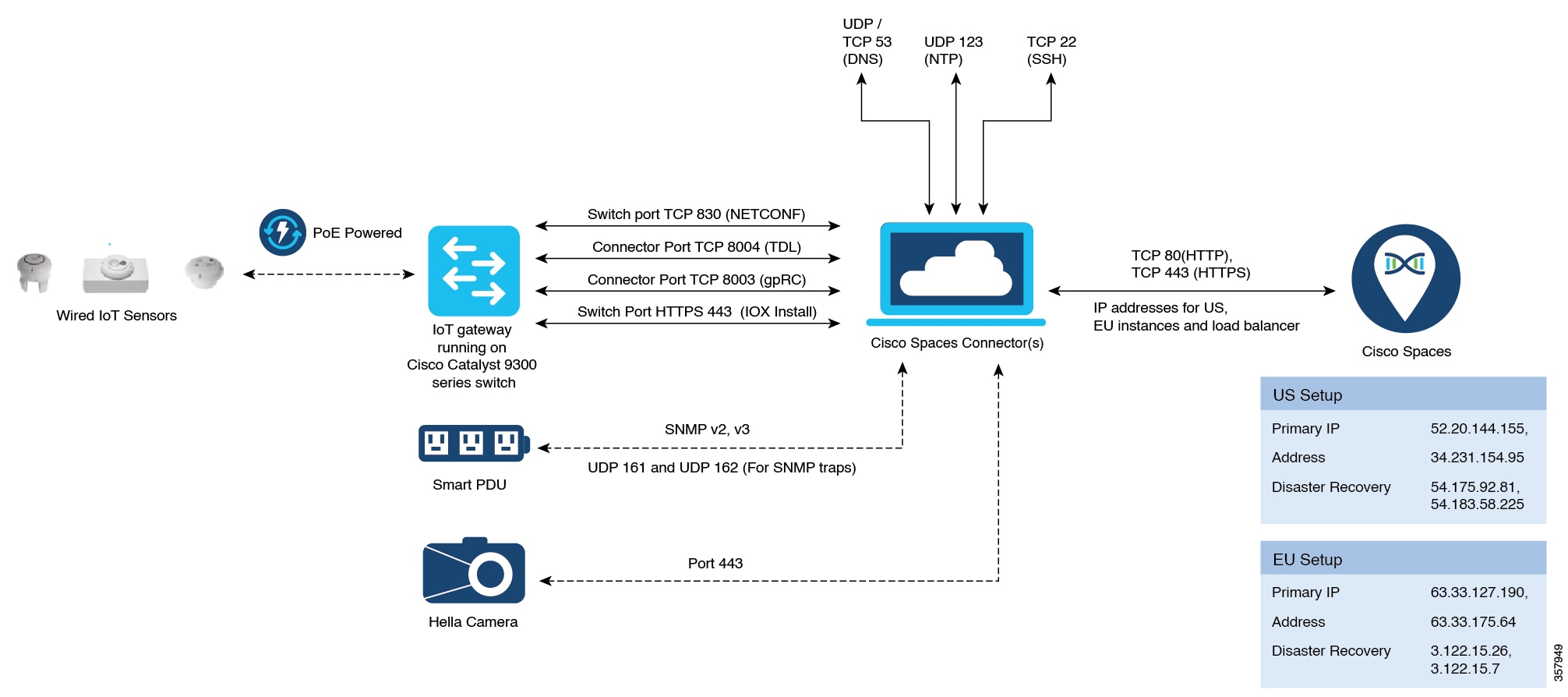
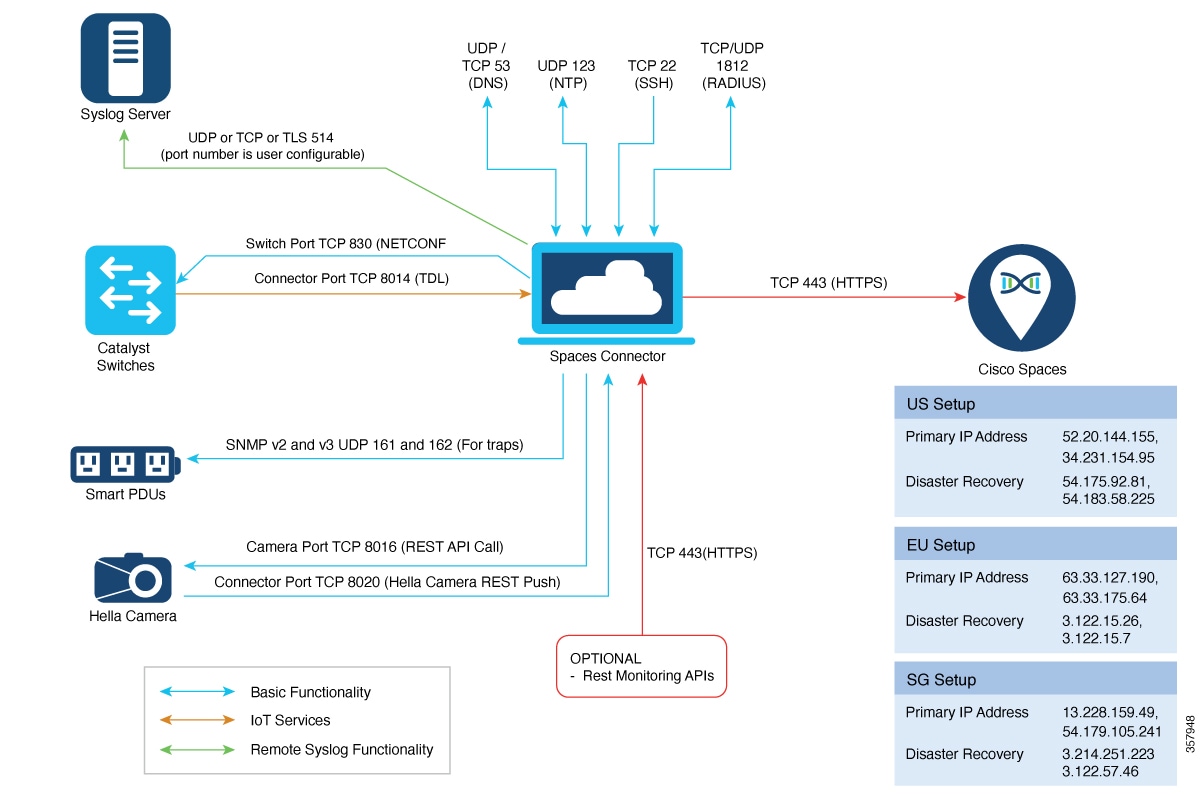
In addition to serving as the management hub for wireless IoT devices, IoT Service can now integrate with Cisco Catalyst 9300 and 9400 Series Switches from Release 17.9.5 or later to receive IoT service (wired) data from sensors, such as:
-
Passive infrared (PIR) sensors for presence detection
-
Sensors with telemetry such as temperature, humidity, CO2, and air quality for environmental analytics
-
Ethernet port information or status for occupancy and energy usage
-
Smart power distribution unit (PDUs) for energy efficiency tracking
Integrating IoT service (wired) with the Cisco Catalyst 9300 and 9400 Series Switches series platform requires the following:
-
Cisco Spaces: Connector
-
A IoT service (wired) gateway deployed and managed by Cisco Spaces
Cisco Catalyst 9300 and 9400 Series Switches can send critical IoT data to IoT service (wired). IoT service (wired) can then transmit the information to:
-
Business outcome applications on Cisco Spaces
-
Cisco Spaces App Center using the Firehose API



















 Feedback
Feedback