Contents
802.11w Protected Management Frames
Wi-Fi is a broadcast medium that enables any device to eavesdrop and participate either as a legitimate or rogue device. Management frames such as authentication, de-authentication, association, dissociation, beacons, and probes are used by wireless clients to initiate and tear down sessions for network services. Unlike data traffic, which can be encrypted to provide a level of confidentiality, these frames must be heard and understood by all clients and therefore must be transmitted as open or unencrypted. While these frames cannot be encrypted, they must be protected from forgery to protect the wireless medium from attacks. For example, an attacker could spoof management frames from an AP to attack a client associated with the AP.
The 802.11w protocol applies only to a set of robust management frames that are protected by the Protected Management Frames ( PMF) service. These include Disassociation, De-authentication, and Robust Action frames.
- Client protection is added by the AP adding cryptographic protection to de-authentication and dissociation frames preventing them from being spoofed in a DOS attack.
- Infrastructure protection is added by adding a Security Association (SA) tear down protection mechanism consisting of an Association Comeback Time and an SA-Query procedure preventing spoofed association request from disconnecting an already connected client.
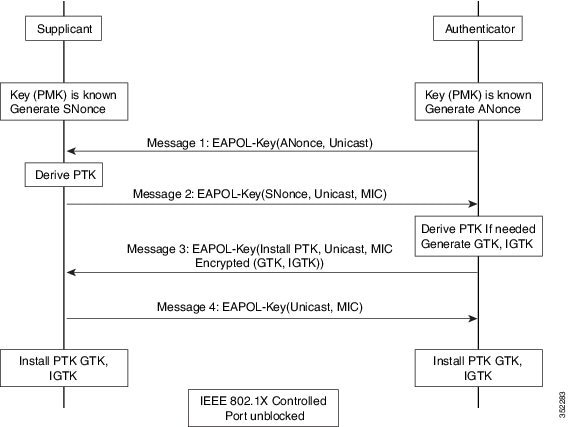
- If the AP later changes the GTK, it sends the new GTK and IGTK to the client using the Group Key Handshake .
802.11w defines a new Broadcast/Multicast Integrity Protocol (BIP) that provides data integrity and replay protection for broadcast/multicast robust management frames after successful establishment of an IGTKSA - It adds a MIC that is calculated using the shared IGTK key.
802.11w Information Elements (IEs)

The WLC adds this modified RSNIE in association and re-association responses and the APs add this modified RSNIE in beacons and probe responses.
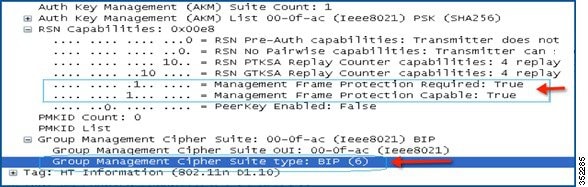
Security Association (SA) Teardown Protection
SA teardown protection is a mechanism to prevent replay attacks from tearing down the session of an existing client. It consists of an Association Comeback Time and an SA-Query procedure preventing spoofed association requests from disconnecting an already connected client.
If a client has a valid security association, and has negotiated 802.11w, the AP shall reject another Association Request with status code 30. This status code stands for "Association request rejected temporarily; Try again later". The AP should not tear down or otherwise modify the state of the existing association until the SA-Query procedure determines that the original SA is invalid and shall include in the Association Response an Association Comeback Time information element, specifying a comeback time when the AP would be ready to accept an association with this client.
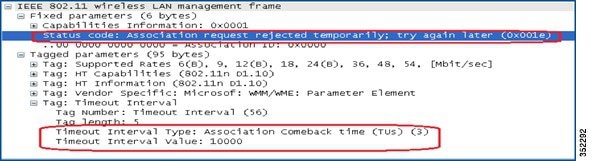
Following this, if the AP is not already engaged in an SA Query with the client, the AP shall issue an SA Query until a matching SA Query response is received or the Association Comeback time expires. An AP may interpret reception of a valid protected frame as an indication of a successfully completed SA Query.
If a SA QUERY response with a matching transaction identifier within the time period, the AP shall allow the association process to be started without starting additional SA Query procedures.
CLI Configuration for Protected Management Frames
Controller(config-wlan)#security wpa akm pmf ? dot1x Configures 802.1x support psk Configures PSK support
 Note | 802.11w feature cannot be enabled on WLANs of None, WEP-40, WEP-104, and WPA (AES or TKIP) encryption. |
 Note | The WLC does not have a GUI configuration for 802.11w. |
Monitoring 802.11w
show wlan name wlan-name |
Displays the WLAN parameters on the WLAN. The PMF parameters are displayed. Here is an example: PMF Support :Disabled PMF Association Comeback Timeout : 1 PMF SA Query Time : 200 |
Configuration Example
wlan 11w-psk 6 11w-psk client vlan 49 security wpa akm psk set-key ascii 0 ciscocisco security wpa akm pmf psk security pmf association-comeback 10 security pmf mandatory security pmf saquery-retry-time 100 no shutdown
Troubleshooting Support
Controller#debug pmf ? all debug Protected Management Frame all events Protected Management Frame events keys Protected Management Frame keys
Controller#set trace pmf ? events PMF events debugging filter Trace Adapted Flag Filter keys PMF keys debugging level Trace Level