Overview of Multipath operation
From IEC6400 Release 1.1.0, Multipath Operation (MPO) is supported on the IEC6400 gateway. MPO is a patented technology that enables the simultaneous transmission of high-priority packets over multiple paths. It enhances the reliability and efficiency of wireless communication in fast-moving mobile systems like trains, buses, and other vehicles.
 Note |
|
Overview of MPO data redundancy
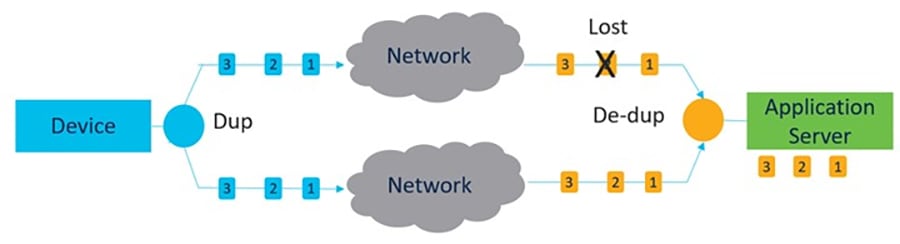
The MPO data redundancy enhances the availability and reliability of wireless communication systems. Each wireless link replicates MPO-protected traffic. Even if one wireless link fails, the other links continue to replicate the traffic. This method ensures uninterrupted communication.
Advantages of MPO
-
It is useful in environments where network conditions are dynamic and can lead to packet losses.
-
It distributes traffic across multiple paths to optimize network performance.
-
It removes duplicate packets, so only one copy is processed, reducing unnecessary load.
-
It sorts packets by priority by sending critical packets through multiple paths and non-critical packets through a single path.
 Feedback
Feedback